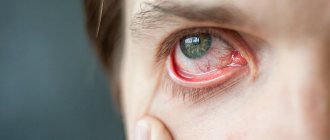
The term “wound” in medicine refers to a violation of the integrity of body tissues: skin, internal organs, bones, blood vessels, and other components of the “elements” of the human body. Such a violation appears as a result of external influence. Wounds can be of various natures, different areas and depths, so they require different measures for neutralization and treatment. A person can cope with some wounds on his own, but with others it is necessary to consult a doctor. However, in any case, every person should know the basic rules and have the skills of first aid and treatment of different types of wounds - such knowledge can be useful at any time.
The main classification of wound lesions in medicine
The type of injury directly affects how exactly it needs to be treated - because, for example, a perforating gunshot wound requires a slightly different “handling” than puncture wounds or wounds after an animal attack, and superficial wounds are treated differently than deep penetrating injuries.
One of the most common classifications of wounds is depending on the nature of the injuries received. So, there are chopped, lacerated and puncture wounds, bitten, for example, after a dog attack. Wounds can also be cuts or gunshots if they are received from bladed or firearms, razors or knives.
Content:
- The main classification of wound lesions in medicine
- Types of injuries differentiated by other criteria
- General rules for providing assistance in the presence of wound injuries
- How to stop bleeding: main techniques
- How to apply a tourniquet correctly
- How to treat abrasions and small wounds
- Puncture and bite wounds: what to do
- In what cases should you consult a doctor?
Slash wounds are quite rare and are considered one of the most dangerous types of wounds. Usually, in addition to damage to the skin and soft tissues, chopped wounds are accompanied by a violation of the integrity of bone structures. Such a lesion is accompanied by bleeding, often severe, and has jagged edges that take a long time to heal and are painful for the patient. The most typical type of slash wound is caused by an ax blow. A person can also receive a similar injury in accidents on various types of transport. Chopped wounds, of course, require some initial treatment, which can be provided to the victim by those around him, and then the victim must be taken to a doctor, and often for stitches.
Lacerations are the result of severe bruises or falls. Such lesions often have a large area, they heal poorly and are dangerous with a high probability of developing an infectious lesion. Characterized by significant crushing of tissue and skin.
Puncture wounds are one of the most common types of wounds, which can easily be caused even in everyday life, for example, by pricking yourself with a needle while sewing, or by stepping on a nail. They are characterized by a small, but deep and penetrating damaged area, which is why internal suppuration can develop in them.
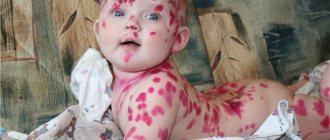
Injuries caused by attacks from animals such as dogs are called bite wounds. Such wounds can be superficial or deep, affecting blood vessels, soft tissues and even bones. Their distinctive feature is that, regardless of the area and depth, they must be seen by a doctor in order to prevent the development of rabies in the bitten person.
Incised wounds are another type of lesion that is often found in everyday life. Careless handling of a knife, razor or broken glass can cause a cut wound, and household wounds are generally of shallow depth and do not pose a danger to humans, requiring only minimal treatment. If the incised wound has a large penetration depth, heavy bleeding may develop against its background.
Gunshot wounds are injuries caused by body contact with a bullet or pellet fired from a firearm. They can be:
- through, when the bullet passes through the body and exits through a hole in the skin;
- blind if the bullet remains in the body.
Such wounds are often accompanied by major bleeding and require medical attention.
Examples of the most common injuries
The skin here is very soft and sensitive, so it is most susceptible to bruises and abrasions. First of all, you need to wash the wound with plenty of clean running water. If necessary, apply ice or a cold object - this will help quickly stop the bleeding. Next, apply a clean cotton swab or gauze bandage to the wound. For several days you need to wash the wound with chamomile decoction, you can use furatsilin. If the wound is serious enough, then it is necessary to show the child to a surgeon.
Another common childhood injury is head trauma. Such injuries are divided into open and closed. If the wound is open, then, as a rule, the soft tissues of the head are damaged and the wound bleeds. In this case, you should immediately call an ambulance. If the injury is closed, it may be accompanied by swelling, swelling, and sometimes scratches and abrasions. In this case, the mother should apply a cold object to the child’s head - ice, a cold compress. It is worth paying attention if the child becomes sleepy after a bruise and shows signs of nausea and dizziness. Such symptoms accompany concussions of varying severity. In this case, you should immediately contact a specialized institution.
A common childhood injury is nasal injury. Children's cartilage is still quite soft, so it does not break. And yet it is quite possible to get a slight displacement or abrasion. Having assessed the severity of the injury, the mother should decide whether to show the child to an otolaryngologist in order to avoid future problems with the nasal septum.
