Seborrheic dermatitis is a common chronic disease that most often has a recurrent nature. This pathology is associated with dysfunction of the sebaceous glands and is a consequence of increased secretion of sebum. That is why foci of seborrheic dermatitis are most often located in places where the sebaceous glands are most densely located: they affect the scalp, are localized on the face, in skin folds on the body, as well as in the upper part of the torso.
The disease is considered one of the most common. It manifests itself especially often in the first years of a child’s life, as well as in people after 40 years of age. This age-related feature of the occurrence of seborrheic dermatitis is explained by the fact that it is during these periods of a person’s life that the sebaceous glands on the body work with high intensity.
Why seborrheic dermatitis occurs: causes and development factors
Seborrheic dermatitis in adults and children occurs due to the active proliferation of the yeast fungus Malassezia spp., which feeds on the secretions of the sebaceous glands. It can be found on the surface of the skin in 75-95% of healthy people. Active growth and reproduction of this microorganism occurs under the influence of various external and internal factors. These include disturbances in the functioning of the sebaceous glands, due to which they begin to intensively produce sebum, as well as changes in the characteristics and composition of sebum. This can be caused by:
- nervous tension;
- stress;
- hormonal changes;
- decreased immunity;
- endocrine disorders;
- diseases of the digestive system, intestines;
- taking certain medications;
- lack of vitamins and microelements, in particular zinc.
The problem may worsen as a result of prolonged exposure to heat or due to increased sensitivity of the skin to external irritants. At the same time, seborrheic dermatitis in children and adults can be severe, regardless of the number of active fungi on the skin.
Psoriasis and dandruff
Dandruff on the head appears not only due to the activity of the sebaceous glands and fungi. Sometimes scales on the hair occur with psoriasis. This is a common disease associated with heredity and the body's immune system. The disease is chronic, its therapy is designed to reduce symptoms.
Signs of psoriasis:
- the appearance of pink or red spots (occur not only on the head, but also on the arms, legs, and other parts of the body);
- gray scales on plaques;
- itching, sometimes pain.
An outbreak of this autoimmune disease can easily be confused with seborrhea. It is important to see a doctor on time, because the treatment of these ailments is very different.
Psoriasis appears between the ages of 15 and 35 years. Outbreaks of the disease can be caused by:
- poor nutrition;
- cold or dry air;
- stress.
The causative agent is not fungi, but the person’s own immunity, which attacks healthy cells, which causes active growth of the epidermis.
Therapy requires close supervision by a dermatologist. Both local and oral medications can be prescribed. Phototherapy, IV courses, and injections help relieve symptoms.
How does seborrheic dermatitis manifest?
The disease affects certain parts of the human body. Typically this is:
- scalp skin;
- face;
- behind-the-ear areas;
- upper body (most often the chest, shoulder blade area);
- large skin folds on the body (for example, groin area, armpits).
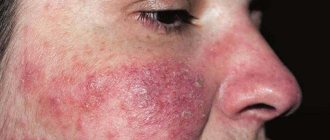
Seborrheic dermatitis in adults and children manifests itself in the form of local redness, covered with greasy scales, and there are papules in the affected area.
The disease can also be recognized at an early stage in adults by the appearance of a sign such as dandruff. As the situation worsens, the scalp gradually begins to become covered with red spots; later they can merge, forming lesions with characteristic peeling of the skin. In advanced cases, when oily crusts peel away from the surface of the skin, a moist secretion is discovered underneath. If you do not take any measures to treat seborrheic dermatitis, then this problem may be complicated by the addition of an infection.
In addition to external signs of seborrheic dermatitis, patients often complain of itchy skin. As a result of constant scratching of the inflammation, even greater tissue injury occurs with a high risk of further infection.
The disease not only causes serious discomfort, but also worsens a person’s quality of life as a whole, provokes self-doubt, makes it difficult to establish contacts with other people, and prevents them from building close relationships with the opposite sex.
Diagnosis of the disease
To make a diagnosis you need:
- Examination by a dermatologist, trichologist.
- Differential diagnosis with psoriasis, atopic dermatitis, lichen and other diseases with a similar clinical picture.
- Dermatoscopy is an examination of the skin under a microscope.
- Blood tests: general, biochemical, hormones, sugar.
Additionally you may need:
- Coprogram.
- Analysis of stool for dysbacteriosis.
- Ultrasound of the thyroid gland, abdominal cavity.
- Trichogramma.
Types of seborrheic dermatitis
If we consider seborrhea and seborrheic dermatitis in children and adults, we can distinguish the following varieties:
- Dry seborrhea. With this nature of the disease, the sebaceous glands produce an insufficient amount of secretion. As a result, the skin does not receive enough moisturizing components, dries out, and microcracks appear on its surface. Typically, dry seborrhea occurs without the formation of acute inflammatory foci. Instead, the patient is concerned about the separation of dry dandruff particles. Most often, this form of the disease is observed in adolescent children.
