Dental periodontal disease is a dental term used to describe a disease that affects the soft tissues of the oral cavity. How to cure periodontal disease - this issue should be taken care of by any person who has discovered the primary signs of this disease, because if it reaches a certain stage of development, it will be impossible to cure it, and the consequences will be the most severe. Advanced periodontal disease can lead to loosening and tooth loss. In this article we will talk in detail about the causes, signs, and methods of effective treatment of periodontal disease.
Diagnosis of periodontal disease
To identify signs of periodontal disease in adults, the following diagnostic procedures are usually performed:
- inspection;
- probing of the gingival sulcus;
- assessment of tooth mobility;
- X-ray examination (orthopantomography);
- biomicroscopy of the gums to determine the degree of microcirculation impairment.
The patient will also need observation from a general practitioner and endocrinologist to detect and treat general somatic pathology.
After a diagnosis of “dental disease periodontal disease” is made, further examination should be aimed at finding the causes of disturbances in the processes of cellular tissue nutrition, predicting the further development of the disease and the likelihood of inflammatory complications.
Gum diseases: causes
Factors that increase the risk of developing gingivitis:
- Insufficient oral hygiene.
- Hormonal changes in the body. They create a favorable environment for the formation of inflammatory processes in the oral cavity. That is why teenagers and pregnant women most often suffer from gingivitis.
- Damage from impacts, burns, incorrectly installed fillings and dentures.
Periodontitis occurs if gingivitis is not properly treated in time. The inflammatory process, under the destructive influence of pathogenic bacteria, spreads to other areas of the periodontium.
Periodontal disease develops due to poor blood supply to the gums and poor nutrition. The most common causes of periodontal disease:
- gastrointestinal diseases,
- diabetes,
- heart and vascular diseases,
- taking anticonvulsants and other medications that reduce salivation.
The problem may also be hereditary.
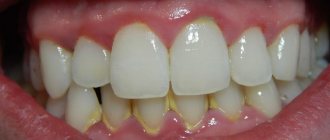
Symptoms of dental periodontal disease
The main symptom of the disease is detected during x-ray diagnosis of periodontal disease. The image shows a uniform decrease in the height of the interdental septa with alternating foci of osteosclerosis and osteoporosis in the deep parts of the alveolar process and the body of the jaw, as well as in other bones of the skeleton. Traditionally, changes are accompanied by the presence of diseases of the cardiovascular or endocrine systems and metabolic disorders.
There are other symptoms of severe periodontal disease that are more noticeable to the patient and others:
- gum retraction;
- exposure of the necks and roots of the teeth;
- pale gum color;
- lesions of teeth of non-carious origin (wedge-shaped defects, hyperesthesia).
Periodontal disease
Periodontal disease is a disease of the tissues surrounding and supporting teeth - gums, ligaments, alveolar bones, not associated with inflammation.
What causes periodontal disease?
The risk of developing periodontal disease increases as you age. It also varies with geography, diet, social status, race, and gender (more common in men). In addition, a relationship can be observed between the severity of periodontal disease and poor oral hygiene.
As mentioned above, the main reason for the development is the increasing age of the patient. Throughout our lives, changes in blood vessels occur (most often in pensioners or the elderly). The vessels decrease in diameter, as a result, the blood supply to the gums deteriorates, which leads to tissue atrophy - as a result, slow tissue degeneration.
If the end result of periodontal disease and periodontitis is similar - resorption of the jaw bones, pathological mobility and tooth loss, then the causes and course of these diseases are different.
Periodontal disease is a multi-cause disease, which at first is completely unnoticeable to patients, and only when the volume of gingival tissue is significantly reduced, and the teeth seem to move forward and become mobile, do patients sound the alarm.
The main reason for such processes is a malnutrition of the tissues that hold the tooth in the bone socket. The search for the primary source of this cause can lead the doctor to various organs and systems, or rather to their imperfections. With a high frequency these are metabolic disorders, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, immune system and cardiovascular diseases.
