Everyone knows that normal blood pressure should be 120 over 80, but the tonometer does not always provide such indicators. In modern life, when doctors increasingly diagnose hypertension and hypotension, pressure surges are not uncommon.
What to think if the tonometer showed a pressure of 100 over 70, can this be perceived as normal in an adult, a pregnant woman or a child, what causes this condition - today we will talk about this. Everyone’s pressure standards are different, so don’t panic if the device records underestimated readings. Whether there is cause for concern is up to a specialist to decide.
What is normal pressure
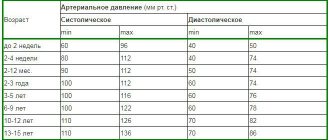
The generally accepted norm for blood pressure (BP) is 120/80 in adults and adolescents over 15 years of age. If the tonometer shows 100/70 or 100/60, this is already considered a sign of hypotension. For children, such indicators are considered normal if the child is under three years old. Women often record their blood pressure as 100/70 and have no complaints about their health, but for men the minimum threshold is higher - approximately 110/75.
As the body grows and ages, the tonometer readings normally become higher and higher, so if the device shows 100/70 in an elderly person, this indicates diseases of the cardiovascular system. For another category of people, 100/70 is a normal indicator: athletes. Regular physical activity contributes to a complete supply of oxygen to the blood and stable functioning of the heart and blood vessels.
When playing sports, the heart muscle is trained, the pulse increases, but returns to normal on its own after the end of the exercise. To measure your own blood pressure and understand whether it is normal for a person’s age, you must comply with the following conditions:
- measure blood pressure in a calm environment, do not talk, do not laugh, do not touch the cuff and tubes of the device with your hands;
- a person should not feel hungry or want to go to the toilet;
- Do not drink drinks containing caffeine before measurement - then the results will be unreliable;
- after the measurement, compare the results obtained with heart rate indicators (if the pressure is normal or slightly below it, and the pulse is above 90 at rest, this is a sign of a problem).
So, for each gender and age, blood pressure standards are different. But today we need to talk about why the tonometer readings remain at 100/70, whether this condition is dangerous, and in what cases it is considered acceptable.
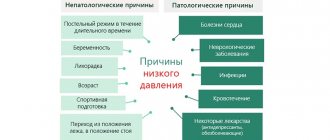
Why does blood pressure decrease?
{banner_banstat3}
Minor, short-term fluctuations in blood pressure downward are not considered a pathology when they spontaneously normalize. Their cause may be lack of sleep, excessive mental or physical fatigue, or stress.
The reason for pressure fluctuations may be the time of day. Under the influence of various reasons, this indicator changes several times during the day. Therefore, doctors recommend monitoring blood pressure twice – in the morning and in the evening.
With numbers of 110 over 70 or similar values, hypotension is not diagnosed; it is characterized by numbers below 100/60.
The cause of a slight decrease may be many external and internal factors, including serious diseases. These include:
- overwork, stress;
- chronic lack of sleep;
- regular physical overexertion;
- smoking, alcohol;
- problems with the endocrine or nervous systems;
- hormonal disorders;
- tumors;
- head injuries;
- bleeding of various nature;
- inflammatory process with high fever;
- prolonged vomiting or diarrhea;
- mental disorders;
- severe infections (tuberculosis, HIV, syphilis);
- some heart pathologies.
Long-term use of certain medications (diuretics, antihypertensives) can also cause a persistent decrease in blood pressure.
Causes and symptoms of hypotension
Blood pressure of 100/70 in a person whose usual readings are 120/80 can be caused by various reasons. If this is not the norm, then it is considered a signal of the presence of pathological internal and external problems:
- diseases of the heart and blood vessels - varicose veins, atherosclerosis, the formation of blood clots and plaques in the capillary cavity, increased cholesterol levels in the blood, iron deficiency anemia;
- head injuries - in this case there is insufficient blood supply and oxygen starvation develops;
- frequent stressful and conflict situations;
- pinched nerves in the thoracic and cervical spine - this leads to blocking of blood flow and a decrease in blood pressure in the vessels;
- bleeding, including internal bleeding - due to blood loss, the volume of circulating fluid decreases, pressure drops;
- vegetative-vascular dystonia - the condition is manifested by increased weather sensitivity, irritability, poor sleep, pressure surges, sweating, dizziness and malaise.
