December 3, 2020
Contact dermatitis is an inflammation of the skin in an area that has come into contact with an irritating substance or environmental factor. Children under 12 years of age are most susceptible to the disease. The point is the structural features of children's skin and the weakness of its protective mechanisms. The disease manifests itself in any area that has been in contact with the irritant, but more often on the face, arms, neck, and groin area.
If the provoking agent is recognized in time and the child is protected from it, the inflammation is well treated and the symptoms quickly pass. When the cause is difficult to identify or parents do not consult a doctor on time, the course of the disease becomes more severe.
Contact dermatitis occurs:
- simple - local irritation by some factor;
- allergic.
The second option will appear when the child has an increased sensitivity to this substance. The first interaction with it is outwardly unnoticeable, but chemicals are formed in the skin that bind to immune cells - T-lymphocytes. Immune cells remember the stimulus. Upon repeated contact, which can occur after a long time, T-lymphocytes trigger an allergic reaction and cause skin symptoms.
How to recognize allergic contact dermatitis in a child
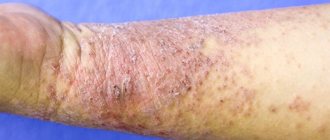
The contours of the inflammation often coincide with the outlines of the object that caused the irritation. The rash spreads little beyond the area of skin that came into contact with the causative factor. The skin here becomes red and swollen, very itchy, blisters, wounds and crusts appear.
Fungal and bacterial infections easily attach to wounds and suppuration occurs. Babies may experience an increase in general temperature.
Frequent exacerbation in the same places leads to unpleasant outcomes: areas of increased or decreased pigmentation, scars, thickening and roughening of the skin.
If you notice a rash or red spots on your child’s skin, be sure to see a doctor to get tests done to determine the exact cause and begin treatment.
The disease may worsen. To prevent this from happening, you need to find and eliminate the provoking causes.
What is dermatitis?
Dermatitis is a skin reaction to external irritants of a biological, physical or chemical nature.
The disease manifests itself in the form of irritation on the skin and can cause the baby not only physical, but also emotional discomfort. The most typical manifestations of dermatitis include:
- redness,
- peeling of the skin,
- rashes that cause itching and pain.
However, dermatitis is not so scary if you know the reasons for its occurrence, be able to distinguish it from other diseases, carry out prevention and seek help from a specialist in a timely manner.
External causes of the development of allergic dermatitis in children
The disease can be caused by one of the factors or a combination of several.
- Physical - friction or pressure on the skin of fabrics, leather products, high or low temperatures, humidity, electric current, ultraviolet or x-rays.
- Chemical - various acids and alkalis, substances included in creams and hygiene products, medicines, tobacco smoke.
- Biological - sap and pollen of plants, bites and secretions of insects and animals.
Of the plant agents, the most dangerous are the juice of celandine, hogweed, nettle, pollen of meadow and weeds.
In industrial cities in winter, there are widespread cases of contact dermatitis under the eyes and on the hands of children. Three factors are combined here: cold, chemical impurities in the air and touching the skin with wet mittens.
In infants, allergic inflammation can be caused by a combination of high humidity in diapers, fabric friction and the action of inappropriate cream.
A special type of contact dermatitis is phototoxic, when sunscreens degrade in sunlight and cause allergic damage to the epidermis.
How to find the “golden mean” and prevent overeating?
So, we “treat” in order:
- regular bowel movements - Materna mixtures contain probiotics and prebiotics, which improve microflora and thereby contribute to the timely removal of undigested food residues from the body;
- if your baby is gaining weight well, and especially if he is ahead of the norm, do not “push up” already good digestion with additional enzymatic preparations, eubiotics, etc.;
- Do not forget that saliva is an “activator” of the digestion process. If you eat slowly, without haste, the benefits of saliva will increase. Make a smaller hole in the nipple, try to take the bottle away for a couple of minutes, maintain optimal heat and humidity parameters in the room to avoid dry mouth, walk in the fresh air more often;
- Materna mixtures have a balanced protein composition characteristic of breast milk - albumin/casein 60/40. Also presented are formulas for children who are intolerant to cow's casein protein (Materna Soy). You can switch your baby to this diet only after consulting a doctor. If the child is gaining more weight and suffers from blood pressure, but an allergy to cow's milk proteins has not been confirmed, you can temporarily try to reduce the concentration of the formula. The main thing here is not to overdo it; a reduction is allowed within half a measuring spoon of dry mixture per standard volume of water. Such a decrease in concentration will help relieve the liver and intestines, normalize digestion and get rid of the symptoms of blood pressure;
- if all of the above measures do not bring results, the child still suffers from rashes; most likely, the ratio of beneficial and opportunistic pathogenic microorganisms (dysbacteriosis) is disturbed in the digestive tract, which makes it impossible for the processes of absorption of beneficial and elimination of unnecessary substances to occur correctly. In this case, you need to consult a doctor and undergo the necessary tests.