Symptoms of periodontal disease?
The following symptoms of the disease should concern us:
- exposure of teeth and necks
- dental hypersensitivity
- tooth mobility,
- bleeding gums (independently or during brushing),
- different odor from the mouth,
- tooth displacement
Consequences of periodontal disease:
The most common effects include weakness and loss of tissue around the teeth, which over time can lead to loosening, misalignment, and eventual loss of teeth. Unfortunately, periodontal disease can also lead to systemic complications. Bacteria and their products can penetrate blood vessels and contribute to atherosclerotic lesions, heart or cardiovascular disease, pneumonia or premature birth.
Preparing to visit the doctor
Follow the recommended schedule prescribed by your dentist for regular checkups. If you notice any symptoms of gingivitis, it is recommended that you make an urgent appointment with your dentist.
Here's some information to help you prepare for your appointment and know what to expect when you visit your doctor.
What can be done?
Prepare a list of questions, such as:
- Do you think gingivitis is causing my symptoms?
- What tests, if any, do I need to do?
- Will my dental insurance cover the procedures?
- What treatment alternatives do you suggest?
- What steps can I take at home to keep my gums and teeth healthy?
- What toothpaste do you recommend using?
- How often should I brush my teeth?
- What toothbrush do you recommend using?
- What dental floss do you recommend?
- How often should I floss?
- Do you recommend using mouthwash?
- Are there any restrictions that I must follow?
- Are there any brochures or other printed materials that I should look into?
- What sites do you recommend?
Feel free to ask other questions during your appointment at any time if you do not understand something.
What questions can you expect from your dentist?
Your dentist may ask you questions about symptoms, such as:
- When did you start experiencing symptoms?
- Have your symptoms been continuous or occasional?
- How often do you brush your teeth?
- Do you use dental floss? How often?
- What medications do you take?
Gum disease: treatment
It is under no circumstances recommended to self-medicate at home or use home methods. Today, the Internet, both Russian and foreign, is replete with miracle water and herbal remedies that will help get rid of all problems. In some cases, rinses and applications may temporarily reduce symptoms, but the disease will continue to actively progress. Many patients turn to the dentist already with tooth movement - as a result of prosthetics.
Do not self-medicate, consult a specialist, save your time and nerves.
Dental treatment for gingivitis, periodontitis
We strongly recommend starting with a consultation with a periodontist. The doctor will conduct a diagnosis and draw up a treatment plan. In addition to a thorough visual examination, diagnostic studies include panoramic X-rays, which allow you to see the condition of teeth, bone tissue, periodontal pockets simultaneously in all teeth, and densitometry. Then the required treatment and prosthetic methods are determined.
Step 1. Removal of dental plaque.
Treatment of gingivitis and periodontitis begins in the same way - it is necessary to remove hard supra- and subgingival dental plaque. Ultrasonic teeth cleaning helps to painlessly get rid of deposits, as well as clean teeth from soft microbial plaque.
Step 2. Anti-inflammatory therapy.
A) Gingivitis.
Due to the fact that gingivitis is only a superficial inflammation of the gums, you can resort to using home methods - rinsing your mouth with an antiseptic and applying gel to the gums.
Stages of periodontal disease
In modern dentistry, there are three degrees of severity of periodontal disease.
Mild degree
How does periodontal disease begin? In the early stages, the disease occurs without pronounced symptoms with gradual atrophy of the gum edge and bone tissue. With periodontal disease of the anterior teeth, a slight exposure of the dental necks occurs; in some cases, patients experience increased sensitivity of teeth to food irritants (hot and cold, sweet and sour). On X-ray images, the onset of periodontal disease is indicated by the first signs of bone tissue atrophy.
