If problems occur in the reproductive system (infertility), in addition to other tests, specialists at the K+31 reproductive medicine clinic prescribe an analysis to detect the level of FSH in the blood. Below is detailed information about what FSH hormone is and its importance to human health.
Follicle-stimulating hormone is produced by the anterior pituitary gland together with luteinizing hormone (LH). It plays an important role in regulating the functioning of the reproductive system. Its main task is to promote the formation and maturation of reproductive cells. The hormone also affects the synthesis of estrogen.
FGS affects the functioning of the male and female bodies differently.
What is FSH
Follicle-stimulating hormone is produced by the anterior lobe of the pituitary gland, regulates the menstrual cycle, affects the timely maturation of follicles, the synthesis of estrogens, and the conversion of testosterone to estrogens.
Its production occurs as a result of a complex process that involves the pituitary gland, hypothalamus, ovaries in women, testes in men, and adrenal glands. The secretion of this compound occurs through a process of feedforward and feedback. Any malfunction or disease of the organ involved in this process can disrupt the synthesis of FSH. The hormone is increased or decreased - this is a sign of a malfunction in the body. The level of this compound in the blood of newborn children increases some time after birth; in boys it falls by six months; in girls, high FSH falls between the ages of one and two years. In the future, FSH will be elevated before the onset of puberty, when children begin to develop secondary sexual characteristics.
Follicle-stimulating hormone analysis is prescribed to solve the following problems:
- Identification of the causes of the development of sexual dysfunctions - primary or secondary nature of the disorders.
- Determining the cause of infertility. In this case, it is also necessary to obtain test results for testosterone, progesterone, luteinizing hormone and estradiol.
- Search for the cause of spermatoginesis disorders.
- Calculation of the menstrual cycle and or menopause.
- Diagnosis and monitoring of early and late puberty.
- Determining the effectiveness of hormone therapy and monitoring treatment.
- Analysis for follitropin (FSH) and luteinizing hormones (LH) allows the doctor to determine the tactics of treating infertility in both men and women.
FSH in a woman's life
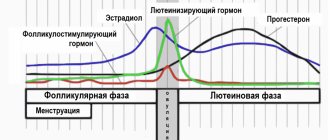
Follicle-stimulating hormone affects the reproductive function of women and men. It is involved in the regulation of a woman's menstrual cycle. It stimulates the development of follicles and egg maturation, which is then completed by luteinizing hormone (LH). FSH stimulates the development of several follicles, some time later only one follicle remains - the dominant one, the development of other follicles stops. FSH hormone is elevated while the dominant follicle is developing. The follicular phase is accompanied by the release of estrogen, the formation of the inner layer of the uterus. The resulting cervical mucus becomes immune to the man's sperm.
In the middle of the menstrual cycle, the levels of FSH, LH and estradiol rise. At the peak of their release, ovulation begins - the release of a mature egg from the follicle. The level of follicle-stimulating hormone drops - the luteal phase begins, which will last until pregnancy. When pregnancy occurs, progesterone begins to be produced, which will support the pregnancy. If pregnancy does not occur, it is the turn of menstruation. At this time, preparations are already underway for the new menstrual cycle - the hypothalamus synthesizes GnRH, GnRH affects the pituitary gland, the pituitary gland begins production of the hormones FSH and LH. A woman's ovaries begin producing estradiol. Soon new follicles will begin to develop.
When to check FSH levels
Analysis of the level of follicle-stimulating hormone is one of the important tests in diagnosing disorders of the reproductive system. The attending physician (gynecologist, reproductive specialist or endocrinologist) may prescribe a study of this hormone in the following situations:
- lack of ovulation (frequent anovulatory cycles);
- history of miscarriage (miscarriages, miscarriage, placental insufficiency);
- infertility (lack of pregnancy with regular sexual activity without using contraception for more than a year);
- menstrual irregularities;
- presence of polycystic ovary syndrome;
- endometriosis;
- uterine bleeding;
- decreased sex drive;
- hypofunction of the gonads;
- chronic inflammatory processes in the genital organs.
When diagnosing the causes of infertility, FSH levels will be analyzed in parallel with the results of studies of LH, progesterone, estradiol and testosterone.
To obtain reliable test results, some preparations must be made before the study:
- the test is taken on an empty stomach, that is, the last meal should be 7-8 hours before the test (you can drink clean still water);
- three hours before the test you should not smoke;
- 24 hours before the study, it is necessary to avoid drinking alcohol;
- on the eve of the test, do not eat fatty foods;
- 24 hours before the study, exclude physical and emotional stress;
- 72 hours before the study, stop taking thyroid and steroid hormones (in consultation with your doctor);
- immediately before the study you need to calm down.
