Among the group of skin diseases, dermatitis of various etiologies is most common. The epidermis in individual patients may be highly susceptible to endogenous and exogenous factors, provoking the development of inflammation and rashes. This leads to a deterioration in the appearance of the skin and the general condition of the body.
Almost every third person has encountered this pathology after contact with any allergen or other irritant. Many suffer from this disorder on a chronic basis. The course of the skin disease is replaced by phases of exacerbation of symptoms and their subsidence. Dermatitis combines a large group of autoimmune disorders and infectious diseases that have their own distinctive characteristics. The article talks about dermatitis photo symptoms and treatment in adults.
Description
Dermatitis is a skin lesion. Foreign irritants can provoke changes in the immune response. For this reason, a pathological process develops. May be present for a long time or occur suddenly. In dermatological practice, this process is sometimes called neurodermatitis or eczema. Dermatitis is characterized by general symptoms. With any type of this disease, rashes and itching are present. Therapy for adult patients takes a long time. In order to treat this pathology, it is necessary to achieve a reduction in the severity of symptoms or complete remission by correctly determining the source of the inflammatory process, type and stage. Depending on what irritant led to the development of dermatitis in men, it is divided into several groups, each of them requires a special type of treatment.
This disease threatens that if the diagnosis and treatment are not carried out correctly, bacterial flora begins to develop. In this case, sometimes damage to the deep layers of the epidermis occurs, accompanied by purulent necrosis, which will greatly complicate the treatment of the underlying disease. Usually, the first signs of the disease become noticeable in childhood, and over time a relapse occurs in adulthood.
Popular promotions
View all promotions
Dermatoscopy free of charge
Dermatoscopy is a non-invasive diagnostic method for the visual assessment of skin lesions, which allows a more thorough examination of both the surface of the skin and its deeper layers.
Read more…
SMAS lifting using the UCOS HIFU device
The procedure for exposure to highly focused ultrasound on the latest HIFU UCOS device is a triple rejuvenating effect on the deep ligaments of the face, subcutaneous fat packets and skin!
Read more…
Chronic tonsillitis
Chronic tonsillitis is not only a sore throat, but also general weakness, fatigue, low-grade fever, etc. Only in November, treatment with the Tonsillor device instead of 450 rubles . per session you will pay 350 rubles !
Read more…
Symptoms
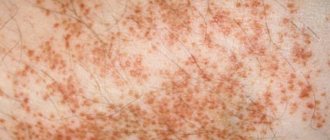
In an adult, the inflammatory process is accompanied by severe symptoms, but they sometimes vary. Its manifestations depend on the type of pathology, as well as on the functional state of the body systems. Typically, this disease is characterized by a variety of rashes and skin redness. The rash can affect absolutely any part of the body: face, torso, limbs or neck. Each type of dermatitis is accompanied by a pronounced itching sensation, which intensifies at night. The epidermis may become covered with papules, plaques and crusts.
The rashes can appear as single papules, but in some cases they form quite large affected areas. In addition to papules appearing on the skin, the patient experiences a feeling of itching and burning. Manifestations of dermatitis sometimes provoke general poisoning of the body with toxins. Sometimes the temperature rises and a feeling of weakness and fatigue appears. Swelling and redness appear in the area of inflammation. With pathology accompanied by the formation of blisters, a person may experience severe pain in this area. Typically, such lesions then crack and turn into crusts. If secondary infection occurs, the wounds become weeping.
Sometimes the symptoms of dermatitis are minimal and almost unnoticeable to a person, but after exposure to an irritant they can appear. Each group of dermatitis must be studied separately, but there are a number of signs that are common to all diseases of this group.
Signs of dermatitis:
- Itching of the skin - the severity of this symptom depends on how irritated the nerve fibers and endings are. Some patients experience it all the time, while others feel its manifestations only at night. It can also worsen during periods of anxiety or stress.
- Erythema is redness of the epidermis, which is most pronounced when blood rushes to the capillaries. In addition to redness, swelling also develops at the site of localization of the pathological process.
- Rashes are small formations whose appearance does not change over time. They play a key role in diagnosis. Rashes with dermatitis can be completely varied, from small dots to fairly large boils. Sometimes they can merge into large formations. The rash usually does not affect the entire surface of the body. They affect individual areas that turned out to be foci of the inflammatory process.
