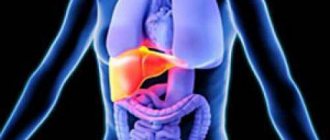
In the hustle and bustle of life, we do not always pay attention to the signs that the body gives us; moreover, we do not immediately notice even its requests for help. One of the common symptoms of many diseases is colorless stool. Below we will look at the main reasons for its appearance, but please note: most often, colorless feces appear with serious liver diseases, including hepatitis, being one of its characteristic signs. And for any type of hepatitis, it is important to start treatment on time to avoid the disease becoming chronic, which can result in cirrhosis of the liver. It’s better to play it safe and see a doctor right away, without expecting that all the unpleasant signs of the disease will go away on their own.
In order to answer the question of why colorless feces suddenly appeared in a person, it is worth understanding how it is colored. It is considered normal if the stool is brown (light brown, dark brown). This is due to its composition, which includes digested food and processed bilirubin. If the process of removing bilirubin from the body is disrupted, the stool becomes discolored. The fact is that bilirubin comes from the liver to the intestines along with bile. There it is converted into a new substance, the pigment - stercobilin, which has a golden brown hue. If the supply of bilirubin stops, the pigment substance ceases to be produced, and the stool loses its brown color.
Causes of grayish-white stool
Errors in diet
The discharge of gray feces in adults is observed after excessive consumption of fatty foods.
Excessive amounts of neutral fats accumulate in the intestines; due to the increased load on the pancreas, lipids are not digested and are excreted in the feces. The consistency changes - the feces become soft, “greasy”, leaving marks on the walls of the toilet. Typically, stool frequency increases up to 3-4 times a day. Usually the symptoms disappear on their own, and the color of the stool normalizes the very next day. The reasons that provoke the passage of grayish-white stool in infants are improper introduction of complementary foods, the use of unbalanced milk formulas. Changes in the color of feces occur against the background of general weakness and lethargy of the child, constant crying and refusal to feed. These symptoms are an indication for consultation with a pediatrician.
Dysbacteriosis
Violation of the composition of the intestinal microflora causes digestive disorders and insufficient digestion of incoming food. The stool becomes liquid and grayish-white or dark gray in color. The frequency of stool with dysbacteriosis increases to 5-7 times a day, defecation is preceded by spasms and discomfort in the left abdomen. The stool has a foul odor and a light gray coating can be seen on the surface.
Hepatitis
Infectious causes cause destruction of liver cells and disturbances in bilirubin metabolism, which reduces the flow of stercobilin into the intestines, which colors stool brown. Gray feces appear at the height of hepatitis; the symptom is combined with a sharp darkening of the urine and yellowing of the skin. An increase in stool frequency and a change in its consistency are typical; before defecation, patients feel rumbling and “bubbling” in the abdomen.
The duration of the symptom depends on the type of liver inflammation. In mild forms of viral hepatitis A and E, grayish-white stool discharge persists for 2-3 weeks. With hepatitis B, the color of stool returns to normal after 1-2 months; in case of severe damage to the liver parenchyma, dark gray feces are excreted for up to six months. Alcoholic hepatitis, complicated by damage to the pancreas, often causes persistent lightening of the stool.
Cholelithiasis
The discharge of grayish-white feces indicates an exacerbation of cholelithiasis and blockage of the bile duct with a stone. In this case, bile does not enter the intestines, and symptoms of obstructive jaundice develop. The person notices that the stool becomes light, almost white, and the consistency of the stool often remains normal. Discoloration of the stool occurs simultaneously with severe pain in the right hypochondrium, nausea, and bitterness in the mouth.
Pancreatitis
A change in the color of stool to white in adults occurs with chronic pancreatitis, which is characterized by enzyme deficiency of the pancreas. The light color is due to the accumulation of undigested food in the feces. The stool is copious, grayish-white in color, with a strong fetid odor. There is an increase in stool frequency; during defecation, patients experience diffuse abdominal pain.
Disorders of pancreatic function are often irreversible, therefore, without prescribing replacement therapy, restoration of normal stool color is impossible. The patient's condition worsens under the influence of external causes - with the abuse of heavy food, drinking alcohol, the disease worsens. During this period, diarrhea with the release of a large amount of light-colored feces, accompanied by intense pain in the left hypochondrium and epigastrium, is a concern.