What symptoms do a person exhibit due to hypotension with a blood pressure of 100/70? He feels dizzy, lethargic and apathetic, and wants to go to sleep. As a result of lack of oxygen, yawning becomes more frequent and shortness of breath may occur. If a high pulse is noted, this condition is considered dangerous and requires medical attention.
Particularly low blood pressure manifests itself in older people - they have ringing in their ears, increased sweating, “spots” flashing before their eyes, and coordination in space may be impaired. The older a person is, the higher his blood pressure should be, so the body compensates for the lack of oxygen and nutrients in the tissues. But when blood pressure drops, irreversible processes occur in the blood vessels and heart muscle, which requires urgent doctor intervention.
What is upper and lower blood pressure?
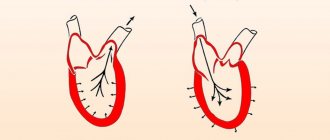
Blood or arterial (hereinafter referred to as blood pressure) is the pressure of blood on the walls of blood vessels. In other words, this is the pressure of the fluid of the circulatory system, exceeding atmospheric pressure, which in turn “presses” (impacts) everything that is on the surface of the Earth, including people. Millimeters of mercury (hereinafter referred to as mmHg) is a unit of measurement for blood pressure.
The following types of blood pressure are distinguished:
- Intracardiac or cardiac , occurring in the cavities of the heart during its rhythmic contraction. For each part of the heart, separate normative indicators have been established, which vary depending on the cardiac cycle, as well as on the physiological characteristics of the body.
- Central venous (abbreviated as CVP), i.e. blood pressure of the right atrium, which is directly related to the amount of venous blood returned to the heart. CVP indicators are of utmost importance for diagnosing certain diseases.
- Capillary is a value that characterizes the level of liquid pressure in the capillaries and depends on the curvature of the surface and its tension.
- Blood pressure is the first and, perhaps, the most significant factor, by studying which a specialist makes a conclusion about whether the body’s circulatory system is functioning normally or whether there are deviations. The value of blood pressure indicates the volume of blood that the heart pumps in a certain unit of time. In addition, this physiological parameter characterizes the resistance of the vascular bed.
Since it is the heart that is the driving force (a kind of pump) of blood in the human body, the highest blood pressure values are recorded at the blood outlet from the heart, namely from its left stomach. When blood enters the arteries, the pressure level becomes lower, in the capillaries it decreases even more, and it becomes minimal in the veins, as well as at the entrance to the heart, i.e. in the right atrium.
Three main indicators of blood pressure are taken into account:
- heart rate (abbreviated HR) or pulse;
- systolic , i.e. upper pressure;
- diastolic , i.e. lower.
What does a person's upper and lower blood pressure mean?
Upper and lower pressure indicators - what are they and what do they influence? When the right and left ventricles of the heart contract (i.e., the process of heartbeat occurs), blood is pushed out in the systole phase (the stage of the heart muscle) into the aorta.
The indicator in this phase is called systolic and is recorded first, i.e. is essentially the first number. For this reason, systolic pressure is called upper. This value is influenced by vascular resistance, as well as the frequency and strength of heart contractions.
In the diastole phase, i.e. in the interval between contractions (systole phase), when the heart is in a relaxed state and filled with blood, the value of diastolic or lower blood pressure is recorded. This value depends solely on vascular resistance.
Let's summarize all of the above using a simple example. It is known that 120/70 or 120/80 are the optimal blood pressure values for a healthy person (“like astronauts”), where the first number 120 is the upper or systolic pressure, and 70 or 80 is the diastolic or lower pressure.
What do the numbers 100/70 mean in a child?
If in an adult a tonometer reading of 100/70 is considered normal or low, then for a child this can be a sign of hypertension. The generally accepted norms of 120/80 and 130/90 are no longer perceived as appropriate here. At birth, a child's blood pressure level is 70/50, and as they grow older, these numbers increase. If the baby is 2 years old, then a blood pressure of 100/70 is normal for him and doctors will not diagnose him with hypotension.
Upon reaching the age of 15, the blood pressure norms of a teenager approach those of adults, but due to the individual characteristics of the child’s body, tonometer readings are still sometimes perceived as hypertension. Parents may suspect a problem based on the following signs:
- sleep disturbances – the child has difficulty falling asleep, he wakes up in the middle of the night and is capricious;
- increased irritability - it is accompanied by touchiness, tearfulness for no apparent reason, outbursts of aggression;
- lack of interest in what peers are doing;
- poor appetite - the child is not interested in food, unlike children who are in good health.