Remember the main thing, do not under any circumstances overload the child’s intestines with excess food (do not exceed the amount of dry formula per feeding and the frequency of formula feedings per day). For a child suffering from allergic dermatitis, it is sometimes better not to feed additionally and to allow the body to remove all that is unnecessary, than to overfeed and load the digestive system with backbreaking work.
Dermatitis in a child and psychosomatics
Skin health directly depends on a person’s mental well-being. Stress changes hormonal levels and metabolism, causing disruptions in the functioning of the immune system. Therefore, a calm emotional state will prevent exacerbation of the disease and delay the first appearance of symptoms.
When faced with contact dermatitis, analyze the causes and identify the allergen that caused it.
It's not always easy. To be sure of the correct diagnosis, conduct the necessary tests and receive treatment, come for a consultation at our center. In addition to treatment, you will learn how to properly prevent this disease. December 3, 2020
Author of the article: dermatologist Mak Vladimir Fedorovich
What is an allergy? How does it arise?
An allergy is a condition in which the immune system begins to react to completely harmless substances (allergens) as if they were dangerous viruses and bacteria. Therefore, antibodies to them are formed and active substances (mediators) are released, which cause various manifestations of allergies.
At the same time, the formation of mediators aimed at combating real bacteria and viruses is suppressed. This explains why children with allergies often suffer from ARVI, and proves, first of all, the need for proper treatment of an allergic disease, and not the prescription of immunostimulating drugs.
Why do some people have allergies and others not?
Allergies are genetically determined diseases, i.e. The predisposition to developing allergies is inherited. So, if one of the parents suffers from allergies, the probability of an allergic disease in the child is 25-40%. If both parents suffer from allergies, the probability increases to 50-75%. It also depends on a number of other factors that contribute to the development of allergies in children, which include: the level of antigenic load (living conditions, unhealthy diet), ecology, etc.
Unfortunately, today every fifth person suffers from allergies, and according to some data, every third person. At the same time, in recent decades there has been a steady increase in the prevalence of allergic diseases.
Most often, allergic diseases begin in children with atopic dermatitis!
What is atopic dermatitis?
The first manifestations of this disease in everyday life are most often called diathesis and, accordingly, they do not take it very seriously. If your baby develops small rashes on his elbows or his cheeks turn red, it’s okay, it will pass. In this approach lies one of the biggest mistakes of parents - when children with minor skin lesions (exudative diathesis) are either not treated at all, or are treated incorrectly. Today it is reliably known that atopic dermatitis, which mothers, pediatricians, dermatologists and allergists begin to fight at the earliest stages, goes away in 92% of cases. This allows us to conclude that with proper treatment and care by adolescence, your child and you together have a chance to forget about this problem.
What are the first manifestations of atopic dermatitis?
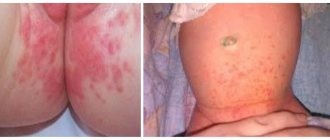
Atopic dermatitis, as a rule, occurs in a baby in the third month of life and can manifest itself as slight redness of the cheeks, rashes in the form of peeling, and dry skin. If treatment is not started in time, skin lesions can spread throughout the body and intensify; lesions with severe redness, weeping, cracks, and induration may appear. The disease is almost always accompanied by painful itching. Atopic dermatitis occurs in waves: a period of exacerbation is followed by remission. Problems may also arise from the gastrointestinal tract: bloating, regurgitation, unstable stool with mucus.
How dangerous is atopic dermatitis? What is the “atopic march”?
The “atopic march” is a consistent expansion of the range of allergic diseases in a child with age. That is, atopic dermatitis can serve as the initial step for the development of a systemic allergic disease: first - the upper respiratory tract (allergic rhinitis, laryngitis, adenoiditis), and then the lower respiratory tract (allergic bronchitis, bronchial asthma). Thus, 50% of children with atopic dermatitis subsequently develop bronchial asthma. By controlling the course of atopic dermatitis, doctors try to prevent the “atopic march” and the development of bronchial asthma.
