Fluid retention
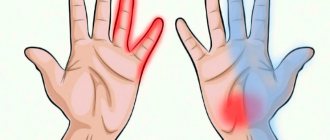
Swelling on all fingers at once can occur if excess fluid appears in the body.
This happens Hand swelling during exercise: A concern? / Mayo Clinic, for example, in athletes who exercise and sweat a lot. Along with sweat, they lose sodium, which normally holds water in the bloodstream. Otherwise, it comes out of it and permeates the tissue, which leads to swelling. Liquid is also retained by Savelyeva G.M., Serov V.N., Sukhikh G.T. Obstetrics. National guidance due to hormonal changes in women during pregnancy.
What to do
If swelling in your fingers is related to sports, try Hand swelling during exercise: A concern? / Mayo Clinic:
- Remove the rings from your fingers before training;
- During exercises, periodically make circular movements with your hands to improve blood flow;
- Stretch your fingers and clench your fists between sets.
- Drink enough fluids containing electrolytes to retain water in your blood. For example, mineral water will do.
And pregnant women with swollen fingers should tell their gynecologist about this. Usually the symptom does not indicate serious problems, but it happens that edema is the first sign of a dangerous condition - preeclampsia.
Prevention and nutrition
Preventive measures include primarily:
- Banal adherence to a healthy lifestyle, playing sports, swimming, eating right.
- Remove bad habits: alcoholic drinks, smoking.
- Drink at least 2 liters of clean water during the day, and stop drinking liquids at least 3 hours before bedtime.
- Once a year, undergo a full medical examination, for yourself, and not as a diversion.
The diet should be healthy and include the following foods: seasonal vegetables, fruits, juices, fish, herbs, various cereals, potatoes baked in their skins, watermelons, legumes, dairy products, steamed veal are healthy.
Injury
If you hit your finger hard, break it, dislocate it, or get a sprain, swelling will occur Dislocations / US National Library of Medicine. It will be accompanied by redness, pain, and sometimes bleeding.
What to do
For minor bruises, you can apply a cold compress to your finger and take an over-the-counter pain reliever. But if the pain is severe, the wound is large or the finger is bent unnaturally, you need to consult a doctor. For a dislocation, reduction will be required, and for a fracture, fixation and restoration will be required.
Rheumatoid arthritis
Joint inflammation most often begins in the hands. Rheumatoid Arthritis / American Academy of Family Physicians is believed that the disease is associated with autoimmune reactions, when the body attacks its own tissues and produces antibodies to them.
In addition to swelling of the fingers, other symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis include:
- joint pain;
- joint stiffness, especially after sleep;
- temperature increase;
- redness of the hands;
- fatigue and loss of appetite;
- bumps under the skin of the fingers are rheumatoid nodules.
What to do
With such symptoms you need to go to the doctor. He will conduct an examination, which includes blood tests, x-rays of the joints, and possibly a test of joint fluid. Only after confirming the diagnosis will the specialist prescribe treatment. It will not be possible to completely get rid of rheumatoid arthritis Rheumatoid Arthritis / American Academy of Family Physicians, but the following will help reduce symptoms:
- over-the-counter pain relievers;
- immunosuppressants;
- hormonal medications;
- antirheumatic drugs.
In addition, you will have to lose weight if you are overweight, quit smoking, adhere to proper nutrition, reduce the load on your joints, but at the same time engage in aerobics and physical therapy.
In severe cases, surgery may be necessary.
Diagnostics
Orthopedic traumatologists are often involved in determining the cause of hand swelling. If indicated, patients are referred to surgeons, rheumatologists, vascular surgeons, and other specialists. The diagnosis is made based on the results of the following procedures:
- Questioning, physical examination
. The specialist determines the circumstances and time of swelling, identifies other symptoms, and monitors the dynamics of the disease. Evaluates the localization, prevalence, severity of edema, range of motion in joints, color, density, tissue temperature. - Radiography
. Prescribed for injuries, joint diseases, and some purulent processes. Allows you to confirm the presence of fragments or displacement of the articular ends of the bone, inflammatory and degenerative changes. - Ultrasonography.