If a child sleeps well, eats well, is alert and cheerful, then there is nothing to worry about, and blood pressure readings of 100/70 are normal for him.
Why can a diagnosis of hypertension be made in childhood? There may be several reasons, one of them is heredity. If the mother or father is hypotensive, then for the child the upper pressure within 100 is considered elevated. Also, pressure indicators depend on living conditions or changes in climatic conditions - they often determine the normal blood pressure level.
Regular sports and physical labor lead to greater stress on the heart and the body as a whole. At the same time, blood circulates fully through the vessels, and the heart does not need to increase pressure in order to normalize blood supply. As it became clear, the reasons why pressure can vary are different, and indicators of 100/70 are not always perceived as pathology.
Diagnostics
Conducted by a cardiologist. According to indications, consultations with a neurologist, nephrologist, or endocrinologist are required. List of studies:
- General assessment of the patient's condition and life history. Allows you to determine the vector of further actions.
- Measure blood pressure in both arms and, if necessary, in the legs.
- Listening to heart rhythm and sound.
- Daily monitoring using an automatic Holter tonometer. Shows blood pressure dynamics over 24 hours.
- Electrocardiography. Used to identify primary and secondary heart pathologies.
- Echocardiography. Method for visualizing organ tissue. With hypotension, typical abnormalities are not observed, unless there are specific congenital and acquired malformations.
- General blood test, biochemical test, hormone test (T3, T4, TSH, aldosterone), as well as clinical urine test.
- Assessment of neurological status (several specific tests, checking reflexes).
The system may be different depending on the diagnostic purposes. She usually looks like this. In special cases, they are referred for ultrasound of the kidneys, MRI of the brain, adrenal glands, scintigraphy of the thyroid gland or excretory system.
Is this blood pressure normal for pregnant women?
In women, a pressure of 100 over 70 during the period of bearing a child is perceived as quite normal, especially if at such indicators the pregnant woman feels well, and tests indicate the correct formation of the fetus. The female body is more changeable in terms of hormonal status and blood pressure due to the fact that its main functions are bearing children and childbirth.
Therefore, changes in hormonal levels affect the tonometer readings, especially since an additional circle of blood circulation appears in the body. An increased load is placed on the heart and blood vessels of the expectant mother, as a result of which pressure indicators also change. As the fetus develops in the womb and grows, the body tries to independently ensure relaxation of the uterus and prevent increased muscle tone and premature birth.
Therefore, the tonometer readings are recorded as underestimated, even if before pregnancy the normal blood pressure for a woman was 120/80 or 130/90. If the fetus is feeling well and is developing properly, there is no reason for concern in such a situation. The expectant mother should be wary if her blood pressure range is constantly fixed at 102-103 over 65 or 95 over 60.
Such symptoms of hypotension signal a threat of premature delivery or early miscarriage. If blood pressure drops to such limits and remains at this level, the child may have a heart attack in utero, oxygen starvation may begin, a blood clot may form in the placental tissue, or internal organs may not form properly.
If such symptoms occur, doctors try to monitor the pregnant woman in a hospital setting, where they can take emergency measures to stabilize the woman’s blood pressure and well-being. Moreover, with low blood pressure, she constantly has a headache, lethargy, drowsiness and tinnitus.
Do not think that blood pressure of 100/70 for a pregnant woman is a bad diagnosis. In the first trimester of pregnancy, such indicators are observed in most women, since during this period the hormone progesterone is intensively produced. It is necessary for the normal functioning of the uterus, full access to it of oxygen, vitamins and microelements. After a while, the pressure may return to normal levels and the woman’s condition will stabilize.
When is 110/70 normal?
{banner_banstat1}
Such tonometer numbers are a fairly common indicator and are in no way related to pathology. There are a lot of people for whom this level is comfortable and ideal.
Moreover, we are talking specifically about healthy people. These include:
- Teenagers. The blood pressure of a growing organism is prone to some fluctuation. During puberty (12-16 years), it is especially close to 110/70.
- Young women. Girls under 25 years old have indicators slightly above the lower normal limit.
- Persons of asthenic type. If you have a thin, toned physique, this is the most common level of pressure.
- Athletes. The decrease in performance is due to their long years of training with significant physical effort.
- Pregnant women. For women in the first trimester, a slight decrease in blood pressure of up to 10-15 points is typical. This is explained by the onset of hormonal changes.
