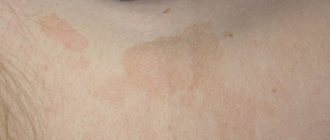
The appearance of dubious spots on the skin, which sometimes itch and flake, is a serious reason to consult a doctor and check for dermatological diseases.
Pityriasis rosea (Giber's disease, roseola exfoliates, pityriasis, pithiasis) is an acute skin disease with specific rashes, a peculiar course and a tendency to seasonal relapses. It manifests itself in the formation of pink spots on the skin of the chest, back, limbs and other parts of the body, located along the lines of maximum extensibility (Langer's lines). Over time, the rashes become like large medallions. From the moment the first maternal plaque (large spot) is detected until the symptoms of the disease completely disappear, 30-45 days pass.
At CELT you can consult a dermatologist.
- Initial consultation – 3,500
- Repeated consultation – 2,300
Make an appointment
Causes of pityriasis
Despite the fact that Gibert's disease is very common, the mechanism of the disease is not fully understood. The following factors are believed to play an initial role:
- Exposure to viruses (type 7 herpesvirus, etc.), bacteria and other infectious agents. This is confirmed by tests that prove the presence of pathogens in the body. Very often, skin disease appears against the background of influenza, acute respiratory infections and other infections.
- Attachment of allergic reactions.
- Bites from bedbugs, lice and other blood-sucking insects.
- Reduced immune defense.
- Frequent hypothermia and stress.
- Violation of gastrointestinal functions and metabolism.
- Introduction of vaccines.
Kinds
Of the total number of skin diseases, this disease is one of the 10 most common. The following types of lichen in humans are distinguished:
- shearer;
- pink;
- encircling;
- red;
- pityriasis
Important! Each of these forms has its own causes, specific symptoms and treatment.
To make a correct diagnosis and prescribe treatment, you need to distinguish lichen alba in the photo, pink lichen from other skin diseases.
Symptoms of pityriasis
Clinical manifestations of pityriasis rosea are caused by exposure to infectious pathogens and the development of allergic reactions. The skin disease is manifested by the following symptoms:
- General weakness, enlarged lymph nodes, elevated body temperature.
- The formation on the body of small pinkish and mauve spots that have a symmetrical shape and appear along Langer’s lines. Rashes appear on the back, limbs, chest, neck, groin and other parts of the body.
- The appearance on the skin of 2-3 bright red maternal plaques (their diameter is 4 cm), dotted with scales. After a week, small pink rashes form from these large spots.
- Dropout spots spread throughout the body and increase in size (their diameter is 1-2 cm), can peel off, and resemble medallions in shape.
- Severe skin itching.
- Increased irritability.
With proper therapy, the symptoms of pityriasis disappear after 5-8 weeks, and the patient fully recovers. Longer therapy is required if the rash has dense nodules, blisters or papules. In exceptional cases, pityriasis rosea turns into eczema, purulent inflammation of the skin, folliculitis, streptococcal infections, etc. develop. The development of complications is facilitated by the patient’s excessive sweating, a tendency to allergies, constant friction of the skin and improper treatment.
Description of the disease
Depending on the type of lichen, the rash may be dry or weeping, pale pink or bright red.
Most often, the disease affects the back, face and chest of the child (it is in these areas that the largest number of sweat glands are located). The disease is infectious in origin and is caused by viruses or fungi. The disease most often manifests itself in the spring-summer season, when it is warm and humid outside. At the moment, a large number of varieties of lichen are known. Many of them are highly contagious and potentially dangerous to the child’s immediate environment. That is why, if there is any suspicion of an infectious disease, it is necessary to immediately show the patient to a qualified specialist.
Diagnosis of pityriasis
If you find suspicious spots on the skin, you should promptly contact a dermatologist. During a visual examination, the doctor assesses the nature of the rashes, their shape, size, location on the body and is able to make the correct diagnosis. After dermatoscopy, the following studies are additionally carried out: biochemical tests of blood and urine, RMP (microprecipitation reactions with antigens), skin scrapings from injured areas.
A more complex diagnosis is carried out if the skin disease lasts more than six weeks. In these cases, discharge from the affected lesions is sent for bacterial culture. A biopsy and subsequent histological studies will help make the correct diagnosis. In order to distinguish Zhiber's disease from other types of lichen, toxicerma, psoriasis, complicated syphilis and other pathologies, fluorescent diagnostics are carried out, scrapings are checked for the presence of pathogenic fungi, RPR tests are done for syphilis, etc.
