Skin cancer is a malignant disease of the skin. This form of the tumor process is considered one of the most common in the world. Until now, specialists in the field of oncology have not established the exact causes of the pathological focus. Like many other oncological neoplasms, skin cancer is a multi-etiological disease. There are predisposing factors and precancerous diseases, the presence of which increases the possibility of developing a skin tumor process. Depending on the stage and type of cancer, appropriate treatment is selected. You can suspect the presence of skin cancer yourself by examining the skin, paying special attention to nevi. The prognosis for life and disease when a tumor of the skin surface is detected also depends on the form and stage of the process. In accordance with the international classification of diseases (ICD-10), skin cancer is coded C43-C44.
What formations on the skin should raise suspicion?
Most moles, brown spots and growths on the skin are harmless - but not always. If you have a lot of moles and freckles, you need to be very careful about any changes in pigmentation. When a mole begins to bleed or ooze fluid , you need to go to a dermatologist.
It is also necessary to monitor new formations on the skin. Many skin cancers are essentially colorless. They often appear as pink or pearly papules or scaly patches. These are signs of a primary neoplasm, and it is advisable to show them to the doctor. Bleeding and weeping skin lesions are of particular concern.
ABCDE technique for cancer detection
The first five letters of the English alphabet are a guide to help you recognize the signs of cancer.
- A is asymmetry. Most skin cancer lesions are asymmetrical. If you draw a line through the middle of the hearth, the two halves won't line up, so it looks different from round to oval.
- B is the border. The borders of cancers tend to be jagged and may have jagged edges, while regular moles tend to have smoother, more even borders.
- C is color. Multiple colors are a warning sign. While benign moles are usually one shade of brown, cancerous moles can be various shades of tan, brown, or black. Red, white, or blue colors may also appear as they grow.
- D is the diameter. It is already worth paying attention to the spring if its size is more than 6 mm. Some experts say it's also important to look for any damage, regardless of size, that is darker than others. Sometimes, amelanotic melanomas are colorless.
- E is for evolution. Any change in the size, shape, color or height of a spot on your skin, or any new symptom in your skin, such as bleeding, itching or crusting, may be a warning sign of melanoma.
If you notice these warning signs or anything new, changing, or unusual on your skin, contact your dermatologist immediately.
Clinical guidelines
After treatment is completed, the doctor draws up an examination plan for timely detection of a possible recurrence of skin cancer. To do this, you will need to regularly visit a dermatologist, take a general and biochemical blood test, evaluate the level of the LDH enzyme, and periodically do tomography. Source: Watson M, Thomas CC, Massetti GM, McKenna S, Gershenwald JE, Laird S, Iskander J, Lushniak B. CDC GrandRounds: Prevention and Control of Skin Cancer // MMWR MorbMortalWklyRep. 2015 Dec 4;64(47):1312-4. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.mm6447a2
Methods for preventing skin cancer:
- Refrain from sunbathing, especially during hours of high solar activity (from 11 to 16). During this time, wear light clothing that covers your body and limbs.
- Conduct monthly self-examination of the skin.
If you notice symptoms of skin cancer, make an appointment with your doctor immediately.
Sources:
- Yu.A. Goncharova. Skin cancer // Chief Doctor of the South of Russia, 2015, No. 2(43), pp. 25-30.
- V.M. Litvinenko. Skin cancer: causes, classification, treatment methods and prevention // Science, technology and education, 2014.
- Boada A.LeadershipintheTreatmentofSkinCancer // ActasDermosifiliogr. Jul-Aug 2019;110(6):423. doi: 10.1016/j.ad.2019.03.003. Epub 2021 Apr 18.
- Watson M, Thomas CC, Massetti GM, McKenna S, Gershenwald JE, Laird S, Iskander J, Lushniak B. CDC GrandRounds: Prevention and Control of Skin Cancer // MMWR MorbMortalWklyRep. 2015 Dec 4;64(47):1312-4. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.mm6447a2
The information in this article is provided for reference purposes and does not replace advice from a qualified professional. Don't self-medicate! At the first signs of illness, you should consult a doctor.
Who is most at risk of skin cancer?
People with fair skin that burns easily in the sun are more likely to develop skin cancer. The skin generates its own protection against ultraviolet radiation using keratin and melanocytes , cells that produce melanin. They create a tan, protecting the skin from damage. However, when you get sunburned and your melanocytes are unable to respond quickly, you are at serious risk of developing skin cancer. Moreover, the greatest danger haunts those with blond and red hair, as they burn faster.
Causes and risk factors
The following people are at particular risk of developing skin tumors:
- With Bowen's disease;
- Those who are elderly;
- Light-skinned, with a genetically reduced melanin content;
- With senile keratoma;
- With melanoma-dangerous pigment spots;
- Having Queyra's erythroplasia;
- Suffering from cutaneous horn;
- With xeroderma pigmentosum;
- Having inflammatory skin pathologies;
- Suffering from nicotine addiction;
- Staying in the open sun for a long time;
- Abuse of visiting the solarium.
