- What is flat foot?
- Foot development
- Causes of the disease
- Types of flat feet in children (longitudinal and transverse)
- Transverse and longitudinal
- Signs and symptoms of flat feet in children 3-4 years old
- Diagnosis of flat feet in children
- Plantography of the flat foot in a child
- Podometry
- Podography
- Electromyography
- Why is congenital flatfoot dangerous in infants (children under one year old) and in a child 3-4 years old?
- What treatment is needed
- Massage and manual therapy
- Orthopedic shoes
- Physiotherapy
- Physiotherapy
- Kinesio taping
- Operation
- What type of doctor is needed?
- Does the treatment of children 2-5 years old differ from the treatment of flat feet of a child 6-12 years old?
- Prevention
- Conclusion
When a boy’s parents are diagnosed with a foot deformity, some mothers are happy that such an illness will not allow their child to go to military service. At the same time, they do not think at all about the future fate of the young man, because this is not only a cosmetic defect, but is also fraught with the development of diseases of the musculoskeletal system and even internal organs in a more mature age. When a child begins to take his first steps, little attention is paid to a flat leg, because we know that it can have a layer of fat (if the baby himself is very plump). Identification of flat feet in preschool children occurs in the third or fourth year of their life, when the most active period of skeletal formation begins. A diagnosis does not mean that your baby will experience discomfort while jogging or standing in one place for long periods of time throughout his life. If you notice the first signs of the disease in time, successful treatment is possible.
Foot development
There is nothing unusual in the fact that until the age of two, a child does not have the notch we are accustomed to. After all, in this place there is a fat pad, which replaces the arch necessary for an adult. It is necessary to sound the alarm if flat feet are noticed in children at the age of three. Until this time, for proper bone formation, strengthening muscles and ligaments, parents are recommended to allow the baby to run on uneven terrain, preferably barefoot. Let the baby walk on his heels or toes; this, in its own way, will be a special training without the use of medical devices and complexes.
Specialized Accessories
At home in your room, preventive measures include walking on an orthopedic rug, the surface of which imitates grass, pebbles, and has small thorns or buttons. Such a carpet can become an alternative in a children's room.
Insoles that will distribute the load on your feet will also be a must-have in your wardrobe. They are made individually or professionally selected.
After this, you will not think about how to treat your 5-6 year old child, because you will teach healthy habits from a young age.
Causes of the disease
Unfortunately, it is not always possible to identify a congenital disease immediately after birth. In our country, only three percent of children are immediately diagnosed correctly. And, as a rule, this is a hereditary predisposition.
Mothers of older children often ask pediatricians: why do children have flat feet?
Factors contributing to the occurrence of the disease:
- Genetic predisposition. If close relatives had such a pathology, then there is a chance that the baby will also have it.
- Connective tissue deficiency. A poorly developed ligamentous-muscular system leads to constant stress on the muscles, leading to compaction and thickening of the inner part of the foot.
- The increased weight of the baby contributes to improper bone development.
- Traumatic situations (fractures, dislocations).
- Rickets not only deforms the lower part of the leg, but also the entire skeleton.
- Congenital cerebral palsy and previous poliomyelitis lead to paralysis of the musculo-ligamentous apparatus.
What causes?
Foot deformities in children can be congenital or acquired.
At the stage of intrauterine development they are provoked by:
- abnormal location of the fetus in the uterus;
- prematurity;
- congenital pathologies of the musculoskeletal or nervous system (cerebral palsy, impaired innervation of muscles, connective tissue dysplasia);
- oligohydramnios, multiple pregnancies, small space for the fetus leads to mechanical pressure on the lower limbs, causing deviations in their development;
- intoxication, smoking, taking alcohol or drugs by a woman during pregnancy;
- intrauterine infections;
- hereditary factor.
Common causes of acquired foot deformities are lack of physical activity and improperly selected shoes.
With a lack of physical activity, the foot muscles weaken over time and are less able to hold the bones in the anatomically correct position.
Contributes to this:
- moving mainly on hard, flat surfaces: smooth floors in an apartment, tiles or asphalt outdoors;
- lack of exercise;
- refusal of preventive massage, exercises to maintain foot muscle tone.
Bad shoes have a detrimental effect on the formation of a child’s foot in the first years of life. Therefore, there are a number of requirements for its selection. It should ensure proper formation of the foot and distribution of the load, supporting the arches. For this purpose, shoes for small children are equipped with instep supports, a small heel, a flexible sole, and heel fixation.
Acquired foot alignment disorders also cause:
- increased load on the joints of the legs due to excess weight, early walking (in children they are very mobile and are easily displaced);
- diseases of the musculoskeletal system;
- birth injuries;
- fractures, bruises, sprains, deep cuts, burns in the foot area;
- long-term immobilization of the limb after injury (wearing a cast, orthosis);
- vitamin deficiency;
- past polio;
- suffered acute respiratory viral infections with complications in early childhood;
- metabolic disease;
- endocrine diseases (hypothyroidism, diabetes mellitus);
- advanced rickets, leading to disturbances in bone mineralization, muscle development, and ligaments;
- inflammatory processes in muscles, ligaments, joints.
