Advantages of treatment in our clinic:
|
Loss of sensation in the toes may be accompanied by tingling or burning, and difficulty walking often occurs. The reason for contacting Dr. Savyak’s clinic is chronic numbness in the lower limb. This condition is dangerous due to injuries and wounds that cannot be felt due to decreased or complete loss of sensitivity. Mobility problems increase, which means the risk of falling increases.
Why can the tips of my toes go numb?
Factors contributing to the development of paresthesia (decreased sensitivity) may include:
- injuries, including minor ones (for example, due to wearing shoes that are too tight);
- neurological disorders, in particular after head or spinal injuries;
- spine pathologies;
- spinal cord injury;
- nerve compression;
- circulatory disorders, vascular diseases;
- endocrine pathologies;
- joint diseases.
It must be taken into account that diseases can be combined. For example, decreased sensitivity can be caused simultaneously by a disease of the spine and circulatory disorders.
What measures should be taken for numbness?
If the causes of numbness are external, you can cope with them on your own. For example, change your shoes to something more spacious that doesn’t squeeze your toes and feet. If the reason is an uncomfortable position, large vessels may be squeezed, causing the fingers to go numb. Changing your posture will solve this problem too.
Light massage movements, as well as baths in which warm water will alternate with cold, will help restore blood circulation and restore sensitivity to the fingers. Exercise and morning jogging will also help improve blood circulation.
You should also pay attention to your diet. It should contain a sufficient amount of foods containing vitamins B6 and B12. These are eggs, chicken and quail, meat, milk, cereals, legumes, sprouted wheat. It is better not to abuse coffee and strong black tea. But it is advisable to get rid of bad habits altogether.
Self-help and self-diagnosis
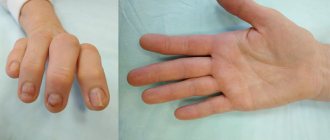
To answer the question of what to do if your toes go numb, you need to understand the causes of this condition. Loss of sensitivity in the fingers, local increase in temperature, swelling and decreased mobility may indicate a disease of small joints: arthritis, arthrosis or gout. Arthrosis and arthritis are characterized by a slow and gradual increase in symptoms. With gout, the toes go numb and burn, swell greatly, while the discomfort is paroxysmal in nature and is accompanied by an increase in temperature. If these symptoms occur, you should consult an orthopedist or rheumatologist. What to do if your toes go numb due to uncomfortable shoes:
- perform a light foot massage;
- take a warm bath with sea salt.
These actions relieve discomfort, but it should be remembered that constantly wearing unsuitable shoes often leads to the development of degenerative diseases of the joints of the lower extremities. Osteochondrosis, spondylosis, arthrosis of the spine, protrusions and hernias, tumors in the spine and soft tissues can also cause numbness in the fingers. All of these diseases can cause circulatory problems, nerve compression, and spinal cord damage. The following symptoms are typical for numbness of the fingers caused by spinal pathologies:
- decreased mobility;
- impaired coordination of movements;
- crunching, clicking when moving;
- pain in the back and chest;
- headache;
- changes in hearing, vision;
- dizziness;
- periodic “disobedience” of the limbs;
- causeless weakness;
- pressure surges.
If such signs appear, it is important to consult a neurologist or orthopedist as soon as possible. Without treatment, dangerous complications such as paralysis, spinal cord damage and cerebral hemorrhage may develop. In case of foot injuries, numbness and pain, as well as changes in the shape of the finger and skin color, swelling may not appear immediately, but several hours or in the morning after sleep. If these symptoms are detected, urgent assistance from a traumatologist is required. In the case of pathologies of the cardiovascular system, paresthesia is usually combined with coldness of the legs, the appearance of hematomas without bruises, a pronounced vein pattern and the formation of spider veins. If such signs are detected, you should visit a therapist or phlebologist.
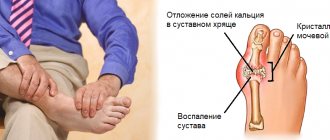
MAIN CAUSES OF numbness in the extremities:
CARDIOVASCULAR CAUSES. The reason is poor circulation in the limb.
The cause of the disorder may be hypothermia, narrowing of blood vessels (atherosclerosis), thrombosis, coronary heart disease, stroke, diabetes, vascular stenosis. NEUROLOGICAL CAUSES. In cases where there is damage to the nervous system, numbness can occur throughout the body. Serious diseases such as encephalitis, brain tumors, multiple sclerosis, myelitis, hypothyroidism destroy the nervous structure, which is why numbness is systemic. In cases where there is damage to the nervous system, numbness can occur throughout the body. Serious diseases such as encephalitis, brain tumors, multiple sclerosis, myelitis, hypothyroidism destroy the nervous structure, which is why numbness is systemic.
ORTHOPEDIC REASONS. Loss of sensation in the arms and legs often acts as a concomitant symptom with various diseases and injuries of the musculoskeletal system.
RADICULITIS. This term refers to compression of the nerve root of the spinal cord. Depending on the location of the pinching, radiculitis can be cervical, thoracic, lumbar and lumbosacral. There is pain in the spine, which radiates to the limbs and is accompanied by a burning and tingling sensation.
TUNNEL SYNDROME. A special case of numbness in the hands. Occurs as a result of compression of the median nerve of the hand. Accompanied by pain in the wrist area.
OSTEOCONDRITIS OF THE SPINE. Degenerative changes in tissues lead to the formation of a hernia, which pinches the nerve endings. This causes numbness in the arms and legs. As a result, there may be a feeling of numbness and tingling in the legs, arms, hands, and feet.
