August 29, 2019
8185
0
3.5 out of 5
A disease known to everyone since childhood, scoliosis is diagnosed more and more often every year. According to statistics, approximately every sixth person suffers to a greater or lesser extent from scoliotic spinal deformity.
If left untreated, it poses a serious threat to health and, in severe forms, can lead to disability. Modern medicine has many opportunities to eliminate this pathology of the musculoskeletal system and is able to restore the joy of movement to most patients.
The latest methods of conservative and surgical treatment of scoliosis in Moscow are now available to everyone at the SL Clinic. We have everything necessary to conduct a full diagnosis and treatment of spinal scoliosis in adults and children. You no longer need to waste time and travel throughout the capital in search of different specialists; doctors whose help is needed by patients with scoliosis are waiting for you at the “SL Clinic” at (address).
Scoliosis: what is it
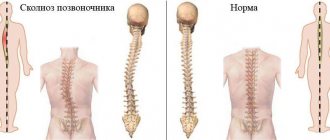
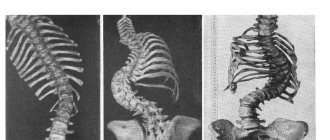
Scoliosis is a steadily progressive lateral curvature of the axis of the spinal column, followed by twisting of the vertebrae and increased physiological curves. This is accompanied by a change in posture and body proportions. Patients have protrusion of the shoulder blades, asymmetry of the shoulders and skewed hip line. Without appropriate therapy, under the influence of physical activity, the deformation constantly intensifies, the chest is distorted, and in severe cases, the body becomes so distorted that the internal organs begin to suffer seriously.
The most dangerous periods for the occurrence of pathology are considered to be the stages of intensive growth of a child, occurring at 4–6 years and 10–14 years. It is at this age that stage 1 spinal scoliosis in children is most often diagnosed for the first time and treatment begins. Although there are often cases when pathology is first detected in adults.
The reasons for the development of the disease lie in:
- developmental anomalies;
- neuromuscular diseases, including SMA (spinal muscular atrophy, cerebral palsy, muscular dystrophy;
- metabolic disorders;
- suffering severe injuries;
- degenerative-dystrophic processes;
- different leg lengths.
Often the cause of scoliosis cannot be determined and treated. In such situations, an idiopathic form of the disease is diagnosed, and all efforts are directed toward eliminating the curvature of the spinal deformity.
Causes
Scoliosis in children mainly begins to develop between the ages of 5 and 14 years, and especially at the ages of 4-6 years and 10-14 years, since it is at this time that the child’s active growth is observed. Since the spine remains quite plastic, improper distribution of the load on it, as well as a number of other factors, provokes the deviation of individual vertebrae from the main axis in one direction or another, thereby forming a scoliotic arch. This can occur in only one part of the spine, for example, in the lumbosacral region, or in several simultaneously.
There is also a congenital form of the disease. In such cases, deformation of the spinal column is caused by developmental disorders and the presence of fusions of the ribs, vertebrae with each other, the presence of additional vertebrae, etc. But this is much less common than acquired scoliosis.
In the absence of congenital deformities, the causes of scoliosis in children may include:
- Poor posture when sitting at a desk, working at a computer, or walking;
- uneven distribution of the load on the spine (wearing a backpack on one shoulder, heavy bags, packages);
- premature start to heavy sports;
- weakness of the muscle corset due to a sedentary lifestyle;
- spinal injuries, including compression fractures, severe bruises, fractures of the pelvic bones, much less often the lower extremities;
- unbalanced nutrition that does not ensure the supply of the proper amount of vitamins and minerals to the growing child’s body;
- diseases of the spine, including rickets, cerebral palsy, etc.
Scoliosis is more often diagnosed in girls, although medicine cannot yet provide convincing explanations why boys suffer from it less often.
Prerequisites for the development of the disease are:
- excess weight;
- neurological pathologies (neurofibromatosis, spastic paralysis, poliomyelitis, syringomyelia);
- nonfusion of vertebral arches;
- sacralization or lumbalization.
