Sebaceous glands
(
glandulae sebaceae
) - skin glands, the secretion of which serves as a fatty lubricant for the hair and skin surface.
Sebaceous glands are found only in the skin of mammals. In birds, amphibians and other animals, the glands of the skin only resemble the Sebaceous glands, without being such in essence. Being fundamentally similar in histological structure, the Sebaceous glands can have significant differences in size, location and structural complexity not only in different animal species, but also in different areas of the skin of an individual.
Embryology
There are conflicting opinions regarding the timing of the formation of the Sebaceous glands. Thus, according to I.I. Podvysotskaya (1971), their formation occurs both in the early postnatal period and during puberty. According to other data, the bookmark of the S. zh. in humans it occurs within 3-6 months. embryonic development in the upper third of the outer root sheath of the hair in the form of a flask-shaped accumulation of epithelial cells growing into the surrounding dermis. The secretory section is formed from the expanded part of this accumulation of cells, the excretory duct is formed from the cord connecting to the external root sheath, and the capsule of the genus is formed from the surrounding connective tissue. The simple gland formed in this way, growing, turns into a branched, and sometimes complex, lobed one.
Let's sum it up
There can be many reasons for the occurrence of increased oiliness in the dermis, but the solutions to all problems are basically the same. Therefore, it is very important to figure out how to reduce or remove, get rid of excess oily skin on the face, what to do when the chosen gentle products no longer help, and what you can count on. Modern cosmetology offers many different options for influencing the dermis, but not all of them are equally safe and effective, and many problems can be completely solved with high-quality home care.
Topography
Sebaceous glands are located almost throughout the skin with the exception of the skin of the palms and soles and are overwhelmingly associated with hair follicles (hair sebaceous gland - gl. sebaceae pili). It is most saturated with large S. liquids. skin of the scalp, cheeks and chin (400–900 glands per 1 cm2). S., located in areas of the skin devoid of hair (lips, corner of the mouth, glans penis, inner layer of the foreskin, clitoris, labia minora, nipples and areola of the mammary glands) are called free, or individual, S. and. (gll. sebaceae separatae).
Anatomy, histology and age-related changes
The structure, size and location of the Sebaceous glands in the skin depend on the timing of hair formation (see). S. zh. are located in the reticular (reticular) layer of the dermis, lying in a somewhat oblique direction between the hair follicle (folliculus pili) and the hair lifter muscle (m. arrector pili). When it contracts, the hair straightens, which, by exerting pressure on the hair, promotes increased secretion (see Piloerection).
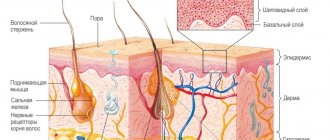
Microscopic specimen of skin with a sebaceous gland and a hair follicle located in it: 1 - hair follicle; 2 - excretory duct of the sebaceous gland; 3 - a sac of the sebaceous gland, filled with secretion from decayed secretory cells; 4 - germ layer of sebaceous gland cells; 5 - muscle-lifter hair; hematoxylin-eosin staining; x 80.
The formed simple Sebaceous gland (Fig.) consists of an excretory duct (ductus gl. sebaceae), lined on the inside with stratified squamous non-keratinizing epithelium, and a terminal secretory part - a sac (sacculus gl. sebaceae), surrounded on the outside by a thin connective tissue capsule. Along the periphery of the sac (under the capsule) there is a continuous layer of undifferentiated cells lying on the basement membrane and having high mitotic activity, the so-called. germinal layer of cells of S. g. These cells are rich in RNA and have an underdeveloped endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi complex. Closer to the center of the sac are larger secretory cells with a developed Golgi complex and non-granular endoplasmic reticulum, containing individual small fat vacuoles. The closer the cells are located to the center, the more pronounced are the signs of death of the nucleus and the entire cell, the larger and more abundant the fat vacuoles, which can merge into conglomerates. In the center of the sac there is cellular detritus, consisting of disintegrated secretory cells, which is the secretion of the gland.
Blood supply of the s. provide blood vessels that nourish the root system of the hair (see Hair).