The task of parents is not to miss the moment and to “capture” the disease at the very beginning of its appearance.
What to do and how to help the child?
Treatment of a child with atopic dermatitis should be comprehensive - the prescription of medications is selected individually, depending on the severity and severity of the disease, as well as associated complications.
Treatment of atopic dermatitis includes several items:
What are the causes of atopic dermatitis?
The most important thing in the treatment of any allergic disease is to identify and remove the allergens that are its cause.
In young children, food allergens (cow's milk, eggs, citrus fruits, chocolate, fish, poultry) are decisive in the development of atopic dermatitis. Sometimes skin reactions are caused by foods that are harmless in the generally accepted sense, for example, some cereals, potatoes, apples. This can be either one product or a whole group.
After 3 years of age, the importance of food allergies decreases, but the role of inhalation allergens (dust, pet hair, aquarium fish food, bird feathers, detergents, house dust mites, mold spores, etc.) increases. Therefore, in addition to diet, it is necessary to take measures aimed at reducing the concentration of allergens in the apartment where a child with atopic dermatitis lives. To do this, it is recommended: replace woolen, down blankets and pillows with synthetic, flannelette, and cotton ones; remove carpets from the premises, do not have animals, glaze bookshelves in cabinets, reduce their number, and also use modern vacuum cleaners to clean the premises (in the absence of a child), purchase an air purifier. In addition, daily wet cleaning of the apartment is mandatory. These measures help reduce the allergenic load on the child’s fragile immune system.
How to determine the significance of a product in the development of a disease?
At the first stage, you need to describe in detail to the doctor the connection between the occurrence of the child’s symptoms and the consumption of the products; the appearance of symptoms without eating foods; sequence of symptoms and their duration.
If necessary, the doctor may recommend an allergy examination: skin prick tests and/or determination of the level of specific immunoglobulins E (IgE) in the blood serum.
What is an allergy screening?
Allergy testing reveals only increased sensitivity to allergens contained in various products, and does not confirm the presence of an allergic reaction to them at the moment.
How to choose a diet?
The doctor concludes that it is necessary to exclude a certain product from the child’s diet. The exclusion of the allergen should be as strict as possible, while taking into account the possibility of its hidden presence as a component in other foods and the presence of cross-hypersensitivity. Thus, some foods have similar allergens to others, and cross-allergies can occur between them. For example, with an allergy to cow's milk, in 90% of cases there is an allergy to goat's milk and in 10% of cases to beef meat.
| Allergenic food product | Foods and non-food antigens that cause cross-allergic reactions |
| Cow's milk | Goat's milk, products containing cow's milk proteins; beef, veal and meat products from them, cow wool, enzyme preparations based on the pancreas of cattle |
| Kefir (kefir yeast) | Molds, mold cheeses (Roquefort, Brie, Dor-Blue, etc.), yeast dough, kvass, penicillin antibiotics, mushrooms |
| Fish | Sea fish, river fish, seafood (crabs, shrimp, caviar, lobsters, lobsters, mussels, etc.); fish food (daphnia) |
| Egg | Chicken meat and broth; quail eggs and meat; duck meat; sauces, creams, mayonnaise, including chicken egg components; feather pillows; medications (interferon, lysozyme, bifiliz, some vaccines) |
| Pork | cat fur |
| Carrot | Parsley, celery, L-carotene, vitamin A |
| Strawberry | Raspberries, blackberries, currants, lingonberries |
| Apples | Pear, quince, peaches, plums; birch, alder, wormwood pollen |
| Potato | Eggplants, tomatoes, green and red peppers, paprika, tobacco |
| Nuts (hazelnuts, etc.) | Other types of nuts, kiwi, mango, flour (rice, buckwheat, oatmeal), sesame, poppy, birch and hazel pollen |
| Peanut | Soybeans, bananas, stone fruits (plums, peaches, etc.), green peas, tomatoes, latex |
| Bananas | Wheat gluten, kiwi, melon, avocado, latex, plantain pollen |
| Citrus | Grapefruit, lemon, orange, tangerine |
| Beet | Spinach, sugar beet |
| Legumes | Peanuts, soybeans, peas, beans, lentils, mango, alfalfa |
| Plum | Almonds, apricots, cherries, nectarines, peaches, wild cherries, cherries, prunes, apples |
| Kiwi | Banana, avocado, nuts, flour (rice, buckwheat, oatmeal), sesame, latex, birch pollen, cereal grasses |
The most acute issue of diet therapy is in young children who have hypersensitivity to cow's milk proteins. If the child is breastfed, then foods containing allergens are excluded from the mother's diet. If breastfeeding is not possible, it is necessary to use special formulas for children with allergies to cow's milk proteins.
