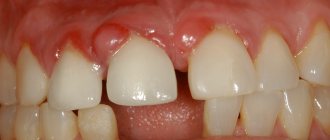
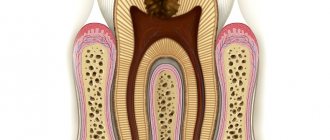
Dental periodontitis is an inflammation of an infectious nature that occurs at the membrane of the tooth root and affects the tissues of the oral cavity located next to it. Periodontitis is difficult to confuse with other dental diseases, because it has a clear symptom – severe and constantly increasing pain, which cannot be relieved by taking tablets from the pharmacy.
Treatment of periodontitis must be carried out urgently, because you risk not only losing a tooth, but also acquiring complications that are dangerous to the overall health of the body! How periodontitis occurs, what signs will help to identify the disease in a timely manner, how periodontitis is treated in dentistry, at what prices the service is offered in Moscow - we will talk about this in detail in this article.
Causes of dental periodontitis
Various reasons can lead to the appearance and development of dental periodontitis, but in the vast majority of cases the disease appears:
- Against the background of untreated dental caries and pulpitis;
- Due to poor quality treatment of tooth canals, or more precisely, mistakes made when filling the canals.
Less commonly, periodontitis occurs after injuries, incorrectly installed dental fillings, or violation of the dosage of dental medications.
Whatever the cause of periodontitis, its treatment cannot be delayed due to fear of dentists. It is important to understand that you will not stop the inflammation on your own, with pills or folk remedies, and the more it progresses, the less chance you have of saving the tooth. In addition, periodontitis can also affect neighboring healthy teeth.
How to identify periodontitis and not confuse it with caries or pulpitis? We already talked about the most striking symptom of the disease at the very beginning of the article, but the signs of periodontitis may vary depending on the form of the disease. Therefore, below we will consider the main types of dental periodontitis, as well as talk about their characteristic symptoms.
Take a short test and calculate the cost of treatment!
Take a short test
- Which teeth have caries?
- Visual assessment
- Reaction to stimuli
- Cost calculation
×
Manukyan Artavazd Genrikovich
Chief physician of the clinic
Causes of the disease
- Deep caries
- Pulpitis
- Periodontal trauma due to external influences (for example, sports injury)
- Infection through the bloodstream if there is any infection in the nasopharynx or upper respiratory tract (for example, with sore throat or tonsillitis)
- Poor quality treatment of dental canals (perforation of the root, leaving fragments of dental instruments);
- Bad habits (biting a pen or pencil, biting thread with teeth, etc.)
- Chronic problems in the endocrine system
- Decreased immunity, regardless of the cause
Important: only after an examination (including hardware) will the dentist be able to determine what caused the disease. Our network of clinics has all the necessary equipment that allows a specialist to accurately determine the stage, form and cause of the pathology.
Signs of acute periodontitis
Symptoms of acute periodontitis are always pronounced. Among them:
- Acute aching pain, the intensity of which is constantly increasing;
- Pain increases when trying to eat;
- If treatment for periodontitis was not started on time, attacks of pain will appear more and more often, and the intervals between them will become shorter and shorter;
Against the background of intense pain, a person cannot eat, speak, sleep, and may develop an elevated temperature. In the acute form of periodontitis, significant tumors and swelling often appear in the area of the diseased tooth. The cheek may also swell. This occurs due to the active accumulation of pus in the soft tissues of the oral cavity.
Operative (surgical) treatment of periodontitis
Surgical techniques for the treatment of periodontitis are used if conservative therapy turns out to be ineffective or initially inapplicable due to clinical reasons. In 90% of cases, doctors try to perform tooth-preserving operations, that is, resort to a type of intervention that will eliminate inflammation, but at the same time preserve the dental unit. These types of interventions in the treatment of periodontitis include:
- Resection of the root apex. It is indicated for use when cysts and granulomas are identified during diagnostic procedures. The essence of the operation is to remove all infected tissues along with the apical part of the tooth root;
- Cystectomy. During this type of intervention in the treatment of periodontitis, the formed cyst or granuloma is removed, and the apical part of the root is excised, in which inflammation has caused pathological tissue changes.