Ringworm on the skin: treatment
Treatment of the disease is especially effective at an early stage. Ringworm can be cured in all patients, regardless of age. In this case, you need to consult a doctor even with minor manifestations. For diagnostic purposes, a dermatologist conducts a visual or instrumental examination (using a special lamp), prescribes a series of tests - studying urine, blood, as well as immunological studies and skin scrapings.
After establishing the exact cause and type of lichen, treatment is prescribed. Most often it is associated with the use of special ointments externally (antifungal drugs). The course of therapy lasts from 2 weeks to 3-4 months.
Main areas of treatment:
- Etiotropic – the use of drugs that eliminate the cause of the disease. These can be fungicides or antiviral agents (based on Acyclovir).
- Elimination of itching, spots and other unpleasant symptoms.
- Carrying out procedures - UV therapy, physiotherapy, increasing resistance (strengthening the immune system), maintaining personal hygiene.
- In rare cases, it is necessary to disinfect the premises, especially linen, furniture, and personal belongings.
It is not recommended to treat lichen yourself at home. This is dangerous because you can waste time and also infect other people. In addition, the patient often cannot determine which drug to treat the pathology with. For example, a person “prescribes” an antimicrobial ointment while he develops herpetic (viral) lichen. In rare cases, lost time can result in severe consequences such as blindness, arthritis, and other complications.
Pityriasis rosea in pregnant women
Pityriasis occurs more often in women than in men. It is especially dangerous when the skin disease occurs in pregnant women. If you notice any rashes, it is important to immediately visit a dermatologist and undergo treatment. It is unacceptable to risk the baby’s health and expect the plaques to disappear on their own. If the disease is not treated, then bacterial infections appear, which are much more difficult to deal with.
If a pregnant woman has not been diagnosed with pityriasis rosea, it is nevertheless important to adhere to the following recommendations:
- clothing made from cotton and linen is preferable to synthetic and woolen fabrics
- limiting heavy physical activity
- For hygienic purposes, use only warm water
- timely moisturizing of damaged skin areas
What tests need to be taken for pityriasis rosea?
The diagnostic method and set of necessary studies are determined by a dermatologist. Typically, the patient takes a blood test to study general indicators. Tests are often ordered to detect antibodies to viral agents, including syphilis and herpes. To exclude fungal damage to the skin, microscopic examination of scrapings from the site of the lesion is carried out.
Additionally, the doctor may prescribe an immunogram if there is a suspicion of a significant decrease in the body's defenses. The cause of pityriasis rosea is an allergic reaction, so testing for allergens is possible. If necessary, the doctor prescribes additional examinations and consultations with specialists. Typically, such measures are taken in case of protracted or atypical course of the pathology.
Treatment of pityriasis
When a patient is diagnosed with Gibert's disease, the dermatologist develops an individual treatment regimen to avoid dangerous complications. There is an opinion that pityriasis rosea will go away on its own in a few weeks. As a result, complications arise, and the patient comes to the dermatologist with an advanced form of the disease.
Drug treatment includes the following medications:
- antihistamines that relieve the patient from itching, swelling and redness on the body
- corticosteroid, desensitizing and antipruritic ointments. Medicinal compositions containing betamethasone, hydrocortisone, etc. are applied to the affected skin and lightly rubbed in. The medications eliminate rashes, get rid of peeling, and effectively restore the skin.
- drying agents containing zinc to accelerate skin healing
- Broad-spectrum antibiotics are indicated in cases where a bacterial infection is associated with pityriasis rosea. It is unacceptable to start taking antibacterial drugs on your own, since they are selected individually, taking into account laboratory tests.
- antifungal medications: drugs containing clotrimazole and other active substances are prescribed topically in the form of gels and ointments
- antiviral drugs containing acyclovir and other active components. Dermatological tests have confirmed that if antiviral drugs are prescribed in combination with antibiotics from the first days, the patient quickly recovers.
- neutral water-shaken preparations Dermatologists prescribe pharmacy talkers containing zinc oxide, menthol and anesthesin to patients with pityriasis rosea. These products relieve itching and pain in damaged areas and speed up recovery.
- iodine is an aggressive, but extremely effective remedy. Injured skin is treated with iodine in the morning and evening. Initially, the skin begins to peel off more actively, but then there are no extra scales left on it. Not all experts recommend that their patients cauterize damaged areas with iodine, since this drug can be harmful if used incorrectly.
