When the muscles stop obeying. What is amyotrophic lateral sclerosis?
Despite the rapid development of medical science, diseases continue to occur, the causes of which still remain a mystery. We are talking about one of these pathologies - amyotrophic lateral sclerosis - with Ekaterina Aleksandrovna Zhidkonozhkina, a neurologist at the Expert Clinic Voronezh.
- Ekaterina Aleksandrovna, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis - what kind of disease is this?
— Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (otherwise known as ALS) is a degenerative disease of the nervous system associated with the death of motor neurons. Moreover, both central and peripheral neurons can be involved in the pathological process. It first manifests itself as paralysis of individual muscles, and subsequently one can observe complete atrophy of the entire muscle.
In the USA, Canada and some other English-speaking countries, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis is also often called Lou Gehrig's disease. It received this name after it was discovered by the famous American baseball player of the 30s of the 20th century, Lou Gehrig.
— What causes amyotrophic lateral sclerosis? Are the causes of this pathology known?
— The exact reasons have not been clarified at this time. Today, about 10 genes responsible for the development of this pathology have been identified. In 5-10% of cases, the disease is associated with heredity. These are the so-called family forms. In other cases, it occurs sporadically.
The onset of the disease is most often observed between 50-70 years. Earlier forms are less common.
— By what symptoms can amyotrophic lateral sclerosis be recognized?
— The first signs that should alert the patient are the appearance of muscle weakness and atrophy in the distal parts of the upper or lower extremities (hands or feet). That is, a person may notice a decrease in the volume of one or both limbs, retraction of certain parts of the limb, difficulty in holding objects.
Since there are several forms of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, the disease can begin with such signs as impaired speech, articulation, swallowing, that is, exclusively with damage to the facial and cranial muscles.
Over time, symptoms progress and larger muscle groups are involved. The process can begin with the hands and then spread to the lower limbs, and vice versa.
— How to diagnose this disease? Are there diseases that have similar symptoms to ALS and that can be confused with it?
— The gold standard in the diagnosis of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis is a functional method of studying the nervous system—electroneuromyography. It allows you to identify changes associated with damage to motor neurons of the spinal cord in the absence of disturbances in the conduction of impulses along the nerves.
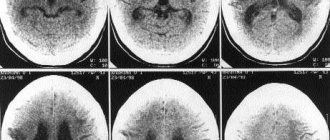
In order to distinguish amyotrophic lateral sclerosis from other diseases, we also use MRI of the brain and spinal cord, and transcranial magnetic stimulation. Among such pathologies are the spinal form of multiple sclerosis, cerebellar ataxia, tumors of the brain and spinal cord (craniospinal tumors): the symptoms of these diseases are similar to one or another form of ALS. I would like to note that with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, the oculomotor muscles are not involved in the process, and this makes it possible to distinguish it, in particular, from myasthenia gravis.
Read materials on the topic:
Electroneuromyography: one of a kind Young but absent-minded. What is multiple sclerosis
— Is amyotrophic lateral sclerosis treatable? What is the prognosis for this disease?
— At the moment, there is no therapy aimed at the mechanisms of development of the disease. There are drugs that allow you to have a short-term effect on these mechanisms, but these drugs are not registered in our country.
Treatment is mainly nonspecific, symptomatic, allowing to improve the quality of life.
The main recommendation for patients with ALS is not to get tired and avoid excessive physical activity. At the stage of difficulty in daily activities, physical therapy is important. Physiotherapy methods are actively used, technical means of rehabilitation and orthoses are individually selected, allowing one to perform certain actions independently.
When breathing problems develop, the patient is given therapeutic exercises at the initial stages. Subsequently, non-invasive and, if necessary, invasive ventilation is used. If difficulties arise with eating or swallowing, the patient is provided with nutrition through a gastrostomy tube or nasogastric tube.
Despite the current lack of specific treatment for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, it is important to know that there are cases where quality care and rehabilitation of the patient allow him to live a long and productive life. One of the striking examples of this was the world famous theoretical physicist and researcher Stephen Hawking, from whom this disease took away the ability to move, but in no way affected the speed of his thought. For 30 years he served as professor of mathematics at the University of Cambridge.
Read more about the life of Stephen Hawking in our article
— Will physiotherapeutic procedures be useful for patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis?
— Hardware physiotherapy for this pathology is ineffective.