Other liver pathologies
Damage to liver cells of various etiologies is accompanied by parenchymal jaundice, which is typically characterized by the appearance of a grayish-white color of stool. Such changes persist for a long time, for several months. Abnormal bowel movements are associated with dull pain and heaviness in the right hypochondrium, nausea and vomiting with bile. Most often, stool discoloration is caused by the following reasons:
- Cirrhosis
: alcoholic, postnecrotic, biliary. - Space-occupying formations
: hepatocellular carcinoma, hydatid cyst, polycystic liver disease. - Functional disorders
: Gilbert's syndrome, Crigler-Najjar syndrome, cholestasis of pregnancy.
Complications of pharmacotherapy
A short-term change in the color of stool to grayish-white is a natural reaction after taking barium sulfate orally for X-rays of the digestive tract. Light-colored stool passes 10-12 hours after the examination; the atypical color of stool persists for 2-3 days. Normally, these changes are not accompanied by dyspeptic disorders or abdominal pain.
Gray feces are also provoked by other reasons: taking antacids, iron. Microelements, which are contained in large quantities in these medications, accumulate in the feces and cause the appearance of a characteristic grayish-white color. When using iron supplements, the color becomes darker, even black. Discoloration of stool is possible with prolonged use of antibiotics and anti-tuberculosis drugs.
Rare causes
- Inflammatory bowel diseases
: Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis, chronic enteritis. - Celiac disease
. - Malignant tumors
: cancer of the head of the pancreas, cancer of the duodenum. - Bile duct atresia
.
Basic therapy
What to do and how to treat light-colored stool depends on the etiology of the symptom. If a change in the shade of stool is due to a violation of the digestive function, first of all a diet correction is required. If you have diarrhea in the first days, you need to adhere to a dietary diet with the exception of fatty and fried foods. Food is taken in ground form.
After several days, it is recommended to include fruits and vegetables and fermented milk products in the diet. Decoctions and infusions of medicinal herbs are useful. Food is taken fractionally, that is, in small portions, but often throughout the day. This makes it easier for the digestive system to function.
If the symptom is due to an infectious disease, antibacterial drugs are required. With a parasitic etiology of the symptom, antiparasitic drugs in the form of tablets will be required.
For liver diseases that occur with stool discoloration, hepatoprotectors are prescribed.
During the period of exacerbation of certain diseases (for example, pancreatitis or hepatitis), the patient is hospitalized urgently. If the symptom occurs due to the formation of a tumor-like neoplasm, chemotherapy or radiation therapy and surgery are prescribed.
Diagnostics
A gastroenterologist is involved in identifying the cause of gray stool. The specialist collects anamnesis and complaints to determine why dyspeptic disorders appeared. Diagnostics includes instrumental visualization methods, which, if indicated, are supplemented with invasive techniques. To clarify the diagnosis, laboratory tests are prescribed. The most informative methods:
- Coprogram
. Microscopic analysis of grayish-white stool reveals remains of undigested food, muscle fibers, and starch grains. The absence of stercobilin is pathognomonic. To confirm the diagnosis of pancreatitis, a fecal elastase level test is performed. Bacteriological analysis is necessary to identify dysbiosis and bacterial overgrowth syndrome. - Blood chemistry
. With obstructive jaundice, cholestasis syndrome is determined - an increase in the amount of cholesterol and the enzyme alkaline phosphatase. An increase in ALT and AST levels indicates cytolysis and parenchymal jaundice. To test the exocrine function of the pancreas, the concentration of pancreatic lipase and amylase is measured. - Ultrasonography
. In order to detect the organic cause of a grayish-white stool, a survey ultrasound of the abdominal cavity is performed with targeted scanning of the organs of the hepatobiliary zone. The study allows you to visualize signs of the inflammatory process of the gallbladder, heterogeneous echogenicity of the liver parenchyma, and rounded volumetric neoplasms. - Duodenal sounding
. To assess the flow of bile into the intestine, several portions of bile are taken sequentially after stimulation with secretory drugs. Typically there is a slow release of bile or its complete absence in case of blockage of the common bile duct. The collected material is sent to the laboratory for bacteriological analysis. - Cholangiopancreatography
. White feces usually appear when the biliary tract is damaged, so RCCP is required. The method involves examining the papilla of Vater and bile ducts using endoscopic technologies. The study reveals stones in the bile ducts, signs of inflammatory and tumor pathologies.
Complications and prevention
One of the common complications when lightening stool is icteric syndrome. This can be explained by increased accumulation of bile fluid in the organs. Characteristic symptoms are yellowing of the skin and mucous membranes.