After the operations, treatment and hermetically sealed dental canals are also carried out.
Another surgical method for treating periodontitis is an operation to amputate the apex of the tooth root. But it is possible only on multi-rooted teeth and taking into account the healthy state of the other roots of the dental unit. During intervention for the treatment of periodontitis, the crown part of the tooth can be preserved completely or partially removed. In our dental clinic in St. Petersburg you can receive services for safe and painless treatment of periodontitis. At all stages of the treatment process, dental specialists will use ultra-modern dental techniques and instruments to ensure the effectiveness of the treatment as a whole and guarantee the absence of complications.
Symptoms of chronic periodontitis
Chronic periodontitis is a very insidious form of the disease, since it can develop completely asymptomatically. It is extremely rare for a person to feel a slight pain when trying to bite something on a sore tooth; sometimes unpleasant sensations appear when consuming hot food and drinks.
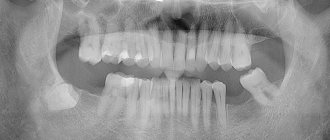
Chronic periodontitis of the tooth is diagnosed with an x-ray, which clearly shows the process of bone destruction at the apex of the tooth root. This form of the disease has its own classification, according to which there are: fibrous, granulating and granulomatous periodontitis. With fibrous periodontitis, there is almost no pain, which is why it is most often recognized either in the acute phase or during an examination by a dentist and x-rays.
Treatment of this form of periodontitis is quite simple and is carried out in 1-2 visits to the doctor. Granulomatous chronic periodontitis most often develops asymptomatically, but under the influence of certain external factors it easily turns into an acute form. The disease has its own characteristic symptom, manifested in the formation of granulomas - capsules with pus, which separate tissues affected by inflammation from healthy ones. The treatment process for granulomatous periodontitis is long and complex, it can last for several months and even require surgical intervention!
Diagnostics and treatment protocol
The main diagnostic method is radiography. After analyzing the patient's complaints given in the previous section, the dentist will assume the presence of periodontitis. Using the method of percussion (tapping), probing, and determining the reaction to cold, the doctor receives additional information about the condition of the dental unit and surrounding tissues. But it is possible to make an accurate diagnosis only after performing an X-ray or computed tomography. The doctor will see on the image (or monitor screen) internal carious cavities, sparse periodontal tissue and, possibly, formed granulomas and cysts. The exception is the situation with an acute form of pathology. The disease begins quickly, changes in the structure have not yet occurred, so radiography in this case will not be informative.
The treatment algorithm depends on the form and stage of the pathological process.
Treatment options: conservative (elimination of pathogenic microflora in the endodontist), surgical (removal of the root or part of it, the entire tooth), combined. The doctor’s efforts are aimed at eliminating the causes of the disease and its current manifestations. Treatment protocol for acute periodontitis:
- creation of endodontic access to the root canal and removal of necrotic masses;
- antiseptic treatment;
- placement of the medicinal product (applying a periodontal bandage);
- antibacterial drug therapy (course);
- checking the condition of the canals after about 3 days, if the condition is satisfactory, installing a temporary filling;
- X-ray to monitor the condition after 2 months, fixation of a permanent filling.
Treatment protocol for chronic periodontitis:
- creating access to the channel, cleansing;
- drainage;
- endodontic therapy;
- treatment of the canal with a solution of silver salts;
- checking the condition of the periodontium using radiography;
- when the condition returns to normal, a filling is installed. If there is no improvement, removal of the apical part of the root (resection), the entire root or the entire tooth. The use of partial or complete extraction is mandatory in the presence of granulomas and cysts.
How does the acute phase of chronic periodontitis manifest?
