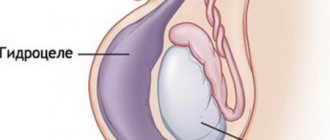
Hydrocele is an accumulation of fluid in the tissues of the testicles and chambers of the scrotum. The disease lies in the area of urology and andrology. Sometimes the condition can occur in newborn boys. In this case, the dropsy resolves on its own during the first few months of life, when the hole in the peritoneum through which the testicle descends into the scrotum is blocked. But if fluid accumulates in adult men, mandatory treatment is required.
There are several reasons for the development of testicular hydrocele in adults:
- injuries to the external genitalia, including the scrotum;
- surgical intervention in the genital and perineal area;
- infectious diseases - gonorrhea, tuberculosis;
- impaired lymphatic drainage;
- varicocele;
- inflammation in the area of the testicles and their appendages.
Causes of fluid accumulation in the ovaries
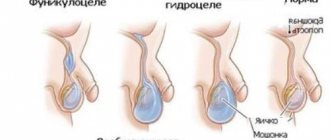
Typically, hydrocele occurs on only one testicle; in rare cases, mainly due to trauma, two are affected.
Congenital dropsy is formed during the period of intrauterine formation of the child, when the process of development of the testicle takes place, which descends into the scrotum through the inguinal canal. After which the gap between the peritoneum and the appendix closes:
- if this does not happen, fluid accumulates in the tissues of the scrotum, which flows from the peritoneum along the vaginal process, called communicating;
- if the process of closing the valve has passed, and there is water around the testicle that does not pass into other cavities - isolated.
In case of congenital dropsy of the ovarian membranes, the operation is not performed immediately, since the fluid can resolve. Therefore, up to 18 months, the child is examined monthly by a doctor, establishing the dynamics of the development of the disease.
Acquired hydrocele occurs in adolescents and adult men when the outflow of lymph from the testicle is impaired, which is formed in the process of:
- early surgical intervention, for example, removal of an inguinal hernia;
- damage or compression of lymphatic vessels (trauma, tumor);
- inflammatory processes during the development of infections, including colds.
According to the nature of the disease, hydrocele is divided into acute and chronic forms.
Diseases and circumstances that are often accompanied by the occurrence of hydrocele
- Cryptorchidism (undescended testicle)
- Hypospadias
- False hermaphroditism
- Epispadias and exstrophy
- Ventriculo-peritoneal shunt
- Prematurity
- Low birth weight
- Liver diseases with ascites
- Defects of the anterior abdominal wall
- Peritoneal dialysis
- Burdened heredity
- Cystic fibrosis
- Inflammatory diseases of the scrotum leading to the development of reactive hydrocele
- Testicular torsion
- Injury
- Infection
- Previous operations affecting the lymphatic system of the testicle
Visual symptoms
The acute form of the disease develops abruptly: the volume of the scrotum increases, and severe pain appears, accompanied by an increase in body temperature to 39 degrees.
In the chronic form, the disease begins with a feeling of heaviness in the testicular area, one side increases in volume. The size of dropsy may change during the day: after sleep it decreases, during the daytime it increases. For a long period, the man does not feel any pain factors.
The first symptom prompting the patient to consult a doctor is heavy urination and the appearance of sharp pain during sexual intercourse. On palpation, an elastic formation is felt, shaped like a pear.
If symptoms similar to hydrocele are detected, you should seek advice from a specialized clinic that will provide professional assistance and qualified services. A direct indication for the Winkelmann operation for dropsy is a sharp and dynamically developing enlargement of the scrotum.
Preparing for the intervention
Preliminary examination of yourself:
- blood tests (clinical, coagulogram, determination of blood group and Rh factor, biochemistry, hospital infections), as well as a general urine test;
- fluorography or chest x-ray;
- electrocardiography;
- the therapist’s conclusion about the absence of contraindications to the operation;
- consultation with an anesthesiologist on the day of surgery;
- consultations with narrow specialists (if necessary).
Adult patients need:
- Avoid alcohol intake for 24 hours;
- immediately before the operation, shave the hair in the groin area and empty the bladder;
- Avoid eating on the day of surgery (you can eat the night before);
- 4 hours before surgery, stop taking any liquid.