Children often cut their eyebrows. In this case, such an injury is accompanied by severe bleeding. In this case, you should also stop the bleeding by applying a cold compress or ice. Next, treat the wound with brilliant green and apply a bactericidal patch.
Children can often lose a tooth in children's games. If a child has lost a baby tooth, rinse the mouth with plenty of water. If a molar tooth has fallen out, you need to find it, wash the tooth with cold water and contact the dentist for tooth reimplantation.
The cheeks can also be frequently injured in children. With such an injury, the degree of injury should be assessed; if the soft tissues inside the cheeks are damaged, they should be treated with chamomile decoctions or disinfectant solutions. Parents cannot always protect their baby from injury. But knowing the first rules of necessary assistance in case of injury, you can significantly alleviate the baby’s suffering, and for any minor bruises or wounds, you can always use Lekker products.
When we were children, our parents usually treated any bruise or abrasion with iodine or brilliant green.
These are two completely different in properties and composition of the means, the result of the use of which has always had the maximum impact on the injury. Times are changing and now you can use both iodine and brilliant green in a convenient and economical form from the Lekker company.
Types of injuries differentiated by other criteria
If we consider tissue damage according to the degree of penetration, we can distinguish the following types of wounds:
- superficial;
- tangents;
- deep;
- end-to-end;
- blind.
Superficial wounds affect only the skin or mucous membranes, without disturbing the integrity of the soft tissues underneath - for example, abrasions or light scratches.
Tangential wounds pass by vital organs or bones without touching them, but can be quite deep and are accompanied by bleeding.
Deep wounds are injuries in which the integrity of bones, organs and internal tissues of the body is disrupted.
Penetrating wounds always have two holes - the place of entry and exit of a wounding object, for example, a bullet or a dagger.
As for blind wounds, they always require the intervention of doctors, since in this case part of the object that struck the person remains in the body, and it must be removed from the tissues or organs.
What to expect from treatment?
With proper care, the surface of the ulcer closes after 1.5 months. The use of vacuum therapy speeds up healing:
- Optimizes blood flow,
- Reduces swelling of local tissues,
- Removes excess fluid that can slow down cell growth,
- Reduces the number of bacteria.
- In addition, negative pressure changes the structure of cells in the wound layer, causing a cascade of intracellular signals that increase the rate of cell division and formation of granulation tissue.
There are a number of contraindications for vacuum therapy:
- malignant wounds;
- osteomyelitis without adequate treatment;
- necrosis with crust formation.
In such cases, cleansing is carried out using enzyme preparations and active surgical dressings. It is important to understand that cleansing trophic ulcers is an auxiliary method of treatment and in itself cannot lead to healing of the ulcer without eliminating the causes of its appearance.
General rules for providing assistance in the presence of wound injuries
Medical care for wounds can be of two types:
- primary;
- prescribed by a doctor after examination.
Some types of wounds can generally be successfully treated at home, without going to the doctor.
Providing assistance to the victim begins with assessing the extent and nature of the injury. First of all, medical intervention requires wounds with bleeding, and manipulations should be aimed at stopping the bleeding and preventing large blood losses that could cost a person his life. The basic rules for assistance with any type of injury are as follows:
- the affected area of the body must be immobilized and isolated from environmental factors;
- before starting any activities, hands and available tools must be freed from dirt and thoroughly disinfected;
- If possible, use sterile medical gloves;
- after treatment, the damaged area should be covered with sterile material to prevent infection from entering the wound;
- if primary treatment of a wound is performed, it is better not to apply any ointments or powders to it, so as not to aggravate the healing process in the future;
- alcohol preparations, iodine or brilliant green should not be poured into a deep open wound for disinfection, as this can cause painful shock in the victim;
- if any organs or bones protrude from the wound, for example, the brain, intestines or a piece of bone, it is forbidden to set them inside - they must be covered with sterile material, and the patient immobilized and taken to a medical facility;
- removal of foreign bodies from the wound should only be carried out by a doctor;
- Qualified medical care must be provided to the victim within the first 6 hours after being injured.
If the affected person needs urgent help, and there are no sterile materials nearby, you can carry out minimal disinfection of the available materials by ironing them on both sides. This material can cover the wound.
Primary treatment of wounds has several goals, the main of which is to prevent any infection from entering the damaged tissue, as well as to prevent blood loss. If bleeding threatens large blood losses, it must be stopped, even if the requirements for the sterility of objects and materials used in the process have to be neglected.
Before applying a bandage, the edges of the wound should be treated with an antiseptic, and movements should be carried out in the direction from the wound. If the damaged area needs to be bandaged, this is done from left to right, moving the bandage in a circular motion. Sterile gauze pads are applied under the bandage to the wound site.
