Indicators of normal eye pressure
Experts say that the normal ophthalmotonus of a person over the age of 35 is 10-23 millimeters of mercury. This indicator helps preserve the required level of microcirculatory and metabolic processes that occur in the organs of vision. In addition, this ensures the maintenance of an appropriate state of the optical qualities of the retina.
If you do not begin to treat increased ocular hypertension in time, it will provoke the appearance of glaucoma, which can lead to blindness. , normal fundus pressure may change throughout the day . Therefore, if there is a suspicion that ophthalmotonus may be high, then it is worth keeping a graph of this indicator for at least one week.
It happens that patients' blood pressure rises in the morning, and decreases closer to the lunch period. But it also happens that in this or that person it can regularly “jump” throughout the day and this situation is normal for such a patient. You just need to remember that the difference between the evening and morning parameters should not be more than three millimeters of mercury.
IOP indicators in glaucoma
Diagnosis of glaucoma certainly includes an assessment of ophthalmotonus. The diagnosis is also supported by complaints of various visual impairments, changes in the fundus and perimetry.
Classification of IOP level:
- A – normal pressure (no more than 21 mm Hg);
- B – moderately high blood pressure (from 22 to 32 mm Hg);
- C – high (more than 33 mm Hg).
If the pressure level exceeds the norm by 2-3 mm Hg. Art. and there are no other symptoms, observation by an ophthalmologist and preventive examinations are necessary to detect glaucoma in the earliest stages. At this stage, it is possible to prevent the influence of negative factors that cause the progression of the disease.
For glaucoma, the main goal of treatment is to reduce IOP levels to individual values in order to prevent optic atrophy and vision loss. This pressure is called tolerant. If the disease is detected for the first time, then the target pressure level is 20-30% lower than the initial level.
With glaucoma, the patient is recommended to periodically visit the doctor for follow-up examinations: this helps to draw conclusions about the effectiveness of treatment. As necessary, the ophthalmologist adjusts the prescribed treatment regimen.
Why does eye pressure rise?
Eye pressure can increase due to a variety of factors. The most common reasons are:
- ailments associated with the cardiovascular system. These include atherosclerosis, varicose veins and a huge number of other diseases that affect the normal functioning of the heart;
- vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- diabetes;
- poisoning with substances of chemical origin;
- kidney disease: a wrinkled kidney and severe glomerulonephritis affect the retina and provoke high eye pressure;
- post-traumatic glaucoma. With glaucoma resulting from mechanical damage to the eyes, ophthalmotonus may be higher than normal;
- spending a long time in front of the display of a tablet or laptop.
These are just the most common factors that provoke an increase in intraocular pressure. People over the age of 40 are also at risk, since the older the person, the more often the disease appears. However, children are also susceptible to the disease, so parents are obliged to closely monitor the health of children and adolescents.
Risk factors that may cause increased IOP
Increased pressure inside the eyeball can also be caused by some common human diseases. That is why the doctor collects in detail all the data about your lifestyle, hereditary diseases, and even what activities you like to do in order to accurately establish the clinical picture. For example, an increase in ophthalmotonus can provoke disturbances in the functioning of internal systems or organs.
1. Diabetes mellitus. This is a group of endocrine diseases characterized by increased blood sugar, as well as the inability of the pancreas to produce the hormone insulin. The body experiences constant jumps in sugar from normal levels to high or, conversely, low. In this regard, problems begin with the condition of the blood vessels, causing an increase in arterial and intraocular pressure. 2. Vegetovascular dystonia. Persons suffering from VSD may complain of interruptions in heart function, decreases or surges in blood pressure, as well as headaches and dizziness. At the same time, the functioning of many body systems is disrupted. VSD can also cause an increase in ophthalmotonus. 3. Diseases of the cardiovascular system. Their list is quite extensive. These may be atherosclerosis, congenital heart disease, impaired elasticity of blood vessels, varicose veins and many other ailments affecting the normal functioning of the heart and blood vessels. 4. Kidney diseases. Severe and long-term glomerulonephritis, as well as a wrinkled kidney, can lead to retinal lesions and increased eye pressure. 5. The presence of uveitis, astigmatism, farsightedness and some other disorders can also cause an increase in IOP. 6. Post-traumatic glaucoma. Occurs after mechanical or chemical damage to the organs of vision. 7. Spending a long time in front of a computer monitor. Research by scientists has long confirmed the fact that prolonged exposure to a screen and intense visual work can provoke an increase in ophthalmotonus. The eyes are under constant tension, the person begins to blink several times less often, a headache may occur and the IOP may increase.
We have listed several factors that can cause increased intraocular pressure. In addition, people over 40 years of age are at risk, since the older the age, the more common the disease. However, increased eye pressure can also occur in children, so parents should be vigilant. If he has any visual impairments (myopia, astigmatism, lazy eye syndrome, etc.), then this is a reason to keep eye pressure readings in children under control.