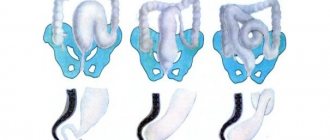
Types of flat feet in children (longitudinal and transverse)
Doctors diagnose three degrees of development of the disease and several subtypes in preschool children.
Transverse and longitudinal
Longitudinal is when the sole lies completely on the floor, resulting in flat feet and an increase in the width of the leg size. It is very painful for the child not only to stand, but also to move long distances. He is not comfortable wearing regular shoes.
There are three degrees of difference:
- Upon visual inspection, bone deformation is not noticeable. During diagnosis, the arch angle is determined to be 130-140 degrees. The child begins to complain about “legs” only during long walks.
- The baby also experiences pain and heaviness. Here the arch angle is more significant and is equal to 141-154°. If a pathology is detected, doctors recommend keeping your toes straight when walking, and not spreading them to the sides.
- With this degree, surgeons perform operations because the baby simply cries from severe pain when walking. Changes are visible to the naked eye.
Transverse degrees of flatfoot in children appear at a later age. Special characteristics of the disease: the toes are strongly curved, resembling round hammers. At the same time, the baby complains about the forefoot; it hurts him to step and stand on his toes. Often, calluses form on the fingers, like those of older people (corns). The leg stops growing in length, takes on a “spread out” appearance and resembles a diving fin.
Doctors also identify a third type (combined), which combines all the signs of previous deformities. In this case, the toes look outward, and the feet themselves form the letter “X”.
Optimal load on the legs
In order for the treatment of flat feet in a child to be safe and effective, it is necessary to select the most rational load, which will be carried out continuously throughout the entire recovery process.
- You should not stand in one position for a very long time, or carry heavy weights;
- It is advisable that the child does not walk barefoot on stone or hard surfaces for a long time;
- The child should at least sometimes walk on loose soil, and also walk on sand. But at the same time, parents must be sure that there is no glass or wire on these surfaces;
- The child should not wear warm shoes in any room.
Signs and symptoms of flat feet in children 3-4 years old
If your baby often complains to you and experiences pain, then first check his legs for pathology at home. To do this, smear them with oil paints and ask the child to stand on white paper. The fingerprint can be used to make a preliminary diagnosis.
In addition, the development of the disease can be suspected based on the following signs:
- A month after purchase, the sandals quickly wear down.
- The baby complains of pain and fatigue.
- The deviation of the thumb is noticeable.
- The foot itself is severely deformed.
- The child is “clubfooted.” Your comments about correcting the gait lead nowhere.
- My legs swell in the evening. The first calluses and ingrown nails appear.
Diagnosis of flat feet in children
At the first suspicion of pathology, it is necessary to promptly contact an orthopedist for consultations and possible treatment. Even if the child does not complain, then at the age of five he must be shown to a doctor for examination. If the deformity is discovered in the maternity hospital and it is congenital, then from the first days of life the baby is prescribed specialized treatment, which involves correcting the arch of the foot.
The acquired disease cannot be determined immediately, only after 3-4 years, when the subcutaneous fat of the pad disappears. It is very important to conduct a full examination at an early age.
At the first visit, the doctor will definitely examine the legs, palpate them, measure the width and length, and see how the baby moves. Also examines shoes for worn-out heels.
Next, he will conduct an examination using special equipment and tests.
Plantography of the flat foot in a child
A few years ago, the usual classical method was used using paint and paper. But the results were not very true, since it was impossible to force the child to stand straight and not move. After all, it is difficult to give an assessment if the baby does not put the body load on both feet.
Today, many medical institutions are equipped with an electronic plantograph. With its help, it became possible to make a high-quality print of the foot, and images on the side and back of the sole. Thanks to this, doctors determine the degree of deformation. All information is stored in a computer, and upon repeated examination, the orthopedist has the opportunity to compare indications and prescribe effective treatment for any stage of flat feet in children.
Podometry
The method involves measuring the parameters of the foot in height and length. The results obtained are multiplied by 100, and the ratio is calculated according to Flindland. An index of 20 to 31 percent is considered the norm.
Podography
The method involves assessing the child’s rhythmic gait. At the same time, special boots are put on his feet. While walking on a metal walkway, the orthopedist watches how the movement occurs and how the heel rolls.
Electromyography
Using electrical currents (where electrodes are placed directly on the lower leg or needles are inserted subcutaneously directly into the muscles), the activity of the muscular system is measured. Typically the method is used for paralysis or leg injuries.