How long to stick to the diet?
The duration of exclusion of a significant product from the diet of children with food allergies depends on the allergen and is at least 1-2 years. Since the immaturity of the immune system and gastrointestinal tract plays a significant role in the occurrence of food allergies, most children, subject to all doctor’s recommendations, “outgrow” food allergies over time. In particular, by the age of 3, food allergies disappear in 70-90% of children. However, in relation to the most “evil” allergens, the reaction persists into older age. Thus, by the age of 5, hypersensitivity to cow's milk remains in 10% of patients, to eggs - in 20%, to peanuts - in 60% of patients.
What is a hypoallergenic diet?
Hypoallergenic (without specifying a specific allergen) is a diet that excludes from the child’s diet, first of all, the so-called triggers or provocateurs, which may cause an exacerbation of allergies. These include: non-perishable products containing dyes, spices, preservatives, stabilizers, food additives marked on the packaging with the letter “E”, canned foods, meat broths, chocolate, cocoa, red and orange vegetables and fruits, fish, seafood, tomatoes , mushrooms, honey, nuts, sauerkraut, sausages, pork liver, spinach. Triggers are also foods high in tyramine: cheeses (Roquefort, Camembert, Brie, Grillard, Cheddar, processed), brewer's yeast, pickled herring, avocado. However, as a rule, it is impossible to confirm an allergic reaction to them with examinations. This can only be done by observing the child.
This diet is recommended for all children with allergic pathologies, especially children under 3 years of age.
How are medications prescribed for atopic dermatitis?
Only a doctor should prescribe medications to a patient with atopic dermatitis, since the prescription of certain external therapy agents for each specific patient must be strictly individual. In addition, constant monitoring of the dynamics of the disease is necessary in order to timely replace the medication.
To exclude hypersensitivity to a topical drug, a pharmacological test should be carried out before its application to patients with hypertension. To do this, the product is applied to a limited area of healthy skin in the forearm for 15-20 minutes. In the absence of a local reaction, the drug can be used for treatment.
What drugs are used for exacerbation of atopic dermatitis?
According to the mechanism of action, external agents for relieving exacerbations can be divided into several groups:
External (topical) corticosteroid drugs that have a pronounced anti-inflammatory and antipruritic effect. Drugs in this group are divided, depending on activity, into classes: strong, medium and weak.
Calcineurin inhibitors, which have a local immunosuppressive effect, have anti-inflammatory and antipruritic effects.
When a secondary infection occurs, it is necessary to use antibacterial and antiseptic agents.
Most of these drugs are prescription drugs and are used only on the recommendation of a doctor.
An alternative to hormonal drugs can be a group of drugs based on activated zinc pyrithione (Skin-cap), which can be bought at a pharmacy without a prescription. The skin cap does not contain hormones, but at the same time has a pronounced anti-inflammatory effect, antibacterial and antifungal effect.
The drug is selected depending on the severity and severity of clinical manifestations, using a stepwise approach.
In case of an acute inflammatory process, medications are prescribed in the form of lotions and wet-drying dressings (for weeping), emulsions, pastes, creams, mash and aerosols (the use of ointments that can contribute to weeping is contraindicated).
In case of severe exacerbations (severe redness, weeping, infiltration, swelling of the skin, cracks, etc.), it is necessary to prescribe strong topical corticosteroid drugs, as they have a pronounced anti-inflammatory, antiallergic and antipruritic effect. This leads to rapid relief of the pathological skin process and the disappearance of itching (for weeping - in the form of aerosols, emulsions; for acute inflammation without weeping - ointments, creams).
To reduce the burden of hormonal drugs, it is advisable to combine them with the non-hormonal drug Skin-cap, which has a complex effect (anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, antifungal).
As a rule, for widespread manifestations, the use of antihistamines is recommended.
In some cases, with very severe exacerbations , it is necessary to use systemic (by injection or orally) corticosteroid and/or antibacterial drugs.
For mild and moderate exacerbation, it is advisable to use non-hormonal drugs based on activated zinc pyrithione (aerosol and Skin-cap cream), and topical calcineurin inhibitors.
As a rule, during an exacerbation, a secondary infection develops on damaged skin, which is most often of a mixed nature (microbes and fungi). Therefore, in local therapy, preference is given to drugs that have a complex effect (anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, antifungal (Skin-cap)).