But in reality, it is not always possible to establish exactly what exactly caused the development of scoliosis.
Types of scoliosis
Depending on the degree of curvature, scoliosis is distinguished:
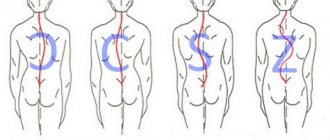
- c-shaped – the most common form, which is characterized by the formation of 1 pathological bend;
- s-shaped – there are 2 arcs, the second of which is formed as a result of compensatory mechanisms;
- z-shaped - the heaviest variety, characterized by the presence of 3 bends, but this shape is very rare.
The disease is also classified according to the direction of the curvature into left-sided and right-sided scoliosis, and according to the location of the curvature into:
- cervicothoracic – rare, but can occur with serious changes in the functioning of the respiratory system and cardiovascular system;
- chest - often right-sided, accompanied by difficulty breathing, disruption of the heart and the formation of a rib hump, which leads to severe pain;
- lumbar – the most common form, usually occurs mildly and is accompanied by osteochondrosis and lower back pain;
Particular attention is paid to the treatment of stage 1 thoracic scoliosis, as it progresses faster than that of the lumbar region.
In most cases, first-degree scoliosis is diagnosed in childhood during routine medical examinations. Its formation produces:
- position of one shoulder higher than the other;
- difference in distance between arm and waist;
- asymmetrical position of the shoulder blades.
The condition of the spine is assessed when a person stands straight with his arms hanging freely along his body.
If symptoms of the disease are detected, it is very important to immediately carry out comprehensive treatment for grade 1 scoliosis in children. Otherwise, the rapid growth of the body will lead to a rapid worsening of the deformation and disruption of the functioning of the heart and respiratory organs. It is also possible that radicular syndrome and compression of the spinal cord may occur, which is associated with severe pain. Treatment of scoliosis in children and adolescents in Moscow is successfully carried out at the SL Clinic.
Diagnostics
Most often, signs of scoliosis in children are detected during preventive examinations, since even a very caring and attentive parent is not always able to notice the initial manifestations of deformation of the spinal column in a child. The doctor assesses the position of the spine, shoulder blades and pelvis in the following ways:
- The child is placed face down on the couch and places his arms along his body. The doctor palpates the spine with light pressure, determining the position of the vertebrae.
- The child stands with his back to the specialist and bends over, bending his back in an arc and lowering his arms. The doctor evaluates the position of the shoulder blades and spine in this position of the body. He also pays attention to whether the ribs are protruding on one side or another of the body.
If during a visual examination the doctor suspects that there is a curvature of the spine, he will order an x-ray of the spine in the straight axis. This simple and accessible study is often sufficient to accurately diagnose scoliosis and determine the degree of its development.
Scoliosis degrees
According to the international classification, there are 4 degrees of deformation:
- The angle of curvature does not exceed 10°. There is a slight stoop, signs of asymmetry in the waist and shoulder level. The patient involuntarily keeps his head down. An x-ray reveals a tendency to rotate the vertebrae.
- The curvature reaches 11–25°. When changing body position, the curvature of the spine does not disappear. With right-sided scoliosis of the 2nd degree, there is a prolapse of the right half of the pelvis, distortion of the waist triangle and the outline of the neck. A protrusion forms on the right side in the chest area, and a muscle roll forms in the lumbar region. When curving to the left side, the changes are mirror-like in nature. X-rays show twisting of the vertebrae.
- The angle of curvature is in the range of 26–50°. To the above signs is added protrusion of the anterior costal arches and the acquisition of clear outlines of the costal hump. At the same time, the tone of the abdominal muscles decreases.
- The angle exceeds 50°. The body is severely deformed. All of the above symptoms are intensified many times over.
Physical and neurological testing
The doctor takes a careful look at the patient's medical history, and the doctor may use the following physical tests to see and measure the curvature:
- Adam's Forward Bend Test.