The type of negative consequences largely depends on the primary disease. For example, with the development of hepatitis, complications such as inflammatory diseases of the biliary tract and hepatic coma occur.
To prevent the occurrence of light-colored stool, the following recommendations should be followed:
- adhere to a balanced diet, do not abuse unhealthy foods (fatty and fried foods, as well as alcoholic beverages);
- observe the diet and eating conditions: frequent meals are useful, but in small portions, at the same hours every day, foods are subjected to heat treatment to eliminate pathogenic microorganisms;
- avoid overeating (standard portion - 300-400 ml in liquid form);
- control weight, treat obesity in a timely manner;
- stop smoking and taking drugs, eliminate stressful situations;
- lead an active lifestyle.
If the stool is discolored, this indicates a malfunction of a certain internal organ. The cause can only be determined by the results of a comprehensive diagnosis prescribed by a doctor.
Treatment
Help before diagnosis
Grayish-white stool caused by dietary errors does not need to be treated. The patient is advised to eat easily digestible foods (stewed vegetables, soups, lean meat) for several days and reduce the size of portions. You can't drink alcohol. If during this time the stool has not returned to normal, you should consult a doctor to determine the cause of the disorder.
To avoid diarrhea and stool discoloration when taking antibiotics and other toxic drugs, it is advisable to drink natural kefir and yogurt, which are rich in beneficial bifidobacteria and lactobacilli. Self-administration of enzyme preparations to improve digestion is not recommended, as this can cause disruption of the pancreas.
Conservative therapy
Treatment of dyspeptic disorders, including grayish-white feces, is mainly aimed at eliminating the cause of the symptoms, after which the color and consistency of the stool normalizes. Medications must be supplemented with a special therapeutic diet, which is selected depending on the disease. In clinical practice, the following drugs are used:
- Enzyme preparations
. Medicines containing pancreatic extract improve the processes of parietal and cavity digestion in the small intestine. Gray feces disappear a few days after starting medication, and the severity of other dyspeptic disorders decreases. - Probiotics
. They are a mixture of beneficial bacteria that populate the large intestine and prevent the proliferation of pathogenic microflora. In adults, they are prescribed for long-term antibiotic therapy and combined with prebiotics, which stimulate the growth of bifidobacteria. - Choleretic agents
. They increase the contractility of the gallbladder and dilate the ducts, improve the colloidal properties of bile, due to which it is released into the intestines in the required quantities. Additionally, hepatoprotectors are recommended, which protect cells from the toxic effects of bile acids. - Antiviral drugs
. For chronic hepatitis of viral etiology, special treatment regimens with interferons and RNA polymerase inhibitors are used. Medicines reduce the viral load in the blood and inhibit viral replication in liver cells. They are combined with detoxification agents.
Nutrition
However, when you see colorless stool, you should not immediately start to panic. Its appearance can be caused by various reasons, some of them completely harmless. For example, having come to the village to relax in the summer, everyone unanimously attacked the fat cottage cheese, sour cream, and cream. And also homemade butter and lard... And now there’s a deviation from the norm. Therefore, if you notice changes, you should think about your diet and observe changes in stool color for several days. If you change your food, everything will return to normal in a couple of days.
After taking medications
There are a number of medications that can cause lightening of excrement. These include:
- antibiotics;
- anti-inflammatory drugs;
- antipyretics (aspirin, ibuprofen, paracetamol);
- antifungal agents;
- drugs for the treatment of tuberculosis;
- gout medications;
- drugs for the treatment of epilepsy.
If you have undergone an examination such as an x-ray of the gastrointestinal tract or other procedures in which it is necessary to take barium sulfate, then 2-3 days after the stool will very sharply lighten. When the barium is completely removed from the body, the excrement will return to its normal color.
After alcohol
What can be light in stool after alcohol abuse? Everything is connected with the fact that when drinking alcohol, the liver needs to cope with its functions - remove toxins from the body. If a person also abuses fatty foods, such a load on the organ is unbearable. A person may also notice the appearance of light-colored diarrhea.
In our body, the liver acts as a filter. Its main task is to pass all harmful substances through itself. If a person regularly drinks alcohol, the cells begin to break down. It takes time for the structure to recover. If it is not there, the process slows down each time, and hepatitis begins to develop. One of the symptoms of this serious disease is light-colored stool. Hepatitis can also be accompanied by darkening of the urine, yellowing of the sclera of the eyes, stabbing pain in the abdomen, etc.