There are different types of cells in the blood. One of them are monocytes. These are large cells that literally absorb bacteria, damaged structures of their own body and destroy them. An increase in the level of monocytes is a normal reaction of the body during an infectious disease or inflammatory process. But often an excess of monocytes can also indicate pathology. To reliably establish the cause, it is necessary to carry out appropriate diagnostics.
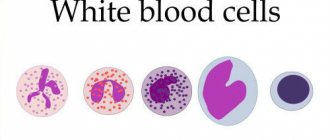
What are monocytes in the blood
Monocytes are a type of leukocyte - white blood cells. These are large formations with large nuclei. They are involved in protecting the body from inflammatory processes. Monocytes can penetrate the walls of blood vessels, leaving the blood and rushing to the site of inflammation. They destroy bacteria, viruses, as well as dead cells of their own body. It turns out that monocytes perform an important sanitary function.
This is especially important during infectious diseases. For example, if a person is sick with the flu, at this moment many cells of the oropharynx and nasal cavity are destroyed. Then monocytes will arrive in large numbers to the appropriate areas and digest the dead parts of the cells. In this case, the tissues will recover faster, which will contribute to overall recovery.
Decreased cell level
Monocytes and lymphocytes can rise and fall.
This deviation also indicates the presence of pathologies in the body or the influence of physiological factors. As for monocytic cells, their level will decrease in the following cases:
- If bacteria have entered the body and caused the development of severe infectious diseases or sepsis.
- If there are helminthic infestations in the digestive organs. To destroy them, many monocytes are produced, but most die in the process of fighting parasites.
- If a malignant neoplasm develops. In this case, the bone marrow is often affected, which then loses the ability to produce cells. As a result, lymphocytes, monocytes and neutrophils are reduced.
Lymphocytes decrease due to infectious, colds, and inflammatory diseases. Doctors identify provoking pathological conditions: AIDS, hepatitis, tuberculosis, pneumonia, sepsis, lupus, rheumatism, kidney failure, influenza, mononucleosis.
In addition to diseases, a reduced concentration of lymphocytes in a child’s blood is caused by radiation or chemical therapy, or taking certain medications.
What does it mean if monocytes are elevated?
In a normal state, the number of monocytes in the blood is as follows (per 1 liter of blood):
- for adults: from 0.04 to 0.08*109 cell units;
- for children: from 0.05 to 1.1 * 109 cell units.
If we talk about the norm in relative terms, then the number of monocytes should be 1% -10% of the total mass of leukocytes. Moreover, for children the optimal range is from 2% to 7%, and for adults – from 1% to 8%. If the concentration is greater than the specified values, this indicates increased monocytes in the blood. This disorder is called monocytosis.
Causes of monocytosis and lymphocytosis: what provokes deviations from the norm?
If we consider each formed element separately, then their increase can be caused by a variety of factors. When the number of monocytic cells increases, they speak of monocytosis. And when the level of lymphocyte bodies increases, the condition is called lymphocytosis.
Reasons for the development of monocytosis
- Acute infectious diseases or exacerbations of chronic inflammation (tuberculosis, influenza, endocarditis, candidiasis, syphilis);
- Autoimmune disorders (sarcoidosis, rheumatoid arthritis);
- Malignant neoplasms;
- Poisoning with toxic drugs, phosphorus;
- Oncological diseases of hematopoiesis (myeloid leukemia, lymphogranulomatosis);
- Appendicitis, sepsis.
The degree of increase in parameters indicates the severity of the immune system’s response to the development of the disease. The stronger the inflammation, the more macrophages are required for phagocytosis of foreign bodies.
- Increased level of lymphocytes in the blood
Reasons for the development of lymphocytosis
- Viral infection (mononucleosis, hepatitis, measles);
- Chronic lymphocytic leukemia;
- Poisoning of the body with chemicals (arsenic, lead);
- Taking medications (Levopod, Phenytoin, narcotic painkillers);
- Toxoplasmosis, leptospirosis;
- Crohn's disease;
- Endocrine diseases.
Increased lymphocyte levels are associated with a significant response to antigenic stimulation. They become larger than normal when a viral/bacterial infection occurs, as well as when cancer cells develop in the body.
The main reasons for the increase in monocytes in the blood
The main causes of monocytosis include:
- Infectious processes of bacterial origin, including syphilis, brucellosis, tuberculosis, endocarditis.
- Viral infections – hepatitis, mononucleosis.
- Diseases of the hematopoietic organs - leukemia.
- Malignant tumors.
- Rheumatism.
- Systemic lupus erythematosus.
- Recovery from infectious diseases.
- Previous surgical interventions.
- Entry of non-infectious substances (mainly through the lungs).
Important!
An increased level of monocytes does not always indicate a disorder. In some cases, this is a normal physiological state, for example, after eating, at the end of the menstrual cycle, and also in children under 7 years of age.
Simultaneous cell enhancement
Monocytes and lymphocytes are two types of white blood cells that determine the functioning of the immune system. If their level increases, this indicates that the immune system is fighting pathogenic microflora in an enhanced manner. The child’s defense mechanism works properly and clearly reacts to foreign agents.
When the level of lymphocytes and monocytes is increased in a child during the period of recovery from an infectious pathology, the disease has receded. This deviation from the norm is positive. It is also observed after surgery.