- Exudation - develops when the inflamed area is large enough. This stage is characterized by the appearance of papules, which are filled with liquid contents. When affected over a long period of time or when symptoms intensify, the inflamed epidermis becomes thicker and cracks. This type of dermatitis in adults and children is quite severe and is accompanied by numerous complications. The general condition of the patient is serious, which interferes with normal life activities. Papules sometimes break through, leaving dry wounds in their place.
- Peeling is a skin condition that is present in all forms of dermatitis. This is due to the fact that the skin at the site of the rash is quite thin and prone to dryness. Dry skin may occur even when the severity of other symptoms decreases.
In addition to the main symptoms, which are noticeable on the surface of the skin, other symptoms of the disease may occur that appear against the background of inflammation: fever, decreased resistance to stressful situations, and lack of appetite. With allergies, there is usually involuntary sneezing, runny nose, tears and other symptoms that worsen the general condition of the patient’s body.
Symptoms
The manifestations of dermatoses are varied and contradictory. The most characteristic symptom of skin pathology is an itchy rash. The patient may develop small red spots, blisters, papules, warts, small tumors and other abnormal skin structures. The nature of the rash helps doctors determine the cause of the disease.
Other possible symptoms:
- Redness and swelling of the skin.
- The appearance of ulcers.
- Blister formations.
- Severe peeling of the skin.
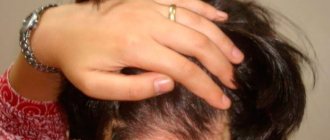
- Brittle nails and hair loss.
- Excessive dry skin.
- The appearance of a crust.
- Constant fatigue.
- Decreased performance.
- Sleep disturbance.
Cosmetic defects that occur with dermatitis negatively affect a person’s mental state. Some diseases that manifest as profuse acne are difficult to treat, so patients are forced to adapt to their appearance.
Causes
Each type of inflammatory process has only its own causes of development. For example, taxidermy is provoked by food allergens or drugs with antimicrobial activity.
The reasons leading to the occurrence of dermatitis can be different.
The likelihood of developing any type of pathological process increases in patients with mental disorders. In addition to all this, this group of pathologies can develop with long-term use of oral contraceptives. The reason for this is a change in hormonal levels.
Causes of dermatitis in children:
1. Hereditary conditioning. Parents who suffer from one of the types of skin lesions give birth to children with a similar pathology in 95% of cases. The likelihood is halved if only one parent suffers from dermatitis.
2. Predisposition acquired over time. Patients who were exposed to atopic dermatitis in childhood are susceptible to all other skin diseases.
Exogenous factors:
- irritation of the epidermis with accessories;
- wearing clothes made of artificial materials;
- use of household chemicals with aggressive additives in personal care and home care;
- prolonged effects of cold on the skin;
- use of low-quality makeup products;
- contact with poisonous plants that release poisons; perfumery products; chemicals.
Risk factors
In addition to the direct causes of pathology, doctors take into account the influence of additional factors related to heredity, lifestyle and the patient’s individual history.
Possible risk factors:
- Excessive ultraviolet exposure.
- Using personal hygiene products that are harmful to the skin.
- Insufficient skin hygiene.
- Genetic disorders (eg, epidermolysis bullosa.)
- Allergic history. If a person suffers from allergies, the risk of dermatosis increases.
- Diseases associated with a high risk of skin pathology: bronchial asthma, congestive heart failure, HIV infection.
- Professional activity that requires constant contact with chemicals and other irritants.
- Age. Inflammatory dermatoses occur more often in children and young patients.
- Hormonal changes in adolescents, pregnant women and other categories of patients.
Considering risk factors helps dermatologists prescribe preventative measures.
Types of dermatitis
In medical practice, several dozen of this pathological process are identified, but some of them are most common. The classification of dermatitis is based on the signs and course of the disease.
Dry
Simple dermatitis occurs only during cold periods of the year. The initial stage phase is usually invisible. Often found in elderly patients. The development of the disease is provoked by the following factors:
- low air humidity;
- prolonged exposure to cold air;
- disorder of one of the body systems;
- heredity or psychosomatic conditioning.
Dry dermatitis occurs on the feet and is rarely localized to other parts of the body. Manifestations of this process include:
- increased dryness of feet;
- cracking of the lesion;
- constant feeling of itching;
- redness.
This type of dermatitis on the back is characterized by the fact that it appears in the autumn-winter period.
Allergic
In this case, the factors leading to the development of skin lesions are completely diverse. Usually these are exogenous stimuli:
- pollen of some plants;
- everyday life;
- cat or dog hair;
- Food;
- medicines and substances for disinfection;
- cosmetic products.
A distinctive feature of the pathological process is the lack of effectiveness of any treatment; all symptoms disappear after eliminating the allergen from the surrounding area.
Contact
It resembles an allergic one, the only difference is that it develops only after prolonged contact with the allergen. For example, when wearing clothes made of artificial materials, in a person with very sensitive skin. This type of dermal disease also includes photodermatitis. Symptoms:
- localized redness of the skin;
- unexpressed itching;
- dryness of the epidermis and its peeling.
This type of dermatitis is the easiest to detect and quite easy to treat. But if you ignore the signs, mild redness with small blisters will turn into a more serious form.
Seborrheic
This pathological process occurs when the balance between beneficial and pathological microflora in the body is disturbed. The internal environment of the human body contains saprophytic organisms, which sometimes begin to actively divide. The waste products of this flora negatively affect the sweat glands. There is a change in the chemical composition of the secreted secretion, which provokes the onset of the disease.
This condition usually occurs when the immune system is weakened. Dermatologists distinguish two types of the disease: dry - the skin begins to peel off greatly, and the face is torn with small scales; oily - the epidermis is affected by small ulcers, the face looks greasy and shiny. Seborrhea occurs in people of different age groups and is easily treatable.
Perioral (perioral)
Typically found in people under 30 years of age, it appears as red spots on the lips that can extend to the nose or eyelids. The lesion can be of various shades - from light pink to burgundy.
A pathological process develops after exposure to any specific substances such as toothpastes, glosses and lipsticks, shaving products.
Usually develops against the background of a weakened immune system and hormonal regulation. Getting rid of this inflammatory process is quite easy - you just need to change your care. If you ignore red spots on the face, they can turn into thick thickenings.
Atopic
Develops as a complication of an allergic disease. Sometimes this pathology is genetic in nature. The process of inflammation is sometimes present in the body for quite a long time, but it does not fade away. Symptoms may only appear when exposed to specific factors. This usually occurs due to nervous feelings, an emotional outburst, or poor personal hygiene. Atopic dermatitis is characterized by the following symptoms:
- skin redness;
- quite severe itching;
- appearance of crusts.
Atopic dermatitis is quite dangerous. The patient experiences strong manifestations of it, and the quality of life changes. If the disease is not diagnosed and treated in a timely manner, it quickly progresses to the chronic stage, which requires complex staged treatment.
Infectious
With this type of inflammatory process, the deeper layers of the skin can be damaged. The disease develops for the following reasons:
- previous infection;
- when the epidermis is injured;
- when staphylococci enter the body.
This type of dermatitis is characterized by pronounced symptoms: rashes with purulent contents, abscesses and the formation of boils.
Mycotic
It develops only in the presence of fungi on the body. Therefore, it is important to always follow up on them. When the immune system is weakened or the sebaceous glands work excessively, their increased growth begins. With their products they disrupt the barrier properties of the skin, which leads to rashes.
Ear
During this skin disease, severe itching is always present. The pathology can last a long time or only sometimes worsen. Symptoms of ear dermatitis include:
- feeling of itching inside the ear;
- gradual development of crusts without wet discharge.
The reasons for the development of lesions include irritation of the dermis in the ear area, fungal diseases, and injuries to the auricle.
In some cases, allergic dermatitis may spread to this area of the body.
general information
Dermatosis is the name of congenital and acquired skin diseases, manifested by rash, redness of the skin, burning and other symptoms.
In most cases, we are talking about inflammatory pathologies caused by allergic reactions or infections. Dermatoses can be associated with dangerous conditions of the nervous and endocrine systems. At the same time, nails and hair are also exposed to pathological effects. Almost every person has experienced at least one form of dermatosis during their lifetime. This may be a temporary irritation of the skin when exposed to an allergen or a severe chronic condition. Inflammatory skin diseases are more common among women. Some types of dermatosis, such as psoriasis, are difficult to treat, but modern means can successfully eliminate the most unpleasant symptoms of such ailments.
Forms of dermatitis
There are two known forms of manifestation of the disease:
- Acute dermatitis. It begins with a sharp itching of the epidermis, the temperature increases by 1 section of the thermometer scale and nasal congestion. After a short period of time, rashes begin to appear on the skin. Their type depends on the underlying disease present in the body.
- Chronic dermatitis. It occurs in one of two stages: remission - the severity of symptoms is minimal or absent at all, relapse - all manifestations are of maximum severity.
Treatment
How to cure dermatitis? Complex therapy includes the mandatory use of antihistamines, which help reduce the severity of signs of the disease and neutralize pathogenic microorganisms. Before prescribing treatment, a complete diagnosis is carried out to identify the type of dermatitis. It is necessary to try to completely eliminate from the environment the factor that led to the development of pathology.
Local medications are used as symptomatic therapy. Traditional medicine in this case is no less effective.
How long the dermatitis will take depends on how neglected it is. Treatment of skin dermatitis involves following a special diet, which involves excluding highly allergenic foods from the diet. In fairly complex cases of the disease, it is necessary to take drugs with antimicrobial activity, physiotherapy procedures and rehabilitation courses.
If widespread dermatitis is detected, it is recommended to exclude all sweets, fruits, canned food and drinks containing alcohol. The consumption of tonic drinks is also limited. Therapy is carried out under the close supervision of a doctor.
Drug therapy
Medicines are selected depending on the etiology, stage and severity of signs of pathology. Treatment of dermatitis throughout the body can be aimed at getting rid of the underlying pathological process or affect only its manifestations.
It must be borne in mind that even if the symptoms disappear, treatment must be continued. Otherwise, the pathological process will resume.
Hormonal drugs include:
- Prednisol. Prescribed for atopic dermatitis. Do not use for fungal infections. The duration of treatment lasts up to 5 weeks, no more. The dosage of the drug is selected by the attending physician.
- Flucinar. It is used for almost all types of disease. Use for treatment of dermatitis for no more than 2 weeks, on the face - no more than 1 week.
- Lorinden. A drug with an anti-inflammatory effect. Prescribed for atopic dermatitis. Lubricate the foci (sites) of the rash until the symptoms disappear completely.
- Fluorocort. Highly effective product. Helps cure allergic dermatitis in a minimum period of time. Can be used for no more than 10 days; further use is prescribed by a specialist.
All of the listed remedies help eliminate the manifestations of dermatitis and are usually prescribed for advanced stages. They are used only in short courses due to the risk of complications.
Treatment with ointments
To treat skin rashes, the following medications with anti-inflammatory effects are prescribed:
- Akriderm. Prescribed for dermatitis of allergic etiology. It can be used with a contact form. Do not use for oral pathology.
- Advantan. Apply a thick layer to the affected area. The drug is completely safe. Can be used for up to three months.
- Triderm. It is also prescribed as part of complex therapy for all types of disease. Excellent for relieving redness and swelling. It also has antibacterial and antifungal effects. Copes with the infectious process in places where dermatitis is localized. If the remedy does not have a positive effect, then it is necessary to undergo additional examination.
Traditional methods of treatment
Treatment of dermatitis can be carried out using folk remedies. The most popular are products based on celandine. When using the plant, it is important to avoid irritation. Usually celandine juice is used. It is prepared by infusing the herb in water. Apply the product using a cotton and gauze swab. It is enough to apply it to the site of the rash. It is strictly forbidden to use alcohol tinctures, they can cause the formation of wounds. This will lead to increased pain.
A decoction based on a string. The powder is steamed with boiling water and infused until a brown tint appears. For application use a paper napkin. It is moistened and applied to the rash site. You can leave it on overnight, securing it with gauze. The compress is changed several times a day.
Tar soap is a popularly known highly effective remedy used to treat many skin rashes. Can be applied in the form of compresses, lotions and ointments. To prepare a dosage form based on this product, take 100 grams of ordinary soap, 2 tablespoons of any fat or oil, 2 spoons of tar and add water to the required consistency. All rashes on the body are thoroughly lubricated with the product. Apply as a compress. Use until complete healing.
Fighting the disease
Diseases can be chronic. Some are considered incurable. In any case, it is necessary to undergo courses of treatment and be observed by a doctor.
Treatment of dermatitis includes the use of external preparations (ointments, creams, lotions), vitamin and mineral complexes.
Physiotherapeutic procedures may be prescribed. Diet therapy and drugs that restore the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract are added to drug treatment. In some cases, your doctor will prescribe systemic corticosteroids.
If the skin is affected, regardless of the size of the affected area, avoid prolonged exposure to the sun. Sometimes the rash is a reaction to ultraviolet radiation.
Nutrition for dermatitis
When treating a disease, it is important to adhere to a certain type of diet. This measure is necessary in the treatment of allergic rashes. With the help of diet correction, you can not only achieve remission, but also improve the condition of the body.
With dermatitis, it is important to adhere to a certain diet.
If you study your diet and compare it with the list of foods that can trigger allergies and other negative consequences, then by eliminating several foods you can speed up your recovery. It is usually recommended to do this before visiting a doctor.
Even if the symptoms of dermatitis disappear after eliminating any product, it is still necessary to contact a specialist for examination. This will help reduce the risk of developing the disease in the future.
So what can you eat if you have dermatitis, and what should you avoid?
Food products with minimal risk of developing an allergic reaction:
- protein products: perch or cod, lamb, veal with minimal fat content, low-fat cottage cheese, butter;
- products of plant origin: green vegetables, pearl barley, gooseberries, rutabaga and currants;
- drinks: compotes from seasonal fruits, weak tea, fermented milk products without synthetic additives, mineral waters;
- desserts: dried fruits and prunes.
If, when these products are included in the diet, no signs of dermatitis occur, then products with moderate allergenicity can be included in the menu.
Products that carry a high risk of developing an allergic reaction:
- protein products: pork, red fish, all dairy products, smoked meats and canned food;
- plant products: sauerkraut, all legumes, red berries and tropical fruits;
- drinks: coffee, carbonated drinks, yoghurts with fillings;
- desserts: chocolate products, honey and other confectionery products;
- other additives: fatty sauces, seasonings and colorings.
Diagnostics
If symptoms of a skin disease appear, you should make an appointment with a dermatologist. During the consultation, the doctor will ask the patient about complaints and collect medical history information to identify risk factors for dermatosis. Then a general examination of the skin is performed to identify characteristic clinical signs of pathology. To clarify the diagnosis, the dermatologist needs the results of instrumental and laboratory tests.
Additional diagnostics:
- Laboratory blood tests. In the treatment room, a nurse collects venous blood and sends the material to the laboratory. Specialists evaluate the ratio and quantity of formed components, and also study the biochemical parameters of the blood. A blood test can detect signs of infection, autoimmune inflammation or other pathology.
- Dermatoscopy. Using a special device, the doctor takes an enlarged photo of the affected area of skin and studies the features of the rash. Dermatoscopy is important for differential diagnosis and exclusion of dangerous diseases such as melanoma.
- Laboratory examination of exudate. The specialist collects secretions from ulcers or other skin formations. The resulting material is studied in the laboratory to detect pathogenic microorganisms or signs of inflammation.
- Histological examination of the skin. A biopsy is performed if it is necessary to exclude oncology.
- Carrying out allergy tests. The doctor places microscopic particles of the irritant on the skin and monitors the condition of the tissue. This study is necessary to find the source of the allergy.
If necessary, the dermatologist may prescribe additional tests, including a general urine test. A timely appointment with a doctor helps to quickly clarify the cause of the rash and select effective treatment.
Prevention of dermatitis
In order to prevent the development of the disease or minimize its manifestations, you must follow the following recommendations from doctors:
- give up all addictions; observe the work and rest regime;
- adhere to a balanced diet;
- include foods rich in vitamins in your diet;
- introduce physical activity into your daily routine;
- try to avoid stress;
- be careful when working with chemicals;
- before going outside, apply sunscreen to areas of the body not covered by clothing;
- It is imperative to treat all diseases.