In addition to the risk group, doctors identify some other factors that contribute to the development of skin malignancy:
- Complication due to dermatitis of radiation origin;
- Chemical exposure to carcinogens, such as arsenic compounds, tar found in cigarettes, or lubricants;
- Damage at the site of an old scar;
- Radiation exposure;
- Consumption of products containing carcinogenic substances such as nitrites, nitrates, marinades, smoked foods, preservatives and excessively fatty foods;
- Exposure to various types of thermal factors or thermal radiation;
- Violation of the integrity of the mole;
- Oncology at the site where there was previously a deep burn;
- Abuse of tattooing;
- Presence of hepatitis or HIV infection;
- Living in southern countries.
How to detect skin cancer on the body?
The best way to detect skin cancer is to examine yourself. When checking, you should look at the spots on the skin. And you should check everything from the scalp (parting the hair to check the entire scalp) to the spaces between your toes and the soles of your feet.
If possible, ask your partner to help you. He can examine hard-to-reach areas of the scalp and back.
By getting into the habit of checking your skin, you will be able to notice changes. Checking monthly can be helpful. If you have had skin cancer, your dermatologist will be able to tell you how often you should check your skin.
People of all ages get skin cancer.
Skin testing can help you detect skin cancer early, when it is highly treatable.
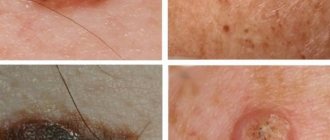
What does skin cancer look like? Photos and description of signs.
Skin cancer manifests itself on the body in different ways. It might look like:
- A mole that changes or a mole that looks different from your others
- Dome-shaped growth
- scaly spot
- A wound that doesn't heal or a wound that heals and comes back
- Brown or black streak under the nail
It can also manifest itself in other ways.
To detect skin cancer on your body, you don't need to memorize a long list. Contact your dermatologist if you notice a spot on your skin that:
- Differs from others
- Changed
- Itchy
- Bleeding.
Find out if the treatment is prescribed correctly
Consequences
Each type of skin cancer has its own set of cells with varying aggressiveness, which is why such neoplasms behave differently.
Why are skin cancers dangerous?
- Basalioma
is not prone to metastasis, is characterized by slow growth, and is often found in the nose. - Squamous cell skin cancer
, on the contrary, grows rapidly and metastasizes throughout the body. - The most dangerous form is considered melanoma
, which is difficult to treat and often causes a lot of complications.
How do basal cell and squamous cell skin cancers manifest?
Most people have basal cell or squamous cell carcinoma . The most important thing to know about these types of skin cancer is that they are very superficial. They do not penetrate too deeply into the layers of the skin. Therefore, if cancer of one of these types is detected early enough, the doctor prescribes a simple resection. A dermatologist or physician may perform a biopsy to determine the nature of the growth.
Squamous cell and basal cell carcinomas are often identified by external characteristics .
It may take the form:
- clearly colored plaque;
- clusters of brown nodules;
- ulcers raised above the skin.
Such tumors are frozen, burned or excised. All of the above methods are equally effective.
It is important to start treatment as early as possible, since malignant neoplasms of these types do not grow deep into the skin . The best option is to treat cancer in Israel. In rare cases, when left untreated, basal cell and squamous cell tumors increase in size and spread into deeper layers of tissue.
Survival prognosis
The practice of recent years shows that the prognosis for five-year survival for squamous cell carcinoma of the initial forms is about 90%, and for its final stages no more than 60%.
If the patient’s body has responded adequately to anticancer treatment, then there may be no further relapses.
The prognosis for malignant melanoma is also good.
At the initial stages, survival rate is a little more than 95%, and at the final stage - no more than 20%.
How does melanoma manifest?
Melanoma differs from basal cell and squamous cell skin cancer primarily in that, unlike previously described types of cancer that do not penetrate into the deeper layers of tissue, this tumor has the potential to grow and spread. The deeper it penetrates the skin, the higher the risk of its further spread throughout the body. Metastatic melanoma is an extremely dangerous disease. However, melanoma can be completely cured if it is detected at an early stage, before it has time to grow deeper into the skin and form metastases in the internal organs.
Melanoma not only penetrates deeper into the skin, but individual cells spread around the primary tumor. Therefore, when resection of melanoma, the surgeon necessarily removes a fragment of normal tissue. For example, if the tumor is comparable in size to a pencil cut, you need to additionally remove about a centimeter of healthy skin around the entire circumference of the melanoma - and possibly more if the cancer has penetrated into the deeper layers of the tissue.