Average degree
With an exacerbation of periodontal disease, not only the necks, but also the roots of the teeth are exposed - by 2 - 3 millimeters. X-ray images show destruction of bone tissue along half the length of the root and the presence of foci of sclerosis.
Severe degree
With severe periodontal disease, exposure of the roots of the teeth reaches 4–5 millimeters, bone tissue atrophy on X-ray photographs covers two-thirds of the root.
Why does periodontal disease occur?
Ordinary people not connected with medicine often confuse the concepts of “periodontal disease” and “periodontitis”. The first is rare, no more than 8% of all people, mostly elderly. But even among young people, sudden and fleeting development of periodontal disease occurs.
The most commonly cited reasons for this problem are:
- Insufficient oral care. In particular, poor brushing of teeth, resulting in the formation of plaque.
- Unstable hormonal levels: pregnancy, puberty, menopause.
- Weak immunity due to a serious illness.
- The presence of diseases that primarily affect the immune system: cancer, HIV, diabetes.
- Bad habits. It has long been known that smoking destroys gum tissue, which means it contributes to the development of periodontal disease.
- Wrong lifestyle. Insufficient consumption of fresh fruits and vegetables weakens the immune system. Internal organs do not receive enough vitamins and minerals and begin to take them away from the bone tissue of the teeth.
- Long-term use of certain medications that reduce the normal flow of saliva. It provides gums with protection from external factors, such as eating rough food.
Periodontal disease – what to do?
At the initial stage of periodontal disease, you should consult a periodontist. No folk remedies will help get rid of the disease. Only a specialist will be able to carry out the necessary diagnostic procedures and prescribe, based on the identified symptoms of periodontal disease, treatment aimed at slowing down degeneration in periodontal tissues and preventing inflammatory complications. It is also necessary to eliminate non-carious dental lesions and undergo a thorough examination by a therapist to diagnose and treat common diseases that provoke the development of periodontal disease.
Complex therapy of periodontal disease involves the following measures:
- Timely removal of dental plaque.
- Normalization of occlusal relationships (grinding teeth, prosthetics, splinting).
- The use of vitamins and agents that improve microcirculation (nicotinic acid, aloe extract, heparin).
Surgery for the treatment of periodontal disease
Surgical intervention is used at critical stages of the development of periodontal disease, in which the depth of the periodontal pocket reaches ten millimeters or more. A periodontal canal is a depression formed when the natural attachment of the soft gum tissue to the tooth is disrupted. If such a pocket is shallow, then in the process of treating periodontal disease you can do without using the surgical method. However, in the third and fourth phases of development, the pocket depth can reach 7-11 millimeters and the use of medications in such circumstances will not give any positive changes in the treatment of periodontal disease, and only surgical intervention can help correct the situation.
During the operation, the dental surgeon restores bone tissue, using for this purpose special materials that catalyze the growth of natural bone material. This manipulation allows you to strengthen loose teeth and prevent further development of the disease.
Also, in the treatment of periodontal disease, prosthetics may be prescribed. It is mandatory even if only one tooth is missing in the dentition. If all the patient’s teeth are intact, but periodontal disease has caused the formation of significant gaps between them, the defect is eliminated by installing metal-ceramic bridges.
Another technique that can be used for periodontal disease is laser treatment. This technology should be considered exclusively as an auxiliary means of therapy that can help remove the unpleasant symptoms of the disease as quickly as possible - swelling of the gums, bleeding.
Let us write once again that complete treatment of periodontal disease is always a whole complex of the most diverse measures, and only such therapy can save you from this unpleasant disease.
Treatment methods
Methods and procedures used to treat periodontal disease in dentistry:
- exposure to high pressure oxygen in hyperbaric chambers;
- electrophoresis;
- diadynamic currents;
- amplipulse therapy;
- darsonvalization of gums;
- UHF therapy;
- gum massage;
- local hypo- and hyperthermia;
- ultrasound therapy.
