Signs of lichen in humans (photos), treatment and prevention
Ringworm is an infectious disease that affects human skin; When infected, nodular formations, inflammation and tissue necrosis occur. The etiology of lichen in humans is predominantly viral or fungal.
In most cases, the disease is contagious (with the exception of some of its varieties), and if untreated, it is dangerous for others. On the human body, lichen affects any area, but the rarest manifestations are on the neck, genitals, and mucous membranes.
In this article we will look at the main types of lichen in humans, the first signs and current methods of treatment at home. In order to more accurately diagnose the disease, the material contains photographs of lichen in the initial and advanced stages.
Classification
Ringworm is an unpleasant disease, but it can be completely cured. There are even some types of lichen that do not require treatment and go away on their own.
In 2021, the most common types of lichen in humans are (see photo):
- Pityriasis, it is also known as "colored" or "variegated".
- Pityriasis rosea or Gibert's disease.
- Ringworm (aka “hairworm” or trichophytosis).
- Lichen planus, affecting the skin, mucous membranes, and, less commonly, nails.
- Scaly, popularly known as psoriasis.
- Shingles, sometimes called herpes.
- Microsporia. A highly contagious form that is often confused with ringworm.
Each type is caused by a specific pathogen and is subject to strictly defined treatment. The consequence of untreated lichen can be permanently disfigured skin or lost hair.
Help from a dermatologist in Moscow
Diagnosis and treatment of pityriasis rosea is the field of activity of a dermatologist. Depending on the form of the disease and the extent of skin damage, the patient is provided with recommendations. With lichen, the emotional and psychological background of a person is important, so promptly making a correct diagnosis allows you to quickly overcome the disease.
You can make an appointment with a dermatologist at Meditsina JSC (academician Roitberg’s clinic) by phone. You should not self-medicate. The reason is that, according to external signs, skin rashes may turn out to be differential diseases, for example, toxicerma, psoriasis, mycosis, secondary syphilis. In these cases, it is necessary to prescribe another therapy, taking into account the specific clinical picture and medical history of the patient.
General recommendations
Most types of lichen are successfully treated. Visit a dermatologist. The choice of treatment method depends on:
- varieties;
- causes and provoking factors;
- contraindications;
- presence of concomitant diseases.
To combat skin infections, medications and traditional recipes are used. The duration of the course of therapy and the selection of medications are determined by the doctor.
Helpful Tips:
- limit the patient’s contact with family members;
- wash and iron bed and linen daily;
- select separate dishes;
- After caring for the patient, disinfect your hands with Citeal. Prepare the solution according to the instructions;
- Wash the floor daily with Alaminol or Alpinol.
Measures to prevent the disease
Since there can be many causes of lichen infection, it is impossible to completely exclude the possibility of the disease. However, compliance with preventive measures will reduce the risks. Prevention of lichen includes:
- timely treatment of acute respiratory diseases;
- compliance with hygiene procedures;
- taking a vitamin complex;
- increasing the level of immunity;
- use of shampoos with antifungal gels;
- hardening of the body;
- providing quality oral care, treatment of caries, gums and throat diseases;
- proper nutrition;
- avoiding contact with people infected with the fungus;
- vaccination of pets and periodic examinations at a veterinary clinic;
- giving up bad habits (smoking, alcoholism);
- preventing hypothermia of the body.
When diagnosing a chronic form of lichen, it is recommended to periodically visit a dermatologist’s office in order to identify possible foci of the disease.
Pityriasis rosea
Pityriasis rosea (pityriasis, Zhiber's lichen) is a common dermatological disease, the key symptom of which is the appearance of relatively large, scaly, pink spots on the patient's skin. According to statistics, people aged 19-40 years most often experience manifestations of this disease. In children under ten years of age, as well as in older people, Zhiber's lichen is extremely rare.
The exact causes of pityriasis have not yet been determined. Meanwhile, modern scientists believe that the pathology is of viral origin and is provoked by herpetic virus type 7 or 6. Some researchers have suggested that Zhiber's lichen is of an allergic nature, but this theory does not have clear evidence.
The first signs of pityriasis rosea in humans (see photo):
- Light brown or pink round or oval spots appear on the surface of the skin
- In the center of the spot the skin is dry and slightly peeling
- Over time, the spots grow and smaller pink lesions begin to appear on new areas of the skin
- The spots can be up to several centimeters in size
- Pityriasis rosea is accompanied by itchy skin
No treatment is required for typical pityriasis rosea. Only in case of severe itching, the doctor can prescribe antipruritic drugs (topically). But there are restrictions that make it possible to alleviate the course of the disease.