Recommendations for patients
During the treatment period, the patient is recommended to adhere to the following recommendations:
- Follow a hypoallergenic diet: avoid nuts, citrus fruits, chocolates, honey, etc. Products containing artificial colors should be excluded from the menu. It is worth limiting the consumption of fried foods, carbonated drinks, fast food, strong alcohol and coffee.
- Limit water treatments within reasonable limits and give preference to the shower.
- Refuse to use aggressive hygiene and cosmetic products for the body. Gels and other detergents should not dry out the skin.
- Give preference to underwear made from natural fabrics.
- Moderate sunbathing - ultraviolet light helps the skin recover faster.
- Follow the recommendations of a dermatologist, apply to the skin only products recommended by a specialist.
- Folk remedies can be used only after consultation with your doctor.
Ointments used for pityriasis rosea
For severe, disturbing itching, anti-inflammatory and antiallergic creams and formulations are prescribed. Ointments are used to treat the disease:
- Hydrocortisone – has an anti-inflammatory effect, relieves itching;
- Olettrinovaya is an antibacterial drug;
- Prednisolone - a composition with healing properties that can relieve inflammation;
- Loriden A - ointment with antipruritic, anti-parotid, anti-edematous effects;
- Sinalar – eliminates inflammation due to antibacterial properties;
- Lassara paste is an antiseptic that discolors stains;
- Rioloxol - antibacterial and anti-inflammatory;
- Flucinar – effectively relieves itching, eliminates flaking and inflammation;
- Sulfur – inhibits the inflammatory process.
Tsindol suspension also helps dry the skin, eliminate inflammation and itching. Ointments are applied to the pink plaques in a thin layer in accordance with the instructions and directions of the doctor. The treatment course is 2-3 weeks, the frequency of use of each drug is determined individually. At the same time as using medications, you should be careful with the affected skin.
However, any ointments, like all other medications, should be used exclusively as prescribed by a doctor, so as not to aggravate the situation. In addition, the effectiveness of each of the listed external remedies greatly depends on the patient’s age, the state of his immunity, the degree of spread of lichen, the presence of chronic pathologies and other characteristics of the body.
Shingles
The disease is caused by the herpes virus. Children over the age of 12 are prone to it. Symptoms of shingles appear only in those who have already had chickenpox. From this moment on, type 3 virus remains in the body for life. A number of predisposing factors contribute to the appearance of the disease:
- frequently ill children;
- newborns;
- with oncology;
- in the presence of chronic diseases;
As soon as the immune defense becomes insufficient, the herpes virus, which is in a dormant state, begins to actively manifest itself.
Symptoms
It is not immediately possible to recognize herpes zoster in children. Elements often appear on the leg and torso. The following signs are characteristic:
- Increase in body temperature.
- Chills.
- Enlarged lymph nodes.
- Burning, stinging or itching in the areas where the rash appears.
- Decreased appetite.
At the beginning of its development, the first signs in the form of ARVI may appear. After 1-2 days of development of nonspecific symptoms, lichen colds begin to actively manifest themselves. Pink bubbles appear along the nerves (intercostal spaces are a common location for rashes). Gradually they merge. After a week, the elements dry out and the surface becomes covered with crusts.
Knowing everything about lichen, parents should exclude the possibility of scratching the elements on the child’s skin. At an older age, he needs to explain this. The presence of an open wound in an infant when scratching will lead to a secondary infection. Against the background of reduced immunity, it will begin to actively multiply, which will result in the addition of concomitant pathology.
Ringworm
The presented form is not common in childhood. Its etiology is varied and in some cases, it is not possible to determine the source. The causes and treatment are closely related. Medicines are prescribed after identifying the factor that provoked the development of the disease. The etiology of lichen planus consists of the following options:
- hereditary predisposition;
- drug intoxication;
- autoimmune factors;
- allergic lichen;
- neurogenic form;
- viral infection.
There are several forms along the way - acute, subacute and chronic.
Symptoms
The onset of the disease occurs differently in each child. Lichen planus appears after 7-10 days against a background of general malaise, weakness and loss of appetite in the form of a rash. For other patients, this form of development of the disease is not typical and they develop specific elements without affecting their well-being.
The most favorite places for rashes of red lichen are identified:
- underbelly;
- on the fingers;
- in the lumbar region;
- on the butt;
- elbow bends;
- on the feet;
- axillary fossae.
Ringworm most often does not appear on the head, which becomes one of the main distinguishing features. The rash consists of papules that do not have a cavity inside. They have an umbilical depression in the center of their elements and a polygonal shape.