Main manifestations of wounds
Pain
In this case, pain occurs due to damage to the nerve endings that were located at the site of the injury. Over time, swelling may increase, which also leads to increased pain. The severity and degree of manifestation of pain depends on factors such as:
- location of the defect, concomitant damage to large nerve trunks;
- type of weapon or conditions of damage (asphalt, garden, bicycle, sharp object, etc.);
- psychological state of the child.
In essence, pain is an adaptive defense reaction of the body.
Bleeding
Any damage to the skin or mucous membranes is in one way or another accompanied by damage to blood vessels (capillaries, arteries, veins). The nature and degree of bleeding depends on the type of damaged vessel. The larger the vessel and the higher the pressure in it, the more massive the bleeding, and vice versa. It is worth highlighting those places on the body that are accompanied by more heavy bleeding: face, head, neck, hands . In these places, the tissues are better supplied with blood. The condition of the blood coagulation system plays an important role. If a child has a minor abrasion or scratch, which is accompanied by prolonged and heavy bleeding, then it is necessary to consult a pediatrician and pediatric hematologist in order to exclude a disease of the blood coagulation system. This may also be indicated by the appearance of a large number of bruises for no reason.
If a small abrasion is accompanied by prolonged and heavy bleeding, then it is necessary to consult a hematologist.
Hiatus
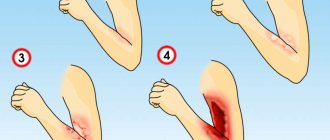
This phenomenon is associated with a reduction in the elastic fibers of the skin. As a result, the skin edges of the lesion diverge. Many surgeons know what Langer's lines are. They indicate the course and direction of the fibrous structures of the skin. For this purpose, incisions are made along these lines, which leads to rapid healing of the incisions and reduction of gaping. Accordingly, when a defect appears perpendicular to these lines, a wide divergence of the edges of the defect develops.
How to cure a chronic wound?
But what to do if prevention does not help? Treatment of long-term non-healing wounds depends on their type, the condition of the patient and the underlying disease. The main thing is to identify the root cause of the resulting pathologies in order to prevent the condition from worsening.
Treatment of diabetic foot syndrome:
- Taking antibiotics prescribed by a doctor against infection, treating and cleaning wounds by the doctor himself.
- Quitting bad habits and reducing the load on the foot.
- Selection of shoes and socks on the recommendation of a doctor, changing them regularly.
- Continue therapy at home: clean the wound, monitor discharge, and protect it from infection.
Treatment of trophic ulcers:
- Conservative therapy - taking medications to eliminate the symptoms of trophic lesions: antibiotics, phlebotonics, antiplatelet agents, as well as ointments for treating the skin (Solcoseryl, Actoverig, Tocopherol).
- Treatment of affected tissues with an ointment containing an antiseptic, an anesthetic or enzymes that accelerate healing (Levomekol, Levosin, Curiosin). Used with compresses.
- Surgery – after the ulcers have healed, the doctor restores blood flow through shunting and phlebectomy.
Treatment of bedsores:
- Restoring blood circulation using anti-decubitus circles, anti-decubitus mattresses, pillows.
- Cleansing the damaged area of necrotic tissue. If necessary, the doctor prescribes antibiotics to prevent infection. Surgical removal of necrotic masses is also possible.
- Procedures for healing bedsores include regular dressings with the use of wound-healing drugs.
Types of wounds
They can be:
- Operating: applied deliberately for the purpose of performing an operation.
- Accidental: as a rule, these are household damages.
Depending on the nature and conditions of the damage, wounds are distinguished:
- chopped;
- I stab;
- bruised;
- torn;
- crushed;
- chopped;
- bitten;
- mixed;
- firearms.
In children , cut, puncture, bitten, mixed, and also superficial (abrasions, scratches, etc.) predominate. Particular attention is paid to bites that result from an animal or human bite (for example, another child), as they are the most infected. This is due to the large number of harmful bacteria in the oral cavity. They are most often complicated by infection.
According to the degree of infection there are:
- Freshly infected. As a rule, this damage occurs within 3 days from the date of its application. Defects with soil contamination are especially infected.