- During water procedures, you should not use hard washcloths or aggressive detergents.
- Contact of affected areas with hard, woolen or synthetic fabrics should be avoided.
- The use of cosmetics and perfume should be limited. It is strictly forbidden to apply them to affected areas.
- Do not use ointments, powders, etc. For unknown reasons, they cause the disease to progress, increasing the number of plaques that appear on the skin.
In 6-8 weeks the disease will pass. However, when scratching the “medallions”, a bacterial infection can join the lichen. In this case, the doctor may prescribe antibiotics.
What you need to know about diagnosis and treatment
Diagnosis of pityriasis rosea is based on taking the patient's medical history. To confirm or refute and analyze complex cases, a number of laboratory tests are prescribed. They include clinical examination of blood and urine. It is necessary to exclude syphilis and mycosis, therefore serological and microscopic studies are additionally carried out. If these methods do not provide enough information to verify the diagnosis, the patient is referred for a biopsy (biopsy histology).
Treatment for pityriasis rosea is not always required. The disease is prone to voluntary self-healing within 5 weeks. However, dermatosis should not be considered harmless. First of all, antipruritic therapy is required. For this purpose, topical glucocorticosteroid drugs and antihistamines are used externally. Ointments, gels, pastes cannot be used without a dermatologist's prescription. Otherwise, the rash may increase the extent of skin damage, covering new areas. Antibiotics and antiviral drugs may be prescribed depending on the indications. Ultraviolet therapy has a good effect.
Ringworm (microsporia and trichophytosis)
Ringworm most often affects children. Localized on the scalp, on the skin of the face, neck, shoulders. Infection occurs through close contact with a sick animal or person (using the same comb or hat).
- Trichophytosis is a spot in the form of a red or pink ring with peeling. The hair darkens to black and breaks off above the skin because its root is affected. Children from their grandmothers often get sick. You can also get infected from animals.
- With microsporia, a pink spot appears on the skin, with clear edges and peeling. The hair is broken off above the skin at a level of 4-5 mm. Most often, infection occurs from cats and dogs, but infection is also possible from people.
The first signs of ringworm in humans (see photo):
- First, swelling appears - one pink, red spot on the hairline with clear boundaries
- Then the swelling increases and crusts and blisters appear around the edges
- In the center of the spot, the skin begins to peel off, the scales have a whitish color
- The existing hair on the lesion breaks off from the root by 4-5 mm. or thinning out
- The disease is initially asymptomatic, is not recognized immediately, and over time manifests itself as itching at the site of the lesion.
- If lichen occurs on hairless skin, it looks like pale pink spots with a roller-like edge around the edges.
Before starting treatment, the doctor performs tests to determine which pathogen is causing the disease. Then complex treatment is carried out. It combines the effects of ointments, shampoos, tablets, and other antifungal agents.
Treatment can proceed approximately according to this scheme.
- Local ointments, gels, creams or sprays such as Clotrimazole, Mycoseptin, Terbinafine.
- In the morning: treatment with iodine. In the evening: treatment with an ointment containing salicylic acid.
- Vidal's milk. It is prepared in the recipe department and includes six components aimed at combating fungus.
- Orally for 2-3 weeks: Griseofulvin. The doctor can replace this natural antifungal agent with a narrowly targeted action with other drugs that can fight the pathogens of ringworm Microsporum canis and Trichophyton tonsurans.
In parallel with antifungal drugs, a dermatologist can prescribe immunomodulators and vitamin complexes to boost immunity.
Shingles
The causative agent of shingles is the herpes virus. Herpes zoster is localized mainly in the intercostal space, along the intercostal nerves, and can also occur in other parts of the body where large nerve trunks pass.
The first signs of shingles in humans (see photo):
- Pain and itching in the rib area, most often on one side of the chest
- Over time, small bubbles with clear liquid inside form on the affected area
- After a few days, the bubbles empty, forming a small crust
- The most distinctive symptom of shingles is severe pain, as the virus attacks the intercostal and other nerves.
- A dangerous form of shingles is ocular, since without timely and effective treatment you can lose your vision
How to treat? At home, treatment for shingles is aimed at relieving painful symptoms.
