In some cases, tonsils may become enlarged without fever. Enlarged tonsils without fever require the same attention and treatment approach to avoid the development of complications.
Author:
- Chuprikov Roman Sergeevich
ENT pathology expert
3.15 (Votes: 26)
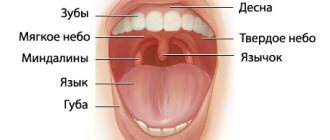
Tonsils (tonsils) are an important organ of the human immune system, involved in protecting the body from harmful carriers and preventing their spread. Their main task is to identify pathogenic microorganisms and produce antibodies to fight them.
Enlarged tonsils themselves are not a disease, but a symptom. They can increase:
- with infection;
- with genetically determined hypertrophy;
- for blood diseases (lymphoproliferative diseases);
- for autoimmune diseases;
- for allergic inflammation and swelling.
Usually these processes are accompanied by an increase in temperature, but in some cases the tonsils can enlarge without an increase in temperature. This often forces one to delay a visit to the doctor, since temperature is considered a marker of the disease. But enlarged tonsils without fever require the same attention and treatment approach to avoid the development of complications.
Symptoms:
- red, swollen tonsils with white or yellowish coating or streaks;
- a sore throat;
- difficult and/or painful to swallow;
- fever (temperature above 38.0);
- cervical lymph nodes are enlarged;
- hoarse or hoarse voice;
- headache;
- stiff neck muscles;
- abdominal pain (especially in young children).
In infants:
- drooling due to pain in swallowing;
- anxiety;
- refusal to eat
- With chronic tonsillitis, your breath may smell bad.
What other tonsils are there in the pharynx?
Other tonsils that form the lymphoid pharyngeal ring are: adenoid vegetations, or, more simply, adenoids, which are not a paired organ. They are located in the dome of the nasopharynx. It is impossible to see them with the naked eye. In order to recognize the condition of the adenoids, it is necessary to perform an endoscopic examination of the nasopharynx. Inflammation of the adenoids is called adenoiditis and is more common in children.
Also in the pharynx there is a lingual tonsil, located at the root of the tongue, which, like the adenoids, is an unpaired organ.
There are also tubal ridges, which are also called tubal tonsils. They are located at the entrance to the pharyngeal mouth of the auditory tube. The tube ridges are located deep in the nasopharynx, on the lateral (medial) surfaces of the nasopharynx on the right and left. Tubal tonsils perform an important function - they protect against infection entering the auditory tube. Since each of the tonsils of the lymphoepithelial pharyngeal ring deserves separate close attention, in this article we will only talk about the palatine tonsils and chronic tonsillitis. Other tonsils and the pathology they cause will be described in detail separately, in other relevant ENT articles.
Complications of tonsillitis
- Labored breathing.
- Sleep apnea (holding your breath during sleep).
- Spread of infection to the tissue near the tonsils (peritonsillitis), peritonsillar abscess - accumulation of pus behind the tonsil.
- Acute cervical lymphadenitis is inflammation of the cervical lymph nodes.
Streptococcal tonsillitis can cause complications such as:
- acute rheumatic fever, affecting the joints, heart and other organs;
- glomerulonephritis (inflammation of the kidneys, which can lead to serious consequences, including kidney failure).
Treatment with antibiotics significantly reduces the likelihood of complications after streptococcal sore throat.
The right approach
Sore throat, tonsillitis - treatment in children and adults is important to carry out immediately for all diseases of the oral cavity and nasopharynx that bother you. If breathing through the nose is impaired, and mucus or mucopurulent discharge flows down the back wall of the pharynx, then these symptoms should be given special attention.
Chronic tonsillitis - treatment (effective) can be conservative and surgical. Due to the fact that the removal of tonsils can cause serious harm to the defenses and immunity of the human body, otolaryngologists should try their best to preserve the tonsils and restore their functions without resorting to surgery to remove the tonsils. Modern methods of treating tonsillitis provide a greater chance of recovery without intervention.
Friends! Timely and correct treatment will ensure you a speedy recovery!
Chronic purulent tonsillitis - treatment of a conservative type must always be carried out in an ENT clinic, performing a complex, pathogenetically based course of treatment, as well as using a medicinal approach - medications prescribed by an ENT doctor.
Diagnosis of tonsillitis
- For tonsillitis, the doctor will examine the child's throat, as well as his ears and nose, where there may also be inflammation.
- The doctor will examine the child's skin, since streptococcal sore throat sometimes causes a specific rash. This is what is called “scarlet fever” - it is not some kind of separate disease, but a sign of damage to the body by streptococcus.