- Plumb line check: This is a quick visual check to ensure that the axis of the spine is straight. With scoliosis, the plumb line will pass to the left or right of the spine, and not through the middle of the buttocks.
- Scoliometer: If the doctor sees a rib hump, they may use a scoliometer to measure the size of the hump. This is a painless and non-invasive test.
- Leg length: In order to determine the discrepancy, the legs are measured and compared.
- Palpation: The doctor will determine the presence of spinal abnormalities by palpation. The ribs or psoas muscles may be more prominent on one side of the spine than the other.
- Range of motion: The doctor will determine the degree to which the child can perform movements such as flexion, extension, side bending, and rotation of the torso. The doctor also notes the presence of asymmetry.
In addition to the physical assessment, the doctor performs a neurological examination. The goal is to identify the presence of areas of numbness, tingling, weakness and other neurological symptoms, which may include changes in bowel or bladder function.
Conservative therapy
Treatment of childhood scoliosis of 1st and 2nd degrees is the task of an orthopedist. It is this specialist who can easily recognize the first symptoms of deformity development and select the optimal tactics for correcting it.
Treatment of spinal scoliosis in school-age children of grade 1 and 2 is carried out through conservative therapy. It involves a whole range of measures:
- drug therapy;
- exercise therapy;
- wearing an orthopedic corset;
- physiotherapy;
- massage;
- treatment by an osteopath.
In adults, treatment of grade 1 spinal scoliosis consists mainly of taking measures to prevent its worsening and regular examinations. Hard work, active sports and a number of other factors can provoke the progression of the disease. It is important not to miss this moment and take timely measures and start therapy. But it must be taken into account that conservative treatment of left-sided or right-sided thoracic scoliosis of the spine in adults, as well as deformities of other parts, is effective only until the end of the formation of the skeleton. In the future, it is possible to eliminate the symptoms of the disease without surgery only if it is caused by pathologies of the intervertebral discs.
All scoliosis treatment methods are available to you in our clinic. Qualified doctors will select the optimal types of treatment that will give the most pronounced results and eliminate spinal curvature.
Drug therapy
Treatment of grade 2 scoliosis of the lumbar and thoracic spine rarely requires the use of painkillers. However, if discomfort occurs, you can take NSAIDs.
The main direction of therapy is strengthening bone tissue. For this purpose, vitamins B and D are prescribed, as well as calcium supplements. The dosage is selected strictly individually.
Physiotherapy
Exercise therapy is the basis of conservative treatment of grade 2 scoliosis in adolescents and adults. Classes, especially in the initial stages of therapy, are conducted under the guidance of a specialist. He can correctly calculate the load and select the optimal set of exercises, based on whether C-shaped or s-shaped scoliosis of the 2nd degree is being treated.
Recommended exercises include the following:
- Stand on your toes and stretch your arms up, smoothly spreading them to the sides. During the following repetitions, simultaneously with stretching the spine, turn the body to the left and right.
- Lying on your back, bend your knees and pull them towards your stomach, pressing your back tightly to the floor.
- Standing on your knees and placing your hands on the floor, while inhaling, bend your lower back and raise your head up, but as you exhale, lower your head and bend your back.
- Remaining in the same starting position, while inhaling, extend the right arm and leg. Return to starting position. Repeat, changing arms and legs. During the exercise you need to breathe evenly.
- Sit cross-legged. Place your hands on one of your shoulders. As you inhale, turn your body toward your arms, and as you exhale, they return back. Change the position of your hands and repeat again.
It is especially important to do therapeutic exercises while wearing a corset, since it provokes a decrease in muscle tone. Otherwise, there is a high probability of relapse of the disease.
Yoga and swimming are very useful for patients of any age. Regular visits to the pool twice a week helps strengthen muscles and rotate the vertebrae into a normal position.
