Ferritin
plays an important role in the normal functioning of the body.
This is a protein that is responsible for iron deposition, tissue and organ regeneration. Normal ferritin levels should be 100 micrograms per liter (mcg/L), regardless of age or weight.
In some laboratories, current reference values exceed 100 μg/L. It is necessary to monitor this indicator from childhood, since there is a category of people who have low ferritin levels from birth. As a rule, it is inherited on the maternal side.
Low ferritin levels
When ferritin levels are low, the regeneration process slows down.
This negatively affects the functioning of primarily organs that have an aggressive environment - the stomach, urethral canal, intestines, vagina, and oral cavity. The outflow of lymph is disrupted, it is retained in the tissues, which leads to lymphostasis. The skin suffers because ferritin is involved in the formation of collagen.
What symptoms indicate that you should check your ferritin levels?
Oral cavity.
Seizures in the corners of the mouth, dry, chapped lips, recurrent and long-lasting stomatitis. Damage to the tip of the tongue, tingling, sour taste - this occurs not only due to reflux and esophagitis, but also when the oral mucosa cannot recover.
Stomach.
Ulcers, erosions, bad breath that does not go away with the drug treatment received.
Intestines.
Frequent diarrhea, loose or pasty stools, gas and bloating.
In addition to treating the gastrointestinal tract, it is imperative to check your ferritin level.
Vagina and urethral canal.
Persistent and recurrent candidiasis, cystitis, which can occur without pain.
Lymphostasis.
Lymph consists of 80% protein - ferritin. It is a transport fluid that takes toxins from the site of intoxication and delivers them to the blood. In this way, the body self-cleanses. Disruption of this process has several manifestations - swelling and frequent or prolonged colds. Swelling is most pronounced in the first half of the day and goes away on its own by lunchtime or evening. Not only the face swells, but also the limbs. Colds are sluggish and recur.
Poor skin healing.
Low ferritin levels lead to poor collagen production. The skin loses its protective properties, since the collagen it contains is not enough to withstand ultraviolet radiation and temperature changes (cold or heat). Pigment spots may form on the skin, including those of the vitiligo type. Turgor decreases. Small wounds and cuts do not heal for a long time. Spots form at the sites of damage that do not go away within 2-3 years. After plastic surgery, instead of invisible seams, scars are formed, sometimes with pigmentation. When applying a tattoo, instead of the desired black shade, you may end up with a greenish or gray shade, which will also not stick well. Facial asymmetry with Botox injection can also occur due to low levels of collagen in the skin.
How to replenish ferritin levels?
Iron supplements do not increase ferritin levels because ferritin is a protein. Patients who have taken iron supplements for 2-3 months, or received iron intravenously, are faced with the fact that the level of iron in the blood is increased, while the level of ferritin has not changed. Despite the fact that ferritin can be obtained from food, it is not possible to compensate for the deficiency in this way. It is necessary to take artificial drugs. During inpatient treatment, the patient receives droppers with plasma and plasma-substituting solutions. In outpatient settings, spirulina, chlorella, and collagen are used to increase ferritin levels.
Algae with pyruline and chlorella
Spirulina and chlorella
- These are blue-green freshwater algae. They do not contain iodine, so they can be prescribed to patients with thyroid diseases. Spirulina and chlorella are identical in chemical composition. The difference lies in the percentage of microelements and electrolytes in their composition. Chlorella contains 30% less protein than spirulina. Collagen can lead to crystallization of bile and urine. If the patient has a history of cholelithiasis or bile sludge due to long-term use of contraceptives and hormones, then collagen is prescribed in a short course, no more than 1 month, under dynamic ultrasound control of the gallbladder. Therefore, of the three drugs, preference is given to spirulina, as the most effective and safe.
The average course of taking spirulina is 3 months.