Psychosomatics of periodontal disease
Based on the results of many years of research, American scientists have come to the conclusion that dental diseases such as periodontal disease are directly related to high anxiety, depression and an acute sense of loneliness. This is explained by the fact that increased levels of the stress hormone - cortisol - in the blood negatively affect the condition of the gums and jaw bones. In addition, during periods of nervous tension, people begin to pay less attention to oral hygiene and increase the doses of alcoholic beverages, nicotine and medications, which also contributes to the development of various diseases.
Prices for periodontal disease treatment in Moscow
Without an examination and a series of tests, it is impossible to say exactly how much periodontal disease treatment will cost. The price of the service will take into account those measures that will be included in the treatment plan drawn up for you at the dental clinic, and will also depend on the stage of development and form of periodontal disease. To find out the exact amount of treatment, visit our dentistry in Moscow “Vanstom” and get detailed advice from our specialists. We are located in the center of Moscow, next to the Baumanskaya metro station.
It is important to know that the sooner measures are taken to treat periodontal disease, the higher the chances of its final cure. If the disease reaches critical phases of development, medicine will be powerless, since chronic periodontal disease is incurable. Therefore, if, based on a number of symptoms, you suspect that you have periodontal disease, do not delay a visit to the dentist. In our clinic in Moscow “Vanstom” you will find services of the highest level of quality, innovative techniques for the treatment of periodontal disease, modern equipment and materials, and an individual approach to each patient. Address of our dentistry: Moscow, Baumanskaya metro station, st. Bakuninskaya, 17/28.
Consequences of periodontal disease - why is it dangerous?
- Firstly, due to the absence of pronounced symptoms, this disease can progress unnoticed over many years and lead to total destruction of the teeth and jawbone - and then teeth fall out with periodontal disease.
- Secondly, the destruction of bone tissue leads to disturbances in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract with the subsequent occurrence of diseases of the digestive system.
- Thirdly, advanced periodontal disease can provoke periodontitis - acute inflammation of the tissue and tooth loss.
In addition to the above consequences, generalized periodontal disease in an advanced stage causes another dangerous disease - osteomyelitis, that is, purulent bone damage.
Periodontitis
Periodontitis in its final form is a serious infection that damages soft tissue and destroys the bone that supports the teeth. Periodontitis can not only lead to tooth loss, but worse, it can cause an increased risk of heart attack or stroke and other serious health problems.
Periodontitis is a common disease, but largely preventable. Periodontitis is usually the result of poor oral hygiene. Brushing at least twice a day, daily, and regular dental checkups can significantly reduce the chance of developing periodontitis.
Symptoms
You may find that you have gingivitis:
- Swelling of the gums (edema)
- Bright red or purple gum color
- Gums sensitive to touch
- Gum that “pulls away” from your teeth, making your teeth appear longer than usual
- Pus from under the gums
- Bad breath
- Bad taste in mouth
- Movable teeth
There are different types i.e. severity of periodontitis. Periodontitis is characterized by a chronic course, with exacerbations occurring.
When to see a dentist
Healthy gums are firm and pale pink in color. If your gums are puffy, dusky red and bleed easily, or show other signs or symptoms of periodontal disease, see your dentist as soon as possible. The sooner you seek medical help, the better your chances of reversing the damage from periodontal disease, potentially preventing other serious health problems.
Causes
Periodontitis is thought to begin with plaque, a sticky film made primarily of bacteria. Plaque forms on teeth when sugar starches in foods interact with bacteria that are normally found in the mouth. Brushing and flossing remove plaque. But plaque re-forms quickly, usually within 24 hours.
Constant inflammation eventually leads to pockets between the gums and teeth that become filled with plaque, tartar, and bacteria. Over time, these pockets become deeper and bacteria accumulate, moving under the gum tissue. This deep inflammation is the cause of bone resorption. If too much bone is destroyed, you may lose one or more teeth.
What can cause periodontitis?