It should be understood that in severe cases, if we are talking about car accidents or natural disasters, it is possible to provide assistance to victims only if you have at least a basic level of medical training, obtained, for example, in first aid courses, otherwise you can cause irreparable harm to the victim, incorrectly applying a tourniquet or trying to set internal organs if they have fallen out of an abdominal wound.
How to speed up healing
The speed of wound healing varies. It depends on the nature of the injury and the individual characteristics of the patient, such as age, nutrition, and medications taken.
To speed up healing, it is necessary to provide optimal conditions for tissue regeneration at each stage. This role is fulfilled by therapeutic dressings designed for each stage of healing.
The method of hydrotherapy has a positive effect. Its essence consists in the sequential use of two dressings HydroClean and HydroTac. Using the first, the wound is cleaned, and then a second is applied, creating optimal conditions for granulation and epithelization.
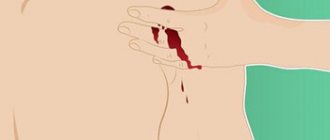
How to stop bleeding: main techniques
First of all, it is necessary to assess the intensity of bleeding - it can be weak, when blood oozes slightly, medium, or strong, if blood flows profusely or gushes out of the injury.
It is necessary to wash your hands and treat them with disinfectants. The skin around the wound also needs to be disinfected.
If the bleeding is profuse, and the flowing blood flows in a stream and has a bright scarlet color, then the arteries are damaged, but if the blood flows out calmly and has a darker, cherry hue, then the bleeding is venous. Such bleeding requires immediate measures to stop it - if it is impossible to ensure complete sterility, in this case you can even neglect the rule of asepsis, since if more than 35% of the total blood volume is lost, a person faces death.
To stop external bleeding, the following techniques are used:
- finger pressure;
- pressure bandage;
- tight tamponade;
- application of a tourniquet;
- flexion of a limb at a joint.
Finger pressure is the easiest way to stop moderate arterial bleeding - the artery is pressed against the bone between it and the wound, which causes blood to stop flowing into the damaged vessel.
A pressure bandage is relevant if bleeding of weak or moderate intensity is localized on the head or limbs. The bandage does not just cover the wound - it is applied with pressure, with effort. If a bleeding wound is located on the neck, a pressure bandage with a tourniquet may be applied to it.
Tight tamponade is used for arterial bleeding in the extremities if other options for stopping blood loss cannot be used, for example, for deep wounds.
A tourniquet is required for bleeding from wounds of large arteries, such as the hip or shoulder, if medical attention is delayed.
If the bleeding is not too heavy, the method of bending the limb at the joint can be used if the wound is located above it.
Phases of the wound process
- Purification stage
If there is copious purulent discharge or the presence of necrosis or an unpleasant odor, the ulcer must be cleansed of infection and dead tissue. This is achieved by washing the ulcer with a sponge soaped with laundry soap. To separate dead tissue, chymotrypsin powder or mesh with enzymes (parapran) is used, which is placed into the ulcer after washing and covered with a napkin. Dressings are repeated 2 times a day before bedtime and after waking up. Before each dressing, the ulcer is washed with a soft sponge and laundry soap. In the morning, a compression stocking or golf stocking of 2-3 compression class is put on over the bandage; in extreme cases, a fresh elastic bandage is used. If the skin around the ulcer is eczematous, then it is necessary to reduce inflammation; if there is redness of the skin around the ulcer, hormonal ointments (Lorinden, fluorocort) are used, which are applied in a thin layer under a dry cloth at night and not rubbed in. Hormonal ointments are used for no more than 5 days.
- Healing stage (granulation)
When good granulations appear - the ulcer is bright red, relatively clean, and its depth is reduced, treatment is required to stimulate healing and protect the granulations from damage. We use special wax mesh (voskopran) on top of which we apply ointments that promote healing - olasol, curiosin, gel dressings. The compression rules remain the same. You can wash the ulcer at this time without a sponge and carefully. Dressings once a day. Improving blood flow is achieved by elevating the leg during sleep (15-20 degrees), and mandatory compression with a stocking or bandage while awake. Elastic compression is necessarily used for venous ulcers; for arterial ulcers it is contraindicated, since on the contrary it can cause harm.
- Epithelization stage (final covering with new skin)
After the ulcer begins to heal, only light protective coverings like the same mesh are used, and gel dressings such as “hydrocol” can be used. If a small dry crust forms, there is no need to remove it specifically. After the appearance of young skin, it will fall off by itself. For venous ulcers, after eliminating venous congestion (sclerotherapy, laser or surgery), the ulcerative surface closes in 2-6 weeks. For arterial ulcers, the situation depends on the degree of restoration of blood circulation. With good blood circulation, ulcers usually heal within 1-3 months.