It is carried out to confirm thrombosis, determine the condition of venous and lymphatic vessels, and assess the prevalence of purulent processes. - Other imaging techniques
. In doubtful cases, MRI is performed for a detailed study of soft tissues, and for the study of hard structures. - Laboratory research
. Tests help detect signs of inflammation, markers of rheumatic diseases, and renal dysfunction.
Pressotherapy of hands
Carpal tunnel syndrome
In this disease, the nerve that runs from the forearm to the hand is compressed by Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Fact Sheet / National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke in the tissues of the wrist between the ligaments and bones. Unpleasant symptoms appear:
- numbness and tingling in the fingers, especially the thumb, index and middle fingers;
- soreness and swelling in the fingers;
- weakness in the arms;
- muscle atrophy at the base of the thumb in advanced cases.
Numbness, tingling and pain may occur at night or in the morning on one or both arms. And then these signs begin to bother you during the day. For example, when a person holds a phone near his ear or drives a car.
What to do
You need to see a doctor. He can recommend the Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Fact Sheet/National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke:
- Wear a splint. This is a special device that is fixed to the hand overnight;
- Avoid activities that increase symptoms;
- Take over-the-counter pain relievers;
- Use hormonal drugs from the group of corticosteroids;
- Inject a local anesthetic into the joint.
If treatment doesn't help and symptoms get worse, surgery may be necessary.
Folk remedies
Folk remedies will help as the main treatment. We will describe the most effective recipes for treating swollen fingers:
- Decoction of pine buds : 1–2 tsp. kidneys, pour 300 ml of boiling water, keep in a water bath for 10 minutes, when it cools down, drink during the day. Take throughout the week.
- Fresh pumpkin juice: drink 200 ml of freshly prepared juice every day for at least a month. The recipe is healing, swelling does not return after such treatment.
- We make baths: with essential oil, calendula oil, eucalyptus oil. Add 10 drops of essential oils to well-warm water (1–2 liters) and immerse your hands for 15–20 minutes. Do this every evening until complete healing.
- Fresh cucumbers also help a lot; we make juice and drink it when we’re thirsty. You need to drink at least 500 ml per day. Or just eat fresh, preferably homemade, cucumbers and plenty of them.
- We take table 3. l. anise seeds , pour 300 ml of boiling water and cook for 5 minutes. When it cools down, take 1-2 tbsp. l. 3 times a day, about 2-3 weeks.
Gout
Due to pathology, uric acid is retained in the body Gout In Hands / American Society for Surgery of the Hand. It settles in the kidneys and also forms crystals in the joints and damages them. That's why they swell and hurt a lot. Usually the big toe is affected first, followed by other bone joints. The fingers can also swell, and tophi sometimes form on them. This is the name given to painless bumps made from uric acid deposits.
What to do
At the first symptoms you need to go to the doctor. He will conduct an examination and prescribe Gout In Hands / American Society for Surgery of the Hand treatment. It is impossible to completely get rid of gout. Therefore, a person will have to follow a low-protein diet for the rest of his life, as well as take over-the-counter painkillers and hormonal medications.
Raynaud's disease
This is a disease in which small arteries in the hands suddenly constrict (Raynaud's disease / Mayo Clinic) due to cold or stress, causing blood to stop flowing to the fingers. Therefore, they become numb, sore, pale and cold. When the attack passes and blood flow is restored, the fingers may swell.
What to do
In order for vascular spasms to recur less often, you need to protect Raynaud's disease / Mayo Clinic from cold, and also avoid stress and sudden temperature changes. If these measures are not enough, your doctor may prescribe medications. Usually these are drugs from the group of calcium channel blockers or antispasmodics. In some cases, experts recommend nerve surgery or injections of Botox and local anesthetics.
What are the causes?
Identifying the onset of development of elephantiasis in the hands allows you to prescribe the most effective treatment. This mechanism can be triggered by various factors, which are often interrelated. Among the most common factors leading to the progression of arm lymphostasis are the following:
- surgery to remove lymph nodes;
- negative effects of radioactive radiation in the treatment of oncology;
- serious injuries accompanied by damage to lymph nodes and blood vessels;
- fractures with a violation of the integrity of bone tissue in the form of comminuted fractures;
- infectious diseases and pathological neoplasms in the lymphatic system.
