- What does upper and lower pressure show?
- What can lead to a decrease in lower pressure?
- Types of arterial hypotension
- Causes of low lower pressure
- Mechanisms of reduction in systolic and diastolic pressure
- Symptoms
- Diagnostic procedures
- Treatment methods
The state of low blood pressure is called arterial hypotension. It occurs if the readings fall below 100/60 mmHg. In some patients, upper and lower pressure (systolic and diastolic) decreases. Sometimes a situation arises when the upper indicator is normal, and the lower indicator falls below normal. This is regarded as isolated arterial hypotension and requires the attention of specialists.
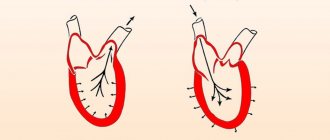
What does upper and lower pressure show?
The upper pressure is called systolic. It refers to the force with which blood is pushed out of the heart and moves through the vessels, saturating organs and tissues with oxygen. Diastolic - lower pressure, indicates the pressure of blood on the walls of blood vessels at the moment between heartbeats.
As a rule, as people age, they experience an increase in upper blood pressure. Elevated lower levels are more common in patients under 50 years of age and then begin to decline. Problems with diastolic pressure begin due to deterioration in the elasticity of blood vessels. The capillaries narrow, become stiffer, and this leads to excess blood pressure on their walls. This phenomenon is observed even at rest.
What can lead to a decrease in lower pressure?
Arterial hypotension can act as an independent disease (primary form) or one of many symptoms (secondary form). According to statistics, low upper and/or lower blood pressure is more common in women than in men. This phenomenon can also occur in adolescents.
In older people, lower blood pressure decreases due to decreased vascular tone. The main culprit of the problem is atherosclerosis. Secondary hypotension can occur against the background of neurological and cardiac diseases, and hormonal disorders.
Physiological factors in the development of hypotension
Isolated arterial diastolic hypotension often develops for pathological reasons. But there is no need to write off natural, physiological ones either.
They are approached first and only then are they looked for for any disease. Physiological factors include:
- Long-term lack of nutrition or insufficient, meager diet. Representatives of the fairer sex with an obsession with losing body weight are especially prone to bad eating habits.
As a result of catabolism, fats are broken down and heat and energy are released. The body spends accumulated resources. When there is no fat left, your own muscle fibers are used.
Hypotension is associated both with the peculiarities of metabolic processes and with a lack of vitamins and organic acids: B12, folic acid, vitamin A, etc.
- Features of genetic material. If there was a relative in the family who suffered from low blood pressure, with a high probability such a feature will manifest itself in the phenotype and genotype of one or more descendants.
Moreover, it is not always the case that if an ancestor’s health was normal due to hypotension, the scenario will be repeated in children or grandchildren. All organisms are different.
- Long periods of physical labor. Hypotension develops especially often in athletes and workers of metallurgical enterprises. Heavy physical activity and difficult environmental conditions lead to the formation of adaptive mechanisms.
Such people can also be recognized by chronic bradycardia (pulse rate less than 60 beats per minute), which usually does not cause them any discomfort.
- Abuse of alcohol and tobacco products. How a particular body will react to the next dose of alcohol or nicotine - no one can say in advance. A common occurrence is hypertension. But this is not the only option.
- Insufficient consumption of table salt. Both an excess of this substance and a lack of sodium chloride salt are bad. We need to look for a balance in consuming “white poison”. Optimally 7 grams per day.
- Peak hormonal conditions, such as puberty, the menstrual cycle and pregnancy in the fairer sex, menopause in men and women.
- Elderly years, provided that the patient moves little or is completely bedridden.
- Acclimatization. For example, when moving to unusual living conditions. Including during the holiday period in warm countries. Easier to adapt to cold weather conditions.
There are many physiological factors. But pathological ones are many times more common. According to specialized studies, the ratio is 70% to 30%.
Types of arterial hypotension
There are three types of arterial hypotension:
- physiological;
- pathological;
- symptomatic.
Low blood pressure as a physiological norm may be a congenital feature characteristic of a particular person due to his constitutional type. A similar situation is observed among professional athletes, residents of high mountain areas and tropical latitudes. Thanks to the decrease in pressure, the body adapts to physical activity and climate conditions. In this case we are talking about a compensatory function.
