Home > Articles > Syndactyly of fingers and toes
online registration
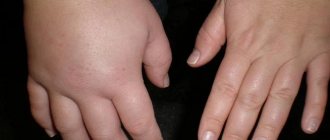
Syndactyly is a congenital malformation consisting in the fusion of one or more fingers with impaired function and cosmetics of the hand. This developmental defect can occur in isolated form - in these cases, the fingers are fully developed, but there is soft tissue or bone fusion between them. In most cases, syndactyly is a symptom accompanying the main diagnosis.
This pathology, alone or in combination with other deformities, including hyperplasia, clefting, clubhand, etc., according to a number of authors, accounts for more than 50% of all congenital hand anomalies.
The absence or limitation of differentiated movements of the fingers with congenital syndactyly is a great obstacle to the normal harmonious development of the child due to impaired grasp and, accordingly, psychomotor, and in some cases, intellectual development.
Congenital syndactyly of the hand is characterized by a variety of clinical manifestations.
By length, depending on the number of captured phalanges, the following are distinguished:
- incomplete form of syndactyly;
- full form of syndactyly.
Depending on the type of fusion, the following are distinguished:
- soft tissue form of syndactyly;
- bony form of syndactyly.
According to the condition of the affected fingers:
simple form of syndactyly;
complex form of syndactyly.
If this developmental anomaly is detected in a child, it is necessary to consult an experienced surgeon. A diagnostic test will require radiography.
Experienced doctors at the MedSwiss clinic perform surgical treatment of this pathology, which allows not only to restore the functionality of the limbs, but also to improve their visual perception.
1.General information
The term “syndactyly” translated from Latin means a joint, combined position of the fingers or, more simply, fused fingers. This is a congenital pathology, which has many varieties, occurs under the influence of various factors and, according to statistics, occurs with an ever-increasing frequency. In different regions of the world, syndactyly is detected in 0.02% -2% of newborns.
According to some sources, the likelihood of such an anomaly does not depend on gender; according to others, it is higher in boys. Syndactyly on the legs is much less common than on the hands. Often, fused fingers are not the only anomaly of intrauterine development and are observed in combination with other developmental defects, for example, the musculoskeletal system. And syndactyly is always eliminated (if elimination is at all possible) by microsurgical intervention.
A must read! Help with treatment and hospitalization!
Surgery for syndactyly in Moscow
The Department of Pediatric Surgery at CELT invites you to undergo surgery for syndactyly of fingers and toes in Moscow. We have been working in the domestic market of paid medical services for more than twenty-five years and provide treatment and diagnostics in accordance with international standards.
Your child will be cared for by experienced pediatric surgeons with the highest qualification category. They have decades of experience and hundreds of successfully completed operations behind them. Good knowledge of child psychology allows them to quickly find a common language with young patients. The correct attitude of the baby plays an important role, as it affects the outcome of the operation.
Surgery for syndactyly of the legs and arms is preceded by a thorough diagnosis. Our multidisciplinary clinic has a powerful diagnostic base that allows us to conduct comprehensive studies, identify contraindications, determine the scope of intervention and draw up a plan. The process uses special anesthetic drugs designed specifically for the child’s body. They do not harm it, but at the same time provide the desired effect, eliminating any pain or discomfort.
The cost of surgery for syndactyly is calculated individually, taking into account the complexity of the case and the technique used. You can find out the exact numbers from your doctor after consultation and diagnosis. Preliminary figures are presented in the “Services and Prices” tab in this section of our official website. We regularly update price lists, although in order to avoid misunderstandings, we still ask you to check the numbers with our operators: +7 (495) 788-33-88.
2. Reasons
Acquired syndactyly is possible only as a result of a burn or chemical “fusion” - and is much less common than congenital forms. The main etiological cause of congenital syndactyly is heredity, burdened by the same or other similar anomalies. However, one cannot discount reliably established and confirmed risk factors, which provide alarming dynamics in the incidence of congenital defects of limb development:
- environmental hazards, incl. mother's work in hazardous industries;
- intoxication during the gestational period: alcohol, smoking, taking medications, etc.;
- radiation injuries.
Visit our Microsurgery page
3. Symptoms and diagnosis
Syndactyly can be simple (fusion of normal soft tissues, membranous junction or common skin sheath) or complex when there is common bone tissue, undivided nails, and associated structural defects of the hand or foot. At the stage of intrauterine formation, two or more fingers may not separate.
Fused toes are diagnosed during a neonatal examination at birth. In some cases, syndactyly can be visualized already during intrauterine ultrasound, especially if there are grounds for suspicion and the study is carried out purposefully. To clarify the situation, additional diagnostic tests (x-rays, etc.) are prescribed.
About our clinic Chistye Prudy metro station Medintercom page!
Symptoms
Symptoms of the disease manifest themselves in visually assessed, abnormal formation of the hand, obvious and less obvious. Parallel symptoms are functional disorders that affect the child’s ability to live a full life.
As a rule, adjacent fingers are fused. It is rare to see fusion of any shape between the thumb and little finger. Very rarely - fusion of all fingers. If syndactyly is bilateral, then, predominantly, the fusion of pairs on one hand is duplicated by the second.
The structure is assessed as normal, as well as moderate underdevelopment. Absence or deformation of some phalanges.
The webbed and basal shapes often do not interfere with the functionality of the hands. If this happens, the consequences affect the overall development of the child. The inability to perform a standard list of actions leads to speech, psychomotor or even intellectual retardation. If the bones are functionally defective, it is more difficult for the child to study, and he faces restrictions in the range of professions available to him in the future.