The sebaceous glands are innervated by cholinergic and adrenergic nerve fibers. The endings of cholinergic nerve fibers reach the basement membrane, located on its surface, while the endings of adrenergic nerve fibers pierce the basement membrane, penetrate the parenchyma and surround secretory cells. There are also species and topographical differences in the nature of the cholinergic innervation of the stomach.
Throughout S.'s life. undergoing significant restructuring. By the time of birth, they are quite developed and function intensively. During the first year of life, the growth of the glands predominates against the background of reduced secretion; later, their partial atrophy occurs, especially in the skin of the legs and back. The period of puberty is characterized by increased growth and increased function of the stomach. In older people, involution of the blood vessels is observed, manifested in a simplification of their structure, a decrease in size, proliferation of connective tissue, and a decrease in the metabolic and functional activity of secretory cells. Part S. zh. may disappear completely with age. Degree of atrophy of the stomach. in different areas of the body it is different, for example, in the skin of the scalp it is less pronounced than in other areas.
What is high fat content
The skin of each of us consists of a very large number of thin layers. It takes part not only in the respiratory process, but also has protective, thermoregulatory, excretory and even metabolic functions. It is considered the most extensive organ of the human body, instantly reacts to any changes in its work, actively “signaling” the presence of such in various ways: rashes, irritation, dryness, comedones, acne and other unpleasant manifestations.
Therefore, if the skin suddenly begins to secrete an excessive amount of sebum and becomes greasy, which was not observed before, then this is a reason to seriously worry and consult a doctor. Such problems lead to a constant unsightly shine, clogged glands, acne, various cysts, and even the development of seborrhea. A healthcare professional will usually order general tests and tests to ensure there are no internal pathologies, and then prescribe therapy.
Physiology
The sebaceous glands secrete approx. 20 g of sebum, which in most glands is brought to the surface of the skin through the root sheath of the hair, and in free glands - directly from the excretory duct. Secretion is secreted according to the holocrine type (see Glands). Secret S. gives elasticity to the hair, softens the epidermis (in the fetus it protects the skin from maceration), regulates the evaporation of water and the excretion of certain water-soluble metabolic products from the body, prevents the penetration of certain substances from the environment into the skin, and has an antimicrobial and antifungal effect.
Regulation of the function of the stomach. carried out by the neurohumoral route, mainly by sex hormones (see), which can cause a physiological increase in the activity of S. (hyperplasia, secretion of a large amount of secretion), for example, in newborns - the influence of progesterone and pituitary hormones circulating in the blood of the mother, in adolescents during puberty as a result of activation of the gonadotropic function of the anterior pituitary gland, adrenal cortex, increased activity of the gonads.
Solving problems with an endocrinologist
If there is an imbalance in the hormonal system, then an endocrinologist will eliminate it. I, Georgy Nikitich Romanov, am an endocrinologist with more than 20 years of experience in the specialty. If you have very oily facial skin, and conventional methods do not help to eliminate this problem, then the best solution would be to contact me for help. I will take a detailed history, prescribe tests based on what I see, evaluate the results, and determine effective treatment. Women of different ages approached me with this problem, and we always found the best solution to this problem.
I provide face-to-face consultations at a medical clinic in Gomel, as well as online consultations. You can sign up for an online consultation in one of the suggested sources: Viber, Telegram, Instagram, WhatsApp, Skype, Vkontakte.
My experience and knowledge work for you to solve skin problems and eliminate existing discomfort.
Pathology
Pathology S. includes developmental defects, functional disorders, dystrophic changes, inflammatory processes, and tumors.
To malformations of S. zh. include congenital asteatosis (lack of sebaceous secretion or its sharp decrease as a result of insufficient development of the gland), as well as heterotopia of the gland. in the mucous membrane of the mouth and the red border of the lips - Fordyce's disease. The appearance of S. in the oral cavity with this disease is not accompanied by subjective sensations; they are detected by chance during examination in the form of small translucent pale yellow nodules on the oral mucosa. No treatment is required for Fordyce disease.