Diagnosis: dropsy of the membranes
Patients who do not consider the disease serious are susceptible to complications, namely:
- internal suppuration;
- spread of inflammation to nearby organs and tissues;
- possible testicular rupture;
- infertility;
- hernia;
- sexual disorders (erectile dysfunction).
The diagnosis of hydrocele is established by a urologist after a thorough diagnosis and receipt of test results. With timely access to a medical center, namely surgical intervention, complications occur extremely rarely.
Methods of surgical treatment, operations:
- Ross;
- Lord;
- Winckelmann and Bergman.
Modern clinics perform Winkelmann surgery in 55% of cases for hydrocele. This method does not require intensive preparation, it is carried out within 40-60 minutes, the approximate price is 25-30 thousand rubles.
Types of surgery
During hydrocele surgery, doctors open the lining of the vagina and drain it. For this purpose, operations are carried out according to Winckelmann, Lord or Bergman. The choice of method is determined by factors such as the presence of an inflammatory process, the stage of the disease and the age of the man.
So, if a small hydrocele is detected, it is advisable to perform Lord’s surgery. If its size is significant or there are signs of inflammation, Bergman surgery with excision of the vaginal membrane is recommended. This method is also indicated for elderly patients. In practice, the Winkelmann operation is most often performed.
Children over 2 years of age who are diagnosed with congenital hydrocele undergo Ross surgery.
Anesthesia during surgery
Typically, surgical intervention in the body of adult men is performed under local anesthesia, and for children - under general anesthesia. The choice of pain relief is made by the doctor, taking into account the indicators received during the tests. If the patient has allergies, several options for special medications are offered.
Examinations for prescribing anesthesia:
- detailed blood test;
- ECG or additional ultrasound to detect the presence of blood clots in the lower extremities.
Local anesthesia completely inhibits the transmission of pain or impulse in the scrotal area. What happens to the body? As a result of the influence of the drug, the work of nerve impulses slows down and stops. The feeling of pain completely disappears. The effect of local anesthesia lasts 1-2 hours.
General anesthesia affects the entire body, the muscles relax, and the person falls soundly asleep. This condition helps the surgeon to easily perform operations; the patient does not feel anything and does not interfere.
Winkelmann's operation in Moscow is performed at the Clinic for Men's and Women's Health.
Diagnostics
The effectiveness of treatment depends on how accurately and timely the correct diagnosis was made.
In particular, it is necessary to differentiate hydrocele from other pathologies:
- testicular tumors;
- testicular tuberculosis;
- inguinoscrotal hernia.
First, the doctor talks with the patient, collecting anamnesis, conducts a visual examination and palpation of the testicles. Additionally, the following studies may be prescribed:
- ultrasound examination of the scrotal organs, during which the size of the testicles, their contours, and the volume of fluid in the membranes of the testicles are assessed (normally about 2 ml). With hydrocele, an increased amount of free fluid is detected in the testicular membranes;
- general urinalysis and clinical blood test;
- spermogram, which allows to identify a decrease in the fertilizing ability of sperm;
- tumor markers (alpha-fetoprotein, human chorionic gonadotropin);
- tests for hospital infections;
- computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging if necessary.
In addition, the patient may need to consult related specialists if an oncological process, tuberculosis or inguinal scrotal hernia is suspected.
Postoperative recommendations
In most cases, the surgical process is carried out successfully, the patient quickly returns to normal life with strict adherence to the surgeon’s recommendations.
First of all, you need to temporarily change fashionable tight trousers to loose ones that do not squeeze or pinch the groin area.
It is mandatory to wear a special support bandage – a suspensor – for three weeks after surgery. The garter minimizes tension in the scrotum.
It is not recommended to play sports in the first two months; you need to rest more often.
You can take water procedures two hours after the operation, but you should not overheat or overcool. You need to give up baths, saunas, autumn or winter fishing for three months.
Additionally, after the operation, the doctor prescribes painkillers and possibly physical procedures. You must come to your appointment regularly throughout the year. The surgeon or urologist will prescribe pharmaceuticals based on the patient’s general condition and complaints.
Sexual relations can be resumed 5-6 weeks after surgery.
Conservative therapy
Conservative therapy is used in the treatment of small and moderate ascites. In other words, if there are no tiring and debilitating symptoms: pain, rapid breathing (tachypnea), etc. Up to 65% of patients have an improvement in their condition when treated with diuretics - this way you can remove up to 1 liter of fluid per day.
