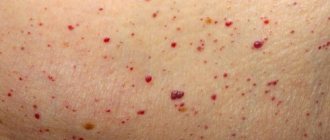
Forms and complications of nevi
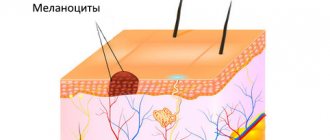
There are melanocytic (containing pigment cells - melanocytes) and non-melanocytic nevi (formed by cells other than melanocytes), which include epidermal nevus, nevus of the sebaceous glands, Becker's nevus and some other benign formations, vascular nevi of the skin.
Melanocytic nevi
There are acquired and congenital melanocytic nevi.
Acquired melanocytic nevi (AMN) are benign skin tumors. As a rule, they do not have a tendency to undergo malignant transformation. Special forms of acquired melanocytic nevi include Spitz nevus, Reed's nevus, spotted nevus (spilus), halonevus (Setton), and blue nevus (Jadassohn-Tiche) lying in the deep layers of the skin.
Atypical (dysplastic) nevi (AN) are classified into a separate group. Unlike common acquired melanocytic nevi, atypical melanocytic nevi may have some clinical characteristics of melanoma, such as asymmetry, ill-defined borders, multiple colors, or a size greater than 6 mm. Their main difference from a malignant tumor is stability, absence of changes over time and similar characteristics in one person. Atypical melanocytic nevi have a relatively increased risk of malignant transformation and require careful monitoring.
Congenital melanocytic nevi occur as a developmental defect (hemartoma) and are usually present at birth. Large congenital melanocytic nevi are also associated with an increased (but still low) risk of malignant transformation. Very rarely, they can be associated with a pathological accumulation of melanocytes in the central nervous system (neurocutaneous melanosis). Congenital melanocytic nevi with the expected size in an adult (over the course of life they will increase in proportion to the child’s growth) also require increased attention and medical supervision.
Nevi of Ota and Ito also have a melanocytic structure, but they are not based on excessive cell division, but on their accumulation in the deep layers of the skin.
Publications in the media
Nevi (moles, birthmarks) are hamartoma-like malformations of the skin that can develop both from elements of the epidermis and the dermis itself (connective tissue, vascular elements or melanocytes). Nevi are pigmented formations that usually protrude above the surface of the skin. Almost every person has moles; they can be congenital or occur throughout life, especially during puberty, in women during pregnancy, and hormonal dysfunctions. The clinical picture is characterized by extreme diversity in the number, size, morphological type and degree of pigmentation of individual elements - spots, nodules, plaques - up to subtotal damage to the skin with the so-called giant nevi. Large congenital nevi are considered to be elements >20 cm or occupying 2.5% of the body surface; they are considered a risk factor for malignancy.
• Epidermal nevi (warty or mole-like) are most often found at birth, although they can also develop in childhood (very rarely in adults). Externally they may be similar to papillomas (viral origin), but are usually represented by large linear plaques or an array of small papules. Epidermal nevi are often asymptomatic. Malignization is rare, with the exception of nevi of the sebaceous glands (basal cell carcinoma occurs in 5% of cases). Histologically they are characterized by acanthosis and hyperkeratosis. Nevus of the sebaceous glands is also characterized by the presence of a large number of sebaceous and apocrine glands. Cellular atypia is not observed. Treatment is mainly for cosmetic purposes. Preventive removal of sebaceous gland nevus is performed due to clinical manifestations (hair does not grow on it), and not the danger of malignancy.