It is possible to treat scoliosis in children according to Bubnovsky. The method involves the targeted impact of moderate physical activity with the almost complete elimination of gravitational forces. Regular exercise on a specially designed exercise machine helps strengthen muscles and give the spinal column the correct position.
Corset
Treatment of lumbar scoliosis of 1st and 2nd degree in adolescents and young children is carried out using a special orthopedic corset. It promotes the formation of the correct position of the spine and the alignment of the vertebrae.
There are different models of corsets:
- Chenault;
- Milwaukee;
- Lyonsky;
- Boston Hard;
- Chest Belt.
The choice of a specific one is made by the doctor. You should be in the orthosis from 16 to 23 hours a day for a long time. This requires endurance and patience on the part of both the patient and his loved ones. You can stop wearing a corset only after the period of active growth has ended.
Physiotherapy
Treatment of adolescent scoliosis and especially the cervical spine in adults, combined with osteochondrosis, is very well complemented by physiotherapy sessions. They activate blood flow, which saturates the tissues with useful substances and strengthens the back muscles.
The most effective appointment is considered to be:
- ultrasound therapy;
- magnetic therapy;
- electrophoresis;
- electromyostimulation;
- hydromassage;
- salt baths;
- thermal procedures.
Manual therapy
A properly performed massage can strengthen the back muscles, saturate the tissues with oxygen and nutrients, and reduce pressure on the spine. Thanks to a course of manual therapy, posture improves, discomfort is eliminated, and displaced vertebrae gradually return to their correct position.
But you should be careful when choosing a specialist. Osteopaths without medical education may not only fail to achieve good results, but also significantly worsen the situation. Therefore, you can trust massage only to qualified specialists.
Monitoring
Treatment is not always necessary for very young children because their spine may straighten as they grow.
But if the curvature does not go away on its own, there is some risk that it may reduce the space for organs to grow, so careful monitoring by a specialist is essential.
A pediatric orthopedic surgeon may recommend regular examinations and x-rays of the spine to monitor the curve and decide whether active treatment is needed.
Regular monitoring may also be recommended for older children with mild scoliosis, as treatment may be needed if progression occurs over time.
Prevention of disease progression
Treatment of scoliosis in children and adults will be ineffective if patients lift heavy objects, engage in strenuous sports, and sit incorrectly. It is recommended to sleep on a flat, fairly hard mattress, and daily long walks should become an integral part of life.
It is important to eat a balanced diet so that the body does not experience a deficiency of the substances it needs. This will ensure the correct development of bone tissue and its sufficient strength, which will serve to prevent the development of other diseases of the musculoskeletal system.
Plastering
This treatment can be used on infants and young children, and casting allows the spine to straighten as it grows.
The plaster brace is worn permanently and cannot be removed, but is replaced every few months as the child grows.
Parents often find it easier to have their child wear a plaster brace while they are very young, rather than having to wear a removable brace every day.
When the child gets older, you can switch to a regular corset.
Surgery
Surgery for scoliosis is indicated for approximately 10% of all patients. It is carried out when:
- severe pain and limitation of mobility that cannot be eliminated through conservative therapy;
- deformities with a curvature angle of more than 40–45° (if it exceeds 50–60°, surgical intervention is required, especially in children during the period of active growth);
- congenital anomalies that provoked the development of the disease - synostosis, the presence of additional hemivertebrae;
- the occurrence of cardiac or respiratory failure;
- threat of damage to the spinal cord, its blood vessels and nerves.
Thus, surgery to correct scoliosis is mainly performed at stages 3 or 4 of its development. It is also necessary to eliminate congenital anomalies. In other cases, our doctors are able to conservatively treat the symptoms of spinal scoliosis and obtain excellent results.
For congenital defects that provoke rapid progression of the disease, surgery is recommended for grade 2 scoliosis in children. This is a preventative measure. Treatment of the cause of scoliosis in children eliminates the prerequisites for repeated curvature of the spine. As a result, it is possible to avoid disruption of the functioning of internal organs and reduce the likelihood of developing other complications.