How to apply a tourniquet correctly
Applying a tourniquet is a last resort measure to stop bleeding, which can only be used for blood loss from the brachial or femoral artery. It is applied at a distance of 5 centimeters from the wound towards the heart. It is prohibited to apply a tourniquet to the lower third of the thigh or middle third of the shoulder. The duration of use of the tourniquet is no more than 45 minutes in summer and 30 minutes in winter.
A gauze or cloth bandage must be applied to the body under the tourniquet. Next, the limb with a tourniquet must be thermally insulated and immobilized until doctors arrive.
Stages of healing
The wound healing process goes through three main stages: inflammation, regeneration, and restoration of the epithelium.
The inflammation phase begins immediately after injury and in an uncomplicated state lasts for 4–5 days. During the hemostasis stage, platelets attach to sites of injury and cause a chemical reaction that activates fibrin, which forms a matrix network and binds platelets to each other. This is how blood clots form, blocking damaged blood vessels and stopping bleeding.
At the stage of proliferation and regeneration, the process of angiogenesis, collagen deposition, and the formation of granulation tissue (young connective tissue formed in places of defects) occurs. The regeneration stage can last 2–4 weeks depending on the size of the defect.
The final stage is the formation of the epithelium. Depending on the severity of the injury, the process can last from several weeks to a year or more.
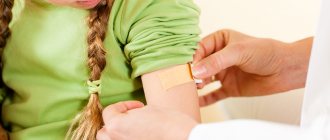
How to treat abrasions and small wounds
The first and basic rule in this case is that you should not wash the wound with running water, since it contains various microorganisms that, if they get into the damaged tissue, can cause suppuration. It is also better not to use cotton wool - only sterile bandages or sterile cotton pads.
The wound should be washed with an aseptic solution, such as chlorhexidine or hydrogen peroxide. Cauterizing preparations like iodine or brilliant green should not be applied to the open wound itself if it is very deep, but they can be used to treat the edges of the wound. As a last resort, vodka or moonshine is suitable if there are no medications at hand, but you should remember that their disinfecting ability is somewhat less powerful than that of specialized medical products.
After the initial treatment, when all foreign objects are removed from the wound, it is covered with sterile material and a not too tight bandage is applied on top. The abrasion, if it is heavily contaminated, should be rinsed well with a peroxide solution or boiled water before treatment.
What to give preference, brilliant green or iodine?
Everyone's favorite brilliant green (from the French "brilliant"), originally from Latin and meaning "brilliant", was used as a dye for silk, wool and other fabrics. As it turned out, according to the method of exposure, iodine and brilliant green have great distinctive features. To effectively use both tools, you need to understand exactly how they differ from each other.
Did you know that iodine successfully dries the skin, but if used in excess it can burn it? Now you know! To avoid this, you need to apply the basic rule: under no circumstances apply iodine to open wounds - this can cause severe burns to the surface of the skin, unlike brilliant green. If you cut your finger, get an abrasion, bruise or cut, do not immediately run for iodine - you can aggravate the injury. It is much more logical to use Iodine in cases of sprains, bruises or joint diseases to improve blood circulation. In these cases, the “iodine grid” is the most effective way to recover faster.
Puncture and bite wounds: what to do
When inflicting a puncture wound, you must first remove all foreign objects from it: a nail, a needle, a splinter, glass fragments. If foreign bodies are at a depth of more than 2 centimeters, and the wound is more than 5 millimeters in diameter, it is better to consult a doctor to remove them. A doctor's consultation is also required if, after treatment, signs of an inflammatory process appear around the wound, or if the wound was caused by a rusty metal object.
Wounds that appear after animal bites are always grounds for a mandatory visit to a doctor. If blood is flowing from a wound, the patient must be given first aid to stop the bleeding, treat the edges of the wound with a disinfectant, cover it with sterile material, and urgently transport the victim to a medical facility.
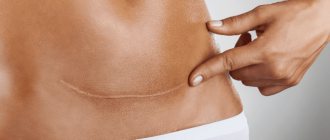
Scarring
Healing of a granulating wound occurs through scarring and epithelization. At the final stage of healing, collagen fibers appear among the cells of the granulating tissue, the number of granules decreases, and the number of fibers increases. Ultimately, the fibrous substance passes into the connective tissue and forms a scar.
When wounds heal by primary intention, delicate scar tissue is formed, which tends to resolve.
In case of healing by secondary intention, a rough scar is formed, which will not be easy to get rid of.