If two indicators increase during a viral pathology, then a bacterial infection may occur. The doctor checks the injection sites, examines the child’s body looking for redness, diaper rash, and purulent processes in the throat.
Low levels of indicators are observed in some diseases. Lymphocytes are reduced and monocytes are increased during inflammatory processes in the body. In this case, the doctor takes into account other research indicators, complaints and symptoms of the disease.
Monocytosis in children
An increase in monocytes in childhood is also often associated with infectious pathologies, mainly of a viral nature. If monocytosis is diagnosed based on a blood test, this means that the body is actively fighting disease-causing processes.
Also, a similar condition is observed with helminthic lesions - enterobiasis, ascariasis and others. After the destruction of helminths, the content of monocytes returns to normal. The cause may also be associated with tuberculosis, but such pathologies are rare. Monocytosis can be observed due to oncological processes. The most common are leukemia and lymphogranulomatosis.
Other common reasons:
- poisoning;
- allergic reactions;
- inflammation in the gastrointestinal tract;
- autoimmune pathologies;
- rheumatoid type arthritis;
- Crohn's disease;
- infections due to surgical interventions.
General information
Monocytes in the blood are representatives of a young group of cells; they are sent to tissues, from where monocytes emerge as mature histiocytes and macrophages. In addition, they migrate to the mucous membranes and skin, where they first meet agents of foreign origin.
Thus, macrophages and histiocytes perform phagocytosis of the pathogen. When monocytes become elevated, this is a sign of the presence of an agent of foreign origin in the tissues; accordingly, the monocyte level increases, since there is an increased need for macrophages. During their delivery to the tissues, the amount in the blood also increases, which is demonstrated in tests along with an increase in leukocytes and changes in other blood parameters.
Another important indicator that is often considered together with monocytes is lymphocytes. In the body, different functions lie on the “shoulders” of these cells:
Norm of ESR in children 2723
- What does it mean to have a decrease in neutrophils and an increase in lymphocytes in the human body?
- the process of starting and stopping the immune response;
- recognition of proteins of foreign origin;
- production of immunoglobulins;
- destruction of the pathogen cell;
- storing information about it and recording it in the genetic code.
Thus, lymphocytes perform immunity work in two directions. These are cellular and humoral immunity. Very often, the analysis does not use 100 percent of only one cell. For example, if neutrophils are low, this does not make it possible to make a diagnosis directly. It is important to consider high and low indicators together, and not separately. That is why it is often important for doctors to see the combination of monocyte and lymphocyte levels.
Against the backdrop of an integrated approach to deciphering the analysis, you can understand what stage the pathological process is at, make a prognosis for the development of the disease, understand its causes, confirm the diagnosis and understand how impaired the immune system is.
Symptoms of monocytosis
An increased content of monocytes can be reliably determined only by the results of a blood test. In this case, the disorder manifests itself with certain symptoms:
- apathy, decreased or lack of appetite;
- weight loss for no specific reason;
- high fatigue, general weakness of the body without an objective reason;
- depression;
- high level of anxiety, even panic states;
- emotional overexcitation for no specific reason;
- aversion to meat, aversion to it (occurs suddenly);
- bloating;
- constipation;
- diarrhea;
- discharge of large volumes of mucus with feces;
- dry cough that lasts for a long time (sometimes with blood discharge);
- muscle pain in the back area;
- pain in the legs;
- skin rash;
- rash in the genital area.
Functions of blood cells
Monocytes are white blood cells that are found in the blood and then move into tissues where they transform into mature cells. They are sent to places where pathogenic microorganisms actively multiply.
An increase in the number of monocytes indicates that a foreign agent has entered the body. When it penetrates, the immune system rapidly produces cells to destroy the irritant.
Lymphocytes are responsible for ensuring that the immune response starts and stops on time. They identify bacteria and eliminate them, produce immunoglobulins, and remember information about a foreign substance.
Monocytes and lymphocytes are important for the normal functioning of the body. Deviations in their content indicate the presence of pathologies, which helps with diagnosis.
Monocytes and lymphocytes
Symptoms
Elevated lymphocytes in a child are accompanied by the following symptoms:
- dyspnea;
- deterioration of general condition;
- fever;
- lethargy;
- sleep disturbance;
- the appearance of a rash;
- increase in body temperature.
The child will become capricious and his lymph nodes will enlarge. Against the background of the disease, the spleen and liver may increase in size.
Take into account! After recovery, the level of lymphocytes does not stabilize immediately; this may take from several weeks to several months. The process of lowering the level of lymphocytes is gradual.
When to see a doctor
If you have any of the above diseases and symptoms, you should consult a doctor. The doctor will assess the situation, taking into account the baby's age. If a child has elevated lymphocytes, then blood donation is prescribed to check the level of monocytes. If it is exceeded, this is a sign of a viral infection.
An immunologist-infectious disease specialist at Meditsina JSC (academician Roitberg’s clinic) will determine the cause and eliminate it in a short time, carrying out a suitable diagnosis. The clinic is located in the center of Moscow.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis depends on the cause, on what is affecting the child’s body that led to an increased level of white blood cells. The main diagnostic methods include computed tomography or ultrasound. A number of laboratory tests are also prescribed, and the child is required to undergo a blood test. Diagnostics allows you to draw conclusions, determine the level of danger and risks, and prescribe effective treatment (depending on what was the cause).