How to warn?
To prevent foot deformities in children, doctors advise parents to follow simple recommendations:
- You shouldn’t put any weight on your baby’s legs before 7–8 months, don’t try to force him to stand on his legs, teach him to walk early. When the child is ready, he will do it himself;
- consult a pediatrician about preventing rickets, walk more in the fresh air on sunny days to ensure a sufficient supply of vitamin D;
- choose the right shoes for your child with a high, rigid heel that helps keep the heel on the axis of the shin, a bendable sole, and an instep support;
- make sure that the child is active, moves a lot, and does not gain excess weight;
- provide adequate nutrition, rich in vitamins and minerals necessary for the proper development of the musculoskeletal system;
- do leg exercises with your child;
- undergo regular examinations by an orthopedist (at 1, 3, 6 months, at 1 year, at 3 years, from 4 years - once a year), especially if there is a hereditary predisposition to orthopedic diseases.
0 0
What treatment is needed
After the diagnosis has been made, you must immediately proceed to the prescribed procedures until complete ossification of the skeleton occurs. Then it is more difficult to correct the deformation of the feet. Therefore, the orthopedist prescribes a technique that helps strengthen muscles, ligaments and joints, and improves blood supply.
Massage and manual therapy
To achieve better results, not only the lower legs are massaged, but also the lumbar region, buttocks and calf muscles. A relaxing, stimulating and tonic procedure must be carried out for at least 10 days exclusively by a qualified employee of a medical institution (massage therapist or chiropractor).
Orthopedic shoes
Pay special attention to this section! For the slightest defects in the legs, the doctor recommends that parents purchase special insoles that are inserted into ordinary boots or shoes. They will help in shaping the arch of the foot.
If the symptoms are significant, you cannot do without specialized shoes. Buying an orthopedic pair is not possible if you decide on your own. Only a doctor can give you a written recommendation after all the required measurements, which include the parameters for height, width, angle of deflection and turn when walking.
Very strict requirements are imposed on such shoes. The boots are made with a high back that clearly fixes the ankle. The socks are wide and rounded so that the toes fit freely against each other. They are also equipped with a lightweight sole with a heel, arch supports and insoles.
Unfortunately, in small towns and villages it is not always possible to find specialized stores or pharmacies that sell orthopedic shoes. People have to go to the regional center to purchase. And this is a waste of time and money on the road. Therefore, the best option is to purchase goods online. For example, it presents a wide range of products for boys and girls of all sizes (up to 40). Boots, boots, felt boots, pumps and sandals will surprise you not only with their colorful colors, but also with their fashionable, modern design. All products are certified. The company provides a warranty of 30 days from the date of purchase.
Physiotherapy
It is necessary to do gymnastics every day for 15-30 minutes. The complex includes rotational movements of the feet, wiggling the fingers, walking on uneven surfaces of a special massage mat, and practicing on the wall bars.
Physiotherapy
Magnetic therapy, shock wave treatment, electrophoresis and applications using paraffin and ozokerite are prescribed for moderate foot deformities.
Kinesio taping
Adhesive tapes are applied and fixed, which distribute the load across different leg muscles. It is recommended to wear them for several days in a row without taking them off at night, since the therapeutic effect is also present in the resting position.
Operation
If after prolonged treatment there is no positive dynamics, then surgical intervention is resorted to. It is prescribed to children who have been diagnosed with grade 3-4.
What type of doctor is needed?
Infants and children up to three or four years old will receive help from an orthopedist, massage therapist, chiropractor and physiotherapist. In adulthood, if there is a suspicion of scoliosis and neurotic diseases, they turn to a neurologist.
Does the treatment of children 2-5 years old differ from the treatment of flat feet of a child 6-12 years old?
At different stages of the disease, regardless of age, doctors adhere to an already established methodology. In the nursery group, therapy is significantly different. Only qualified specialists can choose the right course.
Orthopedic insoles
One of the main conservative interventions for pediatric flatfoot is orthopedic orthoses and arch supports in shoes. Research has shown that while orthotics can help correct soft tissue deformities, they do not affect bone structures. Dynamic stabilization insoles and custom foot orthoses have a significant positive impact. In general, it is believed that asymptomatic flat feet do not require orthoses. However, prescribing orthoses for symptomatic flexible flatfoot may help reduce pain and avoid surgery.
Over time, leg orthoses significantly reduce leg pain and increase functionality. The use of dynamic foot orthoses for pediatric flexible flatfoot helps restore structure and support to the medial and lateral aspects of the foot. One of the primary purposes of using functional orthoses is to control the degree of pronation of the subtalar joint, thereby providing support and alignment to the talocalcaneal joint. For more severe flatfoot deformity or ligament laxity in patients with ankle instability or posterior tibial tendon symptoms, ankle orthoses or more proximal devices may be more appropriate.