Symptoms of ocular hypertension
signs indicate high ophthalmotonus :
- pain above the eyebrows and in the temple area. Pain also appears when the eyes move up;
- persistent headaches that do not disappear even after taking the medicine;
- cracked blood vessels on the whites of the eyes;
- feeling very tired in the evening;
- blurred vision after waking up, when it takes time for vision to normalize;
- when working visually, the eyes get tired quickly;
- When moving from a light room to a dark one, visibility decreases.
Eye pressure should be measured frequently . Symptoms of so-called ocular hypertension may sometimes not appear. Therefore, it is better to play it safe.
How are indicators measured?
To maintain normal eye pressure, ophthalmologists recommend that you undergo an examination and tonometry every year after reaching 40 years of age. Even if a person does not complain about eye health, this does not mean that problems do not exist. Ways to determine whether intraocular pressure is normal:
- The Maklakov method is the most disliked by patients, but has not lost its relevance over the years. During tonometry, an anesthetic is dripped into a person's eye, and then a weight weighing 5-10 grams is pressed against the pupil. The imprint that remains on the load is transferred to graduated paper and the result is read.
- Pneumotonometry - resembles the measurement of IOP according to Maklakov, but is not very accurate. Compressed air is directed to the patient's apple, and changes are recorded and interpreted as normal, increased or decreased.
- Electronography is a modern method of measuring ophthalmotonus, which is non-contact and characterized by high accuracy. It is not always possible to carry out the procedure in a regular clinic, since expensive equipment is required.
An annual examination is carried out as planned, this is especially important for patients diagnosed with arterial hypertension. It has been established that surges in blood pressure directly affect the condition of the fundus.
How to measure pressure?
At home, measuring eye pressure is very simple using the palpation method. You need to palpate the eyelids of the eyeball. You need to gently press on your closed eye with your fingers. At normal pressure you will feel a moderately round elastic ball. If the pressure is high, then it will be very hard and will not deform. This method does not provide reliable indicators and is suitable exclusively for primary “home” diagnostics.
If this method does not give accurate results, then how is intraocular pressure measured to obtain an accurate indicator? This is done using a non-contact tonometer or Maklakov tonometer.
Prevention of increased intraocular pressure
For minor IOP deviations, a positive result can be obtained by following the following recommendations:
- Enriching the diet with foods rich in omega-3, vitamins A, C and E.
- Buy a high-quality high pillow that provides an elevated position of the head during sleep.
- Do regular eye exercises.
- Wear safety glasses when working on a computer monitor or tablet.
- Correctly organize the workload on the eyes. Take breaks every half hour.
- Avoid excessive participation in strenuous sports.
- Replace caffeinated drinks with herbal infusions with blueberries.
- Do not be nervous. To do this, learn to cope with stressors through relaxation and sports.
Have your vision checked annually by an ophthalmologist. This is especially necessary to do in adulthood. Small changes in intraocular pressure occur unnoticed, but they negatively affect the condition of the visual apparatus. If you want to keep your eyes healthy and your vision clear into old age, don't neglect eye exams.
What to do to reduce blood pressure?
People suffering from ocular hypertension are interested in how to reduce eye pressure. Special drops best cope with this task, but they must be prescribed by an ophthalmologist. If it is not possible to see a doctor in the near future, then reduced with the help of a tincture of sleep grass, wild pear shoots and nettle. A decoction prepared from these herbs should be taken three times a day before meals.
Doctors also recommend instilling a solution made from onion juice and good honey into the eyes.
What is low ophthalmotonus
In addition to increased IOP, low blood pressure also occurs, although much less frequently. This condition may be caused by the following reasons:
- retinal detachment;
- inflammatory processes in the eyes;
- eye injuries;
- low blood pressure;
- dehydration and some others.
With reduced ophthalmotonus, the following symptoms are observed: dry eyes, painful sensations when blinking, pop-up dots, burning, blurred vision. Low IOP is no less dangerous than high IOP. Clinical examination of this condition reveals papilledema, venous congestion, maculopathy, papillar atrophy, vitreous opacities, and keratopathy. Visual functions deteriorate significantly.
How to treat illness and its prevention?
The most effective treatment for elevated intraocular pressure is surgical intervention. This is the most radical way. They resort to it if it was not possible to achieve the desired result with the help of physiotherapeutic procedures such as vacuum massage or color pulse therapy.
prophylaxis will help prevent both the operation and, in fact, the onset of illness . If you are at risk, it is incredibly important to adjust your own diet. You should limit the consumption of salt and fast carbohydrates, and enrich the menu with vegetables, red fruits, and dark chocolate.