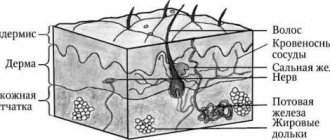
• Dermal nevi •• Connective tissue nevi are predominantly congenital and are often represented by dense, single papules and flesh-colored plaques. The number of hair follicles in them can be significant (“pigskin”). This variant of nevi is idiopathic and is not associated with other diseases, with the exception of “shagreen skin” in tuberous sclerosis. Histologically, they consist of dense conglomerates of collagen and elastic fibers. Prognostically safe and removed solely for cosmetic reasons •• Vascular nevi (hemangiomas) are vascular formations lined with endothelium, mainly capillary, but cavernous structures can also occur, especially in large nevi. Three clinical types are considered typical: strawberry nevus, cherry nevus and cavernous hemangioma. Strawberry nevus and cavernous hemangiomas more often undergo spontaneous regression, while cherry nevus continues to grow throughout life. Surgical treatment is carried out for cosmetic reasons, for functional disorders (localized in the conjunctival area, lips) or thrombosis of the cherry nevus (due to suspicion of malignancy) •• Melanocytic nevi are of the greatest clinical importance, given the need for differential diagnosis with melanoma •• Pathohistology. Nevus cells are located in the form of nested clusters of various sizes and configurations in the dermis, subepidermally and between cell complexes. Sometimes the accumulations become diffuse and are located very close to the epidermis along the basement membrane, and atrophic changes in the epidermis are noted. The cells are large, of various shapes and sizes, with a clearly visible nucleus, sometimes several hyperchromatic nuclei, arranged in the form of “rosettes” or lumpy clusters. In some elements, the shape of the cells is spindle-shaped, which makes the nevus resemble a neurofibroma. Pigment content may vary. In “young” nevi, the stromal component is weakly expressed; over time, the connective tissue stroma begins to predominate; such a nevus is considered “fibroepithelial.” Localization of nevus cells among basal keratinocytes and in the zone of the basement membrane without its disruption is characteristic of a border nevus, and in combination with the intradermal component - of a mixed nevus.
Clinical types of nevi • Basal cell nevus - a hereditary disease (109400, 601309, BCNS gene, 9q22.3, Â) - characterized by (usually benign) skin lesions of the eyelids, nose, cheeks, neck, upper jaw, looks like a flesh-colored papule, without signs erosion, histologically does not differ from basal cell carcinoma. • Verrucous nevus is a skin-colored (or darker) lesion of the epidermis similar to a wart, often linear, appearing at birth or in early childhood; can be of different sizes and localization, single or multiple “verrucous nevus. • Hairy nevus is a mole covered with a large amount of growing hair. • Giant pigmented nevus is a large congenital, with pronounced hair growth, pigmented nevus with a predominant localization on the lower extremities “pigmented hairy nevus” .
• A blue nevus is a wide-based papule or plaque of varying shades of gray-blue color. Histologically, clusters of process melanocytes with a high pigment content are found in the dermis, located parallel to the epidermis, which determines the optical effect of blueness when incident rays of the visible spectrum “Jadassohn-Tische nevus”. • Intradermal nevus - a nevus with localization of nests of melanocytes in the dermis, and not at the border between the epidermis and dermis. • Ito nevus - pigmentation of the skin area innervated by the lateral branches of the supraclavicular nerve and the lateral cutaneous nerve of the shoulder; nevus cells lying randomly in the dermis.
• Strawberry nevus - a small vascular nevus similar in size, shape and color to strawberries - a bright red solitary formation of spongy density. It is observed in 3% of newborns and often spontaneously obliterates by 6-7 years of age. « cavernous hemangioma « cavernoma « cavernous hemangioma. • Unilateral nevus is a congenital linear nevus, which is located along the nerve either on one side of the body or on part of a limb also on one side linear nevus. • Ota nevus (oculodermal melanosis) - skin pigmentation in the area of innervation of the trigeminal nerve and conjunctiva of the eye in the form of bluish-gray spots; occurs in Asia, more often in women. The treatment is cosmetic. • Nevus dark blue orbital-maxillary .