Lymphedema
It develops Lymphedema / Mayo Clinic when something blocks the lymphatic vessels and prevents them from collecting fluid from the tissues. This can happen due to rare hereditary factors, in people with cancer or lymph node infection, or after surgery or radiation therapy.
With lymphedema, not only the fingers, but also the entire leg or arm swell. In addition, there is a feeling of heaviness and restriction of movement, and the skin may become rougher and tougher. Another symptom is frequent infections.
What to do
There is no cure for the disease, but swelling can be reduced Lymphedema / Mayo Clinic in the following ways:
- Perform exercises that improve lymph flow.
- Practice tight wraps.
- Perform lymphatic drainage massage periodically.
- Use pneumatic compression when you put a special sleeve on your arm and pump air into it.
- Wear compression garments if your feet and toes are swollen.
Why do my hands swell?
Physiological reasons
Unilateral swelling can occur when the lymphatic and blood vessels of the arm are pressed by the body or clothing during sleep.
Small symmetrical swelling of the fingers and distal parts of the hands, especially noticeable when wearing a wedding ring, is observed after drinking alcohol, consuming salty foods and large amounts of liquid in the evening. In women, swelling of the hands, caused by hormonal changes, is often expressed during gestation. As pregnancy progresses, the symptom increases from mild pastiness to a significant increase in volume. Some patients note morning swelling of the fingers before the onset of menstruation, especially against the background of premenstrual syndrome.
Traumatic injuries
Local swelling while maintaining limb function is characteristic of bruises. Accompanied by minor or moderate pain, hyperemia, and sometimes abrasions and bruises. With hematomas, the symptom is more pronounced, and fluctuation can be detected. With sprains, tears, and ruptures of ligaments, swelling is usually more noticeable than with bruises. The pain intensifies when attempting to move or deviate the arm in the direction opposite to the injured ligament. With a complete rupture, some of the functions of the limb are lost.
Fractures are manifested by rapidly increasing swelling, deformation, loss or significant limitation of function, pathological mobility, and severe pain. In case of injuries without displacement of fragments, epiphysiolysis in children, pathological fractures, some of the listed symptoms are absent or weakly expressed, the swelling is insignificant. Dislocations are characterized by clearly visible, rapidly progressing swelling, which is complemented by severe deformation in the joint area, pain, and springy resistance when trying to move.
With frostbite, swelling affects the fingers and spreads to the hands. It can reach a significant volume, which is why the hands resemble pillows. Against the background of increasing swelling, a tingling sensation occurs, turning into a burning pain. The formation of blisters and areas of necrosis is possible, and in severe cases, some of the fingers are torn away. In patients with burns, swelling is combined with sharp pain, redness, and blistering.
Local infectious processes
Swelling, rapidly increasing twitching pain, cyanosis, hyperemia are the main symptoms of all forms of panaritium. In patients with superficial forms of the disease, swelling of the finger is local, minor or moderate. In deep forms of felon, the swelling is significant and extends beyond the finger to the hand. A more rare lesion of the fingers is chinga, a disease that occurs in people who cut up the carcasses of marine animals. Most often the proximal joint of the finger swells.
Boils and carbuncles appear on the shoulder, forearm, and less often on the back of the hand - where there are hair follicles. The swelling in these pathologies is limited; a dense bluish-purple formation with one or several yellowish areas in the follicle zone is detected. With abscesses, the purulent focus is larger in size, and the edema covers a significant part of the segment. Cellulitis does not have clear boundaries; following pus, swelling spreads along the limb.
With infected wounds, the edges and nearby tissues swell, serous and then purulent discharge appears. Erysipelas is characterized by pronounced swelling and the presence of a clearly defined red spot, reminiscent of a geographical map. The appearance of swelling and other symptoms is preceded by fever; in severe cases, disturbances of consciousness and delirium are possible.