If necessary, antihistamines can be used.
Is it harmful to use corticosteroid drugs?
Drugs in this group should be prescribed only by a doctor for severe exacerbation of atopic dermatitis, when the severity of the disease outweighs the risk of side effects.
To prevent the development of side effects, you should not use these drugs uncontrollably, without a doctor’s prescription. It is important to follow the basic rules for prescribing topical glucocorticoids in children:
- Use only for the treatment and not for the prevention of atopic dermatitis.
- Do not apply simultaneously to more than 20% of the body surface.
- Use in short courses (no more than 14 days) (at the discretion of the doctor, in some cases the duration of their use can be extended to 3-4 weeks).
- If the skin inflammatory reaction decreases, switch to therapy with modern non-hormonal drugs (Skin-cap).
In what cases is it possible to use topical calcineurin inhibitors?
Local immunosuppressive drugs can only be prescribed by doctors for mild to moderate exacerbation of atopic dermatitis without weeping, not complicated by a secondary infection. It is not recommended to apply the drugs to skin affected by an acute viral infection. Their use is contraindicated for herpes virus infection. In the case of bacterial or fungal skin lesions, the use of calcineurin inhibitors is recommended after the infection is cured. Excessive sun exposure and UV therapy are not recommended during the period of drug use.
When to use Skin-cap?
The drug Skin-cap is used for moderate and mild exacerbation of atopic dermatitis. For severe exacerbations of atopic dermatitis, the drug can be used in combination with topical corticosteroid drugs. For rashes with pronounced swelling of the skin and weeping, Skin-cap aerosol is prescribed, after the weeping disappears, Skin-cap cream is prescribed.
The drug is recommended for rashes complicated by secondary infection, as it has a complex effect: anti-inflammatory, antifungal, antimicrobial (including against Staphylococcus aureus).
Timely use of the drug with minimal manifestations of atopic dermatitis allows you to stop and stop the development of inflammation, prevent the development of severe exacerbations, and reduce the frequency and duration of use of topical corticosteroids.
Is therapy necessary during remission of the disease?
It is necessary, since this therapy in most cases makes it possible to prevent the development of exacerbations and progression of the disease, and to stop the “atopic march”.
During the period of remission of the disease, basic therapy is selected for the patient, which consists of eliminating the allergen, proper skin care, and, if necessary, prescribing membrane-stabilizing drugs, antihistamines, products containing polyunsaturated fatty acids, vitamins and various physiotherapeutic procedures.
Taking care of your baby's skin - is it really that important?
In the skin of children suffering from atopic dermatitis, disturbances occur in the structure of the epidermis (upper layer of skin), which leads to disruption of its protective (barrier) function, loss of moisture, development of dryness and, as a result, itching, formation of microcracks, which further promotes penetration allergens and microorganisms and the development of inflammation.
Sometimes only proper care for atopic skin can prevent or sharply reduce the number of exacerbations of blood pressure, as it allows you to protect it from harmful external factors, retain moisture, and prevent infection. These measures can significantly increase the duration of remission.
Is it possible to bathe a child with atopic dermatitis? What cleaning products should I use?
A common mistake is to prohibit children with atopic dermatitis from bathing, especially when it worsens. It is necessary to bathe the child daily, which cleanses and moisturizes the skin, enhances the penetration of external medications, creates a feeling of comfort, and gives him pleasure. A 20-minute bath in the bath is optimal for saturating the stratum corneum with water. When swimming, you must follow the following rules:
- It's better to take a bath than a shower.
- Bathing water should not be hot (35-36? C) and, preferably, dechlorinated (water should settle for 1-2 hours).
- When bathing, you should not use washcloths.
- After bathing, you only need to pat your skin dry with a towel without wiping it dry. After swimming in a pond, dry it more thoroughly.
- For washing, use high-quality detergents (special soaps, gels, mousses) with a neutral pH of 5.5.
- In case of exacerbation of atopic dermatitis, it is necessary to use detergents with anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial effects (gel, Skin-cap shampoo).
How to properly moisturize your skin?
In patients with atopic dermatitis, the skin becomes depleted of lipids (ceramides, cholesterol, etc.) and other essential substances, which leads to loss of moisture and dryness, and disruption of the protective layer. Therefore, modern products for the care of atopic skin not only moisturize it well, but also partially replenish the defective structure of the epidermis, which helps restore the barrier function.