• Borderline nevus - a nevus consisting of nests of nevus cells near the basal layer, the border of the epidermis and dermis, appears as a small, slightly raised, flat, non-hairy, pigmented (dark brown or black) tumor epidermal nevus. • Acquired nevus is a melanocytic nevus that is not detected at first after birth, but appears in childhood or in adults. • Flaming nevus ( port wine stain) is a large, vascularized nevus with a purple coloration, usually located on the head and neck. Unlike other vascular nevi, in this case there is no proliferation of a large number of vascular elements, but an expansion of the normal number of skin vessels. As the size of the vessels progresses, protrusion appears and the color of the nevus changes from pink to purple-red. See also Sturge-Weber syndrome in the appendix to this article. • Sebaceous nevus (Jadassohn) - congenital hyperplasia of the sebaceous glands with papillary acanthosis of the epidermis. • With thick curly hair, nevi are congenital foci of growth of spirally twisted hair in the scalp “limited [symmetrical] allotrichia.
• Atypical nevus syndrome (ICD-10: D22 Melanoform nevus; *155600, #155601 [mutation of the CDKN2A cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 2A gene, OMIM 600160.0001]) is an inherited disease (Â)) of pronounced familial nature. Prevalence: in the USA up to 5% of the general population; in the late 90s, about 40 thousand familial cases and 4.6 million sporadic forms were registered. Synonym: dysplastic melanocytic nevus •• Clinical picture. Usually spotted elements, but there are papular, plaque-like elements with a central papule or micropapules, oval or irregular in shape, sometimes with processes, 5 mm in size or more, with a finely scalloped clear outline, of varying intensity of brown color (up to black), with an erythematous rim along the periphery •• Pathohistology. There are no generally accepted criteria for diagnosing dysplastic nevus. The architecture of a dysplastic nevus suggests uneven hyperplasia of the epidermal processes with hypertrophy of the terminal sections. Melanocyte cells of adjacent processes are often connected. Among epidermal melanocytes, a spectrum of cytological changes is observed: from moderate pleomorphism to obvious atypia. The pronounced degree of the latter can be interpreted as melanoma in situ. • Red-blue vesicular nevus syndrome (*112200, Â)). Blistering hemangiomas of the skin, especially the trunk and upper extremities, night pain, regional hyperhidrosis, bleeding gastrointestinal hemangiomas, angiomatous gigantism, cerebellar medulloblastoma.
• Mucosal spongy white nevus is a congenital keratosis of the mucous membranes, manifested by a thickened white spongy fold of the oral mucosa. • Vascular nevus - congenital uneven red coloring of the skin due to the proliferation of skin capillaries “vascular nevus” hemangioma. • Spitz nevus is a benign juvenile melanoma (see below Juvenile nevus). • Elastic Levandowski nevus - clusters of smooth or bumpy papules of ivory or flesh color, found symmetrically on the trunk and limbs “collagenous nevus”.
• Juvenile nevus •• Spindle cell and/or epithelioid cell nevus (juvenile melanoma, benign juvenile melanoma, Spitz nevus) is a benign melanocytic nevus, usually acquired, having a characteristic histological structure different from other types of melanocytic nevi. Initially it was believed that it occurs mainly in children, but it has now been shown that juvenile nevus is more common (up to 60%) in adults •• Clinical picture. Usually the exophytic formation is hemispherical, less often flat; dense elastic consistency, with clear boundaries; color - from light red to dark brown, sometimes black; the surface is smooth or papillomatous •• Pathohistology. According to its architectonics, a nevus can be borderline, mixed (most often), intradermal. According to the cellular composition, it can be spindle-shaped, epithelioid cellular, and more often mixed. The pigment content in melanocytes is variable. Characteristic is the presence of eosinophilic accumulations - fragments of the basement membrane (the so-called Camino bodies). Spindle-shaped melanocytes are elongated with an elongated nucleus and a large eosinophilic nucleolus. In the epidermis, melanocytes have long cytoplasmic processes and form large elliptical nests, the long axis of which is usually perpendicular to the skin surface. In the dermis, spindle cells are often located parallel to each other in the form of bundles or cords. Polygonal or round epithelioid cells with abundant fine-grained, reticulate or vacuolated cytoplasm. Giant multinucleated cells are often found.