Various factors influence the conduct of the study. Inadequate indicators can be obtained when:
- recent magnetic resonance imaging;
- taking oral contraceptives;
- taking radioisotope drugs;
- taking drugs that increase FSH levels (bromocriptine, finasteride, somatoliberin, GnRH analogues, etc.);
- taking medications that reduce FSH levels (anabolic steroids, estrogen- and progesterone-containing drugs, anticonvulsants, etc.);
- pregnancy.
FSH analysis is performed on days 6-8 of the menstrual cycle, unless other dates are specified by the attending physician.
FSH is elevated in women
In women, the concentration of this compound is increased if endometrial cysts have formed, the woman is taking medications that affect the increase in concentration, or a pituitary tumor has developed. Very often the cause of high rates is a woman’s alcoholism. FSH is elevated if a woman is being treated for a malignant tumor with radiation therapy or chemotherapy. This condition in women can manifest itself as a lack of ovulation, menstrual irregularities, uterine bleeding, endometriosis, infertility, in girls (more common than in boys) premature sexual development (breast growth, pubic hair), in boys genital growth or developmental delay, growth retardation. This pathology often develops due to damage to the central nervous system, ovarian cysts or ovarian tumors, due to the development of a hormone-secreting tumor, and in boys due to a testicular tumor. The following factors cause high FSH:
- Polycystic ovary syndrome is a dysfunction of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal-ovarian system, which, with certain mutations, leads to damage to the insulin receptor and provokes the development of PCOS against the background of insulin resistance. Gene mutations can lead to PCOS due to adrenal hyperandrogenism. The disease can develop after suffering stress, chronic infection, or as a result of obesity.
- A pituitary tumor is a benign or malignant tumor that causes a disruption in the production of biologically active substances.
- Endometrial cyst - the cause of development is unknown, causes hormonal imbalance and severe infertility.
- Endometriosis – the causes of the disease are unknown. It is believed that the development of the disease is influenced by endometrial hormone-sensitive receptors and gene mutations.
- Menstrual irregularities – absence of menstruation, dysfunctional uterine bleeding caused by hormonal imbalance, dysfunction of the ovaries.
- Kidney failure.
- Radiation therapy.
- Chemotherapy.
- Autoimmune diseases.
- Thyroid diseases.
- Diseases of the adrenal glands.
- Ovarian tumors - disrupt hormonal synthesis in the ovaries, causing a malfunction in the hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal-ovarian system.
The consequences of increasing FSH levels are:
- Miscarriage.
- Infertility.
- Decreased libido
If a woman has such disorders, the doctor prescribes a test. Along with the analysis of the level of follicle-stimulating hormone, a study of the level of LH, estrogen, and progesterone is prescribed. When studying hormonal levels, great importance is attached to the ratio of the FSH-LH hormones. If the ratio is disturbed, this may indicate the development of the disease. FSH hormone is increased in women during menopause and postmenopause. It is elevated because the ovaries no longer respond to the hormones produced by the pituitary gland, the body receives more and more follicle-stimulating hormone and luteinizing hormone, which oversaturate the body, causing poor health.
FSH is increased in a woman of reproductive age to 40 mIU/ml - pregnancy will not occur. It is increased with dysfunction of the gonads, after removal of the ovaries, with an increased level of testosterone in a woman’s body, with Shereshevsky-Turner syndrome, and can be a signal of the onset of early menopause. Very often, high FSH is an indicator of poor egg quality and reduced ovarian reserve in a woman’s body. Treatment of the disorder has a beneficial effect on the quality of female reproductive cells and increases the chances of pregnancy.
FSH hormone is the norm for women, men and children
In women, unlike men, there are several norms of this hormone, since in different phases of the menstrual cycle its level has different values. For individual phases in women, the following norms of follicle-stimulating hormone are indicated:
- less than 12 IU/l in the follicular phase;
- from 20 to 90 IU/l during ovulation;
- less than 10 IU/l in the luteal phase.
Changes in FSH levels during the menstrual cycle
FSH levels also change during periods characterized by significant changes in the endocrine sphere. For example, in menopause, this is a level in the range from 40 to 250 IU/l. In the future, the concentration of this hormone in the blood may increase even more. And in case of pregnancy, the woman’s body must contain a small amount of follicle-stimulating hormone.
For men, a single norm has been established for follicle-stimulating hormone - between 4 and 25 IU/l.
As mentioned above, sometimes follicle-stimulating hormone levels are also measured in children. The FSH standard for children under eleven years of age is less than 2 IU/L.
If a test for FSH levels was prescribed due to infertility, it is recommended to simultaneously test for lutropin. This is important, since the ratio of lutropin (indicated by the symbol LH) to the FSH hormone is of great importance in the diagnosis of infertility.
Why should LH, FSH, and estradiol be tested in our center?
Our medical center specializes in the treatment of infertility of various natures. Every year we help hundreds of happy families become parents. We can conduct not only FSH analysis, but also other examinations that will help doctors understand the condition of your reproductive system and prescribe effective treatment.