- In the first three days from the onset of illness, the antiviral Acyclovir is prescribed. It is not effective for later calls.
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed to reduce pain. It could be Meloxicam, etc. drugs.
- To relieve itching, antiallergic drugs are prescribed.
- To relieve general intoxication - droppers and diuretics.
- The affected areas are treated with brilliant green, ointments with acyclovir, etc.
Sometimes shingles affects the nervous system, causing sleep disturbances, anxiety, and neuroses. To eliminate these symptoms, the doctor has the right to prescribe mild sedatives or hypnotics, antidepressants.
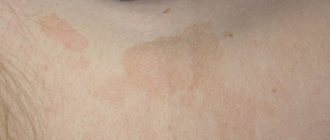
Pityriasis versicolor
Pityriasis versicolor (varicolored) is usually called a chronic disease of the stratum corneum of the epidermis, accompanied by the appearance on the patient’s skin of flaky pigmented spots of pink, brown, yellow and brown shades. According to statistics, most often young people aged 25-35 experience manifestations of this disease. And, on the contrary, lichen versicolor is least often detected in children under seven years of age.
The causative agent of the disease is a yeast-like fungus that can exist in three forms that transform into each other:
- Pityrosporum ovale;
- Pityrosporum obriculare;
- Malassezia furfur.
The first signs of pityriasis versicolor in humans (see photo):
- Spots of various shapes and sizes are formed. Most often, the lesions are large, oval or round in shape; if the spots are small, they merge and form large lesions with curved edges
- On tanned skin, spots appear discolored
- In winter, pink and brown lesions stand out and become darker than natural areas of the skin
- Pityriasis versicolor is a protracted disease that lasts for years.
- Over time, the color of the affected areas changes from greenish to brownish
- The skin with lichen versicolor peels off a little.
How to treat? In most cases, topical medications are prescribed for treatment. It can be:
- Antifungal ointments or sprays: Ketoconazole, Mycozolon, etc.
- Lotions, soaps and shampoos containing salicylic acid: Nizoral, Sulsena, etc.
- For severe lesions, the doctor may prescribe antifungal medications (for example, Fluconazole) by mouth.
Interestingly, folk remedies are often used in the treatment of pityriasis versicolor.
- Infuse in a bathhouse a mixture consisting of 3 tablespoons of eucalyptus and the same amount of string, poured with 800 g of boiling water. Use for ablutions, baths, compresses.
- Wipe stains with freshly squeezed onion juice three to four times a day.
During treatment, it is imperative to carry out work to disinfect or completely destroy objects with which the sick person has been in contact.
- Discard the washcloth, heel graters, brushes and nail files.
- Boil all laundry.
- Wash clothes in chlorine-containing solutions.
- Treat the room with the same solutions.
It is important to know: even with timely and qualified treatment, lichen can recur if preventive measures are not followed.
What consequences can lichen cause?
The most common and harmless type of lichen is pink. The course of the disease passes without complications.
Shingles can cause the following complications:
- inflammatory process in the membrane of the spinal cord and brain;
- partial or complete loss of vision;
- dysfunction of the musculoskeletal system;
- viruses that infect the respiratory organs and liver;
- postherpetic neuralgia.
Ringworm and versicolor often provoke the appearance of a secondary infection, which complicates the treatment process. In most cases, antibiotics are necessary. In addition, trichophytosis often leaves bald patches at the site of the fungal infection, which can remain forever.
A flat red fungus contributes to the manifestation of bacterial infections and the development of an inflammatory process in the patient’s oral cavity.
More often than others, the following categories of patients suffer from various types of lichen:
- pregnant and lactating women;
- people who do not care about their health and do not observe personal hygiene rules;
- children;
- pet owners;
- people with a low level of protective properties of the body.
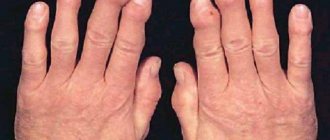
Lichen planus
Lichen planus is a chronic dermatosis that affects the skin, nails and mucous epithelium of the human body. According to statistics, representatives of different age groups are equally susceptible to infection, but women experience manifestations of this disease much more often than men.
The exact mechanism and causes of lichen planus have not yet been elucidated. Researchers believe that its development is based on a wide variety of disturbances in metabolic and immune processes that provoke an inadequate tissue reaction.
