Increased blood pressure can otherwise be called arterial hypertension.
Arterial hypertension occurs for a long time without obvious manifestations. However, soon enough it can lead to acute cerebrovascular accidents in the form of TIA (the so-called transient ischemic attack or, in other words, all manifestations of a stroke, but within 24 hours), strokes, as well as to hypertrophy of the walls of the heart and/or enlargement of cavities hearts.
In addition, arterial hypertension is a risk factor for the formation of atherosclerotic plaques in blood vessels and the occurrence of myocardial infarction.
The relationship between blood pressure levels and the risk of cardiovascular disease is linear.
The higher the blood pressure, the greater the likelihood of myocardial infarction, stroke, heart failure and kidney damage.
The prevalence of arterial hypertension (AH) in the Russian Federation is 39.3% among men and 41.1% among women, while blood pressure is properly controlled in only 17.5% of women and 5.7% of men.
Systolic blood pressure increases steadily with age, while diastolic blood pressure rises until age 60 in men and age 70 in women, after which it tends to decrease.
WHAT IS SYSTOLIC DIASTOLIC AND PULSE PRESSURE
Blood pressure is the pressure that blood exerts on the walls of the arteries.
There are:
- systolic pressure
- diastolic pressure
- pulse pressure
Systolic pressure (upper)
This is the maximum pressure in the arterial system developed during contraction of the left ventricle.
It is determined by the volume of blood that the heart pumps out in one contraction, as well as the elasticity of the aorta and large arteries.
Diastolic pressure (lower or heart)
This minimum pressure in the arteries during relaxation of the heart is determined by the amount of tone of the small arterioles.
Pulse pressure
This is the difference between systolic and diastolic blood pressure.
So the reasons for high blood pressure:
Causes of high blood pressure
Depending on which of the two pressure indicators is elevated (upper or lower), it is customary to consider the picture of the state of health.
Common causes of high blood pressure include:
- being in a state of prolonged, chronic stress and nervous tension;
- short-term bursts of emotional or mental activity, since adrenaline (stress hormone) speeds up the heart, affecting the tone of blood vessels;
- a high concentration of sodium and calcium in the blood, at which frequent spasms of the smooth muscles from which the entire vascular system is “woven” occurs.
- high cholesterol, the formation and accumulation of atherosclerotic plaques on the walls of blood vessels, which over time leads to a narrowing of the lumen of blood vessels, which impairs blood flow. In this case, the heart is forced to work harder to move blood through the vessels, which causes the development of chronic hypertension.
- regular use of alcohol, tobacco, smoking mixtures, psychotropic substances. Under the influence of the chemical composition of which fluctuations in vascular tone occur, the functioning of the kidneys and other body systems is disrupted.
- course or frequent use of medications: oral contraceptives, appetite suppressants, glucocorticoids.
- diabetes mellitus, kidney and liver diseases, thyroid diseases
- excess weight and inactive lifestyle, asthenia
- blood thickening and dehydration, which make it difficult for the cardiovascular system to pump blood
- violation of diet, consumption of mineral salts, smoked spicy foods on a regular basis
- diseases of the spine, in which pinched nerve roots occur, increased muscle tone, which lead to impaired blood supply to blood vessels.
- heredity
However, looking at the readings of the measuring instruments, one should distinguish between high upper pressure and high lower pressure. Because both the risks of health complications and the choice of therapy depend on this.
High top pressure
When the upper (systal) pressure increases, aching headaches appear, with pulsation occurring. There may be pressure on the eyeballs, a feeling of swelling of the face.
The symptoms of high upper pressure are similar to intracranial pressure. Which develops as a consequence of impaired circulation of cerebrospinal fluid.
- if the upper pressure is increased, an irregular heart rhythm (arrhythmia) and aching chest pain may occur. Some people, if they have such symptoms, may panic and attribute their occurrence to heart problems.
- when the upper pressure increases to 150 mm Hg. Art. an adult may develop a hypertensive crisis, which causes pathological changes in the coronary arteries and heart muscles.