The pathological form of the disease is of two types: orthostatic and neurocirculatory. Orthostatic hypotension occurs when there is a change in body position when a person gets up after resting or sleeping. The neurocirculatory form is associated with disruption of the autonomic nervous system. The patient may periodically experience low blood pressure or have hypotension, in which diastolic pressure is chronically low.
Symptomatic hypotension is secondary. Its causes are disruption of the functioning of various organs and systems, intoxication.
Causes of low lower pressure
According to statistics, the main cause of primary hypotension is neurocirculatory dystonia (NCD). It is otherwise called heart neurosis. With neurocirculatory dystonia, various disorders of autonomic regulation are observed, and this condition is not associated with damage to the endocrine or nervous systems.
NCD and the resulting decrease in diastolic pressure are most often observed in women during puberty and at the onset of menopause, with impaired ovarian function. In young people and middle-aged patients, hypotension occurs against the background of chronic fatigue, stress, psycho-emotional and physical overload. The high-risk group includes people with alcohol and tobacco addiction, patients who have recently experienced psychological trauma, and who are depressed.
Secondary arterial hypotension can be acute or chronic. Low diastolic pressure is encountered by patients with stomach ulcers, diabetes, low thyroid function, osteochondrosis, arrhythmia, heart failure, and chronic infectious processes. In people with such diseases, blood pressure may be constantly low, but due to the body's ability to adapt, the disease does not manifest itself with pronounced symptoms.
A sharp drop in upper and lower blood pressure occurs with significant blood loss, dehydration, anaphylactic shock, or poisoning. These conditions are extremely dangerous for health and life, as they lead to serious circulatory disorders.
One of the possible reasons for a decrease in diastolic blood pressure is a lack of vitamins B, C and E in the diet. The body can also respond to a strict diet or an overdose of drugs (adrenergic blockers, anti-hypertension drugs) with arterial hypotension.
Questions from our readers
— Ivan Ilyich, our readers ask a lot of questions about hypotension, here are a few of them.
Heat and low blood pressure
— Why does the heat reduce blood pressure?
— Not only hypotensive people, nor hypertensive people, suffer from a decrease in blood pressure during the hot season; some benefit from it, while others cause problems with their well-being. The reason is the increase in temperature and subsequent increase in the concentration of carbon dioxide. The gas has the properties to influence blood vessels, dilating them, and as a result, reducing blood pressure.
Smoking and blood pressure surges
-I quit smoking, low blood pressure appeared, why?
— The reason is the effect of nicotine on the body, which has a constricting effect on blood vessels. With prolonged smoking, the functioning of the cardiovascular system is completely disrupted, which leads to pressure surges. Both its increase and decrease can be observed.
Drop in blood pressure after exercise
— Why is my blood pressure low after training?
— This is an abnormal reaction of the body from a physiological point of view and you should consult a doctor. The reason for this reaction of the body can be both physiological factors and dangerous pathologies:
- overwork;
- mitral valve prolapse;
- angina pectoris.
Low blood pressure with hypertension
— Why did a hypertensive patient’s blood pressure become low?
- In this case, you should consult a doctor. A sharp decrease in blood pressure against the background of prolonged hypertension may indicate serious pathologies of the body, including heart disease, bleeding, infections, and neurological disorders. It can also be caused by taking inappropriate medications.
How does a hot bath affect blood pressure?
— Does a hot bath increase or decrease blood pressure?
— The effect of water, no matter hot or cold, on the body has long been studied by science called balneotherapy. It is used for therapeutic effects on the body using water procedures. Water is considered hot if it is higher than the temperature of the human body 38°-39°C.
When using a bath at such temperatures, it makes sweating more difficult, increasing body temperature. The heart muscle begins to contract more often. And this leads to an increase in pressure on the walls of blood vessels, and accordingly to an increase in blood pressure.
Low Hell as a sign of pregnancy
- Low blood pressure before a missed period can be a sign of pregnancy?
- Yes, this may be the first sign. The first signs of pregnancy, which are noticeable even before the onset of menstruation, are fatigue, which will accompany her condition throughout the first trimester. It's all about the increased production of progesterone, which has already been mentioned. Namely, this hormone entails disruptions in blood pressure and disruptions in heart rhythm.
Lowest blood pressure in the body
— Lowest pressure in capillaries?