Types and features of operations
All types of surgical treatment of the disease used today involve the installation of special fixation systems on the spine. Most of them were first tested in the last century and are still successfully used to eliminate grade 3 and 4 deformities.
Installation of fixing structures is carried out under general anesthesia and takes about 3–4 hours. They are metal rods or cylinders that are secured to the spine using locking pedicle screws.
Each operation is associated with certain risks, since more than 20 fixing elements are required to be installed. The introduction of each of them can damage nerve fibers and lead to serious consequences, including disability. Therefore, surgical treatment of scoliosis should be trusted only to highly professional spinal surgeons with extensive experience in this field.
When operating on children, preference is given to movable fixators (growing structures). They do not interfere with the growth of the spine and ensure its correct formation. For patients over 14 years of age, fixed structures are usually installed.
Simultaneously with open surgery to correct vertebral deformity, surgical treatment of stenosis, intervertebral hernias, etc. can be performed. Surgical treatment does not involve repeated operations to remove metal structures. Therefore, it is worth being scrupulous in the choice of the method of its implementation and the quality of the implanted fixators. When you contact the SL Clinic, you will receive the maximum amount of information about various methods for correcting spinal curvature and recommendations from highly qualified spinal surgeons.
We treat scoliosis using high-quality materials. The high level of professionalism of surgeons ensures a low risk of complications and accidental damage to nerve endings. By contacting us, you protect yourself from receiving low-quality services and the possibility of breakdown of the installed structure.
Minimally invasive surgical treatment methods
Reducing operational risks and increasing the efficiency of procedures are the main goals of scientific research in the field of spinal surgery. The latest advances in medicine in this area are the creation of ApiFix technology and the installation of magnetic rods. An additional advantage of minimally invasive techniques is the absence of large postoperative scars along the entire length of the spine.
The ApiFix technique was developed in Israel and is the optimal solution to the problem of scoliosis for children and adolescents. Its essence is the implantation of a heavy-duty mechanism with very compact dimensions through a tiny incision in soft tissue. Its installation requires only 2 screws, which significantly reduces intraoperative risks.
It is equipped with a pressure intensity regulation system. Thanks to this, spinal surgeons have the opportunity not to radically and simultaneously change the configuration of the spine, but to gradually bring it to the desired parameters. Correction of the degree of pressure is carried out on an outpatient basis using a special needle. As a result, the patient does not experience severe pain, characteristic of the recovery period after open surgery, and easily tolerates the treatment. To achieve significant results, 3–5 months are enough, and the operation itself takes no more than an hour.
The method of surgical treatment of scoliotic deformity using magnetic rods, developed by Irish doctors, came into use in spinal surgery even later. It involves the introduction of small rods into the spine, the position of which is changed as the normal position of the spinal column is restored using a special remote control.
The procedure is also characterized by a low degree of invasiveness and high effectiveness. Like the installation of the ApiFix system, it does not cause traumatic shock and allows you to avoid postoperative pain, prolonged wearing of a corset and other inevitable factors of rehabilitation after classical operations.
After minimally invasive interventions, patients can return to their daily lifestyle almost immediately. Restrictions are imposed only on heavy physical labor and the duration of sitting.
Corseting
If the curvature of the child’s spine progresses, a specialist may recommend wearing a corset until the end of skeletal growth.
This will not correct the curvature of the spine, but it may help stop it from getting worse. However, there are some uncertainties about how effectively it works, so bracing is not always recommended by orthopedic doctors.
Corset:
- Made to order, taking into account the child's body
- usually made of rigid plastic, although flexible options are sometimes available
- such corsets are almost invisible under clothes
- usually need to be worn 23 hours a day
- should not interfere with daily activities - the corset should be removed only for showering, bathing, swimming, etc.
Children usually have to wear a brace until their growth is complete. For most children, this means that they can stop wearing a corset when they reach 16 or 17 years of age.