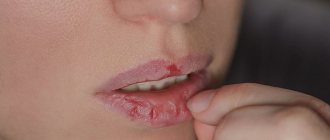
Inflammation of the oral mucosa often occurs due to injury, exposure to infections, or systemic disorders in the body, for example, as a result of hypovitaminosis. In most cases, the disease is not life-threatening, but causes a lot of suffering. It is impossible to forget about it for a minute, the bad smell scares others away from the patient, and eating and brushing teeth become a big problem.
Organization of treatment
With the development of an inflammatory process in the oral cavity, treatment has two directions - general and local.
General treatment
General treatment of the oral mucosa is carried out in case of severe disease. Patients are prescribed drugs for oral administration in the following groups:
- antibiotics – Amoxiclav, Ciprofloxacin, Metronidazole;
- antiviral drugs - Zovirax, Acyclovir;
- vitamins – vitamin complexes or monovitamins in injections;
- means for normalizing blood microcirculation - Trental, Pentoxifylline;
- immunostimulants – Levamisole.
General therapy aimed at restoring the throat mucosa necessarily involves correction of the primary disease. In accordance with the diagnosis, antihistamines, chemotherapy drugs, etc. may be indicated. General treatment to restore the condition of the mucous membrane is prescribed on an individual basis.
Local treatment
The inflammatory process in the mouth requires treatment of the lesions. The ulcers are washed with a soda solution; infusion solutions of sodium bicarbonate can also be used, which can be bought in pharmacies in 200 ml glass containers. It is forbidden to use cotton wool to treat ulcerations, as its fluff may remain in the wound, causing increased inflammation.
After treatment with solutions, the ulcers are washed with antiseptics - Miramistin, Chlorhexidine, and a slightly diluted solution of potassium permanganate. Antiseptics help reduce the intensity of inflammation and quickly achieve the onset of regeneration.
After antiseptics, the ulcers are treated with healing preparations that soften and moisturize the lesions. This is Solcoseryl, sea buckthorn oil. In case of severe pain, anesthetics - Kamistad or Lidocaine - can be used for recovery. For viral stomatitis, the use of Acyclovir is indicated.
Main reasons
The reasons why the mucous membrane in the mouth hurts and focal inflammation forms in the mouth include:
- Caries and other pathologies of the gums and teeth in the absence of timely treatment.
- Tartar.
- Diabetes.
- Wearing incorrectly fitted dentures that injure the mucous membranes.
- Reaction to the use of certain medications.
- Poor oral hygiene.
- Smoking.
- Alcohol abuse, since alcohol greatly irritates the mucous membrane of the mouth with constant contact.
- Chronic lesions of the stomach.
- Problems in the functioning of the immune system associated with overwork, constant stressful situations in life, lack of sleep or past illnesses.
- Hormonal problems.
- Damage to the oral mucosa by bacteria or viruses - laryngitis, pharyngitis, tonsillitis, etc.;
- Frequent surface injury. For example, when actively brushing your teeth with a hard brush or consuming very hard foods.
- Lack of nutrients in the body.
- Symptoms of anemia.
- HIV.
- Insufficient washing of products, after which pathogenic microbes can enter the oral cavity.
- Leakage of dental crowns, which provokes the constant proliferation of bacteria in the mouth.
- Self-medication with drugs that enhance saliva production.
- Dehydration due to large blood loss due to vomiting or diarrhea.
- Influenza, scarlet fever or herpes.
- Lack of iron, vitamin B and zinc in the diet.
- Chemical burn of the oral cavity.
- Toothpaste containing sodium lauryl sulfate. This substance irritates the mucous membranes.
- Oncology of the neck, pharynx, throat, larynx.
Treatment and prevention of inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity
The relevance of the problem is also due to the fact that, in addition to its high prevalence, the course of periodontal diseases in the early stages is characterized by mild symptoms, therefore, in many cases, patients turn to the dentist late, when the disease can no longer develop back. This explains the statistics widely known throughout the world, according to which the loss of teeth due to periodontal diseases is 5-10 times higher than the frequency of their removal due to complications of caries.
Such early multiple loss of teeth causes significant suffering to patients, creates social and everyday inconvenience for them, and causes a number of disturbances in the functioning of the digestive tract and other body systems.
The main local cause of inflammatory periodontal diseases (gingivitis and periodontitis) is poor oral hygiene, which leads to the accumulation of plaque rich in pathogenic microflora. In turn, this leads to the formation of tartar, against which the destruction of periodontal tissue begins. The first signs are redness of the gum margin, bleeding of the gums when brushing teeth and eating solid food, and bad breath. In later stages, suppuration appears from the gums, teeth lose their stability, become loose and fall out.
For both the prevention and treatment of gum problems, we recommend FARMADONT self-absorbable collagen plates for gums.
The plates are available in three types:
FARMADONT I - for inflammatory diseases of the oral mucosa.
FARMADONT II - for pain and increased sensitivity of the gums.
FARMADONT III - for bleeding gums
FARMADONT collagen plates are used for the treatment and prevention of inflammatory, infectious-necrotic, dystrophic and other diseases of periodontal tissue: gingivitis, periodontitis, in children and adults at any stage of the pathological process. The plates are completely absorbable and do not require removal.
