Basic functions of platelets
In appearance, platelets are round or oval red plates with a smooth surface. They are formed in the bone marrow. They mature in approximately 8 days. These components constantly circulate in the bloodstream.
The main function of platelets is to ensure blood clotting. In addition, the ability of these blood components to stop bleeding is important. This is ensured by the fact that individual platelets can stick together and stick to sites of vascular damage. The process is automatically started by the human body when there is a risk of bleeding.
An important question is how long platelets live. Their viability time lasts approximately 10 days. Depending on the age of the red plates, their size changes: from 2 to 5 microns in diameter.
The process of platelet renewal in the blood occurs constantly. Therefore, an important factor to ensure the maintenance of blood condition is the balance between the formation of red plates and their death. Otherwise, there may be a tendency to blood clots or increased bleeding.
Blood test for platelets
A complete blood test can determine the platelet count. The main indications for its implementation are the following:
- Increased bleeding of gums.
- Heavy menstruation.
- The appearance of bruises from minor impacts.
- Frequent nosebleeds.
- Difficulty stopping bleeding from minor injuries.
The number of platelets in the blood is measured in thousands per 1 microliter of blood. Counting is carried out in specialized laboratories in various ways that guarantee high accuracy.
The normal platelet count in the blood depends on gender and age and is:
- For men, 200–400 thousand.
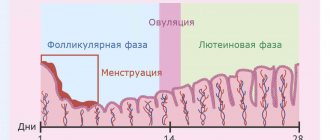
- In women, 180–320 thousand, during menstruation the amount can decrease to 75–220 thousand, and during pregnancy to 100–310 thousand.
- In children, indicators depend on age, and the corresponding values are given in special tables.
To conduct a general blood test, blood is taken from a finger. No special preliminary preparation is required before this. To ensure accurate results, it is better to donate blood in the morning on an empty stomach. At the same time, 12 hours before the procedure it is not recommended to consume fatty spicy foods, carbonated drinks, and alcohol.
Additionally, to determine blood clotting indicators, Sukharev and Lee-White tests are performed. They are informative and allow you to obtain the necessary additional data about the pathological condition. This will allow you to carry out correct treatment measures and avoid dangerous consequences.
Prothrombin time during pregnancy
The study of prothrombin time during pregnancy is an important diagnostic method that is used to analyze the condition of patients. In addition to routine biochemical studies, obstetricians and gynecologists use PTT analysis to assess the condition of a woman during gestation.
Analysis of prothrombin time during pregnancy is indicated for the following conditions:
- the patient had a history of spontaneous abortions or miscarriages, or frozen pregnancy;
- the pregnant woman has been diagnosed with uterine hypertonicity or other conditions that threaten the fetus;
- Obstetricians and gynecologists confirmed the presence of signs of the development of gestosis in a woman, or there is a threat of development of gestosis.
Prothrombin time in women during pregnancy ranges from 11 to 18 seconds. If the PTT is increased, then the doctor will probably suspect the development of bleeding in the patient during the labor or postpartum period. If the prothrombin time is reduced, then there is a threat of developing a dangerous condition - disseminated intravascular coagulation syndrome.
To prevent complications in the childbirth or postpartum period, doctors actively use the PTT study: diagnosis will indicate in time violations of the hemostatic system, which will allow the pregnant woman to begin treatment.
PTV reduced
If, during decoding of the PTT, it turns out that the indicator is reduced, this may indicate the following clinical situations:
- The patient has polycythemia. With this disease, the number of red blood cells (erythrocytes) increases significantly. The blood acquires a “thicker” structure, clots faster, and blood clots form more actively in it, so the prothrombin time is reduced.
- Deep vein thrombosis of the lower extremities. This pathology is characterized by the active formation of thrombi (blood clots) in the veins of the lower extremities, which has a deeper basis - a person may experience both an excess of platelets and too many blood clotting factors. Diagnosis of the primary causes of thrombosis is carried out by the attending physician, and a decrease in PTT in this case is a red marker that indicates the seriousness of the patient’s condition.
- Taking oral contraception. As a rule, PTT is slightly reduced if a woman takes oral contraceptives according to the regimen, both for the purpose of treating gynecological pathology and to protect against unwanted pregnancy.
- Hereditary disorders of the blood coagulation system. Genetically determined pathology in the form of a violation of the amount of one or more factors from the prothrombin complex, hereditary coagulopathies, and - or hypo-fibrinogenemia cause a decrease in PTT in humans.
- Acute DIC syndrome. At one of the stages of development of DIC syndrome, excessive blood clotting is observed, which becomes a life-threatening condition for the patient.
- Violation of the concentration of blood coagulation factors in the serum. Sometimes the reason for a decrease in PTT is a change in the required concentration of antithrombin, antithromboplastin (their increase), or an excess of heparin in the circulating blood.
- Other chronic diseases. Often, in patients with intestinal pathology (diseases of the small intestine, dysbiosis), with damage to the pancreas (chronic pancreatitis, pancreatic cancer), or pathology of the gallbladder, a decrease in PTT is observed. In addition, a decrease in the indicator is characteristic of nephrotic syndrome, which is associated with kidney damage.
- Oncological pathology. Prothrombin time is reduced in acute or chronic leukemia in humans.