In addition, many people live their entire lives with exactly these values, due to the characteristics of the cardiovascular system.
For older people, a reading of 110/70 is low and may be uncomfortable. As a rule, this level indicates poor blood circulation, which causes oxygen starvation of internal organs and the brain. The exceptions are persons of thin build, short stature, or former athletes.
In children of the first year of life, such values are a warning sign. It is significantly higher than normal, which may indicate the development of hypertension.
Pulse is an equally important indicator
If the tonometer readings fluctuate around 100/70, this is not yet a reason to take urgent measures - you need to take into account what the person’s normal working pressure is. Perhaps, due to the individual characteristics of the body, this level of blood pressure does not cause discomfort to a person.
Modern tonometers reflect pressure and pulse simultaneously
But heart pulsation must be taken seriously, since this indicator provides definitive information whether the patient needs therapeutic treatment. Also, the heart rate allows you to determine what kind of help to provide to yourself or a loved one if there is no doctor nearby and there is no opportunity to undergo an examination. So, which condition is considered normal and which is pathology:
Medicines to increase blood pressure in tablets
- Pressure 100 over 70, pulse 60-65-70-75 - these indicators are within the normal range, especially if the person does not experience any discomfort and does not show additional signs of hypotension. A rapid heartbeat can occur with anxiety, increased physical activity, or stress.
- Blood pressure 100 over 70, pulse 80-85-90-95 - this condition is sometimes also considered normal, but more often it indicates an attack of tachycardia. With a rapid heartbeat, the body tries to compensate for the insufficient supply of blood and oxygen to the heart muscle. The doctor can make an assumption about the onset of anemia and refer the patient to donate blood to determine hemoglobin levels.
- Blood pressure 100 over 70, pulse 100-110 - what does this mean? As a result of a decrease in blood pressure, which no longer fits within the normal range for a particular patient, heart problems arise. There is another explanation for this condition - it is a pinched nerve in the thoracic spine, which results in the development of symptoms similar to cardiac pathology.
If a person feels that an increase in pulse with low blood pressure to 100/70 (if previously such pressure was normal for him) affects his well-being, such symptoms should not be ignored. Any deviation from the norm should be a reason to visit a specialist, undergo an ECG and ultrasound.
Signs of emergency conditions
- Sharp headache. It's like being hit with a hammer. Baling, pressing, accompanied by other signs.
- Speech disorders. The tongue is not obeyed. You can test yourself at home by simply trying to say a simple phrase.
- Facial distortion. As a result of paralysis of facial muscles. Indicates damage to the cranial nerves.
- Inability to control half of the body.
- Severe, aching, dull pain behind the sternum with the development of shortness of breath and suffocation. Accompanying heart damage.
- Transient (passing) blindness or deafness.
These are symptoms of a heart attack or stroke. The intensity doesn't matter. Temporary ischemic attacks are possible. They precede a full-blown emergency.
If at least one sign is detected, you need to call an ambulance. Getting to the hospital on your own is dangerous.
Is hypotension dangerous?
If the pressure is constantly in the low range, the person feels unwell (the symptoms of hypotension have already been discussed). But this is only the smallest of the problems, because with the chronic course of the pathology, oxygen starvation of the muscles and internal organs develops. They also do not receive the required amount of blood, as a result of which the natural functionality of the body is disrupted.
The most dangerous situation is considered to be when the pressure is low and the heart rate increases. In this way, the heart tries to compensate for the resulting lack of oxygen - it tries to pump more blood so that the tissues do not experience hypoxia. In this situation, you should consult a doctor to avoid serious consequences.
As already mentioned, hypotension in pregnant women can lead to intrauterine malformations of the child and even miscarriage. Therefore, you should not take low blood pressure as a trifle; it is often more dangerous than a pressure of 150/100, because the body develops cardiogenic shock.
Typical complications
Contrary to ideas, an arterial indicator of this kind is by no means safe.
The probability of consequences for the body is 5-8%, with a further decrease in blood pressure levels - 12-15%. Treatment should begin at the 90 to 70 stage; this is the best moment when you can be completely cured and forget about the disease.
Possible complications include:
- Fainting. A common problem that can occur to the patient several times a day. Injury and death are possible as a result of loss of control over the situation.
- Ischemic stroke. Insufficient trophism of nerve tissue will lead to the death of entire groups of neurons. The result is neurological deficit of varying degrees of intensity. From minimal changes to total disruption of fundamental functions. Damage to the brain stem can result in death.