When exacerbated, chronic periodontitis of the tooth expresses itself with the same symptoms as the acute form of the disease. That is, there is a strong, aching pain, swelling of the gums and swelling of the cheek. Typically, chronic periodontitis enters the acute phase when the immune system is weakened, the flu, ARVI, or simply severe hypothermia are present. If, during an exacerbation of the chronic form, a fistula appears in the gum area, pus will flow from the area of inflammation and the pain in the tooth will gradually subside.
But this does not mean that periodontitis has gone away on its own; the inflammatory process will continue to develop and will manifest itself again under favorable external factors, which we discussed just above. Based on the type of periodontitis, a treatment regimen is selected. The price of the service depends on the regimen chosen for treating the disease. We will tell you below about all the stages of treatment of dental periodontitis in different forms and prices for procedures. But no matter in what form periodontitis develops, its treatment always begins with diagnosis.
Diagnosis of periodontitis involves examination of the oral cavity, x-rays, and examination of patient complaints. All this together helps to accurately diagnose the form of periodontitis and prescribe adequate and effective treatment.
Clinical symptoms
- Pain in the affected area, radiating to surrounding tissues
- Increased pain when biting or touching
- Swelling of the gums (not always)
- Enlarged lymph nodes
- General malaise caused by intoxication
- Increased body temperature
- The appearance of slight tooth mobility
- Possible discoloration of tooth enamel
- Fistula formation (not always)
- Discharge of pus from the gums near the affected dental element (not always)
Note: symptoms can manifest themselves either as a complex or as several symptoms. Therefore, it is important that the patient, if at least some of them appear, contacts the dentist. You can make an appointment with our specialists by phone or by leaving a request on our website.
Periodontitis treatment price
The cost of periodontitis treatment is always calculated individually, because it consists of a number of factors. The price of the service will depend on the set of diagnostic measures that are carried out not only at the beginning of treatment, but also at its intermediate stages. The price of the service will be influenced by the form of the disease, method of treatment, additional procedures, equipment and drugs that can be used during its course.
If you want to know the price of periodontitis treatment or make an appointment with Uni Dent dentists, just dial our contact phone number!
Periodontitis treatment time
If you have been diagnosed with periodontitis, you should prepare for a lengthy treatment process. You will have to visit the dental clinic more than once, and in addition, strictly follow all the recommendations that the specialist will give you during the treatment process. Violation of medical recommendations can lead to complications that will increase the complexity and duration of periodontitis treatment. In the simplest case, when treating periodontitis, you will have to visit the dentist two or three times; treatment will be longer if it is supplemented by physical procedures and will require repeated placement of antibiotics into the tooth canals and consultation with highly specialized specialists. Remember that high-quality treatment of periodontitis will imply mandatory control photographs after each stage.
Radiography will allow you to track the positive changes achieved after certain procedures for the treatment of periodontitis, and evaluate the quality of canal filling. Only this approach guarantees a stable and positive result in the treatment of periodontitis and eliminates relapses of inflammation and complications.
Prevention
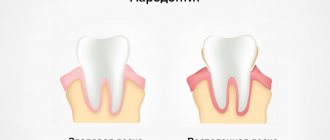
Prevention of periodontitis is not much different from the prevention of caries. To prevent the development of the disease, it is necessary to pay increased attention to the following factors:
- Proper brushing of teeth. Maintaining oral hygiene helps prevent the appearance of plaque, which is an optimal environment for the development and growth of microorganisms that cause damage to enamel and hard tissues.
- Regular visits to the dental clinic. By detecting periodontitis in a timely manner, it can be cured with minimal surgical intervention. During preventive examinations, the doctor will perform a professional teeth cleaning, removing hard deposits in the form of tartar, which will reduce the risk of developing the disease.
- Your own diet. Sweet foods rich in carbohydrates promote the growth of microorganisms responsible for the appearance of plaque, which provokes the appearance of periodontal disease. An excellent preventive measure would be to include in your diet a large amount of vegetables, fruits, and foods high in calcium, which strengthen tooth enamel.
Following these recommendations does not imply serious costs, but it allows you to avoid serious problems in the future.