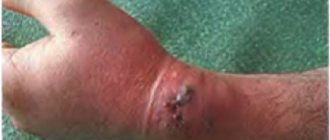
- Purulent. An infectious process develops in these lesions. Microbes, when multiplying, lead to increased inflammation, necrosis, and also contribute to the appearance of pus. Children with purulent manifestations develop symptoms of general intoxication: nausea, headache, dizziness, weakness, lethargy.
10 best ointments for purulent wounds: Syntomycin ointment
Syntomycin liniment is a thick gelatinous composition. The composition of the drug is not an ointment.
- Helps stop the inflammatory process, relieve swelling;
- it is used for burns of varying sizes and severity;
- supports the regeneration of infected wounds, cuts and burns, frostbite associated with infection.
If the ointment is applied to large areas of the body, drinking alcohol may cause tachycardia, cardiac arrhythmia and seizures.
Synthomycin ointment is often used for burns of varying severity and severity.
Gauze turundas soaked with synthomycin are placed in the fistulas. Tampons with the drug for therapeutic effects are injected into the purulent cavity of the wound.
The frequency of treatment and how often the ointment is used depends on the severity of the dermatitis and the concentration of the drug itself.
The average price in pharmacies is 75 rubles.
Wound healing and factors influencing this process
The wound healing process can be disrupted by many factors.
Healing is the process of repairing damaged tissue and restoring its integrity. During the healing process, certain processes occur. We will not dwell on them in more detail, but will only indicate those factors that may disrupt the healing process:
- Age. As a rule, this applies more to older people. The child's body has great regenerative capabilities. This is due to the high level of anabolic (construction) processes in the body.
- Attachment of infection.
- Decreased immunity.
- Poor circulation in the wound area.
- Chronic diseases (diseases of the respiratory and cardiovascular systems, diabetes, tumors and others).
Healing complications
- Attachment of infection . Most often, a nonspecific purulent infection develops. The threat is tetanus, rabies, diphtheria. Therefore, injuries that have been bitten and contaminated with soil or old metal objects should be immediately examined by a surgeon with a number of preventive measures taken (administration of anti-tetanus serum, rabies vaccine).
- Bleeding.
- Divergence of defect edges.
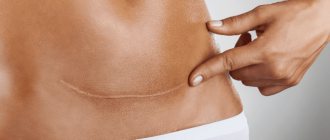
- In some cases, healing may be complicated by a hypertrophic scar or keloid . They are an abnormal scar that can spread beyond the defect area and also contribute to the development of complications.
Wound healing
A wound is a violation of tissue integrity due to mechanical stress (cuts, abrasions, bruises, bites). After damage, the body mobilizes forces to start the healing process. It can take different times depending on the characteristics of the wound and the ability of the tissue to regenerate. With infectious complications, the process may be delayed. You can stimulate the healing process of wounds and reduce the risk of infection with the help of special preparations, for example, cream for external use Argosulfan®.
Stages of wound healing
The wound healing process consists of several stages:
- Inflammation is a typical local reaction of the body to tissue damage and encounters with foreign substances. Blood flow to the wound site increases, leukocytes produce substances that trigger the inflammatory process necessary to cleanse the wound. As a result, its characteristic symptoms appear: redness and swelling. To control the situation, the adrenal glands begin to intensively produce corticosteroids and adrenaline, which have anti-inflammatory activity. This stage takes on average 4 days;
- Regeneration (direct healing) is the next stage, it usually lasts from the 4th to the 10th day. The body produces substances that stimulate cell division and metabolic processes in them, due to which young tissue (granulations) is formed at the site of damage, filling the wound;
- Scarring and epithelization are the final stage of wound healing, lasting from several weeks to several months. The wound is healed with young connective tissue, blood vessels and nerves grow inside it, blood circulation and innervation are restored, and a layer of epithelium is formed on the surface. There is always a trace of damage left on the skin, a scar or scar, the size and shape of which depends on the characteristics of the wound. The longer healing continues, the more connective tissue is formed in the wound, forming a scar.
The duration of each stage may vary, depending on the body's ability to regenerate and the characteristics of the wound itself.