The first signs of lichen planus in humans (see photo):
- A large number of flat red and purple nodules appear on the skin
- On the mucous membranes there are pale pink nodules
- On the nails – destruction of the nail plates, crumbling of the nails
- On the oral cavity, genitals - flat gray or pink tubercles appear on the mucous membranes
- Lichen planus is accompanied by severe skin itching
- The appearance of new tubercles occurs in places of scratches and scratches
- Lichen planus can occur in the form of: rashes in the form of rings - annular, erythematous - in the form of soft red tubercles, warty - tubercles with an uneven surface in the form of warts, erosive-ulcerative - the appearance of ulcers and erosions in the affected areas.
In the absence of pronounced symptoms, the disease does not require treatment and disappears on its own. If it is accompanied by severe itching, then antihistamines are prescribed: Suprastin, Diphenhydramine, Loratadine. It is also necessary to take immunostimulants and vitamins.
During lichen planus, it is necessary to lead a healthy lifestyle, and if the rash is located in the mouth, pay special attention to nutrition.
What does lichen look like in humans?
The external manifestation of the pathology is obvious - lichen is accompanied by a number of signs:
- rash in the form of spots of different colors - red, pink, brownish, yellow;
- itching, burning, unpleasant (painful) sensations;
- scales, bubble formations on spots;
- bald spots on the head in the hairline area (clipping form);
- fever (rare);
- malaise, lethargy.
Lichen squamosus (psoriasis)
Squamous lichen can be located on the torso, extensor surfaces of the arms and legs, on the scalp, on the palms, and on the face.
The first signs of scaly lichen in humans (see photo):
- A specific rash appears on the skin, which is flaky, rounded bumps of pinkish-red color that rise above the surface;
- If you scrape, the whitish-gray scales crumble, revealing a shiny, wet, red surface underneath. If you scrape it too, pinpoint bleeding occurs;
- The tubercles grow and form plaques up to several centimeters in diameter, then merge into solid areas with uneven edges;
- Most often, they begin to dissolve from the middle, forming a garland on the skin. And in the place where the rash disappeared, an area with disturbed pigmentation forms;
- The disease is accompanied by severe itching.
Today, more than 20 methods have been developed for the treatment of scaly lichen, none of which can guarantee a quick and complete cure. Treatment depends on the phase of the disease and the location of the lesions.
- At the first stage, injections of vitamins, sensitizers or histamines are practiced.
- At the same time, corticosteroids and sedatives are prescribed.
- At the stationary stage, injections of staphylococcal antitoxins, autohemotherapy, and ultraviolet radiation are often recommended.
- Severe forms can be cured with plasmapheresis and cytostatics.
Currently, specialists have learned to use various techniques to alleviate the patient’s condition, keeping the disease in a stationary stage.
Prevention
How to protect yourself from a contagious disease:
- Monitor the course of diseases associated with the functioning of the endocrine system;
- Do not touch stray cats and dogs;
- Strengthen your immune system;
- Keep your hands and skin clean;
- Eat right;
- Be less nervous;
- Along with antibiotics, take medications to protect the intestinal microflora;
- Always wash your hands with soap after returning from public places;
- Wear protective gloves when working in your garden.
Now you know how to treat lichen. Do not use medications and traditional recipes without a doctor’s recommendation. Use the whole range of methods - the disease will recede.
Medications
In addition to ointments, the use of other dosage forms of drugs can speed up recovery. The following groups of medications are usually prescribed:
- Antimicrobial. These include antibiotics and antimycotics. A course of taking one of the drugs helps get rid of pathogenic microorganisms and prevent the appearance of new rashes. Tetracycline and Metacycline are often prescribed.
- Antiviral . They not only kill the virus, but also have a beneficial effect on the skin: healing, soothing.
- Anti-inflammatory . Just like ointments, anti-inflammatory drugs for psoriasis for internal use can be hormonal or non-hormonal. Metipred and Prednisolone tablets are often prescribed.
- Vitamins . These can be entire complexes consisting of vitamins A, B1, B6, C. An excellent solution would be to use the colloidal drug Imun Support. It is designed to protect the body from infections, rapid recovery from many diseases, and neutralize the side effects of drug therapy. The drug Imun Support is an immunomodulator, maintains the immune system in harmony and balance..
Thus, lichen is not a disease that you can get rid of in a couple of days. To eliminate skin rashes as quickly as possible, complex therapy is required, which consists of products for external and internal use; many successfully use folk recipes for this.