You should also avoid clothes that have tight collars. You should not tighten your tie and unbutton the top button. In another case, the outflow of blood that comes from the veins of the head is disrupted.
It is recommended to minimize visual and physical stress. Try to avoid emotional stress and overload. As a preventive measure, it is better not to drink excessive amounts of liquid and forget about tea and coffee altogether.
Norms of ophthalmotonus for different ages
What should normal eye pressure be? The statistical norm, which is recorded by the tonometry procedure, ranges from 10 to 21-23 mm Hg. Average values usually range from 15-16 mmHg. for adults and teenagers over 15 years old. After reaching age 60, normal values change slightly as the body undergoes natural physiological changes.
It should be noted that the pressure inside the eyes is not a constant value; it changes under the influence of a number of factors
For older people, an IOP of about 23-26 mm Hg is considered acceptable. This includes active sports, playing wind musical instruments, prolonged eye strain due to working at the computer, etc. The time of day also influences what pressure is considered normal.
It has been established that closer to dawn, IOP begins to increase and reaches maximum levels, but in the evening hours it decreases. And doctors should take this fact into account when performing tonometry. Although at first glance, at night, the secretion of aqueous fluid slows down and the pressure should be lower, this is not the case in all patients.
The norms for ophthalmological pressure indicators differ on general and age-related grounds. Next, we will talk about specific milestones at which the ophthalmotonus begins to differ, and the following table reflects general information about IOP and the risk of developing glaucoma.
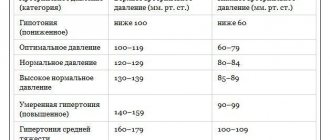
| Pressure | Tonometric (mm Hg) | True (mmHg) |
| Normal | 12—25 | 10—20 |
| Initial stage of glaucoma | Up to 26 | 21—22 |
| Moderate glaucoma | Up to 36 | Up to 26 |
| Average | — | Up to 33 |
| Chronic | — | Over 33 |
Now we need to consider what pressure of intraocular fluid is typical for patients of different ages:
Why does blood pressure rise in the evening?
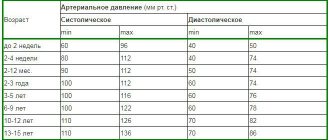
- young patients under 40 years of age - ophthalmological diseases develop quite rarely during these years, but intraocular pressure disorders may still occur. For young people, the norm is 10-18 mmHg;
- patients after 40 years - the body is already beginning to age, the capillaries lose their former elasticity, which is why the IOP rate increases to 10-21 mm Hg;
- patients aged 50 years – their pressure levels out, provided that there are no congenital or acquired anatomical defects of the eyeballs and capillary network. After 50-55 years, values from 10 to 23 mmHg are considered normal;
- patients over 60 years of age - their body is more exhausted, the retina undergoes significant changes, which brings an increase in intraocular pressure to 26 mm Hg.
The female sex is susceptible to diseases of an ophthalmological nature much more often, this is due to the activity of the hormone estrogen. IOP in male patients increases more gradually, which is why ocular hypertension is often diagnosed late, in the presence of serious changes in the structure of the visual organs.
After 70 years, the normal pressure inside the eye is 10-27 mm Hg, and elderly patients, due to irreversible age-related changes, often suffer from glaucoma and cataracts. Surgery is considered a suitable treatment option for them, since drug therapy is not able to produce positive results.
In women, especially during menopause, ophthalmotonus increases more sharply than in men
How to maintain normal ophthalmotonus
To avoid long-term treatment with medications and not lead to surgical intervention, you need to follow simple rules for the prevention of increased ophthalmotonus:
- sleep at least 8 hours a day and avoid stressful situations;
- if there is no need, do not spend a long time in front of a computer monitor;
- work in good lighting to reduce eye strain;
- do not wear clothes with tight collars and buttons to ensure normal blood flow in the cervical-collar area;
- eat right, limiting the amount of salt in dishes, avoiding fried, spicy and smoked foods;
- drink 1.5 liters of clean water per day;
- Raise the pillow during night sleep to ensure proper drainage of aqueous fluid from the eye.
It has been established that bad habits (drinking alcohol and smoking) contribute to pathological narrowing of blood vessels.
As a result, the blood supply to internal organs, the brain and the organs of vision deteriorates. Otherwise, it is fraught with the development of hypertension, other systemic diseases and increased ophthalmotonus. Therefore, if you are prone to eye pressure, it is better to make a choice in favor of a healthy lifestyle.
It must be remembered that normal eye pressure is different for everyone, but it is necessary to adhere to generally accepted standards. If you notice symptoms such as eye fatigue, redness and dryness of the apples, migraine-type headaches, deterioration of visual function, you should immediately visit an ophthalmologist. This will allow you to start treatment on time, if necessary, and reduce the risk of developing glaucoma.