When the FSH hormone is elevated, the norm of which was calculated for specific age-biometric indicators, our specialists at the IVF Center clinic in Tambov will help you cope with this syndrome. We conduct comprehensive examinations of both partners to understand what in a particular case is preventing natural fertilization and pregnancy. To do this, simply sign up for a consultation using one of the numbers presented on our website.
When is a follitropin test prescribed?
- For infertility in both sexes.
- If you suspect the presence of hormonal disorders of sexual function.
- Problems with ovulation and miscarriage.
- If pituitary pathology is suspected.
- Disruptions of the menstrual cycle (unsystematic or complete absence).
- Congenital, genetic diseases.
- Impaired growth (short stature) and puberty in adolescents.
- Chronic inflammation of the reproductive system.
A test for follitropin is prescribed during hormonal therapy to monitor the treatment process and adjust the intake of medications.
Decoding the analysis results
Normal FSH levels in men range from 0.7 to 11.2 mIUml.
The indicator in women depends on the menstrual cycle
Phase I from 2.8 to 12.5 mIUml;
Phase II from 1.2 to 9.1 mIUml;
ovulation period from 5.8 to 21.1 mIUml;
premenopause (beginning of menopause) from 1.7 to 25 mIUml;
postmenopause (menopause) from 21.7 to 153 mIUml.
Treatment for elevated follicle-stimulating hormone levels
As you know, when the FSH level increases to 40, conception becomes impossible, even for young girls. Most doctors believe that FSH levels should drop before the first stage of the IVF procedure begins. But it should be understood that an increase in follicle-stimulating hormone is not a disease, but only a symptom of the disease, and in fact reflects the work of a woman’s ovaries.
Accordingly, treatment for elevated levels consists of treating the underlying disease, in particular ovarian failure (primary or secondary). In primary, the FSH level is increased, and in secondary, FSH and LH are decreased. In both cases, there is a lack of ability to conceive.
Treatment for elevated FSH is carried out using hormonal replacement therapy - estrogens. Doses are selected individually and gradually increased. This stimulates the development of secondary sexual characteristics. Then the patient is transferred to a cyclic treatment regimen.
General information about follitropin and the study
FSH is produced sporadically together with LH hormone by basophilic cells of the pituitary gland. With reduced secretion (deficiency) of hormones, the following symptoms are noted:
For men:
- insufficient growth and general developmental delay;
- congenital and acquired underdevelopment of the gonads;
- inhibition of spermatogenesis processes.
Among women:
- underdevelopment of the mammary glands;
- inhibition of follicle maturation;
- infantilism, frigidity, infertility.
This happens because sex hormones directly interact with cell receptors in the testicles and ovaries. With reduced production, exposure is insufficient to stimulate the development of primary and secondary sexual characteristics during adolescence. Subsequently, hormonal deficiency also affects the development and rate of development of follicles in the ovaries and during spermatogenesis.
LH and FSH hormones: tests
The human body does not always work like a clock. Any failures can cause unpleasant diseases. If FSH deviates from the norm, then existing diseases can develop into various serious pathologies. Disturbance in the production of LH hormone leads to the same consequences.
To determine your hormone levels, you need to take tests. To determine the FSH hormone in women, a blood test is taken 3-5 days after the start of menstruation (follicular phase). Men can do this at any time. Before taking the tests, you need to consider some rules.
- Testing takes place on an empty stomach. It is allowed to drink water without gas.
- You can't take hormones.
- It is necessary to eliminate physical exercise and stress, as well as reduce emotional stress.
- You must refrain from smoking for three hours before the examination.
If you decide to conceive a child, be sure to undergo a full medical examination, including a test for the FSH and LH hormones, to rule out infertility and, in case of problems, undergo the necessary treatment.
Follicle stimulating hormone in men
FSH is a hormone that increases the amount of testosterone in plasma, accelerates protein synthesis, combines sex hormones and spermatogenesis and is responsible for sperm quality.
The level of concentration of follicle-stimulating hormone in men increases and increases until the end of puberty. In the future it remains at the same level. If the concentration of FSH in the blood is low, then the functioning of the pituitary gland and hypothalamus should be checked. If the concentration of the hormone is increased, then most likely tests will show that there is insufficient functioning of the testicles.
Complexes with this research
Check-up No. 1 for children and adolescents Annual preventive examination program 10,950 ₽ Composition
Fitness control of sports nutrition Assessment of liver function, hormone levels and metabolism when taking sports nutrition 5,140 ₽ Composition
Male hormones Assessment of hormonal levels in a man at any age RUB 6,180 Composition
IN OTHER COMPLEXES
- Fitness monitoring 6,780 RUR
- Advanced anti-aging diagnostics in postmenopause RUB 29,230
- Anti-aging diagnostics. Hormonal balance RUB 6,250
- Advanced male anti-aging diagnostics RUB 33,710
- Female hormones. Follicular phase RUB 5,930