Factors that may increase the risk of developing periodontitis include:
- Gingivitis
- Heredity
- Insufficient oral hygiene
- Tobacco use
- Diabetes
- Elderly age
- Decreased immunity, such as leukemia, HIV/AIDS or chemotherapy
- Poor nutrition
- Some medications
- Alcohol or drug abuse
Complications
Some complications associated with gum disease include:
- Complete loss of teeth
- Coronary heart disease
- Stroke
- Problems with pregnancy, low birth weight
- Poorly controlled diabetes
- Breathing problems
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Asthma
Some research suggests that the bacteria responsible for periodontitis can enter the bloodstream through the gum tissue, affecting your lungs, heart, and other parts of your body. For example, bacteria can travel in the arteries to the heart and cause inflammation of the heart muscle, which contributes to heart attacks.
Periodontal disease - contagious or not?
To the questions “Is periodontal disease contagious?” or “Is periodontal disease transmitted by airborne droplets?” Doctors answer unequivocally in the negative. Therefore, you should not believe various dubious articles on the Internet about how periodontal disease is transmitted. The disease is associated with metabolic disorders, and not with the spread of bacteria. Therefore, those who believe that periodontal disease can be contracted or that the disease is transmitted through a kiss are deeply mistaken. However, despite this, we must not forget about the rules of daily oral hygiene in order to prevent the occurrence of other problems with teeth and gums.
Will traditional medicine help?
On the Internet, on many sites, you can find recipes for the treatment of periodontal disease with folk remedies. However, let’s say right away that traditional treatment of periodontal disease may turn out to be completely useless, since it is only possible to stop the development of the disease by using professional techniques. Moreover, the use of some recipes can be harmful, provoking the active development of inflammatory processes.
If you still want to try folk remedies or homeopathy to speed up the pace of periodontal disease treatment, be sure to coordinate all your actions with your doctor.
Calculate the cost of treatment by taking a short test in 20 seconds!
Do not delay your treatment, because in this matter time plays against us.
Periodontal disease of the gums: how to treat with antibiotics
You can take antibiotics for diseases of the oral cavity only after consulting with your dentist. Doctors prescribe broad-spectrum antibiotics to adults in cases where it is necessary to quickly eliminate pathogenic microorganisms. Chronic forms are treated with Metronidazole in combination with Chlorhexidine. Antibacterial therapy is applied for 10 days.
In addition to taking antibiotics, the doctor will prescribe a rational, balanced diet for the patient. It is necessary to eat more fruits and berries, and eat vegetables regularly. It is worth choosing products that are rich in various vitamins. Some dentists prescribe a course of vitamins orally or intravenously. Vitamin and mineral therapy is aimed at improving the general condition of the body and strengthening the immune system. In addition to antibiotics, ointments and gels are prescribed for local treatment: Cholisal, Traumeel S and others. Medicines must be used strictly according to the regimen drawn up by the attending physician.
Symptoms
In the absence of complications, diagnosing the disease is problematic. The disease is often attributed to symptoms characteristic of periodontitis:
- Inflammation.
- The appearance of edema.
- Bleeding.
- Contents of pus.
- Mobility of teeth.
If there are no complications, then symptoms of inflammation will not be observed. Depending on the severity, it may be accompanied by the following symptoms:
- In mild cases, slight itching or burning and aching in the jaw joints may be felt. Throughout the oral cavity, the gums can drop up to three millimeters. But the teeth do not wobble; their stability appears.
- With an average degree, patients complain more about a cosmetic problem: the size of the interdental spaces increases, the size of the crowns of the teeth increases. In addition, many patients complain that tooth sensitivity has increased. The gums may become slightly pale.
- In severe cases, teeth become mobile and may move. Dense deposits are clearly visible on the necks of the teeth. In severe cases, teeth may fall out. This form is characterized by inflammatory processes.
Periodontal disease can easily be confused with chronic periodontitis.