Functional disorders
The activities of the sebaceous glands are caused by damage to the autonomic, central or peripheral nervous system, disruption of hormonal regulation, metabolism, etc. Increased activity of the sebaceous glands. noted in patients with epidemic viral encephalitis as a result of damage to the autonomic centers, with mental illnesses accompanied by symptoms of vagotonia (psychosis, etc.), with lesions of the anterior pituitary gland, adrenal cortex, gonads associated with increased function, for example, with Itsenko’s disease - Cushing's (see Itsenko - Cushing's disease), seminoma (see), etc. A decrease in the function of these endocrine glands as a result of their damage leads to a decrease in the functional activity of the glands, which is noted, for example, during orchiectomy (see Castration , Post-castration syndrome).
A common pathological condition, which is based on a violation of the secretory function of the stomach. with a change in the chemical composition of the sebaceous secretion, seborrhea occurs (see). At the same time, seborrheic skin changes often lead to the formation of seborrhea in the excretory ducts. sebaceous-horny plugs - comedones, as well as atheromas (steatomas) - deep retention cysts of the stomach. (see Epidermoid cyst). Multiple cysts of the stomach, resulting from nevoid dysplasia of the epidermis, can be observed in pilosebocystomatosis (see).
Dystrophic changes
The sebaceous glands can be observed as age-related changes (in old age) or in a number of acquired diseases - scleroderma (see), skin atrophy (see), etc. However, often degenerative changes in the sebaceous glands. are associated with hereditary characteristics of their morphology and functional activity, in particular, thinning of the epithelium lining the excretory ducts of the stomach and the secretory epithelium of the sacs, a decrease in secretory function and the formation of superficial epidermal cysts - milia (see), for example, in dystrophic forms of bullous epidermolysis (see Epidermolysis bullosa).
Inflammatory processes
in S. zh. are often observed, especially during puberty against the background of seborrhea. Characterized by the formation of acne (see), in which the inflammatory process can develop both in the walls of the stomach. and the surrounding tissue (pustular acne), and spread into the deep layers of the skin (indurative acne) around the skin. and hair follicles, often involving subcutaneous tissue (phlegmonous acne).
Benign tumor
S. - true sebaceous gland adenoma - is rarely observed in adults and elderly people in the form of a dense, round, often single nodule on the face or back; it is an encapsulated organoid tumor of a lobular structure. Incorrectly called adenomas of the Pringle, Allopo-Leredda-Darier type (see Adenoma of the sebaceous glands) and Balser-Menetrier type (see Epithelioma adenoid cystic) nevi of the gland. (see Nevus).
To malignant tumors
The sebaceous glands include basalioma (see), characterized by locally destructive growth and being an intraepidermal cancer. Cancer S. g. - a rare type of cancer that develops from the gland, often from the glands of the cartilage of the eyelids, the so-called. meibomian glands (see Skin, tumors).
Bibliography:
Kalantaevskaya K. A. Histomorphology of human sebaceous glands in ontogenesis, Scientific. Izv. Kazakh honey. Institute, vol. 16, p. 174, Alma-Ata, 1960; Korolev Yu. Seborrhea and acne, Minsk, 1972; Podvysotskaya I. I. Age-related evolution of the sebaceous glands, in the book: Theory and practice of dermal-venereolitis, ed. E. V. Maistrakha et al., p. 346, L., 1971; Sokolov V. E., Shabadash S. A. and Zelikina T. I. On the question of the innervation of the sebaceous glands, Izv. USSR Academy of Sciences, ser. biol., no. 6, p. 805, 1980, bibliogr.; The sebaceous glands, ed. by W. Montagna, Oxford, 1963.
S. S. Kryazheva; Yu. K. Eletsky (an., hist., embr.).
How to deal with oily skin
All processes in the body are interconnected; an excess of some hormones leads to an excess or suppression of others. Therefore, the first priority in treatment is to find the root cause. Without properly targeted treatment there will be no long-term results.
If oily skin type has been passed on from birth, then you should not abuse bad habits and not monitor your general health, so as not to aggravate the situation. Proper nutrition, moderate physical activity, healthy, full sleep, positive emotions and a limited amount of stress are the key to a long and happy life without serious diseases. If problems arise, then you shouldn’t solve them yourself; for this, there are experienced specialists who will save money, time and improve the rhythm of life.