Types of wound healing
There are three types of wound healing:
- Primary is possible only for wounds with smooth edges that are in close contact with each other. They should be free of germs, dirt, hemorrhages, and dead tissue. These are only postoperative wounds and those treated by a surgeon on the first day after their application. They heal with the formation of thin, barely noticeable scars;
- Secondary healing occurs if primary healing is not possible. Uneven or non-viable wound edges, gaping, and infection cause suppuration. Only after cleansing the wound and completing the purulent inflammation does it heal with the formation of a scar, sometimes rough;
- Healing under the scab is typical for superficial wounds. A scab is a crust formed from dried blood, lymph and intercellular fluid, released onto the surface of the wound when the skin is damaged. The scab protects the wound from infection and mechanical damage, and underneath it the wound heals quickly. There is no need to remove the crust unless there is suppuration underneath it - if events progress well, it will go away on its own.
Factors influencing the wound healing process
Reasons that slow down wound healing related to the condition of the whole organism:
- Age: the ability to regenerate tissue in older people is extremely low, so their wounds take longer to heal than in middle-aged patients and, even more so, in children;
- state of immunity: with congenital or acquired deficiency of the immune system, the body’s defenses are reduced, it takes more time to cope with foreign agents. The inflammatory stage is prolonged, infectious complications often develop, further increasing the duration of healing;
- Chronic diseases: with long-term illnesses, the body spends a lot of energy fighting them, so there are simply no resources left for healing wounds;
- Diabetes mellitus: glucose, which is too much in the blood during this disease, damages blood vessels, disrupting blood supply, tissue trophism and their ability to regenerate;
- Poor nutrition: If the body does not receive enough nutrients, wounds take longer to heal. First of all, this concerns proteins - they form substances involved in inflammation and new cells that restore tissue integrity.
Local causes affecting wound healing:
- Significant contamination of the wound and foreign bodies in it increase the duration of the inflammatory stage;
- Lack of primary wound treatment is the main cause of infectious complications;
- The location of the wound at the bend site, constant movements of its edges make regeneration and epithelization difficult
Basic rules for treating wounds
If the wound is properly treated immediately, the risk of infectious complications is significantly reduced, which means healing will take less time. It is important to remove dirt and foreign objects (splinters, rust, glass) from the wound surface, and then rinse it with antiseptic agents. After this, you can apply a bandage with an antibacterial agent.
Only superficial wounds can be treated on your own; in other cases, you need to consult a surgeon. To speed up wound healing, after treatment, local agents are used that stimulate cell division and prevent the development of infectious complications. An example of a drug that meets all these requirements is Argosulfan® cream for external use.
Argosulfan® for wound treatment
Argosulfan® cream is a local antibacterial drug with regenerating and antimicrobial properties. Its main component is silver sulfathiazole, which has a wide spectrum of antibacterial action against gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. It dissolves slowly, due to which the concentration of active substances on the surface of the wound remains high for a long time.
Upon contact with skin, silver sulfathiazole breaks down into sulfathiazole and silver ions, both components fight microbes. Sulfathiazole prevents their growth and reproduction, and silver destroys them by destroying the shells. These substances stimulate tissue regeneration, wound healing, and reduce the risk of severe scar formation*.
Argosulfan® can be used to treat both dry, contracted and weeping purulent wounds. It can be applied openly or under a bandage: 2-3 times a day in a thick layer (2-3 mm). By keeping the surface of the wound moisturized, the cream makes dressings less painful. It is recommended to use the drug until the wound is completely healed, but not longer than 60 days.
Advertisement RUS-DRM-ARG-NON-08-2018-1265
* E.I. Tretkova, Complex treatment of long-term non-healing wounds of various etiologies, Clinical Dermatology and Venereology, 3 2013
Products for treating wounds in children
Below we list the most popular and affordable means for treating superficial wounds in children:
- Iodine. Suitable for superficial abrasions, but not for deeper injuries.
- Diamond green.
- Hydrogen peroxide. It is the drug of choice for first aid in the treatment of superficial abrasions in children. Allows you to clean abrasions and scratches well. An equally important property is stopping bleeding.
- Furacilin. To prepare a solution for topical use, dissolve the tablet in water.