Please note that the preparations contain extracts of medicinal herbs, to which patients may have allergic reactions (individual intolerance). Before use, you should consult your doctor.
Collagen plates for gums FARMADONT are used 2-3 times a day, in between meals:
- for bleeding, swelling, hyperemia, sore gums;
- after surgery on the gums and periodontal tissues;
- in case of injury to the gums and oral mucosa;
- after removing tartar;
- to strengthen teeth with their pathological mobility; when using removable dentures (rubbing);
- before and after dental prosthetics to remove and strengthen gums
THERE ARE CONTRAINDICATIONS. BEFORE USE, CONSULT WITH A SPECIALIST.
as an advertisement
Related product: [product](FARMADONT)
Organization of diagnostics
If a person goes to the hospital with complaints of discomfort and pain in the oral cavity, the doctor first conducts a survey to diagnose associated lesions. Then tests are prescribed:
- allergy test;
- bacterial culture from the site of inflammation to identify the type of infection - viral, fungal or bacterial.
A general blood test and blood serum test are required. If necessary, a referral for diagnostics from specialists of a different profile is issued.
Only after a full examination, identification of the etiology and type of the disease is it prescribed how to treat inflammation in the mouth. Independent actions will only aggravate the condition and provoke complications.
- Inflammation of the oral mucosa: causes and treatment
Symptoms of the problem
In almost any form of stomatitis, despite the difference in causes, the symptoms remain similar. The clinic for inflammation of the oral mucosa is as follows:
- severe pain and formation of suppuration;
- discomfort, pain in the gums, preventing you from chewing food or taking a sip;
- swelling, swelling, irritation of the mucous membranes of the lips and cheeks;
- rise in body temperature;
- discomfort that occurs when drinking hot food;
- foci of redness and purulent plaque;
- ulcers and inflammation of the pharyngeal mucosa;
- itching;
- persistent dry mouth, microflora disturbance;
- profuse drooling;
- swollen lymph nodes;
- loss of taste perception;
- pain and discomfort while speaking.
When inflammation in the oral cavity occurs due to poisoning, pigment spots appear on the gums, and a metallic taste is present. Symptoms of general malaise may also develop: weakness, digestive problems, apathy, numbness of the tongue.
With mechanical injuries, inflammation is always accompanied by hematomas.
What does burning and tingling of the tongue indicate?
Burning, tingling of the tongue may indicate developing glossalgia. The causes are usually injuries to the tongue or mucous membranes in the mouth, improper placement of fillings or dentures.
Glossalgia is a functional disorder of the nervous system. Usually the disease develops against the background of problems with the gastrointestinal tract or liver.
Similar symptoms accompany another pathology – leukoplakia. These are lesions of the mucous membranes in the mouth, caused by smoking and alcoholism. This is how mucous surfaces react to toxins in cigarettes and alcoholic drinks. Leukoplakia also occurs in case of a lack of vitamin A, with a genetic predisposition. As a rule, the pathology has a chronic course.
Inflammation due to smoking
This pathological condition should be considered separately. It often occurs in heavy smokers with extensive experience. Despite treatment, it will not be possible to completely get rid of the disease if you continue the bad habit. Nicotine is much stronger and kills all the beneficial components entering the body.
Smokers are diagnosed with stomatitis several times more often than non-smokers. Therapy involves regular rinsing and treating the oral mucosa with special products. Treatment will not give results if you do not give up the bad habit.
Types and forms of stomatitis
Depending on the causes or pathogens that caused the disease, several types are distinguished:
- Infectious: usually affect large areas of the mucous membrane, cause redness, pain, foul odor, characteristic plaque, and can lead to ulceration. Often accompanied by a deterioration in general health: febrile symptoms, weakness. Infectious diseases include viral, bacterial, and herpes. Such stomatitis lasts a long time and is prone to relapse. In severe cases, infections cause necrotization of the affected tissues, requiring surgical treatment.
- Allergic: mild. Inflammation of the mucous membranes occurs as a response to exposure to an allergen. When the harmful product or drug is excluded, the symptoms disappear on their own. Allergies do not cause deep damage. Sometimes there are enlarged lymph nodes and inflammation of the tongue.
- Traumatic: occur as a result of one-time or regular damage to the mucous membrane. Inflammation after mechanical trauma is localized in places of scratches; when exposed to hot or spicy foods, the entire area of the oral cavity usually suffers. The severity of the course depends on the degree of damage to the mucosa. With timely treatment, wounds quickly heal and inflammation subsides.
The catarrhal form of stomatitis is the mildest. It does not affect the deep layers of tissue and is manifested by increased salivation, swelling and redness. This is how allergies manifest themselves, burns from hot or overly sour foods, and the initial symptoms of some infections, including candidiasis.
The ulcerative form is a continuation of the catarrhal form in the absence of treatment, a characteristic picture as a result of deep damage or severe infection. With this stomatitis, the entire thickness of the mucous membrane is affected. Formations can be single or multiple.
Aphthous stomatitis can be a manifestation of a herpetic infection or a symptom of serious systemic diseases. Its sign is the formation of deep round ulcers with a red border and a yellowish surface.