The editors recommend:
THAT for the brain. When to start? Life after a stroke. Step by step - to the old me
For reference:
Zhidkonozhkina Ekaterina Aleksandrovna
Graduate of the Faculty of Medicine of the Voronezh State Medical Academy named after N.N. Burdenko 2004.
In 2005, she completed her internship in the specialty “Neurology”.
Currently working as a neurologist at the Expert Clinic, Voronezh. Receives at the address: st. Pushkinskaya, 11.
Forecast
It should be noted that the high and bulbar forms of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis are the most unfavorable - with them, the life expectancy of patients is significantly reduced. However, no matter what the first symptoms are, the disease quickly progresses, subsequently taking over the entire body, and the patient loses the ability to eat and move independently. Sometimes shortness of breath occurs - with physical activity and sometimes even without it. The patient feels a lack of air, which gives rise to panic. In the future, he may stop breathing on his own, and in order to provide him with oxygen, constant artificial ventilation will be needed. In some cases, at the end of the disease, difficulties with urination may appear. Due to atrophy, the patient loses weight.
Lateral atrophic sclerosis is accompanied by autonomic disorders: the limbs become noticeably cold, areas of the skin become stained, sweating and greasiness of the skin increases.
Life expectancy ranges from approximately 2 to 12 years, but most patients die within 5 years of diagnosis.
Forecast
The prognosis for the recovery of patients suffering from amyotrophic lateral sclerosis is pessimistic. Treatment of the disease is aimed at improving the quality and increasing the patient’s life expectancy. The only drug that affects the mechanism of development of the disease is not imported into the Russian Federation. The most unfavorable prognosis is for high and bulbar forms of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis.
Care and palliative therapy for patients suffering from ALS are provided at the neurology clinic and hospice of the Yusupov Hospital. Doctors in the intensive care unit use modern equipment to support the patient’s vital functions. To get complete information about the disease, the cost of treatment, and to make an appointment with a neurologist, call the contact center phone number. It works 24 hours a day without days off and lunch breaks.
Make an appointment
Pathogenetic therapy
To date, the only drug that can slow the progression of ALS is riluzole. It has been proven that taking it can prolong the patient’s life by an average of three months. This drug is indicated for patients whose disease duration is less than 5 years. The patient should receive 100 mg of the drug daily. In order to avoid the risk of drug-induced hepatitis, it is necessary to check the levels of AST, ALT and LDH every three months. Since men and smokers have lower concentrations of riluzole in the blood, they should either limit themselves to smoking or completely get rid of this bad habit. You will need to take the drug for life.
Scientists have repeatedly tried to use other drugs for pathogenetic therapy. However, such experiments did not prove effective. Among them were:
- xaliprodene;
- metabolic agents;
- anticonvulsants;
- antiparkinsonian drugs;
- antibiotics;
- antioxidants;
- calcium channel blockers;
- immunomodulators.
The effectiveness of taking high doses of Cerebrolysin has also not been proven, despite the fact that this drug can slightly improve the condition of patients.
Symptoms
In the early stages, symptoms of ALS manifest themselves as follows:
- Weakness of muscles in the legs, ankles, or feet.
- Foot drop due to limited ability to lift the forefoot or toes.
- Slurred speech, difficulty swallowing.
- Fibrillations (muscle spasms, twitching) in the arms, tongue, shoulders.
- Weakness of the hands, impaired hand motor skills.
In most cases, the disease is initially localized in the limbs, after which it spreads to other parts of the body. From the very beginning of the disease, symptoms begin to develop rapidly - first the muscles weaken, then become paralyzed. All this is fraught with breathing, chewing and swallowing problems.
Diagnostics
If some of the early symptoms of neuromuscular diseases appear, you should contact your doctor, who, if necessary, will refer you for a consultation with a neurologist. But even a timely visit to a neurologist does not guarantee that the diagnosis will be made immediately, since it takes some time to verify the diagnosis. The neurologist will be interested in the medical history and neurological status.
- Reflexes
- Muscle strength
- Muscle tone
- touch and vision
- Coordination
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis is quite difficult to diagnose in the early stages, since the symptoms are similar to other neurological diseases. The following diagnostic methods are used:
- Electroneuromyography. This method allows you to measure electrical potentials in muscles and impulse conduction along nerve fibers and muscles. For myography, needle electrodes are inserted into the muscle, which makes it possible to record electrical activity in the muscles, both at rest and during muscle contraction. Electroneurography allows you to study conduction along nerve fibers. For this test, electrodes are attached to the skin over the nerve or muscle that is being tested. A small electric current is passed through the electrodes and the speed of the impulse is determined.