- angina pectoris develops, the left ventricle enlarges and cardiac output decreases, therefore heart failure develops, and with it the risks of developing myocardial infarction arise.
High bottom pressure
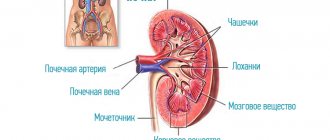
Lower pressure means the pressure in the blood vessels during maximum relaxation of the heart, before a new contraction. An increase in this indicator means that fluid is poorly removed from the body. Lower pressure is also called “renal pressure”. The kidneys, passing blood through themselves, act as a filter, regulate the water-salt balance of the body and remove toxins from the blood along with urine. If the lower pressure indicator fails, then you should start looking for problems in the kidneys, which for some reason cannot cope with their work.
How to reduce high blood pressure at home
High blood pressure is a very serious symptom. Therefore, any therapy should be prescribed strictly under supervision and on the recommendation of a specialist!
However, regular blood pressure medications should be in your home medicine cabinet, especially if there are real prerequisites.
- If the increase in pressure is situational in nature and caused by emotional or nervous shock. First of all, you should balance your breathing, find ways to calm down and relax as much as possible. Among the medications you can use: sedatives of plant origin, for example: novo-passit, persen, valerian tab, motherwort extarct tablet and others.
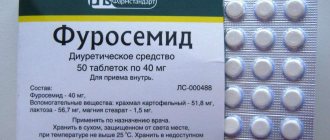
- To reduce blood pressure, diuretics can be used as part of complex therapy or as an independent remedy: Their selection and prescription, as well as the choice of dosage, is carried out by the doctor.
- If hypertension is an established chronic disease and another attack occurs, it is important to take as quickly as possible: Emergency drug Captopril 25 mg sublingually 0.5-1 tablet, and consult a doctor as soon as possible.
What examinations are also prescribed?
In most cases, hypertension is caused precisely by disorders of the blood vessels and heart. In 5-10% of cases, the root cause may be kidney problems, endocrine changes, stress, neurological factors, or even the use of certain supplements and medications. The doctor needs to determine what caused the disease. For this purpose, diagnostics, as a rule, is not limited to simply measuring pressure. Additionally, the following examinations are carried out:
- electrocardiography and echocardiography;
- Ultrasound of the kidneys and other organs of the urinary system;
- Ultrasound of the thyroid gland; computed tomography of the adrenal glands, skull;
- laboratory tests, including urine and blood tests for hormones.
Additionally, consultation with related doctors, including nephrologist, urologist, endocrinologist, neurologist, etc., is recommended.
It is also important to determine the stage and severity of hypertension and the risk of complications. This may require examinations such as:
- stress tests with blood pressure measurement;
- daily blood pressure monitoring;
- fundus examination;
- blood biochemistry for cholesterol, etc.
Diagnosis confirmation
It is not difficult to identify hypertension, but the insidiousness of the disease lies in the fact that it can occur without symptoms at all for a long time. Occasionally it causes headaches, for example due to weather changes. People take pain medication and the symptom goes away. But this is not a treatment for hypertension itself.
The diagnosis of “arterial hypertension” is confirmed by pressure readings (BP) measured using a tonometer of 140/90 mmHg or higher. So, if such values are recorded during a medical examination at least 2 times, then this is hypertension. And it requires therapeutic measures.
Borderline level of hypertension
There is another name for borderline hypertension - labile. The increase in pressure in this case is unstable, its readings vary from normal to borderline elevated. Irreversible disorders do not occur in the labile form of hypertension, there are usually no symptoms, such an increase in pressure does not affect the state of health, it always normalizes on its own, so there is no need to resort to medications. However, people with borderline hypertension are always at risk of developing overt hypertension at some point. Therefore, monitoring blood pressure in this situation will not be superfluous. This is especially true for people who are over 30 years old, as well as those who are overweight or have poor heredity.
Borderline hypertension is most often temporary and can be observed in the following cases:
- during menopause in women;
- in athletes, under excessive loads;
- with alcohol intoxication;
- nervous disorders, in stressful situations;
- during puberty in adolescence.