When melanoma grows deep into the skin, there is a risk of it spreading to other organs. Typically, in cases of metastases, secondary lesions form in the lymphatic system, namely in the lymph nodes. Lymph nodes in the armpits, groin or neck begin to enlarge and can reach considerable sizes. From there, cancer cells can spread to internal organs. Therefore, in cases of deep germination of melanoma, the doctor not only removes the tumor itself, but also checks the lymph nodes. They should not show any signs of cancer spreading.
Check the price with a specialist
Treatment
- Treatment of local local injuries consists of timely detection and surgical intervention. Removal is most often performed under infiltration anesthesia. For excision of large formations, general anesthesia may be used. In addition to malignant tumors, there are a number of pre-melanoma diseases in which the surgical method is indicated.
- Local-regional damage. Treatment includes wide-area excision and lymph node dissection of the affected lymph nodes. Types of unresectable, transiently metastatic tumors are subjected to isolated regional chemoperfusion. In certain cases, a combined approach has proven itself to be effective, with additional therapy that stimulates the immune system.
- Treatment of distant metastases is performed with monomodal chemotherapy. Certain types of mutations are targeted by targeted drugs.
How the quality of medications affects the cure for skin cancer
For advanced skin cancer, especially melanoma, the main treatments are chemotherapy and immune therapy. In this case, the quality of medicines becomes of great importance. This is especially important if the patient is undergoing immune therapy, because... Such drugs are not cheap.
If you have been prescribed drug treatment for skin cancer, it is best to purchase medications in Israel.
- Counterfeiting of medicines is prohibited in Israel.
The Israeli Ministry of Health strictly controls the quality of medicines through test purchases and inspections of pharmacies. A pharmacy or pharmacist who sells a low-quality drug to a client will lose its license and face criminal charges. - In Israel, licensing of innovative drugs is carried out as quickly as possible.
This allows Israeli clinics to quickly introduce into widespread clinical practice all new effective drugs appearing in the world. - The Israeli company TEVA is a world leader in the production of medicines.
Doctors in 60 countries around the world prescribe to their patients medications developed by this company.
Where can I buy Israeli medicines?
- In an Israeli pharmacy - after consulting a doctor.
If you undergo examination at the oncology center, the doctor will prescribe you the necessary medications, which can be purchased in Israel. - At your place of residence - using a telemedicine program.
As part of this program, you will also receive a consultation from an Israeli doctor - but remotely. You can order the medications prescribed by him and have them delivered to your home.
Cost of diagnosing skin cancer in Israel
In the table below, we present the cost of some procedures prescribed for the diagnosis of skin cancer at the Ikhilov Cancer Center.
| Diagnostic and treatment procedures | Price |
| PET-CT | $1491 |
| Examination and consultation with an oncologist-dermatologist | $567 |
| Biopsy revision | $511 |
| Operation Mohsa | $3318 |
| Photodynamic therapy | $361 |
| Removal of epidermal carcinoma | $511 |
| Detailed blood test | $407 |
Read more about the dangers of solarium
Scientists have proven the connection between solarium and skin cancer. American researchers provide terrifying statistics: about 430,000 cases of skin cancer are associated with visiting solariums. Other studies also confirm the dangers of this procedure.
It has been proven that 2 out of 3 people who regularly visit a solarium sooner or later develop skin cancer. Even a one-time visit to such a procedure increases the likelihood of cancer by 20%. And, if a person attended 150-170 sessions, then the risk increases by 50%. This number of sessions “accumulates” in 10-15 years, if you go approximately once a month.
The great harm of solariums is explained by the fact that the radiation from the lamps of the device consists of 98% of waves of the most carcinogenic type - waves of the UVA spectrum.
Why is it worth treating skin cancer in Israel, at the Ichilov Cancer Center?
- Accurate diagnosis.
Modern research methods and extensive experience of Israeli oncologists and pathologists, gained in leading cancer centers in the world, make it possible to accurately determine the type and stage of cancer in order to select the optimal treatment program. - World-class specialists.
The treatment of skin cancer at the oncology center is carried out by top-class professionals, such as oncologist Professor Yakov Shekhter, the author of his own method of immune therapy for metastatic melanoma. The professor selects a personalized treatment protocol for each patient, which allows him to achieve the best possible results. - Innovative treatment methods.
For skin cancer, the oncology center uses:
- Alpha-DaRT brachytherapy is a safe method for removing non-melanoma skin cancer;
- therapy of metastatic melanoma using the TIL protocol (tumor infiltration with lymphocytes).
You can take the first step towards recovery right now. To do this, fill out an application and one of our doctors will contact you within 2 hours.
Or call: +972-3-376-03-58 in Israel and +7-495-777-6953 in Russia.
This consultation does not oblige you to anything and is completely free .
We guarantee you complete confidentiality and preservation of medical confidentiality. We will help you, just as we have helped other patients. [starbox]