The drug is taken 3,000 mg (one-time) per day. Ferritin levels must be checked over time. The analysis is given after 1 month of admission. If the ferritin level has increased by at least 20 units, we can talk about positive dynamics and continue taking the drug for another 2 months. When increasing by 5-10 units, it is necessary to increase the dosage to 5,000 mg (one-time) per day, or combine with collagen. A control analysis also after 1 month of use. The course must be repeated once every six months, since the protein supply is spent to ensure the normal functioning of the body, it must be periodically replenished.
It is not recommended to give spirulina to children as a preventive measure.
Before taking the drug, you should check your ferritin level.
Protein deficiency. Why does the ferritin level not increase during therapy?
Where and how is iron absorbed?
Iron contained in foods of plant and animal origin is absorbed in the duodenum and jejunum. To do this, iron must undergo a series of transformations in the stomach.
Once in the stomach, under the influence of hydrochloric acid, food proteins must be broken down into amino acids. This process is called denaturation or primary hydrolysis of the protein. The synthesis of amino acids and the accumulation of protein in the body are promoted by vitamins B12 and B6 (folic acid), the absorption of which depends on the acidity in the stomach. Normal pH is 2.8, outside the stomach - 3.5.
Iron in the body. Hemoglobin, ferritin
Iron ensures continuous respiration of the cells of our body. This element is involved in cellular energy exchange and forms the basis of enzymes responsible for biochemical and antioxidant processes. Iron is involved in the removal of toxins and the functioning of the immune system.
The daily consumption of iron by the body is 1-1.5 mg. The bioavailability of iron is low and to maintain normal levels, intake should be at least 10-15 mg per day.
Required daily iron intake:
- women - 10-30 mg;
- before pregnancy, during, in the 1st trimester - at least 30 mg;
- men - 8 mg;
- children under 13 years of age - 7-10 mg;
- teenagers:
- boys - 10 mg;
- girls - 15 mg.
2-5 g of iron are constantly present in the body. Most of it is associated with hemoglobin and ferritin.
What is hemoglobin
Hemoglobin is a protein that, with the help of iron, captures oxygen in the lungs and carries it to every cell of the body. Hemoglobin contains 80% of all iron in the body.
Low levels of hemoglobin and formed elements in the blood (red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets) are called iron deficiency anemia .
What is ferritin for?
Ferritin is responsible for creating iron stores in our body. This complex protein complex is found in all organs and tissues. When iron deficiency occurs from blood loss or insufficient dietary intake, stores are used up and ferritin levels decrease.
The table shows average data. Researchers consider the optimal level of ferritin to be no lower than your weight in kilograms.
Depletion of ferritin iron in the body is called hidden iron deficiency anemia .
To detect hidden iron deficiency anemia, it is necessary to take a ferritin test. To establish the exact clinical picture of the disease, additional tests are prescribed: vitamin B12, B9, transferrin, serum iron and others. The laboratories have special packages “Diagnostics of anemia”.
Still have questions? Contact us:
What happens when there is low acidity in the stomach?
Low acidity in the stomach leads to poor protein breakdown. Trivalent iron does not convert into divalent iron, and, entering the intestines unchanged, is poorly absorbed. Low acidity reduces the production of intrinsic factor in the stomach. This is a protein that converts vitamin B12 into an absorbable form and transports it to the intestines. With low acidity, vitamin B9 (folic acid) is almost completely destroyed, and it is necessary for the synthesis of amino acids and the absorption of vitamin B12.
What affects the production of hydrochloric acid?
The key stimulators of the production of gastric juice - hydrochloric acid - are histamine, acetylcholine and gastrin. Gastrin has the greatest effect. It is produced by endocrines - G-cells. The production of gastrin depends on somatostatin, a hormone produced by the pancreas and hypothalamus. Somatostatin suppresses gastrin production. The secretion of digestive enzymes and bile is disrupted, and acidity decreases.
The function of the hypothalamus is closely related to the function of the thyroid gland and pituitary gland. If there is a violation, protein from food will not be absorbed.
