In this article we will tell you:
- Causes of destruction
- Symptoms of destruction
- Diagnosis of destruction
- Methods of treating destruction
- Prognosis and possible complications of destruction
- Prevention of destruction
- Conclusion
Destruction of the vitreous body of the eye is a disease caused by changes in the composition, volume, density and structure of the vitreous substance of the eyeball. The vitreous body itself is located between the lens and the retina and resembles a transparent gel. The pathological process is characterized by an increase in protein fibers in the vitreous body - fibrils, which causes clouding, destruction, that is, destruction of the vitreous body. As destructive processes develop, the patient notices the appearance of floating flies before the eyes and a decrease in visual acuity. Conservative treatment of the disease is possible only in the early stages of development. In case of complications and advanced forms, destruction of the vitreous body of the eye is treated through surgery.
Causes of destruction
Destruction of the vitreous body develops against the background of a number of reasons, both physiological and pathological. The most common ones include:
- Inflammatory processes affecting the eyeball, occurring in a chronic form.
- Age-related changes in older people, leading to complete or partial loss of vision.
- Diabetes occurs in various forms and degrees of severity.
- Severe myopia.
- Various types of vascular diseases. These include hypertension, hypotension, and atherosclerosis.
- Acute chemical poisoning, severe radiation exposure.
- Mechanical damage and trauma to the eyeball, various options for surgical intervention.
- Exhaustion of the body.
- Acute lack of important vitamins, minerals and trace elements in the body.
- Long-term systematic visual loads.
- Various hormonal disorders.
Destruction of the vitreous body can develop against the background of improper functioning and diseases of various internal organs and systems. Some organs regulate the state of the colloidal gel, which makes up the structure of the vitreous body. For example, disorders of the liver and kidneys can lead to retinal detachment, the formation of fibrillary growths, clouding of the vitreous body of the eyeball, and the acquisition of a granular structure by the colloidal gel.
A little anatomy
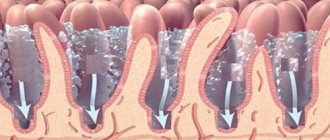
The vitreous body is a gel-like colloidal substance that occupies about 85% of the total volume of the eye and is 99% water.
It has an integral structure due to the presence of the finest fibrillar network. Its main component is hyaluronic acid, the molecule of which has a spiral ornate structure and gives the vitreous fluid a gel-like consistency. On the outside, the vitreous body is surrounded by a membrane consisting of collagen fibers tightly adjacent to each other. Normally, the vitreous body is an optically transparent light-conducting medium. It helps maintain the shape of the eye and also lies in the path of the light ray from the cornea, iris and lens to the retina. The three main attachment points of the vitreous membrane are the area of the optic nerve head, the area of the lens, and the so-called base, where the membrane is attached to the ciliary epithelium.
Sometimes, looking at the sky on a sunny day, any healthy person can notice small “snowflakes” or “cobwebs” slowly floating before their eyes. These are the collagen fibers of the vitreous body that a person can see normally. However, with age, the structure of this part of the eye can change greatly, causing patients significant visual discomfort.
Symptoms of destruction
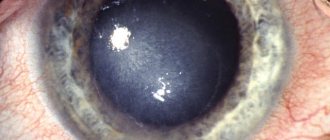
External symptoms of destruction of the vitreous body of the eye are most often absent. Among the most pronounced and common symptoms accompanying the disease of the vitreous body of the eyes is the appearance of so-called “floaters”. Unlike a number of other eye pathologies, including myopia, signs of destruction of the vitreous body are specific:
- Cloudiness, floaters, and granular spots appear constantly, regardless of the degree of visual strain and fatigue of both eyes.
- The size and shape of floating flies are constant.
- The above signs, regardless of the degree of development of the disease, are especially noticeable when the patient looks at a light background under moderate lighting.
Destruction of the vitreous body (vt) is characterized by changes in symptoms as the disease progresses. If filamentous and floating elements acquire a pronounced shape and become more noticeable, this indicates processes of destruction of the colloidal gel. Timely detection of pathology will avoid serious consequences, including multiple fibrillary growths and retinal detachment.
Types of opacities
“Flies” can vary in size, color, and shape. The following types of opacities are quite common:
- Multiple dots, thread-like web. Such opacities, as a rule, appear at a young age and have different sizes and locations.
- Cloudiness similar to floating clouds. Such diffuse opacities are more common in mature and elderly people and may be associated with the aging process of the body.
- Cloudiness in the form of rain or snowflakes. Such opacities are also typical for older people suffering from cholesterol metabolism disorders or diabetes mellitus. “Rain” can have a golden or silver tint, and the crystals of “snowflakes” vary in shape, size and have a golden, beige or brown color.