It is important to note that some drugs used in various fields of medicine significantly affect the PTT rate:
- barbituric acid derivatives (barbiturates);
- hormone replacement therapy (thyroid hormones, androgens, anabolic steroids);
- some types of antibacterial drugs;
- antiarrhythmic drugs to correct the patient’s heart rhythm;
- antidiabetic agents;
- H2 receptor antagonists, which are used in the treatment of chronic gastritis and gastric and duodenal ulcers;
- diuretics, laxatives.
As a rule, a slight decrease in PTT is observed in women in the last trimester of pregnancy, which is considered a physiological norm and is interpreted on an individual basis.
PTV increased
Prothrombin time is increased in the following conditions:
- Deficiency of individual coagulation factors due to hereditary causes or acquired diseases. PTT is increased when the patient has a deficiency of coagulation factors II, V, VII, X - these conditions are congenital disorders. Acquired deficiency of coagulation factors is observed in chronic diseases of the liver, kidneys, as well as autoimmune pathology.
- DIC syndrome. At one stage of development of DIC syndrome, PTT decreases, at another, a significant increase in PTT is noted.
- Use of anticoagulant drugs. The use of treatment prescribed by a doctor (for example, acetylsalicylic acid, which has, among other things, anticoagulant activity) may be accompanied by a decrease in PTT. The targeted use of other anticoagulants (for example, warfarin) naturally reduces PTT, which should be taken into account by the attending physician when interpreting the study results.
PTT is increased when taking antibacterial drugs, steroid hormones, and some laxatives.
Increased platelet levels
Elevated platelets are a pathological condition. It is called thrombocytosis. The main danger of the pathology is the increased risk of blood clots.
The cause of an increase in the level of platelets in the blood can be various diseases. Most often thrombocytosis occurs against the background of:
- Malignant neoplasms.
- Infectious diseases.
- Helminthic infestations.
- Surgical operations.
- Autoimmune pathologies.
- Kidney failure.
High levels of platelets in the blood are observed in older people. Temporarily, indicators may increase after heavy physical exertion, for example, after playing sports.
The symptoms of thrombocytosis are characteristic, but mild. It is imperative to conduct a general blood test if the following symptoms are noted:
- Pain in the fingers and toes.
- Itching of skin surfaces.
- Unreasonable weakness, which leads to decreased performance.
- Lack of appetite.
What is the research used for?
Prothrombin time is an important laboratory indicator that doctors use to diagnose a patient and prescribe the correct treatment. A significant list of indications for performing PTT analysis includes both various screening studies and diagnostic purposes. In addition, prothrombin time analysis is used to monitor the progress of human therapy.
Thus, PTT is an exceptional diagnostic marker, without which correct and effective treatment of a person is impossible.
Decreased platelet levels
Low platelet levels, the norm of which differs between men and women, provoke the development of a condition known as thrombocytopenia. Very often it occurs against the background of uncontrolled use of medications: antidepressants and antibiotics.
The reasons for a decrease in the level of platelets in the blood can be various infectious diseases: ARVI, hepatitis, herpes, etc. Thrombocytopenia can be observed when a large number of blood thinning products are included in the diet. These are ginger, cherries, garlic, onions, etc.
Non-infectious factors that reduce the level of platelets in the blood include pregnancy, vitamin deficiency, alcohol or heavy metal poisoning.
Thrombocytopenia can be suspected based on the following signs:
- Heavy menstruation.
- Frequent nosebleeds.
- The appearance of hematomas.
With a constant pathological decrease in the level of platelets in the blood, the risks of developing severe bleeding and stroke conditions, which are life-threatening, increase.
Restoring platelet levels in the blood
You can normalize the level of platelets in the blood with a balanced diet. It is important to saturate your diet with foods high in materials and microelements. You need to give up spicy food, alcohol, fast food and sweet carbonated drinks, lead a healthy lifestyle and maintain a drinking regime.
If it is not possible to normalize the indicators using natural methods, then you need to undergo a full examination by a hematologist. If platelet levels are elevated, special medications may be prescribed - anticoagulants or antiplatelet agents. They thin the blood and minimize the risk of blood clots. But at the same time, they should be taken only as prescribed by a doctor. It should be understood that stabilization of the condition is possible only after eliminating the underlying causes that provoke deviations from the norm.
Prothrombin
Prothrombin time (PTT) is a laboratory indicator that reflects the functioning of the extrinsic pathway of activation of the human blood coagulation system. Often, the PTT test is prescribed in conjunction with the determination of activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT) - this test shows the activity of the intrinsic coagulation pathway and activation of the coagulation system.
Often, in addition to PTT and APTT, the attending physician refers the patient to determine the prothrombin index (PTI) and international normalized ratio (INR). These indicators are calculated by the laboratory where the research is carried out.
PTT and APTT provide the physician with a wide range of data on the state of both the patient's coagulation and anticoagulation systems. Based on this information, the doctor can begin conservative treatment of the patient, prepare for surgery, or conduct therapy aimed at normalizing the functioning of the coagulation system.
The PTV norm, which is accepted throughout the world, is 11-16 seconds. It is believed that this indicator of prothrombin time is optimal for most healthy people.
Before prescribing a PTT test, the doctor must take into account the patient’s medical history. For example, when taking anticoagulants (especially warfarin), the prothrombin time changes, increasing significantly.