- This is one of the most interesting questions about the human body, like the question where is the low pressure when inhaling? So, the pressure in the capillaries is 20-30 mm Hg, and the lowest pressure during inspiration is in the pleural cavity, its value is negative or lower than atmospheric by 4-6 mm Hg. Art.
Mechanisms of reduction in systolic and diastolic pressure
A decrease in blood pressure is caused by one of four possible reasons:
- the stroke and cardiac output decreases;
- the flow of blood to the heart through the veins decreases;
- vascular resistance decreases;
- the volume of circulating blood decreases.
A decrease in cardiac output and stroke is observed in cases of disturbances in myocardial function caused by infarction or myocarditis. The same situation occurs with an overdose of adrenergic blockers.
Vascular tone can decrease with infectious diseases, intoxication, and anaphylactic shock.
A decrease in the volume of circulating blood occurs against the background of bleeding due to trauma to tissues and blood vessels, rupture of the spleen, and ulcerative lesions of the stomach.
A decrease in venous return of blood to the heart occurs with massive ascites or pleurisy due to blood retention in the smallest vessels.
Symptoms
With a physiological decrease in lower pressure, patients do not experience a deterioration in their well-being. If the problem is caused by pathology, then oxygen starvation gradually develops. It is characterized by the following symptoms:
- weakness and dizziness;
- colored spots before the eyes;
- pallor;
- fainting state.
Patients with chronic arterial hypotension constantly feel fatigue, drowsiness, and a desire to rest. A person with low blood pressure experiences increased sweating and may experience headaches. Low blood pressure makes it difficult to concentrate on work or study and makes a person emotionally unstable. Women with chronic hypotension may experience menstrual irregularities, and men have reduced potency.
In severe forms of arterial hypotension, patients experience vegetative crises. They are accompanied by a decrease in temperature, sweating, difficulty breathing, chest pain, nausea and vomiting, slow pulse, and loss of consciousness.
First aid
If your blood pressure drops suddenly, do not try to lower it yourself. This can cause internal bleeding. Therefore, it is better to immediately call an ambulance, which will provide first aid.
You need to call an ambulance for the following symptoms:
- dark spots in the eyes;
- unpleasant sounds in the ears;
- fainting;
- pale lips.
To provide first aid before the ambulance arrives, you need to immediately put the person in a comfortable position.
Provide him with enough fresh air in the room. You can open the window. Taking medications is prohibited. This can make the situation even worse. If hypotension is accompanied by tachycardia and pain in the heart, you can take pills that were previously prescribed by your doctor.
Diagnostic procedures
To normalize blood pressure, it is important to identify the reasons for its decrease. The approach to diagnosing arterial hypotension is complex. First of all, the doctor needs to assess the blood pressure level. Daily monitoring is best suited for these purposes. The procedure helps to identify how pressure readings change during the day. A technique for measuring blood pressure three times with an interval of 3-5 minutes is also used.
To choose treatment, you need to determine whether a decrease in lower pressure is an independent disease or a symptom of another disease. The patient is prescribed laboratory tests for hormones, electrolytes, glucose and other indicators. Among the hardware methods for diagnosis, electroencephalography, ECG, and orthostatic test are used.
A person with chronic arterial hypotension needs to consult a neurologist, cardiologist, or endocrinologist.
What indicators are we talking about and when can we talk about hypotension?
Diastolic hypotension does not always develop, even if external data suggests it.
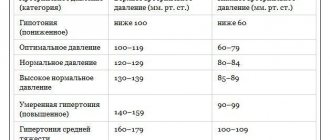
Outdated ideas about the norm of 100 to 70 (at the lower limit) are no longer used in medical practice.
New standards from the World Health Organization are being applied, which allows for a reduction in the standard level. Fluctuations in the optimal value are within 10 mmHg.
Therefore, hypotension is considered to be lower pressure, below 60 mmHg (diastolic indicator).
Depending on the individual characteristics of the organism, the following indicators are distinguished:
- Low blood pressure. 60 mm Hg (lower blood pressure level).
- Hypotension of the first degree is below 60 mmHg, but above 50.
- Hypotension of the second or third degree. Below 50 mm.
- Critical hypotension. About 40 mmHg. It poses a danger to life and health. Cardiogenic shock, collapse and death of the patient are possible.
As already mentioned, the indicators are individual in nature and depend on the physiology of a particular person.
But the diastolic indicator should not drop below 60 mmHg. This is no longer normal. If your blood pressure drops, you should immediately consult a doctor.