- Ring of Weiss. A large ring-shaped opacification, which is a sign of vitreous detachment.
Diagnosis of destruction
The diagnosis of vitreous destruction is made after a series of ophthalmological studies:
- Checking visual acuity.
- Studying the patient's history and complaints.
- Examination of the fundus to identify pathologically altered areas with fibrillar growths.
- Examination using a slit lamp - a device for biomicroscopy of the eye.
When making a diagnosis, the results of all the above studies are taken into account, which make it possible to determine the presence or absence of destructive changes. Determining the degree of DST is of particular importance when making a diagnosis, since an individual treatment regimen is developed based on the data provided.
What to do when flying flies appear?
The best thing to do when flying flies appear is to consult an ophthalmologist. It is advisable to see a fundus specialist - a retinologist. There is a doctor of this specialty in every clinic that deals with laser vision correction, as well as in centers that specialize in diseases of the posterior part of the eye. In addition to examining the fundus, it is advisable to do an ultrasound of the eyes. It is especially important to consult a doctor as soon as possible in case of a spontaneous increase in the number or size of flies and, even more so, when sparks/lightning appear
.
However, you should not panic when flies appear, especially if there are small numbers of them, which cause psychological discomfort rather than real vision problems. There are “floaters” that a person sees in bright light, when looking at snow, at a blue sky, and they are almost constant. Sometimes a person pays attention to them, sometimes not. Do not be surprised that in some cases the doctor will not detect problems with the vitreous humor at all. The size, structure and composition, as well as the location of the floaters, are all important in identifying the cause of the phenomena that bother patients.
Methods of treating destruction
There is no specific treatment for the destruction of the vitreous body, as such.
The therapeutic regimen for DST of the eye is developed on an individual basis, taking into account the specifics and characteristics of the course of the pathology. If moderate destruction of the vitreous body of the eye is detected, treatment is based on the use of conservative therapy and correction of the patient’s lifestyle. The patient may be advised to do gymnastics, eliminate visual stress, and refuse to perform heavy physical work.
If the disease manifests itself mildly and is at an early stage of development, the doctor may recommend that the patient not undergo any procedures, but limit himself to observation. If the granular and filamentous formations are of insignificant or moderate size, the disease does not progress, nothing needs to be done, the patient’s condition, if he follows the correct lifestyle, will stabilize without medical intervention after some time.
If the disease progresses, conservative therapy is necessary. The doctor prescribes an individual treatment regimen, within which the patient may be prescribed the following medications:
- Drops that promote the resorption of pathological formations. These include: Wobenzym, potassium iodide. Most often, course therapy is required.
- Cavinton, as well as Cinnarizine. The use of these drugs stimulates blood flow in the brain area. It is mandatory to undergo a course of such therapy for patients suffering from cerebrovascular accidents.
- Emoxipin. Improves metabolic processes in the vitreous tissues of both eyeballs.
Depending on what particular disease caused the development of destructive processes affecting the structures of the eyeball, the patient may be prescribed drugs for both topical use and oral administration. For example, they stimulate blood flow, improve metabolic and regenerative processes, and also have an immunomodulatory effect.
If a solution to the problem is not found in a conservative way, the use of drops does not give a positive result, surgical intervention is necessary. The operation is not always possible, or it does not give the necessary results. In certain situations, surgical manipulations, including those performed with a laser, can provoke severe complications and negative consequences, for example, vascular thrombosis, retinal detachment. Surgical intervention cannot cure the disease in older people, since it develops due to age-related changes.
There are several surgical options:
- Vitreolysis. It is recommended to perform surgery more often against the background of relatively small pathological formations. The procedure is carried out with a laser, its essence is to split the existing opacities. Using a laser can effectively cure the disease and reduce possible risks to a minimum.
- Vitrectomy. The operation involves replacing the colloidal gel with substances of artificial origin, including saline solution and silicone oil.
In addition to the above methods, the disease is treated using special eye gymnastics. Gymnastics should be done only if there are no contraindications, otherwise it can be dangerous. Most often, this is a set of standard exercises: alternate movements of the eyeballs to the left, right, up, down, rotation clockwise and back, concentrating the gaze on the tip of the nose and looking away into the distance. There are also a number of specially developed systems: Norbekov, Zhdanov, Bates.
How can destruction of the vitreous body be treated?
Destruction is treated in various ways. The choice of method depends on the form of the disease and the degree of its development.
Typically, therapy includes:
- use of medications;
- performing special exercises for the eyes;
- use of folk remedies.
In some cases, surgery is prescribed - vitreolysis or vitrectomy.
