Lymphadenopathy is a condition that is characterized by an increase in the size of peripheral lymph nodes, a change in their consistency and mobility. It develops along with an increase in overall body temperature, an enlargement of the spleen and liver. Even a slight enlargement of the lymph nodes indicates that pathological processes are developing in the body that require adequate treatment. It can cover one or more structures and cause inflammatory processes.
The hematology department of CELT invites you to undergo diagnosis and treatment of lymphadenopathy in Moscow. You have the opportunity to consult with leading domestic hematologists, who have modern techniques and a powerful base that allows you to quickly and accurately establish a diagnosis. They provide treatment in accordance with international standards. You can find out the cost of services in the “Services and Prices” section. To avoid misunderstandings, do not forget to check the numbers during consultation or with our operators.
Lymphadenopathy: what is it?
Enlarged lymph nodes look like soft or dense rounded formations located under the lower jaw, in the cervical, axillary, groin or other areas. They can have a smooth or bumpy surface and very often develop after acute infections and inflammations. Sometimes their appearance is caused by traumatic injuries to the skin or the introduction of a vaccine.
Lymphadenopathy develops due to the accumulation of a certain type of cell in the lymphadenoid tissue. The reaction is often provoked by increased blood flow, an increase in the number of lymphocytes and macrophages in response to the appearance of foreign genes in the body. In just one week, the node can increase five to fifteen times. A pathological condition is spoken of if, along with an excess of size, there is a change in the density, mobility and surface of the structure. When palpated, it can be quite painful or painless.
Reasons for contacting our center for diagnosing lymphadenopathy in Moscow: independent identification of large nodes that do not hurt, a feeling of intense pain during palpation, other symptoms in the form of a rash, increased body temperature, weight loss, and rapid fatigue. Particularly dangerous can be nodes that do not go away for more than two months, located in different areas, with a diameter of more than two centimeters, the enlargement of which occurred for no apparent reason.
Features of the disease in the groin area
Since lymphadenopathy in the groin area is provoked by a pathological process in the body, the disease can have several forms.
There are primary and secondary forms. Primary is characterized by the appearance of infections due to the ingress of microbes. The second form develops against the background of general damage to the body, inflammation and lymphadenitis. Inflammation begins in one part of the body.
Inguinal lymphadenopathy has a pronounced character , is easily palpable and causes discomfort. The main sign of the onset of the disease is frequent colds, inflammation of the nasal pharynx and decreased immunity.
Particular attention should be paid to combining the inflamed lymph nodes into one node, which is often called a conglomerate. After all, this phenomenon often indicates the development of oncology, metastasis, and tuberculosis. Therefore, if suspected, patients are additionally prescribed a biopsy analysis.
If several small compactions are observed, which often happens in children, then we are talking about damage to grapeshot lymph nodes.
They are accompanied by pain, discharge of pus, and a crunching sound when pressed.
All this indicates the development of phlegmon , when the spaces between the cells become inflamed, which leads to the melting of the lymphatic tissue. You can get rid of this only with the help of surgery, a long course of antibiotics, immunostimulants and radiotherapy.
You also need to divide lymphadenopathy into the following forms:
- Local , when inflammation develops in one part of the body.
- Regional , when organs or lymph nodes in adjacent areas are affected.
- Generalized , in which inflammation is observed in more than three parts of the body. This is the most severe form of the disease.
Doctors divide the disease into chronic and acute forms . In the acute form, severe pain, high temperature and swelling are felt. In chronic cases, the disease proceeds slowly, without pronounced symptoms, and worsens during a period of weakening of the body.
This form of lymphadenopathy develops with sexually transmitted infections , which are almost incurable. Therefore, inflammation rarely goes away completely.
The etiology of the disease is as follows:
- Allergy;
- Autoimmune drugs;
- Inflammation and acute infectious lesions.
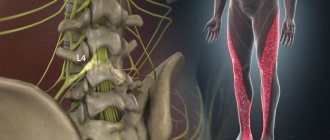
Often the process develops in the groin, axillary area or above the collarbone. If generalized lymphadenopathy is located in the neck, then we are talking about causes related to oncology or hormonal disorder.
If the body reacts sharply to infectious lesions, a reactive form of the disease may develop . Then the source of inflammation is any area of the body, but there will be no pronounced symptoms.
According to the course, the form is divided into: acute, chronic and recurrent.
The disease can take on a tumor or non-tumor form, which is extremely dangerous for human life.
Comparing male and female lymphadenopathy, it can be noted that it does not have any special differences . Although men may experience enlarged testicles, pain during urination, discomfort when straining, and poor spermatogenesis.
Women have the following specific manifestations:
- Decreased libido;
- Changes in genital organs;
- Discharge of pus from the groin area;
- Problems with menstruation;
- Breast augmentation;
- The appearance of lumps in the groin.
Women usually suffer from generalized lymphadenopathy, because foci of inflammation are located not only in the groin, but also in the chest and abdominal region. Therefore, it is possible to identify the disease faster .