4.Treatment
Naturally, there is no need to talk about conservative treatment of syndactyly: no pills, no herbs, no spells - the bones will not be separated and the articular-cartilaginous anatomy will not be restored. A microsurgical operation is required, often very complex, many hours or even multi-stage, requiring the highest qualifications from the entire surgical team.
The decision to eliminate a defect in the foot is made, as a rule, only in cases where there is a real risk of impairment of normal mobility (gait, running, etc.) in the future. Fused fingers are usually separated when the patient reaches 4-5 years of age, but simpler cases can be operated on much earlier. Many specific techniques have been developed and are successfully practiced, including skin grafting (and, if necessary, bone, tendon, muscle), autotransplantation, etc. The period of rehabilitation and formation of full fine finger motor skills can take from several months to several years. As a rule, rehabilitation measures begin one and a half to two weeks after the intervention. According to indications, special gymnastics and massage, sets of developmental exercises to be performed with parents at home, electrical myostimulation, and various physiotherapeutic procedures are prescribed.
The prognosis in most cases is quite favorable: today the proportion of syndactyly eliminated without any consequences for the further development of the child exceeds 80% of the total number of registered cases.
Sign up for a free consultation:
Does this autograft always survive?
On the hands, almost one hundred percent engraftment usually occurs; on the legs, the probability of complete engraftment is less, since immobilization of the feet is often difficult: the patient needs to move around and come for dressings. This area is constantly in motion and inevitably gets injured, even though we apply special bandages that press the flap to the surface of the wound. There may even be a situation where, due to sweating under this bandage, the flap begins to macerate. Maceration of this flap leads to its partial and sometimes complete necrosis. In the literature, there is data on the use of materials of artificial origin or allografts, but we traditionally work with autoskin - this material is always available, does not require additional costs, and the percentage of engraftment of one’s own tissues is very high
What are artificial materials?
Artificial leather, Alloderm and others. But, I repeat, one’s own tissues – free autograft, transferred flaps from the back of the hand – are the “gold standard” of hand surgery. All the publications that I came across on the use of synthetic or allomaterials were of a research and not practical nature.
Will the patient walk with this artificial material all his life?
If we are talking about a classic transplant, it is always an autotransplantation of an epidermal skin flap. Therefore, surgery for cutaneous syndactyly involves a lot of nuances and is not as simple a correction as it seems at first glance.
As for bone syndactyly, this is work for orthopedists and traumatologists. Plastic surgeons, as a rule, do not do this. There are also many correction options here. These could be reconstructive bone surgeries; the fused bone can be split, creating two bone blocks... But orthopedists and traumatologists will tell you better about this.
Will the function of finger flexion after surgery be good or conditional?
With cutaneous syndactyly, the function of flexing the fingers does not suffer at all, the only difference is that the fused fingers bend together, but the tendons of the flexor and extensor muscles of such fingers are their own. After surgery, they will also bend. But since we create a scar deformation, and the scar tissue stretches worse, the flexion may be a little worse at first. The fingers need to be developed, first passively, and then actively, then the scar will not pull. There are isolated cases when hypertrophic scars form, but in most cases everything ends well.
How long after correction of cutaneous syndactyly should one begin to develop the operated fingers?
Development can begin 2-4 weeks after surgery. At first, passively, to prevent the scar from shrinking during the ripening process and to prevent . The scar takes up to six months to form, and all this time you need to work with a brush. After about another 2 weeks, you can already actively develop, for example, using rubber balls or hand expanders. We also quite often use special silicone gels or dressings to prevent severe scarring. How does bone syndactyly behave in terms of flexion?
Bone form of syndactyly
– this is the most surgically complex type of this pathology. The flexion-extension function can be significantly hampered, since the finger bones, joints, and tendons can be significantly deformed. When dividing bone syndactyly, speaking about the results of the operation, one must take into account, first of all, functional aspects. It is not always possible to obtain a satisfactory result.
Syndactyly also occurs in stars. Ashton Kutcher, for example, has zygodactyly - fusion of the second and third toes. This, by the way, is the most common variant of the anomaly. The actor did not undergo surgery, as he considers it not a flaw, but a highlight.
Let's talk more about the operation. What are the nuances of surgical correction? What anesthesia is used?
Correction of cutaneous syndactyly can be done under local and regional anesthesia, but it is not worth it, because in this case it is often necessary to do anesthesia in two places: on the fingers and where we will take the flap. These are additional negative sensations for the patient. It is better to perform this operation under conduction anesthesia, under spinal or epidural anesthesia with an additional intravenous component, that is, with sedation, or under general anesthesia with an inhalation component. This is ideal because the operation can last 2-2.5 hours.
The difficulty of the operation is not in dividing the syndactyly and removing the fibrous cord, but in not damaging the vascular and nervous structures, in transplanting the skin flap, and in the correct pattern of the Z-shaped flap. A straight cut should not be made on the fingers to avoid scar contracture, which will not allow the fingers to move fully. The incision lines must be planned in a certain way so that the edges of the skin do not become necrotic and at the same time are mobile enough for suturing the wound defect.
A Z-shaped scar stretches better than a straight scar. And autodermal flaps are also cut out to fit the resulting z-shaped wound surface. We sew these flaps with special thin threads, and then the flap is additionally fixed with a pressure bandage, which presses it to the entire wound surface. Without this, the flap cannot take root completely. At first, the nutrition of the flap occurs diffusely, then a capillary network begins to form.