- Oily seborrhea. The form differs from the previous one in that the sebaceous glands, on the contrary, work too actively and secrete a large amount of thick secretion. The substance glues together dead skin cells and is deposited on the hair, causing it to take on an unkempt appearance. The problem often affects young women.
- Combined type. It is characterized by the presence of signs of both dry and oily seborrhea. The disease develops in various parts of the body and therefore causes serious discomfort. In most cases, this form is diagnosed in males.
Depending on the location of the foci of inflammation, seborrheic dermatitis of the scalp, face and torso is distinguished.
The first sign of damage to the scalp is the appearance of dandruff. A similar symptom is characteristic of the development of the dry form of seborrhea and is a mild form of the disease. The patient simultaneously experiences complaints of dry skin, irritation, and itching. At first the scales are small, but then they can thicken and cover new areas.
In the absence of proper attention to the problem, a bacterial infection of the skin often develops against the background of seborrheic dermatitis. Small pustular rashes appear on the surface of the skin. In patients with seborrheic dermatitis, over time, the hair becomes sparse, thin, brittle and often falls out.
Focal inflammation on the face is considered no less common. This form of the disease mainly affects teenagers and young people under the age of 25. The cause of seborrheic dermatitis in this case is the high activity of the sebaceous glands in the facial area. During puberty, they begin to work more actively, which can provoke the development of the disease.
At the initial stage, the disease manifests itself as red spots, the surface of which is covered with white-yellow scales. They are accompanied by itching and constantly peel off. As the disease progresses, areas of inflammation may merge. In some cases, inflammation is aggravated by the addition of a secondary infection.
Sometimes the inflammation spreads to the skin of the eyelids. This leads to the development of seborrheic blepharitis. It is characterized by the formation of severe swelling of the eyelids, redness of the eyes, and the formation of cracks in the delicate skin in this area. At the eyelash growth line, inflammatory foci gradually begin to form with a characteristic separation of small scales and crusts. Because of this, patients have to literally “pry” their eyes out in the morning, since the eyelids stick together so much.
On the torso, seborrheic dermatitis is usually localized in the area of the sternum and shoulder blades. The disease occurs with the formation of spots or plaques with clear boundaries, with a smooth, shiny surface, sometimes covered with yellowish scales.
Diet for atopic dermatitis in children
The nutrition of children with atopic dermatitis should be both balanced and gentle. Products must be selected depending on the age of the child and taking into account the characteristics of his development.
Breastfed babies under 6 months of age should have enough breast milk. Refusing to breastfeed, explaining such an action by the imaginary allergenicity of mother's milk, is a fundamentally wrong decision. It is this that largely shapes the baby’s immune system, so it is advisable to breastfeed the baby until six months of age.
As the first complementary food for children suffering from dermatitis, it is necessary to choose safe foods. The main requirements for complementary foods are that they are sufficiently nutritious and hypoallergenic. So that the baby’s body can easily adapt to new food, it is recommended to introduce no more than one new product within 7-10 days. Complementary foods are introduced between 4 and 6 months. The first complementary food product can be vegetables or porridge (water or mixture). Next, meat and fruit purees are introduced.
Nutrition for atopic dermatitis in children over one year old is in many ways similar to an adult diet. Below is a summary table of the diet for dermatitis in children, clearly demonstrating which foods are allowed and which are strictly prohibited.
| What needs to be excluded completely? | What foods should you limit? | What products are allowed and healthy? |
|
|
|
It is recommended to completely eliminate salt and sugar during exacerbations of the disease. They should be introduced gradually, in small doses. It is better to avoid using spices when preparing baby food altogether.
To determine which product causes an exacerbation of the disease in a child, it is useful to keep a food diary. Write down the time of meal, its weight or volume, method of preparation and the baby's reaction to food. If the baby is breastfed with the addition of complementary foods, the mother must keep a similar diary: in it she must record her own diet.
Effective treatment of seborrheic dermatitis: basic approaches and methods
The doctor selects the tactics and treatment regimen for seborrheic dermatitis based on the form in which the disease occurs and in which area the inflammation is localized.
If the disease is mild, then this form is characterized by the presence of a small amount of dry or greasy scales, moderate redness of the skin, and occasional mild itching. With this course of the disease, the doctor, as a rule, limits himself to external therapy. For example, with mild damage to the scalp, or dandruff, the doctor may recommend the use of Skin-cap shampoo. Apply shampoo to damp hair, then massage the scalp until foam forms and rinse thoroughly. After this, you need to reapply the shampoo, leave for 5 minutes, and rinse thoroughly with plenty of water. Skin-cap shampoo can be used both for exacerbation of seborrheic dermatitis according to the scheme 2-3 times a week, and for the prevention of further relapses 1-2 times a week.