Treatment is indicated for dysplastic, nodular and giant pigmented nevi due to their possible malignancy • Indications for excision of any pigmented formation •• Change in color, size, shape and consistency •• Pain syndrome •• Regional lymphadenopathy • Further therapy after excisional biopsy of a healthy area skin are prescribed based on the results of histological examination and localization of the formation.
ICD-10 • D22 Melanoform nevus • I78.1 Non-tumor nevus • Q82.5 Congenital non-tumor nevus
Application. Sturge-Weber syndrome (185300) is classified as phakomatoses, characterized by a triad: congenital cutaneous angioma (flaming nevus), usually along the trigeminal nerve, often unilateral; homolateral meningeal angioma with calcification and neurological signs; angiomas of the choroid, often with secondary glaucoma; in incomplete forms, any two or more signs are possible, sometimes with angiomas of a different localization “encephalotrigeminal angiomatosis” Sturge-Weber disease “nevoid amentia.”
Symptoms of nevi
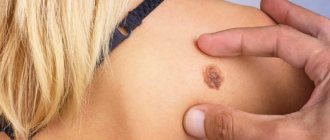
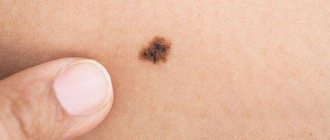
Nevi look like spots or nodules on the skin. Some of them are barely noticeable, others have a rich brown (melanocytic or pigmented) or red (vascular nevi) color.
As a rule, nevi do not cause any discomfort and are not felt.
Nevi can change their appearance and increase throughout life. It is important to correctly assess these changes; such manifestations can not only be a variant of the norm, but also serve as one of the signs of malignant skin formations.
What to do with huge nevi
We are accustomed to the fact that most moles are small formations and are almost invisible on the skin. Giant nevi do not live up to expectations.
As the name suggests, they are very large - with a diameter of 20 cm. Such moles cover a significant part of the arms, legs and face.
Congenital nevi of this type grow in people of any race - they spoil the lives of 2% of the world's population. But it is not their size that is dangerous.
A giant mole is likely to degenerate into melanoma, especially when the nevus grows near the spinal column.
The surface of the new growth is rough, and its color is gray, brown or black. Gradually the nevus grows. The skin on it thickens, and pigmentation intensifies. Very often, hair grows in certain areas of the mole.
The neoplasm looks especially terrifying after the birth of a child - on a tiny body it looks simply gigantic. The baby grows faster than the nevus. Therefore, the mole appears to shrink over time, but in fact it continues to grow.
In 30% of cases, a giant nevus degenerates into melanoma. Transforms at any age. Some people face this threat in their youth, others live with it into old age. It is noteworthy that large moles do not disappear even in old people.
When reborn they:
- Are increasing
- Change colors and shapes
- Bleeding
- Covered with a crust
Doctors recommend removing these nevi. Usually a surgical operation is performed - the doctor cuts off the mole with a scalpel. This method is not always available if the tumor is located in a complex location or for other reasons.
Instead it is assigned:
- Curettage
- Dermabrasion
- Ablative laser therapy
These procedures do not completely remove the nevus, but eliminate its external imperfections: hair, strong pigmentation.
Large moles on the face are especially difficult to deal with.
Stages of changes in nevi
Melanocytic nevi , both acquired and congenital, are characterized by staged changes throughout life. The classic path of development includes 3 stages, which differ in the depth of the formation:
- a simple nevus or borderline nevus is a superficial flat brown spot;
- a complex or combined nevus is located deeper and looks like a brown spot or raised formation on the skin;
- An intradermal nevus is a light-colored, raised formation located deep in the skin.
How they appear
Moles are divided into congenital and acquired.
Congenital nevi
This species represents a defect of embryonic development. Because of it, the transition of melanoblast cells into the skin is disrupted. Nevi appear due to the accumulation of these cells.
Moles appear in the first years of a person’s life.