Integrated approach: ferritin, hormones, iron, folic acid, TSH
For effective treatment, in addition to ferritin levels, it is necessary to check hormonal levels, serum iron levels, vitamins B12 and B9 (folic acid). If the level of iron and vitamins B12 and B9 is low, protein supplements alone will not be able to increase ferritin levels. The problem must be solved as a whole. It is worth noting that the levels of copper, calcium, and vitamin C do not play
.
Symptoms of iron deficiency
Signs of iron deficiency in tissues and blood plasma are the following symptoms:
- general weakness, headaches, frequent dizziness;
- shortness of breath, fatigue, exercise intolerance;
- mental instability, moodiness, tearfulness;
- decreased performance, learning, concentration, memory impairment;
- decreased appetite;
- deterioration of immunity;
- pale skin, mucous membranes, feeling of frozen hands and feet;
- rapid heartbeat, tachycardia, heart murmurs, even with light exertion.
External manifestations of iron deficiency are:
- changes in the color of the skin, mucous membranes, the appearance of jams in the corners of the mouth;
- deterioration of the condition of the nails: fragility, loss of hardness, transverse stripes, concavity of the nail plates;
- hair deterioration: split ends, fragility, dullness, hair loss;
- decreased muscle tone, blood pressure, impaired swallowing functions;
- change in sense of smell: tendency to smell of gasoline, paint, varnish, solvents, car exhaust fumes;
- changes in taste: addiction to raw foods, chalk, dough, toothpaste. Cravings for spicy or salty foods;
- decreased reproductive function.
It is believed that to make a diagnosis of anemia, the simultaneous manifestation of 4 or more symptoms is sufficient.
In the initial stages of anemia, when ferritin reserves are used, obvious and distinct manifestations may not occur. Symptoms may be blurred and not distinct. This is the “insidiousness” of iron deficiency anemia. Its symptoms affect the psychological and physical state without directly indicating the disease.
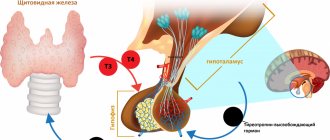
Ferritin and the thyroid gland
The production of ferritin depends on hormonal levels, and, in particular, on the functioning of the thyroid gland. Thyroid hormones affect the synthesis of red blood cells, the absorption of iron in the stomach and the absorption of vitamins B12 and B9.
Among all thyroid diseases, there are 2 diseases that are characterized by hormonal imbalance:
- low levels of thyroid hormone concentrations – hypothyroidism;
- increased production of thyroid hormones – hyperthyroidism.
90% of patients with low ferritin levels are women
90% of patients with low ferritin levels are women. In men, low ferritin levels are diagnosed in childhood in the presence of autistic disorder and inhibited psychomotor development.
How does hypothyroidism affect ferritin levels?
- red blood cell renewal slows down. The less often red blood cells are renewed, the less iron, or catabolic ferritin, is released;
- Acidity in the stomach decreases. In such an environment, anabolic ferritin is not formed, in other words, ferric iron is not converted into ferrous iron. It is either poorly or not absorbed at all in the intestines;
- Castle factor, necessary for the absorption of vitamins B12 and B9, is produced in smaller quantities;
- Hormones are closely interrelated; a decrease in the level of one of them certainly leads to a decrease in the level of the other. The level of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) depends on the level of the hormones thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3). They, in turn, are affected by the enzyme thyroid peroxidase, which is affected by the level of iron in the blood.
The mental development of a child (during pregnancy) directly depends on the level of folic acid, ferritin and thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH).
Women with low ferritin levels need to additionally examine the function of the thyroid gland. This is especially important when planning pregnancy, since the mental development of the child directly depends on the level of folic acid, ferritin and thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH).
When low ferritin levels persist for a long time (1 year or more), it has a negative impact on the functioning of the thyroid gland. Subsequently, due to dysfunction, the thyroid gland will not allow ferritin to increase. Therefore, it is necessary to simultaneously increase ferritin levels and correct thyroid function. It is of no use to take protein supplements unless the TSH level is between 1 and 2 micro-international units per milliliter (µIU/L).