In case of low blood pressure we speak of hypotension. The tonometer readings for hypotension are as follows: 90 to 60 and below. Low blood pressure also causes a lot of trouble. A person in this state feels weakness, drowsiness, chronic fatigue, dizziness, his skin turns pale, and his limbs are constantly cold. Hypotonic people are usually people of asthenic physique.
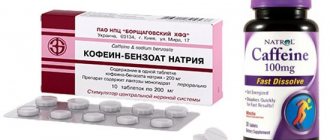
The danger of hypotension is poor blood saturation of the entire body and, as a result, a hypotonic crisis (the pulse weakens, breathing becomes difficult, loss of consciousness, bleeding of the skin and limbs is possible). In such a situation, it is necessary to increase the level of pressure as quickly as possible, for this there are special medications, at home a cup of strong coffee or tea, a contrast shower, a stimulating massage will help, various herbal tinctures (eleutherococcus, ginseng, echinacea) are effective.
Preventing high blood pressure
Preventing high blood pressure is an important measure to prevent dangerous conditions and negative health consequences. Paying close attention to your body will protect it from dangerous diseases of the cardiovascular system. Considering that any disease can be aggravated by unfavorable heredity, it is important to approach the issue of preventing systemic diseases with particular care.
Primary prevention of high blood pressure
Primary prevention of hypertension involves preventive measures against blood pressure disorders in principle, exclusion of potential risk factors from lifestyle: bad habits, excessive physical activity, uncontrolled diet and diet.
Secondary prevention of high blood pressure
Secondary prevention means control of an existing disease and strengthening the stage of remission of hypertension, eliminating risk factors for the development of coronary heart disease, heart attack, and stroke. In addition to lifestyle correction measures, it also includes medications, vitamin health support, and physical therapy. Due to the great capabilities of modern medical equipment production, physiotherapy can be carried out at home.
The concept of mental hygiene plays an important role in the prevention of high blood pressure. Which implies reducing psychological and emotional tension, minimizing stressful situations and the ability to respond correctly to them.
Be healthy!
Still have questions? Ask them to us in the comments, we will definitely answer!
Drug treatment
If the measures described above do not help, then doctors recommend taking antihypertensive medications. They are selected exclusively by the attending physician, taking into account various individual factors. Taking medications is not one-time or even a course, but permanent. Therefore, it is important that specific drugs are not only effective (this requires constant monitoring of blood pressure), but also do not lose their effect over time and do not cause adverse reactions.
But often patients do not resort to treatment immediately, but only after a hypertensive crisis, pre-infarction condition or other life-threatening complications of hypertension. It’s better to do differently and engage in prevention.
Guskov Bogdan Valerievich
Cardiologist, Therapist
- On Lukyanovskaya, st. Kudryavskaya, 31/33
Cost of admission: 450 UAH.
Make an appointment
Management of patients in inpatient and outpatient settings of the following profiles: cardiological, therapeutic, pulmonological and patients who require resuscitation and intensive care.
Other articles by the author
Heartache. Angina pectoris. What to do and how to avoid risks to life? What the intensive care door is silent about About the maternity hospital, vaccines and evolution What cardiologists do and should do
Contact us or ask a question
Call now
093 810 90 90Make an appointment
Ask a Question
Write
Comments
familyhealth27.03.2020
To understand what causes pressure in a person, it is necessary to consider the illness itself. There are two types of hypertension: hypertensive disease and symptomatic arterial hypertension. The first type is a chronic process, the causes of advanced AT in any case cannot be explained by doctors and doctors. If there is symptomatic hypertension, then doctors indicate that the cause of hypertension in a person can be one of the following: unbalanced food, stress, poor lifestyle, loose teeth, overweight.
leave a comment
What influences the appearance of hypertension?
Here's what contributes to the development of high blood pressure:
- Age . Typically, those at risk for developing hypertension include men over 55 years of age and women over 65 years of age. But the disease is also common among young people.