Small-diameter nevi almost never degenerate. In larger ones, this process is most likely, so if there are such nevi, you need to be constantly monitored by specialists. It is forbidden to irradiate these nevi under ultraviolet light, and, if possible, it is better to remove them in a timely manner.
Acquired nevi
Nevi form in new places on the skin, changing contours, relief, and color. It is necessary to monitor these processes and have follow-up examinations with a doctor.
The appearance of moles can be genetic and can be passed on from parents to children.
Often moles begin to appear due to changes in the endocrine system associated with pregnancy or teenage changes. Also, the number of moles increases due to excessive exposure of the skin to sunlight, so excessive exposure to solariums and sunbathing negatively affects health.
By adolescence, the number of nevi increases, but by old age it decreases.
Treatment of nevi
In most cases, no treatment is required, only observation is required, since nevi are benign formations. If a malignant nature is suspected and formations with a high risk of malignant transformation are identified, surgical excision is performed. It is possible to remove the nevus at the request of the patient for aesthetic reasons or because of discomfort (for example, when localized in areas of frequent trauma by clothing).
Features of the treatment method
Surgical excision of the nevus is optimal. This method allows for radical removal with a scalpel followed by suturing of the wound surface. In some cases, when nevi protrude above the surface of the skin, a radio knife, electric knife or laser knife can be used. In all cases of surgical treatment of melanocytic nevi, it is necessary to conduct a histological examination of the removed tissue.
Diagnostics
The set of diagnostic measures includes:
- Examination by a dermatologist/oncologist.
- Dermatoscopy is a microscopic examination.
- Ultrasound of the neoplasm - to assess the depth of nevus growth into the layers of the skin.
Reference! A biopsy of a “living” mole is not performed, since as a result of this procedure the nevus is injured, and mechanical damage can provoke degeneration into melanoma. Therefore, histological examination is carried out after removal of the tumor.
How are nevi treated in the Rassvet blade?
The doctor will examine the patient's skin completely to eliminate the risk of missing melanoma or other skin cancer. Suspicious formations are further studied using a device that allows you to examine the skin with 10 times magnification - a dermatoscope. The patient's chart describes nevi that require observation. The doctor will suggest surgical removal of suspicious nevi, followed by histological examination of the removed material (sent to an expert laboratory). Removal of nevi for aesthetic reasons can be performed at the request of the patient.
Recommendations of a dermatologist for patients with nevi:
- avoid excessive ultraviolet irradiation of the skin (tanning, sunbathing, solariums, ultraviolet drying of manicure and pedicure coatings); when staying outdoors for a long time, use a broad-spectrum photoprotective cream with SPF 30 or higher, clothing that covers the skin, a hat and glasses with an ultraviolet filter;
- try not to injure nevi when shaving, combing, changing clothes;
- undergo an annual preventive examination of nevi with a doctor;
- independently examine nevi according to the ABCDE rule;
- if there are a large number of nevi (50-100 or more), especially in combination with the presence of risk factors (sunburn, visits to a solarium, melanoma and skin cancer previously identified or in close relatives, the presence of atypical nevi), undergo a digital skin mapping procedure.
Author:
Kuzmina Tatyana Sergeevna dermatologist, Ph.D.
Out of sight, out of sight. How to get rid of moles
Not an easy question. Many factors influence the ability to remove tumors. Unfortunately, no pills have yet been invented that will relieve you of annoying or dangerous moles.
Yes, treatment of small nevi usually does not cause problems.
Successful removal depends on:
- Doctor's qualifications
- Mole size
- Nevus locations
The first option is surgery. The doctor cuts off the mole, some adjacent skin, and then stitches the wound. After removal, the nevus heals quite quickly, but a noticeable mark remains.
Whether this is good is up to you to decide.
What about laser surgery?
Yes, modern technologies do offer new treatments, but they do not work miracles, as some people believe. Some skin diseases are treated with lasers. But not all nevi.