Severe swelling is accompanied by purulent lesions of bones and joints - purulent arthritis, osteomyelitis. Pathologies are characterized by intense twisting, tearing, twitching pain, local hyperemia and hyperthermia, and a sharp limitation of movements. Fever and severe intoxication are noted.
Swelling of the hand
Joint diseases
Local swelling is observed in all forms of arthritis. The severity of edema, as a rule, correlates with the severity of the process and intensifies during periods of exacerbation.
- Rheumatoid arthritis.
There is symmetrical damage to the joints of the fingers and hands. The swelling is combined with transient or permanent stiffness, redness, and limitation of movement. - Gouty arthritis.
Manifestation of the disease with symptoms of polyarthritis in the fingers is more common in women. In young people, damage to the elbow, wrist, and shoulder joints is possible. The rheumatoid-like form occurs as oligo- or monoarthritis of the fingers. Typically a rapid increase in edema, sharp pain, dysfunction, general hyperthermia. - Psoriatic arthritis.
The shoulder joints, small joints of the hands and fingers suffer. The onset may be acute or gradual. Patients complain of swelling and pain in the affected joints. The pain syndrome intensifies at rest, at night, weakens with movement, throughout the day. Local swelling and purple-bluish skin color are visually determined. - Infectious arthritis.
It is provoked by viral and bacterial infections. With a viral infection, volatile arthralgia and transient edema are observed. Gonorrheal arthritis typically involves the elbow joint and hands. In the syphilitic form of the disease, the fingers are affected. - Occupational arthritis
. Pain and swelling are detected in the most loaded joints; the location of the lesion depends on the profession. Typists, pianists, and office workers experience swelling in their finger joints. Builders and loaders are often concerned about pain, swelling, and limited movement in the shoulder joint.
Deforming arthrosis is chronic. Swelling of the hand occurs some time after a decrease in resistance to stress, discomfort and pain. In the post-traumatic form of the disease, a connection with a previous injury (dislocation, fracture-dislocation, periarticular fracture) is revealed. In idiopathic arthrosis, there are no obvious causes; a history of joint overload is possible.
Vascular lesions
Swelling of the arm due to thrombosis of the vessels of the upper limb occurs below the location of the thrombus. Accompanied by a feeling of fullness and painful heaviness, intensifying with palpation and lowering the hand. Upon examination, tissue compaction and a purplish-bluish tint of the skin are revealed. Numbness, crawling, and decreased sensitivity are possible.
Lymphatic edema of the arm can be detected in patients who have undergone a mastectomy with removal of regional lymph nodes. Sometimes swelling develops against the background of defects of the lymphatic system, scars after burns, postthrombophlebitic syndrome, lymphangitis, lymphadenitis. At the initial stage, swelling appears in the evening and disappears on its own during the night. Then the swelling becomes permanent, combined with tissue compaction. A distinctive feature of edema due to lymphedema is a dimple that does not disappear for a long time after pressure.
Other reasons
Other conditions that cause swelling of the hands include:
- Erythromelalgia.
Attacks occur suddenly, are provoked by compression or overheating of the limb, and are accompanied by severe pain, swelling, intense hyperemia, and an increase in the local temperature of the fingers and toes. All symptoms disappear within a few minutes, sometimes several hours. - Heart failure.
At first, the swelling is hidden and manifests itself as an increase in body weight. In the final stages, swelling of the legs, arms, and face is observed in combination with ascites, hydropericardium, and hydrothorax. - Kidney diseases.
Swelling is observed in the morning, with prolonged hanging of the arms downwards. At first they are hardly noticeable, identified by the difficulties when trying to remove the wedding ring from the finger. Subsequently they become more obvious. They are distinguished by their softness, wateriness, combined with a yellowish coloration of the skin.
Mixed connective tissue disease
This is a rare autoimmune disease in which a person simultaneously develops Mixed connective tissue disease / Mayo Clinic symptoms of systemic lupus erythematosus, scleroderma and polymyositis, and sometimes Sjögren's syndrome.
At an early stage, a person's fingers become painful and swollen, their tips become white and numb. There is pain in the muscles and joints, general malaise, and a red or red-brown rash appears on the knuckles. Symptoms of Raynaud's disease may also occur.