Medical examination for paresthesia of the toes
Even if the discomfort does not cause you much inconvenience, consulting a doctor is still necessary. Initially minor discomfort can eventually lead to paralysis and other serious complications. When starting treatment early, both its price and duration will be much less than in the case of late consultation with a doctor. After studying the medical history and examination, the doctor will definitely refer the patient for additional examination. To identify the causes of discomfort, various diagnostic methods may be required, for example:
- X-ray and MRI of joints and spine;
- CT head;
- Vascular ultrasound;
- laboratory tests (blood and urine tests, puncture of intra-articular fluid or cerebrospinal fluid).
Diagnostics
Neurologists are involved in determining the cause of foot numbness. Patients with vascular diseases are referred to a vascular surgeon. An endocrinologist takes part in the examination of patients with diabetes. The doctor finds out when and under what circumstances the sensitivity disorder occurred, how the symptom changed over time, and what manifestations it was accompanied by. To clarify the diagnosis, the following procedures are performed:
- Physical examination
. The specialist evaluates the appearance of the foot, color, skin temperature, and pulsation of the arteries. Reveals signs of edema and inflammation, hyperkeratosis, cracks, abrasions, trophic ulcers. - Neurological examination
. The doctor examines reflexes, determines the boundaries of sensitivity disorders, the presence of muscle atrophy, and neurogenic contractures. - Vascular studies
. The condition of the arteries is studied using ultrasound, duplex scanning, rheovasography, capillaroscopy, thermography, and peripheral arteriography. - Electrophysiological methods
. To differentiate neuropathies and clarify the level and severity of the lesion, patients undergo electromyography and electroneurography. - Visualization techniques
. To clarify the genesis of the pathology, ultrasound of soft tissues, radiography of the spine, CT or MRI of the brain, and other studies may be prescribed. - Lab tests
. As part of a laboratory examination, sugar levels are determined and cholesterol fractions in the blood are examined. To establish the nature of the underlying pathology in Raynaud's syndrome, tests are performed for specific markers.
Foot sensitivity test
Treatment of paresthesia
Treatment of diseases that cause numbness in the toes depends on the causes of their development. In general, the treatment plan for most of these pathologies is similar:
- taking medications;
- physiotherapy;
- massage;
- physiotherapy.
If abnormalities are detected at an early stage, it is often possible to do without taking medications. At later stages of the development of joint pathologies, as a rule, anti-inflammatory, analgesic and decongestants, muscle relaxants and chondroprotectors are prescribed.
Physiotherapy improves blood circulation and metabolic processes, relieves pain and excessive muscle tension. Laser treatment, heating, electrophoresis, magnetic therapy and other procedures are usually used. Exercise therapy and massage are necessary to restore joint functions, increase muscle tone and volume, improve blood flow and eliminate compression of nerves. In some cases, you may also need to wear orthopedic shoes. To prevent loss of sensitivity in your toes, you need to choose a healthy diet, give up bad habits, exercise regularly and wear properly fitted shoes. This will avoid the development of articular and vascular pathologies and maintain normal sensitivity and mobility of the foot.
What external factors cause paresthesia?
Numbness of the big toe, little finger, and other toes can be caused by external causes that are not related to the general condition of the body. Paresthesia may occur due to:
- uncomfortable pose. When sitting in a position where one leg is crossed over the other or placed under oneself, the nerve is sometimes pinched and blood flow is reduced. First, a tingling sensation is felt in the fingers, then numbness sets in. When changing posture, all symptoms gradually disappear;
- increased load on the legs. This may cause pain, numbness and fatigue;
- presence of corns. Dead cells deposited in one place on the skin of the fingers or the foot itself reduce their sensitivity. Pain occurs when walking;
- any trauma that causes nerve damage. This causes movement to become somewhat limited as it heals, which can cause pain. The consequences of such an injury may be periodic numbness of the fingers;
- tight shoes or too narrow socks. Regular squeezing of the leg leads to swelling, which impairs its blood circulation, which is accompanied by subsequent numbness;
- poisoning With the regular intake of nicotine or other toxic substances into the body, a gradual narrowing of blood vessels occurs, impeding blood flow. At the same time, the walls of the blood vessels become thinner, which can also have unpleasant consequences.
Treatment
Pre-hospital assistance
If a spinal cord injury is suspected, spinal immobilization and immediate delivery to a neurosurgical hospital are required. First aid tactics for nerve damage are determined by the nature of the injury. Victims with wounds need to apply an aseptic dressing. For all leg injuries, especially those accompanied by severe swelling, it is necessary to ensure that the limb is in an elevated position. If numbness or increased swelling occurs after fixation with a plaster cast, you should urgently go to the emergency room to cut the plaster.
Conservative therapy
In case of neuropathies, the etiofactor is eliminated if possible. Medicines to improve blood circulation, NSAIDs, and B vitamins are prescribed. For pain, trigger point blockades are carried out. The list of non-drug methods includes ultraviolet irradiation, diadynamic therapy, and UHF. Massage, manual therapy, and physical therapy exercises play a significant role.
For vascular diseases, antithrombotic agents, antispasmodics, vitamins, and medications are recommended to reduce red blood cell aggregation. Intense pain is an indication for the use of painkillers and paravertebral and perirenal blockades. Patients with acute occlusion are administered thrombolytics and anticoagulants.
Non-drug methods for treating vascular pathologies include hyperbaric oxygen therapy, ILBI, ozone therapy, mud applications, magnetic therapy, UHF, medicinal electrophoresis, pearl, radon, and hydrogen sulfide baths. Patients with trophic ulcers undergo dressings and laser treatment.
If there is numbness in the feet due to diabetes mellitus, an adjustment of the insulin dose or transfer of the patient to insulin therapy is required. Drug treatment includes antispasmodics, a-lipoic acid preparations, and infusions of solutions. For ulcerative defects, dressings and antibiotic therapy are indicated.