High ferritin levels
High ferritin, close to the normal limit, indicates that tissues and organs receive a sufficient amount of iron every day from the diet, thanks to which the body is able to store reserves of an important element. If the values obtained as a result of laboratory tests gave inflated indicators, significantly beyond the acceptable limits, this is a reason to examine to identify:
- oncology;
- infection with the immunodeficiency virus;
- problems in the functioning of the endocrine system.
Separately, you need to analyze your diet. Perhaps excess iron can easily be explained by a diet rich in this element.
Still have questions? Contact us:
Elevated levels of ferritin and vitamin B12
Both a decrease and an increase in ferritin levels are associated with hormonal imbalances, namely the function of the thyroid gland and pituitary gland. There are a number of other reasons that can trigger an increase in ferritin levels.
Reasons for increased ferritin levels:
- increase in the hormone prolactin with hyperprolactinemia;
- decreased TSH levels in hyperthyroidism;
- acute and chronic liver diseases. The attending physician must determine the cause of the increase in ferritin in this case. For example, chronic cholecystitis and hepatitis are not in all cases the cause of increased ferritin levels;
- hereditary disease – hyperchromatosis. With this disease, iron contained in food is absorbed in excess quantities and distributed in tissues, where it is destroyed. This leads to intoxication and increased ferritin levels;
- hemolytic anemia is a blood disease in which pathological damage and subsequent breakdown of red blood cells occurs;
- inflammatory processes in the body, cancer (bone marrow cancer, breast cancer, Hodgkin lymphoma);
- taking combined oral contraceptives. Taking estrogen for more than 6 months;
- diet abuse, starvation;
- uncontrolled use of multivitamins, dietary supplements, iron supplements (especially in injection form - intravenously or intramuscularly);
- in some cases, drinking alcohol.
Reasons for increased vitamin B12 levels:
A person is born with normal levels of vitamin B12. The reason for the increased level of vitamin B12 is simple - it is an overdose. You cannot take vitamin B12 without getting tested. If vitamin B12 levels are normal, supplemental intake “for prevention” will lead to excess accumulation.
How to reduce elevated ferritin and B12 levels?
It is not possible to reduce elevated levels of ferritin and vitamin B12 with medications
. There is no antidote. Waiting tactics are used. The patient is examined for concomitant diseases. If detected, treatment is prescribed. At the same time, the level of ferritin and vitamin B12 is observed in dynamics. If after 1.5 months the analysis shows that the level has decreased, then we can talk about good dynamics, and it is worth taking the test again after 1.5 months to confirm the result. If the level, on the contrary, has become even higher, then it is necessary to further examine the patient.
You can speed up the decrease in ferritin and vitamin B12 levels with hirudotherapy, bloodletting and eliminating red meat from the diet.
There are contraindications for these methods; the use of any of them should be discussed with your doctor.
Before undergoing a course of hirudotherapy, it is necessary to donate blood for clotting (coagulogram). People with high blood pressure and diabetes should also consult a doctor first.
To reduce the level of ferritin and vitamin B12, 2 courses of hirudotherapy with an interval of 1 week are sufficient. The minimum number of leeches is 7-8 pcs., the maximum is 10-12 pcs.
Currently, there are two methods of bloodletting: taking blood from a vein and Hijama. Venous blood is collected exclusively in the treatment room under the supervision of a physician. The minimum amount of blood taken is 150-200 ml, the maximum is 300 ml. The procedure is repeated 2 times with an interval of 1 week. Cupping is used in the Hijama technique. This happens as follows: an incision is made on the skin, the blood is sucked out using cups.
As for temporarily excluding red meat from your diet, if you can’t completely give up this product, you should at least reduce your consumption. Red meat (beef, pork, lamb, horse meat, camel and other animal meat) should be consumed once every 10 days, or at least once a week. If a person cannot eliminate red meat at all, then white meat (poultry, rabbit, fish) can be added to the diet. Single dose in the amount of 150-200 g. 2 times a week, in the morning, or no later than 16:00.
Why does iron deficiency occur?
The causes of iron deficiency anemia are quite extensive: