It just so happens that we begin to truly value health only when serious problems begin with it. One such problem is hyperthyroidism, a disease in which the thyroid gland is underactive, namely in terms of releasing hormones.
In its advanced state, this disease can cause serious complications, and therefore today we will talk about its symptoms, features, treatment and many other things.
What is hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism itself can be considered an abnormality of the body, in which the thyroid gland begins to produce several hormones too actively.
First of all, this negatively affects the general hormonal state of the body, which ultimately results in more serious consequences.
First of all, the excess production of two thyroid hormones leads to a strong acceleration of the entire metabolic process.
The patient experiences changes in behavior, which are due to the fact that the process of heat exchange with the outside world is disrupted, as a result of which damage reaches the adrenal glands.
This is often accompanied by various external signs, which can be seen in the photo of hyperthyroidism in a patient.
Where is the thyroid gland located in the body?
The thyroid gland is located under the skin on the front surface of the neck and lies on the rings of the trachea. Its density resembles that of adipose tissue. Therefore, a soft thyroid gland cannot put pressure on the neck and cause a “lump in the throat” sensation. These sensations most often appear during times of stress and are associated with the involvement of nerve fibers in the neck. Only dense large nodes, as well as a significantly enlarged thyroid gland, deforming the neck, can lead to such sensations.
Role of the thyroid gland
There are quite a few different glands in the human body, but none of them are as large as the thyroid. If we talk about location, it can be found in the lower part of our larynx.
This leads to one of the symptoms of hyperthyroidism - an enlargement of the thyroid gland, which becomes noticeable to the naked eye, which should not happen under normal conditions.
In its normal state, the thyroid gland is responsible for the production of hormones that contain iodine - an element that is necessary for our life, and this is not a simple exaggeration.
The thing is that iodine is involved in a huge number of processes that are responsible for metabolism, which we already talked about earlier, mental state and thermoregulation, the disruption of which is included in the list of important symptoms of hyperthyroidism.
In some cases, serious changes in hormonal levels can cause a change in the sex hormone produced - from male to female and vice versa.
When a hormone new to the body begins to accumulate in the blood, the first thing that suffers is the nervous system, for which certain parts of the brain are responsible.
Visual signs of thyroid disorders
Excess weight does not go away even on a diet? Do you want to sleep even after 9 hours of full sleep? Have apathy and irritability become the daily “norm”? Have skin, hair and nails long ago ceased to be a reason for pride? Then this article is for you.
Big Boss Metabolism
Many already know that this small, butterfly-like organ is the big “boss” in the body, and it is in charge of all metabolic, “construction” and restoration processes.
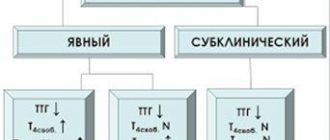
However, the thyroid gland does not make all “decisions” on its own, because its work is controlled by another “boss” - the pituitary gland. If the hormones of the gland (T4 and T3 free) become low, the pituitary gland “writes a fine” (TSH), which encourages the gland to work harder. This condition is called hypothyroidism.
If the thyroid gland “overdoes” with the release of hormones, TSH, on the contrary, decreases so as not to “inadvertently” increase the excessive production of T4 and T3. And this pathology is called hyperthyroidism.
It also happens that the pituitary gland “for no reason” authorizes the thyroid gland. In this case, both T4 and T3 and TSH increase in the blood. And the pathology is most often associated with brain oncology.
Fortunately, there are not many reasons for “thyroid” malfunctions. And in most cases the disease is caused by:
- iodine deficiency,
- autoimmune aggression,
- neoplasms (tumors, cysts)
- or radiation.
And the most common are the first two factors.
Visual signs of violations
“Thyroid” diseases, in most cases, are reflected literally on the face. Therefore, if you pay close attention to your health, it is quite difficult not to notice them.
So, hypothyroidism (hormone deficiency) is characterized by:
- increased fatigue, fatigue, drowsiness, even after a quality 9-hour sleep;
- depressed mood, depression,
- excess weight resistant to diet and exercise,
- swelling of the body and puffiness of the face,
- dryness, inflammation and poor healing of the skin,
- fragility and hair loss,
- low blood pressure, dizziness,
- digestive disorders, constipation.
And for excess hormones:
- excessive excitability, insomnia,
- anxiety, aggressiveness, panic attacks,
- unmotivated weight loss, exhaustion,
- excess oily skin and hair,
- increased sweating,
- high blood pressure, palpitations,
- headache,
- abdominal pain (due to cramps), constipation or diarrhea.
Symptoms can occur in different combinations, and their intensity depends on the degree of disturbance. Among other things, it is important to remember that symptoms can increase gradually over several years. And they do not go away even after harmonizing nutrition, rest and physical activity.
How to check
Basic complex:
- T4 and T3 free,
- TSH,
- antibodies to TPO and TG (risk of hypothyroidism) – to assess the risk of developing or already existing degree of autoimmune aggression
+ Ultrasound.
Expanded complex:
- T4 and T3 are free,
- TSH,
- antibodies to TPO and TG + antibodies to TSH receptors (risk of hyperthyroidism),
- as well as thyroglobulin and calcitonin (thyroid tumor markers)
+ Ultrasound.
Photo of hyperthyroidism
Vitamin deficiency - modern methods of combating and preventing diseases associated with vitamin deficiency (110 photos and videos)Gonorrhea - first symptoms, signs, treatment and prevention of the disease (145 photos + video)
- Furunculosis - causes, treatment options and tips on how to get rid of a boil (110 photos)
Read here! Rubella: first signs, main symptoms, description of the course of the disease and treatment methods (110 photos)
Please repost
0
Diagnostics
Depending on the suspected pathology, the doctor prescribes an individual set of diagnostic procedures. In this paragraph, we will describe all types of diagnostics of thyroid diseases, and the endocrinologist will prescribe the necessary ones for a particular patient.
The following are used for both preventive and diagnostic purposes:
- examination and palpation of the thyroid gland;
- ultrasound examination of the organ (ultrasound);
- donating blood for thyroid hormones (T3, T4, TSH);
- taking a puncture (biopsy);
- computed tomography or MRI.
The Amadeus Clinic has created a diagnostic base for identifying thyroid disease in children, women and men. In our center you can take any test: from hormone concentrations to genetic mutations. We have modern high-precision equipment for ultrasound examination of the thyroid gland, which is carried out by experienced ultrasound diagnostic doctors and endocrinologists.