It is necessary to moisturize the skin daily with special creams recommended for atopic skin, at least 2 times a day, or rather, as much as the skin of a particular patient “requires”. At the beginning of therapy, with severe dryness, it is sometimes necessary to moisturize 4-5 times a day, then, as the skin recovers, you can switch to moisturizing 1-2 times a day (depending on the dryness). But every day!!!
Today there are a large number of different creams and emulsions for the care of atopic and dry skin - it is better to choose them at the pharmacy.
Nonspecific factors that provoke exacerbation of blood pressure are irritants (clothing made of wool and synthetic fabrics, tobacco smoke), excessive dryness and temperature (more than 22°C) in the apartment, emotions, stress, climatic factors (cold season, sudden climate change).
Atopic dermatitis is a chronic disease that requires long-term treatment, the success of which largely depends on active cooperation with the doctor, great attention and patience on the part of parents.
Doctors' efforts are aimed at suppressing allergic skin inflammation and reducing the effect of allergens. A properly selected diet, excluding food allergens from the diet, can significantly improve the condition and outcome of the disease. It is very important, under the supervision of a doctor, to choose effective and most importantly safe products for caring for your child’s skin.
Parents should try to properly organize the environment of an atopic child: eliminate contact with dust, mold, pollen, etc., establish a child’s daily routine, and create a favorable climate in the family.
Child skin care for atopic dermatitis, treatment, ointments
How to moisturize the skin with atopic dermatitis, and what drugs to eliminate the pathology, is determined by the pediatrician. For local treatment of foci of inflammation in the acute phase of their development, solutions, pastes, and aerosols are used that provide a drying effect. Fatty ointments and creams are used to heal affected tissues during the period of subacute and protracted progression of pathology.
Parents should keep in mind that atopic dermatitis in a newborn cannot be treated independently, without a doctor’s prescription, with hormonal ointments.
Pediatricians prescribe the following medications: 1. Zinc preparations (have a pronounced healing property). 2. Elidel (cream can be used to treat children over 3 years old). 3. Panthenol. 4. Skin Cap. 5. Emolium.
Before applying the medicinal cream, pathogenic lesions should be treated with antiseptic solutions - it is important not to neglect this action. To soften the affected areas of the skin, the use of sea buckthorn oil is prescribed. The use of hormonal ointments is justified only in cases where the disease has taken a severe form and is accompanied by pronounced symptoms. Pediatricians prescribe ointments that contain prednisolone.
To relieve itching and reduce redness, the use of antihistamines is indicated. These include Fenistil, Cetrin, Zyrtec. Additionally, pediatricians prescribe the use of enterosorbents: Enterosgel, Polysorb, Lactofiltrum. To normalize the intestinal microflora, it is necessary to take probiotics. The optimal period for their use is 1 month.
To monitor the effectiveness of the treatment, it is advisable to take a photo at home at the time of the start of therapy. Thanks to the images, it is convenient to subsequently monitor whether the signs of inflammation are decreasing.
Despite the positive properties of the listed medications, each of them is characterized by the likelihood of developing side effects. To minimize the risk of such, drugs should not be used without a doctor’s prescription.
In case of severe progression of dermatitis, hospitalization in a hospital department is recommended. In this case, specialists monitor the child’s well-being around the clock and adjust the course of therapy. In cases of uncomplicated dermatitis, the newborn is treated on an outpatient basis.
Causes
The leading cause of the development of skin pathology in newborns is hereditary predisposition. If the baby's parents suffer from allergic reactions, there is a high probability that the baby will also be predisposed to intolerance to specific irritants.
Atopic dermatitis in children under one year of age can be triggered by the following factors:
- Unfavorable hygienic environment - a contaminated room in which a newborn is located.
- Bad habits of the mother during pregnancy.
- Premature transfer of the baby to artificial feeding.
- Poor nutrition of a woman during pregnancy.
- Feeding a newborn with low-quality formula.
- Helminthiasis, which promotes the removal of useful substances from the body.
- Weakened immunity.
- Diseases of the mother during pregnancy.
Also, the development of atopic dermatitis in a newborn occurs when adults touch it with contaminated hands. Allergic skin lesions are directly related to baby food. Foods that cause exacerbation of atopic dermatitis: strawberries, wild strawberries, milk, honey, fish, beans and wheat flour. The likelihood of developing skin lesions increases when sweets, nuts, and citruses enter the body. In every 2 cases, inflammation of the epithelium can be provoked by the use of medications - local (if the drug is applied externally) or systemic (when the drugs are taken orally).