The laser beam vaporizes the outer layer of skin and cells of the mole. The deeper it is rooted, the more difficult it is to destroy it completely - sometimes the surface layer is burned out, but the base remains intact. Then the nevus grows back.
The operation has to be repeated again and again, and there is no guarantee of results. So the surgical procedure is sometimes more reliable than laser surgery.
However, in some situations, a high-tech procedure accomplishes the task. Removes small nevi. Working with large tumors is much more difficult.
We recommend choosing laser nevus removal only after consulting a dermatologist and checking the tumor.
Another important point is the choice of doctor. Many doctors have accumulated vast experience in removing small moles. Everyone has them. Therefore, doctors work with them very often and know well how to quickly remove nevi.
But what about large moles?
They are not common and therefore it is difficult to find a doctor who regularly operates on them. Read reviews about nevus removal on the websites of different clinics. This is useful. You will learn what operations the doctors of these medical institutions performed and the patients’ impressions of their work.
Gather more information.
When you see your dermatologist, ask about available methods for removing moles. Perhaps in your case, surgery and laser therapy are not the best options. Harmless nevi do not need to be removed at all.
Many medical institutions remove moles. But where to go? We would like to recommend one of these clinics.
Dysplastic nevus syndrome
Unfortunately, there is a syndrome that in Russian literature is often called nevus dysplastic syndrome (in foreign literature - FAMMM).
This disease has 2 diagnostic criteria
- the number of dysplastic nevi on the skin is more than 50
- melanoma in relatives
This disease may be associated with a mutation in the CDKN2A gene, which also increases the risk of developing pancreatic cancer
With this syndrome, the risk of developing melanoma, according to different authors, varies from 56 to 100%. The disease requires regular (once every few months) monitoring by an oncologist.
Methods for removing pigmented nevi
- Small nevi are removed using a laser. Local anesthesia is used here and many small nevi can be removed at once in one visit. A crust appears at the site of removal, which will disappear in seven days. The marks are practically invisible, which is why the laser method is used to remove facial moles.
- For large nevi, surgical excision is used. The operation is performed under local or general anesthesia with suturing.
The decision on the treatment method is made as a result of examining the nevus. In some cases, consultation with an oncologist is required. When surgical excision is used, the tumor is sent for histology to determine whether it is melanoma.
You should never remove moles and birthmarks yourself. This is fraught with infection and other troubles.
Conventionally, pigmented nevi can be divided into four categories according to their size:
- small (up to 1.5 cm)
- medium (up to 10 cm)
- large (up to 20 cm)
- giant (more than 20 cm)
Multiple pigmented nevi are quite rare (5%). This nevus consists of a large lesion and small pigment spots and affects the lower body, limbs, back and chest.
Alarm Signals
For those with a small congenital nevus, the risk of it degenerating into melanoma is approximately 5%. And the transformation of a giant nevus into melanoma occurs in 40%.
Mechanical damage - picking, scratching, as well as radiation - sunbathing in direct sunlight and going to a solarium are very dangerous and undesirable.
You should be wary if:
- the pigment spot has increased in height or width
- the mole has lost its clear outline
- the birthmark has changed its color, becoming more or less pronounced
- nodules and crusts appeared on the surface of the nevus, and it also began to bleed
- enlarged lymph nodes in the groin, armpits and neck
In what cases are pigmented nevi removed for preventive purposes?
- It is better to remove nevi in childhood before puberty
- if the mole is located where it can be accidentally torn off or damaged
- the size of the nevus is more than 1.5 cm
- mole color brown or black
A timely removed mole with the above signs will not allow the formation of a malignant tumor in this place.
Removal of pigmented nevi is one of the operations performed in the Diamed network of Moscow clinics. Doctors with extensive experience will be able to painlessly rid their patients of skin lesions. The procedure is carried out at the Diamed Shchelkovskaya and Diamed Maryina Roshcha clinics.
The selection of medications for the treatment of pigmented nevus is carried out only by a doctor and strictly on an individual basis, based on the type, age and characteristics of the patient’s body.