- The doctor will feel the cervical lymph nodes - as a rule, with tonsillitis they swell.
- The doctor will feel the spleen to distinguish a sore throat from mononucleosis, which also causes swollen lymph nodes.
- The streptococcal test is a simple and accurate way to distinguish streptococcal tonsillitis from viral tonsillitis. The doctor takes a scraping from the child’s throat and within 24-48 hours the result is ready.
- In some cases, a general blood test may be needed, the results of which can also indicate the viral or bacterial nature of the disease. It is usually taken if the streptococcal test is negative, but the course of the disease leaves the doctor in doubt.
About the clinic
Euromed Clinic is a multidisciplinary family clinic in the center of St. Petersburg.
- Calling a doctor to your home
- 24/7 therapist appointment
- Tests, ultrasound, x-ray
- Whole body diagnostics
- Hospital and surgery
- Vaccination
Find out more about the clinic
Chronic tonsillitis
Chronic tonsillitis is an autoimmune disease that occurs as a result of frequent sore throats and a decrease in the body’s overall resistance since childhood. With the development of the disease and its exacerbation, a person does not have enough general immunity to keep the palatine tonsils “in working order” and adequately fight the infection.
If harmful microbes get onto the surface of the mucous membrane and into the lacunae of the palatine tonsil, a real battle occurs between the microbes and the human immune system.
The palatine tonsil fights all pathogenic and conditionally pathogenic infections, but not being able to fully resist attacking microbes, it provokes either a new outbreak of sore throat or an exacerbation of chronic tonsillitis (treatment cannot be delayed in any case), thereby triggering an infectious-inflammatory process in palatine tonsils.
As a result of a lost fight, pus accumulates and stagnates in the lacunae of the tonsils, that is, dead leukocytes that come to the aid of the tonsil in the fight against a dangerous infection. The purulent masses irritate and inflame the tonsil tissue from the inside and have a toxic effect on it, thereby causing a sore throat - a severe infectious outbreak of inflammation of the tonsils.
In the absence of quick and adequate treatment, the contents of the lacunae and crypts of the palatine tonsils serve as a breeding ground for pathogenic microbes and a constant source of infection, even after an attack of tonsillitis.
Treatment of tonsillitis
The child should be provided with:
- peace and the opportunity to sleep as much as he wants;
- Drink plenty of fluids to relieve sore throats and prevent dehydration;
- air humidification;
- a sore throat can be relieved by both warm drinks and cold ice cream, especially popsicles;
- for a sore throat, it helps to gargle with a solution of table salt and soda - a teaspoon of salt and a small pinch of soda per 250 ml of warm water;
- Children over 4 years old can be offered lozenges for sore throats. Do not give candy to small children - they may choke;
- do not smoke when your child is sick, avoid strong odors that irritate the throat;
- A sore throat and fever can be relieved by medications containing paracetamol and ibuprofen. Don't give children aspirin; in rare cases, it can cause deadly Reye's syndrome.
Confirmed bacterial tonsillitis (usually streptococcal tonsillitis) is treated with antibiotics. It is dangerous to interrupt or stop the course because it increases the likelihood of infection spreading to the joints, heart, kidneys and other organs. Continue taking antibiotics even if your symptoms are completely gone.
4.Treatment
With a slight, but already uncomfortable enlargement of the tonsils, they begin with conservative treatment. Physiotherapeutic procedures (inhalations, applications, ultraviolet irradiation, electrophoresis, and many others) are widely used, which are believed to reduce the rate of hypertrophy. This takes into account the fact that hyperplastic and hypertrophic processes during the period of pubertal restructuring often show spontaneous reverse development, i.e. Radical treatment may not be necessary.
Drug therapy is reduced mainly to local antiseptic and immunomodulatory preventive measures.
Severe and continuing to progress hypertrophy, complicated by the disorders described above, is an indication for tonsillectomy (surgical removal of the tonsils); if there are indications for adenoid removal, both operations are usually performed as part of one intervention.
Drug treatment of chronic tonsillitis
Dear patients! In this article I will describe only general principles and approaches.
More precise treatment will be offered to you at the initial ENT consultation, where an accurate diagnosis, form and degree of the disease will be made, as well as an optimal recovery plan will be proposed and a prognosis for the duration of remission will be given.
So:
- Antibacterial approach. Antibiotic therapy is important and necessary. But the decision to prescribe antibacterial drugs is made individually and only after a visual examination.