- Heredity . Predisposition to high blood pressure is often due to genetics. If your family had a similar problem, you should take care of this health factor now. You can learn about the risk of developing arterial hypertension and other cardiovascular diseases, and receive recommendations for prevention and treatment using the Atlas Genetic Test.
What can you learn from a genetic test?
- Race. People of African descent are more likely to develop hypertension than other races. In black people, the disease often develops at a young age and has complications.
- Lack of physical activity . Typically, people who do not exercise have a higher heart rate. And the higher the heart rate, the more actively the heart must work and the greater the pressure on the arteries. Lack of physical activity also increases the risk of being overweight.
- Overweight. The more a person weighs, the more blood is needed to supply tissues with oxygen and nutrients. Due to the increased volume of blood flow in the blood vessels, the pressure on the artery walls also increases. A balanced diet rich in fiber, vegetables and fruits will help keep your weight and blood pressure normal. You can receive recommendations for individual nutrition thanks to the Atlas genetic test.
- Smoking. Tobacco use not only temporarily increases blood pressure, but can also damage the lining of artery walls due to the chemicals it contains. And as a result, it can lead to narrowing of the arteries and increase the risk of heart disease.
- High salt (sodium) content in the diet. Excessive consumption of salty foods retains fluid in the body, and this, in turn, increases blood pressure.
High sodium levels are found in processed foods, such as: - bread (≈ 250 mg/100 g), - bacon (≈ 1500 mg/100 g), - cheese balls or popcorn (≈ 1500 mg/100 g), - soy sauce (≈ 7000 - 21,900 mg/100 g), - bouillon cubes (≈ 20,000 mg/100 g). - Insufficient potassium content in the diet. Potassium helps balance the amount of sodium in the body and affects heart health. If you don't get enough potassium or lose too much due to dehydration or other illnesses, sodium can build up in your blood.
Large amounts of potassium are found in various foods: - beans and peas (≈ 1,300 mg/100 g), - nuts (≈ 600 mg/100 g), - vegetables such as spinach, cabbage and parsley (≈ 550 mg/100 g) , - fruits such as bananas, papaya and dates (≈ 300 mg/100 g).Heat processing reduces the amount of potassium in many foods.
- Excessive sugar consumption. Research suggests that added sugars, including fructose, may increase blood pressure and increase heart rate. WHO recommends reducing daily intake of free sugars to less than 10% of total energy intake. That's 200 calories, or about 12 teaspoons (about 60 g) based on a 2,000-calorie daily diet. Examples of added sugars and their calorie content: - 1 tablespoon of tomato ketchup = 12 kcal of added sugars - 1 jar of flavored yogurt (28 g) = 72 kcal of added sugars - 1 45 g chocolate bar = 74 kcal of added sugars - 1 can of soda (330 ml) = 126 kcal of added sugars - 1 piece of chocolate cake (100-150 g) = 196 kcal of added sugars.
- Alcohol. Over time, drinking too much alcohol can harm your heart. Drinking more than one alcoholic drink per day for women and more than two alcoholic drinks per day for men negatively affects blood pressure.
- Stress. High levels of stress can lead to a temporary increase in blood pressure. And habits associated with stressful conditions - overeating, drinking alcohol and smoking - aggravate the situation.
- Chronic diseases. Some chronic conditions can also increase the risk of hypertension: kidney disease, diabetes, and sleep apnea.
- Pregnancy. Many women experience increased blood pressure during pregnancy.
Hypertension is more common in adults, but children are also at risk. High blood pressure in children is caused by kidney or heart problems, poor diet and lack of exercise.
Symptoms of high blood pressure
There are no specific symptoms typical for hypertension. Therefore, sometimes, seemingly without apparent reason or alarm bells, strokes and heart attacks occur even in young people. And those symptoms that may indicate high blood pressure are ignored.
Among the common ones:
- headache in the temporal or occipital part of the head
- dizziness
- weakness and tremors
- nausea
- dyspnea
- blurred vision, flashing spots before the eyes
- tachycardia
- swelling (in case of increased lower pressure)