When the disease occurs in moderate to severe form, the symptoms of seborrheic dermatitis become more pronounced. At this stage, brighter red spots appear on the skin, sometimes noticeable swelling forms on the skin, and the surface is covered with dense gray-yellow crusts. All this occurs against the background of severe itching, which is present almost constantly. Due to discomfort, the patient cannot work fully, it is difficult for him to concentrate on anything, and often in the acute phase of the disease a person experiences problems with sleep.
In this case, there are also generally accepted recommendations on how to treat seborrheic dermatitis. The measures taken are comprehensive; patients may be prescribed hormonal medications. Treatment is prescribed by the doctor, based on the severity of the disease and the individual characteristics of the patient. One of the non-hormonal drugs for the treatment of seborrheic dermatitis is the drug Skin-cap. It inhibits the activity of the Malassezia fungus and helps reduce signs of inflammation and helps reduce flaking. Depending on the location of the inflammatory foci, Skin-cap shampoo, cream or aerosol may be prescribed. Skin-cap aerosol, for example, is suitable for treating the scalp, and the cream is convenient to apply to the face. The duration of treatment for an exacerbation varies, usually it takes from two weeks to 1 month to completely eliminate the symptoms of the disease.
The use of shampoo, cream and aerosol Skin-cap helps to significantly alleviate the condition of seborrheic dermatitis. The active ingredient of the drug Skin-cap has the following effects:
- provides anti-inflammatory effect;
- suppresses the growth and reproduction of pathogenic fungi, which are the main cause of exacerbation of the disease;
- inhibits the activity of bacteria that can increase inflammation.
The drug can be recommended to patients with any form of seborrheic dermatitis; treatment is possible for both adults and children over the age of one year. Products from the Skin-Cap line do not just eliminate the signs of the disease, they help keep the disease under control, preventing relapses.
General symptoms and signs of the disease
In most diagnosed cases, dermatitis occurs during the period of hormonal imbalance in adolescence. In men, the peak incidence occurs between 20 and 40 years of age. For women, the risk of developing seborrhea increases during pregnancy, after childbirth, miscarriage or abortion. The disease is often exacerbated by tumors of the uterus, thyroid gland, and adrenal glands.
There are symptoms characteristic of all types of seborrheic dermatitis:
- the appearance of red spots with a yellow tint on the skin;
- the formation of large blisters covered with fatty scales;
- dense crusts on the head between the hairs;
- cracks and clear discharge from blisters;
- severe itching;
- unpleasant burning sensation.
With dermatitis, a pink rash, black comedones often appear, and the skin becomes rougher and looser in appearance. Hair takes on a stale appearance a few hours after washing.
Prevention of seborrheic dermatitis
Patients with this disease need to know not only how to treat seborrheic dermatitis, but also learn the basic rules for preventing exacerbation of the disease. The main task in this case is to exclude those factors that can trigger the triggering of pathology development mechanisms.
Thus, as part of the prevention of seborrheic dermatitis, it is worth paying attention to several aspects:
- following a certain diet;
- compliance with personal hygiene rules;
- providing quality skin care;
- maintaining an active and healthy lifestyle;
- timely treatment of concomitant diseases.
How to supplement the treatment of dermatitis, besides diet?
Following the rules of a hypoallergenic diet is very important, but diet alone cannot cope with dermatitis. In order for the patient to recover as quickly as possible, we suggest that you supplement the therapy prescribed by your doctor with the use of La-Cri products.
The regenerating cream contains extracts of string, violet, walnut, bisabolol, panthenol and avocado oil. These components have an anti-inflammatory, antipruritic and softening effect.
Intensive cream is used to soften and moisturize very dry skin. Contains wheat germ, shea and jojoba oils, violet and licorice extracts, bisabolol, allantoin and lecithin.
Cleansing gel is an optimal replacement for conventional cleansers. The composition includes licorice and walnut extracts, hypoallergenic detergent components, avocado and olive oil derivatives.
Maintaining personal hygiene
Patients with seborrheic dermatitis are recommended to injure the inflammation as little as possible. Personal hygiene rules include cleansing the skin twice a day using special products with a low pH. To cleanse the skin, it is prohibited to use aggressive agents such as laundry or tar soap.
General recommendations for maintaining personal hygiene:
- the use of washcloths or sponges with hard fibers is excluded;
- For a while, you should avoid cleansing your skin with scrubs and peels containing abrasive particles and aggressive chemical compounds;
- It is recommended to take water procedures using dechlorinated water; for this purpose, it is recommended to first settle or filter the liquid;
- the duration of water procedures should be reduced to 10-15 minutes;
- when choosing shower products, choose products without dyes and fragrances, with a low pH;
- use towels with soft bristles, and it is better to blot your skin with them rather than rub them;
- to reduce the likelihood of skin injury when combing, try to cut your nails as short as possible;
- Avoid using other people's personal hygiene items.