In the later stages of cancer, reducing salt and water intake can reduce quality of life. Therefore, at Euroonko such diet correction is rarely prescribed.
Book a consultation 24 hours a day
+7+7+78
Complications after the surgical procedure
Before performing a surgical intervention, the doctor must inform the patient about the possible negative consequences. Complications after Winkelmann surgery:
- swelling of the scrotum, aching pain, relief occurs after 7-10 days with the use of drug treatment;
- swelling of the testicles, slightly enlarged, hard, full recovery in 7-30 days;
- inflammation of the wound or spreading of the suture with infection, occurs in patients who do not comply with the exercise regime and personal hygiene;
- rejection of suture material with inflammation;
- formation of a keloid scar;
- recurrence of hydrocele;
- infertility if the spermatic cord is damaged during the operation.
Recent data shows that complications occur in 1% of patients who have concurrent chronic diseases that affect the recovery process.
Questions about the article
Konstantin
October 24, 2021 at 08:38
2 weeks ago I had a hydrocele operation according to Bergman. After the operation I had a fever for 2 weeks. On the 2nd day after the operation, the doctor examined the inside after removing the drainage, and said that there was nothing there, no infection either. The temperature was not high, up to 38. When taking painkillers, the temperature dropped. And every day the temperature became lower, and now it has passed. Is this a normal reaction of the body? And now when I touch the testicle, it is somehow large and very hard. There is also pain in the lower abdomen, on the side of the operated testicle, what could it be?
Anton Evgenievich Rotov
October 24, 2021 at 08:39
What you are describing is probably due to post-operative swelling that is more severe than normal due to inflammation. As a rule, the swelling completely disappears within 2-3 months. If in doubt, do an ultrasound of the scrotum
Vyacheslav
September 23, 2021 at 08:09 pm
Hello, on September 7, 2021, Bergman had an operation to remove a hydrocele. As of September 22, 2021, there are a number of problems that concern me, although I have been to the local doctor, I want to make sure that everything is in order. The first problem: somewhere around the 18th, the seam began to bleed from the edges, at the moment there is a “detachment” of the skin from above, but it does not cause any painful sensations (the local surgeon said that the seam had come apart, there was no need to stitch it up, he advised treating it twice a day with Chlorhexidine ) it’s already the 22nd, in my opinion, the seam divergence has not decreased, and I don’t understand how it will heal if it “peeled off”; there is still some liquid in the formed depression due to the seam divergence. Please tell me how normal this is and should I panic? Enough time has already passed, but the seam still doesn’t fit. The second question is how much is it acceptable to enlarge the scrotum after surgery, at the moment, compared to what was, of course, much less (there was 200 ml of water), but now there is swelling, I can hardly feel the testicle
Anton Evgenievich Rotov
September 23, 2021 at 08:18 pm
I am afraid that it will not be correct to assess the condition of the wound in absentia and draw any conclusions. Therefore, I will speak in general terms. Incomplete healing of the wound at this time is acceptable, although usually the wound is already closed by this time. Postoperative swelling of the soft tissues of the scrotum can persist for up to 3 months. If you still have doubts about the course of the postoperative period and you are not sure about the attending physician, then it is better to see another specialist
Peter
June 15, 2021 at 04:38 pm
A month ago I had a Winkelmann operation for hydrocele. The stitches have disappeared, the swelling is still there, but smaller, the wounds are also still present, but there is no bleeding from them. Can I already have sex or is it better to abstain for now?
Anton Evgenievich Rotov
June 15, 2021 at 04:39 pm
Sexual activity can be resumed
Eugene
March 4, 2021 at 12:18 pm
Thank you very much for the answer!
Stages of severity
There are three stages of abdominal hydrops depending on the amount of accumulated fluid:
- Initial stage - up to one and a half liters of fluid accumulates in the abdominal cavity;
- Moderate ascites - manifested by an increase in the size of the abdomen, edema of the lower extremities. The patient is concerned about severe shortness of breath, heaviness in the abdomen, heartburn, constipation;
- Severe dropsy - from 5 to 20 liters of fluid accumulates in the abdominal cavity. The skin on the abdomen tightens and becomes smooth. Patients experience heart failure and respiratory failure. When the fluid becomes infected, ascites-peritonitis (inflammation of the peritoneal layers) develops.