- Miramistin. It is also an antiseptic for topical use. Allows you to prevent suppuration. If a purulent process occurs, it allows you to fight it. A pleasant bonus will be the possibility of using this remedy for acute respiratory viral infections, sore throats and pharyngitis in children.
- Chlorhexidine.
An antiseptic helps prevent suppuration.
To speed up healing, ointments and creams can be used such as:
- Levomekol;
- Betadine;
- Vishnevsky ointment;
- cream Bepanten plus.
Ichthyol ointment
A traditional remedy used in the treatment of purulent wounds is an active substance that has an anti-inflammatory and analgesic effect on the deep layers of soft tissue. It has a healing, keratostatic and antipruritic effect.
- Draws out pus from under the skin in all wounds and inflammations;
- suppresses inflammation and softens the upper layer of the epidermis;
- Used for purulent formations and inflammations;
- Used for skin infections;
- In the case of boils, it is used to accelerate the maturation of boils.
Ichthyol ointment is not used on open wounds.
When treating purulent wounds, they are covered with sterile gauze or a napkin, and the bandage is fixed with medical gauze. After 8-10 hours, the bandage is changed to a new one.
Ichthyol is effective in eliminating infection from the inflamed surface of the skin.
Pharmacists do not recommend using the ointment for children under 6 years of age. Allergic reactions to the dispersion are extremely rare.
In pharmacies the price starts from 64 rubles.
First aid for a child for superficial wounds
When such a situation arises, parents ask themselves: “How to treat the wound? How to properly treat a wound? What is the best remedy for treating a wound?
Before helping a child, parents need to wash their hands with soap and use an antiseptic. Next, in this sequence, you need to follow a number of instructions and actions:
- Assess the extent and nature of the damage. It is very important to understand whether the baby has a deep or superficial wound.
- Rinse and stop bleeding. Hydrogen peroxide is best suited for this purpose. You can also use a solution of furatsilin and chlorhexidine.
- Next, you can treat the skin with a drying antiseptic, for example, iodine solution or brilliant green.
- Apply an aseptic (clean) dressing.
- In the future, it is important to change the dressings regularly. It is also possible to use ointments and creams discussed earlier, which will speed up the healing process.
In case of deeper defects, heavy bleeding, wounds that have been bitten and contaminated with soil or old metal, you must urgently contact a surgeon.
Wounds are quite common, especially in young children. The task of parents is to provide timely assistance to the child in order to prevent infection. You must have a minimum first aid kit in your first aid kit. Do not self-medicate and, if threatening injuries occur, consult a doctor.
Reasons for visiting a doctor
You should consult a doctor if the wound or abrasion is accompanied by problems. In the following cases, you should definitely visit a specialist:
- The wound was caused by a rusty object - it could be a simple nail, but in such cases a tetanus vaccine may be required.
- If the edges of the wound diverge greatly and require suturing. If stitches are not applied, the result will be a strong and deep scar, and healing will be slow.
- If the wound is accompanied by severe bleeding that cannot be stopped within 20-30 minutes. In such cases, either blood clotting may be impaired or a large and important vessel may be damaged.
- If the area around the wound is very swollen, swelling and suppuration appear, all this is accompanied by twitching pain and fever. In such cases, surgical debridement and, probably, drug therapy are necessary, since the symptoms indicate infection of the wound.
IMPORTANT : even the smallest and most insignificant wound is a violation of the skin, which pathogenic microbes and bacteria can use as an entrance gate. Tetanus bacteria are especially dangerous. Be sure to treat everything, even minor abrasions and cuts.
General symptoms
Like any other pathology, a wound has distinctive symptoms. The main sign of damage to the skin is pain. The most intense pain occurs when nerves are damaged.
Another telltale sign of a wound is bleeding. Its bleeding pattern depends on which vessels are damaged. If an artery with a diameter of 3 mm is damaged during the wounding process, death from blood loss can occur within 3-4 minutes. Incised wounds bleed profusely.
With injuries that affect a large area, severe pain can cause fainting. Also, during the treatment of skin damage, body temperature may rise, which is a dangerous sign, as it indicates intoxication of the body.