Prognosis and possible complications of destruction
Destruction of the vitreous body in most cases does not lead to the development of severe complications and consequences.
Remission, which can last several years, occurs quite quickly. The prognosis is often favorable. Exception: patients over 60 years of age - in their case there is a high probability of progression of pathological processes. Pathological changes in the colloid body lead to deterioration of vision and, accordingly, a decrease in quality of life. The need to constantly strain the organs of vision worsens the patient’s mental state and can cause nervous breakdowns and overexertion.
Why destruction of the vitreous body of the eye is dangerous - DST can cause complete or partial loss of vision, retinal detachment.
Classification and pathogenesis
DST can be either partial or complete. As a rule, the process of destruction first affects the central parts of the organ. First, cavities are formed in which liquid and individual collagen masses are found. Subsequently, an increasing number of fibrillar proteins are susceptible to coagulation. They go beyond the structure, the gelatinous substance of the vitreous body liquefies. Films and cords of various origins are formed inside, sometimes fixed on the fundus, which leads to wrinkling and the formation of adhesions. The decreasing volume and deformation of the vitreous body causes tension in the vitreoretinal connections, which subsequently provoke retinal detachment.
CT destructions differ in form: filamentous, granular, crystalline. The cause of the filamentous form of DST is progressive myopia or atherosclerosis. Granular lesions of the vitreous body arise due to inflammation in the inner layer of the retina. In rare cases, damage to the colloidal gel is caused by deposits of tyrosine and cholesterol crystals.
Prevention of destruction
There are no preventive measures aimed directly at preventing the development of vitreous pathology. However, there are tips that will help eliminate the occurrence of factors leading to pathological changes:
- Quitting bad habits (alcohol, smoking).
- Changing your diet, giving up heavy animal foods in favor of plant foods.
- Maintaining an active lifestyle.
The given recommendations will improve the condition of the vascular system and prevent pathological changes in the eyeball. It is especially important for middle-aged people to follow these rules.
Contraindications for vitreolysis
- clouding of the optical media, as well as the appearance of obstacles to the passage of the laser beam (hyphema or suspension in the moisture of the anterior chamber, cataracts, edema and opacities of the cornea);
- luxation of the lens into the vitreous;
- pronounced neovascularization;
- high risk of hemorrhage according to blood parameters;
- retinal disinsertion;
- detachment of the choroid.
Some of these contraindications may be relative.
It is important to know! The modern approach to the treatment of pathological changes in the vitreous body, used in our clinic, can significantly improve the quality of life and eliminate the risk of possible complications and loss of vision in the future!
To make an appointment at Dr. Kurenkov’s clinic or get information about the cost of examination and treatment, call +7 (495) 781-9333.
Current issues
Ë
È
Is it possible to operate on glaucoma again?
For glaucoma, surgery can be repeated. In addition to glaucoma surgery, surgery may be done to improve the blood supply to the eye. Various therapeutic methods are also used for the same purpose. If glaucoma is combined with cataracts, the Excimer Eye Clinic will perform surgery for both of these diseases at the same time.
Ë
È
Please tell me how the specialists at your clinic feel about the use of various eye vitamins in children of primary school age as a prophylactic agent to reduce eyestrain, prevent myopia, etc. How effective and justified is this?
The use of vitamins for the eyes is certainly useful, but it must be borne in mind that in all cases the use of nutritional supplements or vitamins only complements the main type of treatment. In particular, preventing myopia with the help of vitamins is impossible; there are effective methods for this. We recommend that children (especially at primary school age, when the load on the visual system increases) undergo a full diagnostic examination annually. After this, the doctor will prescribe preventive or therapeutic procedures.
Ë
È
I heard that the problem of poor vision due to myopia can be solved with the help of orthokeratology. Tell us what this method is?
Orthokeratology (night lenses) is a method of correcting myopia using special gas-permeable lenses that have a reverse geometry design compared to conventional lenses. Night lenses gradually change the shape of the cornea, making its central optical zone flatter. In the morning, the patient removes the lens, but the cornea retains its new shape, the image is fixed on the retina, and the person sees everything clearly. However, we draw your attention to the fact that orthokeratology (the use of night lenses) does not give a permanent result, namely, it does not solve the problem once and for all. After you stop wearing it, the cornea restores its previous shape, and you still have myopia.
| Ask a Question | All questions |
Sign up for an excimer clinic and learn more about your health!
You can call by phone
Or click the button and fill out the application form and receive a 5% discount on a full vision diagnostic
Make an appointment
Our address: Moscow, st. Marksistskaya, 3, building 1
"Excimer" on the map of the "Excimer" Clinic in other cities