Lymphadenopathy: classification and causes
The classification of lymphadenopathy is based on a number of parameters, starting with the location of the affected structures and ending with their pain and size:
| Localization of the affected node/nodes | Etiological factors |
| Under the lower jaw | Diseases of the eyes, ear, throat, nose, damage to the skin in the head or neck area, dental problems. |
| Neck |
|
| Supraclavicular region | Malignant neoplasms:
|
| Armpits |
|
| Groin |
|
ULTRASOUND OF LYMPH NODES AVAILABLE IN BRANCHES:
Ultrasound of lymph nodes in the Primorsky region
Address: St. Petersburg , Primorsky district, st. Repisheva, 13
Ultrasound of lymph nodes in the Petrograd region
Address: St. Petersburg , Petrogradsky district, st. Lenina, 5
Ultrasound of lymph nodes in Vsevolozhsk
Address: Vsevolozhsk , Oktyabrsky Prospekt, 96 A
Lymphadenopathy: diagnosis
Before starting treatment of lymphadenopathy in adults, CELT hematologists conduct comprehensive studies to accurately diagnose and determine the cause of the development of the pathological condition. The following node parameters must be taken into account:
- Dimensions - determine the degree of the disease (first - 5 mm-14 mm, second - 15 mm-24 mm, third - 25 mm or more);
- Painful symptoms - most often it occurs during inflammatory processes, in particular purulent lymphadenitis;
- Quantity – one, two or several nodes located in one area can be affected. Multiple lesions are a sign of an active pathological process;
- Density - usually inflamed nodes are soft, their fluctuation is a sign of a purulent process, tight plasticity - lymphoma, hardness - metastases;
- Connectivity - several nodes combined into one whole can be a sign of tuberculosis, Besnier-Böck-Schaumann disease, or damage to lymphatic tissue.
In addition to the examination, the patient is prescribed diagnostic tests:
- Detailed blood test;
- Test for hepatitis and HIV;
- Ultrasound scanning of internal organs and affected nodes;
- Histology of biopsy samples from the affected node;
- X-ray examination;
- Magnetic resonance or computed tomography.
Diseases of the reproductive system
Orchitis is inflammation of the testicles. In addition to pain in the groin, there is pain in the perineum and the affected testicle. If the disease has become chronic, then the man experiences aching pain in the groin.
Testicular torsion. Causes severe groin pain in men. It is acute, initially occurs in the scrotum, and very suddenly. The pain is so severe that it can cause nausea and vomiting.
Funiculocele is a cyst of the spermatic cord. Causes discomfort in the scrotum, which intensifies after physical activity, and a feeling of fullness. Pain is more often observed during sexual intercourse.
Varicocele is a varicose vein of the spermatic cord. The pain can be either mild or severe. Shooting and burning pain in the groin in men is most often caused by varicocele.
Other possible reasons:
- acute prostatitis,
- prostate adenoma,
- vesiculitis,
- balanoposthitis,
- prostate cancer.
Lymphadenopathy: treatment
The development of treatment tactics is carried out by CELT specialists based on the diagnostic results obtained and the patient’s individual indicators. First of all, efforts are directed toward eliminating the pathological condition that has become the initiating factor for the development of lymphadenopathy. If purulent lesions of the lymphatic structures or bacterial infections are detected, the patient is prescribed antibacterial therapy. If indicated, surgical removal of the node is possible.
If the etiological factors involve damage by viral agents, the patient is prescribed antiviral and immunomodulatory pharmacological drugs. If he suffers from pain - painkillers. Most often, lymphadenopathy goes away within one to one and a half months after the cause that caused it is eliminated. Otherwise, the hematologist prescribes a biopsy and develops a new treatment strategy.
The hematology department of our clinic receives candidates, doctors and professors of medical sciences. Their practical and scientific work experience ranges from twenty-five years. You can make an appointment with them online or by contacting our information line operators. If necessary, you can make an appointment with specialists at any of our departments and undergo the necessary procedures. In particular, septoplasty is available in the otolaryngology department, which can improve the patient’s quality of life.
At CELT you can consult a hematologist.
- Initial consultation – 3,500
- Repeated consultation – 2,300
Make an appointment
By making an appointment with a hematologist, you can get a comprehensive consultation. The doctor is competent to treat various blood diseases, most of which can be identified in the early stages and prescribe timely treatment to cope with the disease quickly and easily.
When should you sign up for a test?
Indications for prescribing an ultrasound examination are determined by the doctor. He pays attention to many factors. Among them:
- enlarged and painful nodules of the lymphatic system;
- excessively mobile nodules;
- increase in body temperature;
- long-term infectious diseases;
- constant headaches, complaints of insomnia, lethargy and loss of appetite;
- body aches or pain in different parts of the body;
- suspicion of cancer;
- chronic diseases;
- acute phase of infection;
- gum disease
Preparation and examination process
There is no special preparatory procedure for the study, with the exception of ultrasound of the abdominal lymph nodes and regional lymph nodes. Increased gas production may interfere with visualization. It is recommended to stick to the diet for several days.
For the examination, a standard apparatus with a linear sensor of different frequencies is used for certain areas.
The procedure begins with the affected lymph nodes and ends with the opposite side and adjacent organs.
The doctor reads the data from the monitor and deciphers it: compares the norms for tissues and organs with the visual display on the screen.
The procedure is absolutely harmless and has no medical contraindications, with the exception of special cases. These include:
- dermatological diseases in areas of contact with the sensor;
- rehabilitation period after rectal surgery;
- recovery after gynecological operations;
- certain days of the menstrual cycle.