- MRI. This method uses a powerful magnetic field and allows detailed visualization of various tissues, including nervous tissue.
- Blood and urine tests. Laboratory analysis of blood and urine samples can help your doctor rule out other possible causes of your symptoms.
- Muscle biopsy. If there is a suspicion of a muscle disease, a muscle biopsy may be prescribed. During this procedure, a piece of muscle tissue is removed and performed under local anesthesia. The tissue sample is then sent for testing.
Pathological anatomy
Rice.
1.1. Cells of the anterior horns of the spinal cord, normal Fig. 1.2. Cells of the anterior horns of the spinal cord, normal Fig. 1.3 Cells of the anterior horns of the spinal cord, degeneratively changed (thionin staining) Fig. 1.4 Cells of the anterior horns of the spinal cord, degeneratively changed (thionin staining) The spinal cord is somewhat reduced in volume, the soft membrane is hyperemic and thickened, there are degenerative changes in the roots and nerve trunks. There is death of cells of the anterior and lateral horns of the spinal cord, the thoracic nuclei of the spinal cord (Clark's columns), nuclei of the cranial nerves (mainly motor), cells of the cerebral cortex, and to a lesser extent, cells of the subcortical ganglia; The pyriform nerve cells of the cerebellum (Purkinje cells), dentate nuclei, and olives also suffer. The nature of the process is degenerative, which leads to gross changes in the size and shape of the surviving cells (Fig. 1).
Rice. 2. Degeneration of the fibers of the anterior and posterior columns of the spinal cord (in the figure - light areas; stained for myelin) Fig. 3. Perivascular infiltration of lymphoid elements in the medulla oblongata (thionin staining)
Degeneration of the pyramidal fasciculus occurs along its entire length, mostly in the brain stem and spinal cord; in the latter, the anterior and posterior columns are often affected (Fig. 2). Inflammatory changes and perivascular infiltrates are always observed, mainly in the lower parts of the brainstem and spinal cord (Fig. 3). There is a proliferation of all types of glia, especially micro- and oligodendroglia. Cytoplasmic inclusions were identified in the cells of the anterior horns of the spinal cord of people who died from amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and experimental monkeys (T. L. Bunina).
Etiology
The etiology has not been fully elucidated. Some authors consider the disease to be hereditary, others - infectious. Familial cases of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis are probably hereditary and are transmitted in a dominant manner. To substantiate the infectious theory, much has been done by domestic authors (L. O. Darkshevich, M. S. Margulis, N. V. Konovalov). The infectious viral concept is supported by the fact that in most cases the disease amyotrophic lateral sclerosis is sporadic; the process, according to morphological data, affects both the gray and white matter of the brain; electron microscopic studies conducted by N.V. Konovalov made it possible to identify particles similar to viral bodies in the medulla oblongata of a patient with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. For the first time in the Soviet Union (1956), experimental work was started on grafting monkeys with human amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Morphological changes in the cells of the anterior, lateral and sometimes posterior horns of the spinal cord in rhesus monkeys turned out to be similar to those in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Some monkeys, after long-term incubation (2-3 years), developed a disease similar to human amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (L. A. Zilber, N. V. Konovalov).
Differential diagnosis
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis differs from subacute and chronic poliomyelitis (see) by the presence of spastic paresis, from syringomyelia (see) by progression, the absence of dissociated sensory disorders and trophic disorders. With a spinal cord tumor, there is a disturbance of sensitivity, and in the cerebrospinal fluid there is protein cell dissociation. In case of muscle atrophy of syphilitic origin, there is an indication of a history of syphilis, positive serological reactions, a favorable course and success from specific treatment are observed. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis differs from hereditary muscle diseases by its rapid course and the presence of spastic movement disorders. Tick-borne encephalitis in the late period has a benign course, improvement occurs as a result of treatment. There are reasons to classify many sporadic cases of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis as slow infections of the nervous system. In some cases suspected of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, it is necessary to carry out a differential diagnosis with cervical myelopathy in spinal osteochondrosis (see Osteochondrosis).
The prognosis is unfavorable; death occurs from paralysis of the respiratory center.