Diet for atopic dermatitis in adults: menu
Nutrition for atopic, allergic and other types of dermatitis should be based on avoiding potentially dangerous foods. You will have to exclude the consumption of hot, spicy, smoked, salted, fried foods, sweets, baked goods, seafood, exotic fruits, chips, alcohol, citrus fruits, as well as vegetables, fruits and berries with bright colors.
Preference should be given to lean meats, cereals, seasonal green and white vegetables and fruits, and dried fruits.
As for the cooking method, it is best to steam, bake in the oven or boil.
Skin care rules
Skin care prone to symptoms of seborrheic dermatitis is primarily focused on normalizing the functions of the sebaceous glands. It is important not only to reduce sebum production, but also to ensure skin hydration.
General care recommendations:
- Try to reduce the use of comedogenic makeup, as it can cause clogged pores.
- Use care products that do not contain alcohol. It irritates the skin, dries it out, causing the sebaceous glands to work more actively.
- For care, choose special cosmetic products designed for seborrheic skin.
Scalp dermatitis in conditions caused by immunodeficiency
With an active decrease in the protective properties of the immune system, the fungus rapidly multiplies, moving into the pathogenic phase.
Conditions caused by decreased immunity can be primary or secondary.
In the first case, we are talking about the human immunodeficiency virus.
In the second - about a decrease in immunity in acute respiratory infections, acute respiratory viral infections, diabetes mellitus, and chronic pathologies.
In the case of persistent and prolonged immunodeficiency, dermatitis progresses to a chronic form.
It is extremely difficult to treat effectively.
Usually, medications can reduce the severity of the symptoms of the disease.
But they rarely eliminate it completely.
What should you not do if you have seborrhea?
- First of all, forget about rubbing with salt. Salt is sometimes recommended to be rubbed into the skin, which supposedly leads to the disappearance of dandruff. However, in reality, everything happens the other way around: rubbing with salt does give a certain effect, but it is short-lived, and then the already irritated skin will begin to peel off even more.
- For dry seborrhea, you should not use table vinegar, as it will dry out the skin even more, and for oily seborrhea, it is better to use only apple cider vinegar, since table vinegar is too aggressive.
- Even with severe itching, try to scratch the itchy areas less, as this will provoke further development of the process of dandruff formation, both dry and oily.
- If you have dry seborrhea, you should not wash your hair too often, and if you have oily seborrhea, you should not wash your hair too often. If you frequently wash a dry hair, the skin will constantly suffer from dryness, and if you rarely wash an oily head, the abundant secretion will heavily pollute the hair and skin, which will only worsen seborrhea.
Method No. 3. Masks, lotions and oils on a natural basis
(5)
These folk remedies help relieve itching and temporarily eliminate the formation of dandruff. The following mixtures of natural lotions are usually used:
- burdock oil, onion juice and vodka;
- carrot greens, lemon juice, mint and water;
- lemon juice with olive and castor oil;
- walnut shells with diluted alcohol.
Masks are made from raw eggs mixed with nettle infusion and vegetable oil, as well as from castor oil, which is used either alone or together with calendula tincture.
Essential oils that help in the fight against dandruff are lavender, cedarwood, eucalyptus, geranium, mint, rosemary, tangerine, basil, as well as tea tree and patchouli oil. You can also prepare a rinse from natural ingredients, which will serve as an auxiliary remedy for eliminating the symptoms of seborrhea. Rinses are made using lemon zest, chamomile and sage, as well as birch leaves.
Method number 4. Other means
(6)
- The top anti-dandruff remedy traditionally includes baking soda. When rubbed, baking soda gives a temporary antifungal effect and also cleanses the head even of oily dandruff, acting as a scrub.
- Henna is well suited for the treatment of seborrhea at the initial stage - it is used both separately and together with other remedies. An important addition: to prevent your hair color from changing during the procedures, buy colorless henna.
Method No. 5. Hair masks made from natural products
(7)
- Onions, garlic and black pepper have sufficient chemical activity to temporarily relieve the symptoms of seborrhea. For treatment, onion peels are mixed with vodka (8), garlic with burdock oil (9), and ground pepper with various fermented milk products, for example, kefir, after which the resulting mixtures are applied to the scalp. (6)
- Citric acid is another strong irritant for the pathogenic fungus that attacks hair and skin during seborrhea. Just do not use compresses made from pure lemon juice, as this will lead to skin irritation. You need to mix lemon juice with any oil: olive or essential oil that suits you.