Antibiotics can be either light, prescribed for a short course and have no effect on the mucous membrane of the gastrointestinal tract, or heavy, which must be prescribed under the guise of probiotic medications. The choice of antibiotic depends on the severity of chronic tonsillitis and the microflora that supports this condition. - Probiotic treatment is prescribed in case of taking aggressive antibiotics, as well as in the presence of concomitant gastritis, duodenitis, reflux esophagitis.
- Antiseptic approach. Antiseptic sprays, aerosols, and rinses also give a very good effect and are therefore mandatory in the fight against chronic tonsillitis. I prefer a 0.01% solution of Miramistin, a 1% solution of Dioxidine (1 ampoule diluted - 10 ml + 100 ml of boiled warm water) and Octenisept, which must be diluted with boiled warm water or saline in a dilution of 1:5 , or 1:6.
- Decongestant (desensitizing) therapy is mandatory. It is needed to relieve swelling of the palatine tonsils and the surrounding tissue, as well as the mucous membrane of the posterior pharyngeal wall. This is also necessary for better absorption of all medications used. Such modern medications as Cetrin, Claritin, Telfast can cope with these tasks. But if a certain desensitizing drug helps you for a long time, you should not change it to another.
- Immunostimulating therapy. Here I want to draw your attention to the fact that the doctor prescribes drugs that stimulate the immune system. These drugs should not be confused with immunomodulators, which are strictly prescribed by an immunologist based on the results of a blood test. There are not so many drugs that stimulate local immunity at the level of the palatine tonsils and the mucous membrane of the posterior pharyngeal wall. Of the well-known drugs, Imudon comes first. The course must be at least 10 days. You need to take (dissolve) Imudon 1 tablet 4 times a day.
- Homeopathic treatment. In addition to conventional drug therapy of a chemical nature, it is necessary to take homeopathic medications that improve the trophism and, as a result, the nutritional function of the palatine tonsils. The drugs of choice may be tonsillotren and tonsilgon, as well as rinses, steam and ultrasonic inhalations with infusions and herbs: propolis, string, sage, chamomile and some other herbs.
- Emollient therapy is used symptomatically, when, against the background of exacerbation of tonsillitis, as well as taking medications, there may be dryness, rawness and soreness in the throat. In such cases, you can use peach oil, which must be instilled a few drops into the nose, throwing back the head. You can rinse your mouth with 3% hydrogen peroxide (VERY IMPORTANT! 6% and 9% hydrogen peroxide CANNOT be used!!!). To do this, you need to pour half a bottle of peroxide (10 ml) into a cup, put it in your mouth and rinse the entire solution once, for as long as possible. Then the solution is spat out and rinsed from foam and bitterness with warm boiled water. After gargling with hydrogen peroxide, you will feel a significant softening and comfort in your throat. You can gargle twice a day, but no more.
- Analgesic therapy is used if necessary, as symptomatic therapy, depending on the severity of the pain syndrome. Of the tablet forms, it is better to give preference to Nurofen or Ketanal and its derivatives: Ketarol, Ketalar, Ketanof, Ketanal.
- Diet therapy. Nutrition also plays a significant role in recovery. It is necessary to limit the intake of spicy, fried, sour, salty and peppery foods. During treatment, you should exclude hard foods from your diet. It is also recommended to protect yourself from very hot and very cold foods. Drinking alcohol, especially strong alcohol, is also contraindicated.
Prevention of chronic tonsillitis
- Drug therapy
. If an ENT patient undergoes treatment courses in the clinic once every 6 months, then in addition to six-month procedures, he is recommended to take the drug Tonsilotren, with a frequency of once every 3 months, i.e. 4 times a year. The course of taking (resorption) of the drug is for 2 weeks (more precisely 15 days). It is also possible to instill 0.01% Miramistin solution, 4 pumps 4 times a day for 2 weeks, in courses 4 times a year. - Climatotherapy and spa therapy
. An important point in the prevention of chronic tonsillitis is visiting seaside resorts. Sunbathing, humidified sea air, swimming and, as a result, the inevitable entry of sea water into the mouth have a beneficial effect on the prevention of chronic tonsillitis. - Work and rest schedule
. In order for the periods of remission to be long, it is necessary to fully rest and not expose yourself to stress. It is not without reason that chronic tonsillitis, like sinusitis, is classified as a social disease, in which the more stress and workload there is at work, the higher the likelihood of exacerbation of chronic tonsillitis. - Diet
. It is very important to eat right. Under no circumstances should you get carried away with fried, salty, peppery, sour, bitter, i.e. that food that irritates the mucous membrane of the back of the throat and palatine tonsils. Citrus fruits are contraindicated. The consumption of alcoholic beverages, especially strong ones, is also contraindicated. It is not advisable to eat very hot and very cold and solid foods.