- Cognitive problems. Dementia. Decreased memory and intensity of mental activity. As a result of constant hypoxia of the cerebral cortex.
- Problems with vision and hearing as an outcome of the same ischemia.
How to help hypotension
What should you do if your blood pressure suddenly drops to 100/70, but such tonometer readings are not typical for a person? First of all, measure your pulse and, if necessary (if it increases to 85-100), consult a doctor. You can do the following yourself:
- open the windows in the room to ensure the flow of oxygen - this will help overcome drowsiness and eliminate headaches (in stuffy rooms, pressure can drop even in a healthy person);
- drink a cup of tea or coffee - the drinks contain caffeine, which will raise the pressure by 5-10 units, and the person will immediately feel better (it is better if the tea or coffee is with sugar);
- lie in a horizontal position and raise your legs to a level above your head - lie there for 15-20 minutes to ensure blood flow to the heart and brain;
- take a Citramon tablet – it contains caffeine, which increases blood pressure in hypotensive patients;
- calm down if the drop in blood pressure is caused by stress or conflict.
There are few special medications to increase blood pressure, and they are prescribed only by a specialist after examination and clarification of the causes of hypotension. You should not take the pills yourself.
You can reconsider your lifestyle - adjust your daily routine, rest more, sleep at least 7 hours a day, walk in the fresh air more often. Regular cardio exercise is also useful so that the heart muscle is trained and the organs do not experience oxygen deficiency. Such measures will help keep your blood pressure under control and prevent it from falling below the required limits.
If with a blood pressure of 100/70 a person feels well, does not experience discomfort, weakness or dizziness, and the pulse is normal, there is no reason to worry. This means that a slight decrease in tonometer readings is due to the individual characteristics of the body. But visiting a doctor for a preventive examination will not be superfluous, because it is better to keep the work of the heart and blood vessels under control than to then treat long-term and persistent diseases for a long time.
Pathological moments
They differ from the natural origin of the process. In this case, one or another disease is to blame. As a rule, we are talking about problems with the nervous system (brain), endocrine, and excretory structures.
Hypothyroidism
Lack of thyroid hormones in the bloodstream. It develops as a result of poor nutrition or a tumor process in the structure of the organ.
The disease can be detected by characteristic symptoms: weight gain for no apparent reason, neck pain, voice changes, dysphagia, loss of strength, and general decrease in performance.
Hypocorticism
This time it was pathology of the adrenal cortex. Also called Addison's syndrome. It occurs after operations on a paired organ or as a result of inflammatory, degenerative processes (autoimmune, infectious, toxic, medicinal).
It often occurs in people who are overly friendly with the green serpent, as a result of chemical trauma to the glands.
The symptoms are identical to those of hypothyroidism, only the pressure drops to even more significant levels.
In the early stages, when the body somehow compensates for the pathology, a level of 90/70 mmHg is possible. Art.
If you suspect a similar process, you need to undergo an ultrasound of the adrenal glands and an MRI, as well as a brain tomography to exclude pituitary tumors.
Problems with the spinal column
Osteochondrosis of the cervical spine plus vertebrobasilar insufficiency. Often the latter acts as a “pleasant bonus” to the damage to osteochondral structures.
Decreased vision, flickering spots, photopsia, problems with color perception, severe headaches in the back of the head and neck, vertigo, and spatial orientation problems develop.
Nausea and vomiting are also possible. Neurological manifestations do not subside, but gradually increase. The extreme point of the process is an ischemic stroke of the occipital lobe of the brain, which can lead to total cortical blindness.
Kidney diseases
They provoke a violation of the synthesis of renin, a special prehormone participating in the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone exchange system.
The fewer substances, the larger the lumen of the vessels. Constriction is not observed even in necessary cases, which ends in a persistent decrease in blood pressure.
It is easy to suspect pathologies of the excretory system; the following are noted: lower back pain, an increase or decrease in the daily volume of urine, false painful urges to visit the toilet, a change in the color of urine.
Causes of cardiac profile:
- Aortic dysfunction.
- Mitral valve stenosis.
- Heart failure.
- Having had a heart attack or stroke.
- IBS.
Causes of pressure 90 to 70: diseases of the nervous, endocrine, excretory systems or physiological factors. You can differentiate between one and the other both by symptoms and by objective signs, this will be more accurate.