However, there are other reasons that simply oblige both doctors and patients to perform an ultrasound in case of delayed menstruation and the first signs of early pregnancy
(BRS). The main ones are:
- it is necessary to exclude an ectopic pregnancy and make sure that it is uterine;
- it is necessary to exclude hydatidiform mole, which in all clinical and laboratory signs is similar to pregnancy, but is a dangerous disease;
- in the presence of intrauterine pregnancy, it is necessary to determine the quality of the gestational process; if pregnancy pathology is detected, it is necessary to promptly find out the causes of the pathology and begin treatment in a timely manner;
- Ultrasound reliably determines the gestational age: this information also determines the due date;
- in the event that a delay in menstruation occurs, but pregnancy is not detected, an ultrasound will help determine the gynecological disease that is the cause of the delay in menstruation.
Thus, ultrasound during early pregnancy is absolutely necessary
, but there are still ideas about the dangers of ultrasound. However, the safety of medical ultrasound has been proven and reflected in international documents. Recommendations to reduce the duration of each LRS examination are ethical in nature, taking into account the concerns of expectant mothers regarding ultrasound. So what are the capabilities of ultrasound? If menstruation is delayed by only 3-5 days, an ultrasound scanner with a transvaginal sensor can register intrauterine pregnancy for a period of 2.5-3 weeks from the moment of conception. Ultrasound during early pregnancy allows you to determine the embryological stage of pregnancy, i.e. the period calculated from the moment of fusion of germ cells.
The calculation from the first day of the last menstruation, accepted in obstetrics, may be inaccurate; it is difficult to determine the expected moment of birth from it. To convert the embryological period of pregnancy to the obstetric period, it is necessary to add 2-2.5 weeks to the embryological period. In 2.5-3 weeks, the process of implantation of the blastocyst into the uterine mucosa is completed.
From this moment on, it is called a fertilized egg and becomes available for research. At this stage, the blastocyst or embryonic chamber looks like a dark round or teardrop-shaped formation, 4-5 mm in diameter. The embryonic chamber is surrounded by a membrane and does not reflect ultrasonic waves, i.e. she is echo negative. The embryo and extra-embryonic organs have a microscopic structure and parietal localization, therefore they are not yet visible using ultrasound: at this stage the fertilized egg looks like a homogeneous liquid. The site of implantation of the fertilized egg is most often located in the area of one of the tubal angles, but sometimes the localization of the fertilized egg is located low, closer to the isthmus. This proximal localization occurs if the blastocyst moves into the uterine cavity within a few days after leaving the fallopian tube and only then implants into the uterine wall.
If, when menstruation is delayed, an ultrasound does not detect a fertilized egg in the uterus, it is necessary to undergo an examination after one to two weeks so that the fertilized egg increases in size. The absence of a fertilized egg during repeated examination should alert the doctor: in this case, an ectopic pregnancy is possible. However, the diagnosis of ectopic pregnancy cannot be established using ultrasound alone; a more thorough examination is necessary.
Maternity hospital "Scandinavia" More details
In some cases, when a round fluid formation is detected in the uterine cavity, but laboratory and clinical data do not confirm the presence of pregnancy, repeated examination will help diagnose the presence of a glandular polyp, cyst, or myomatous nodule protruding into the uterine cavity. The round liquid formation may appear small. Such problems need to be solved only in a specialized institution licensed to work with pregnant women. It is also necessary to undergo an ultrasound of the LRS (and any other stage of pregnancy).
In a antenatal clinic, maternity hospital, perinatal center, only a professional - an echoscopist - is competent in the field of physiology and pathology of the female reproductive system, obstetrics and applied embryology. Currently, centers that provide diagnostic services are very common - these centers do not provide professional examination at the proper level and make a large number of errors when making a diagnosis.
So, pregnancy is detected, the fertilized egg has implanted into the wall of the uterus and is growing very quickly in size. 17-20 mm is the diameter of the fertilized egg at four weeks of pregnancy. The fertilized egg becomes oval, the size of the uterus increases slightly, and asymmetry of its walls appears - one wall becomes thicker than the other. The embryo will become visible only at 5 weeks of pregnancy, but in the meantime the yolk sac, which stores a supply of nutrients for the developing embryo, is clearly visible. An elongated 5-week embryo is several mm long; an amniotic leg, the future umbilical cord, stretches from the embryo to the inner surface of the fertilized egg. From this moment, the embryo can move freely in the fluid of the embryonic chamber - it leaves its parietal position.
At 5 weeks of pregnancy, it is already possible to determine whether one embryo or two have settled in the embryonic chamber. The number and structure of the amniotic membranes and chorion - the future placenta - determine the type of future twins. If the germinal material in the blastocyst is doubled, identical (monochorionic) twins with a completely identical set of chromosomes develop. Children from such twins are always same-sex and absolutely similar to each other.
But if, before conception, two follicles ovulate in different ovaries, then two pairs of germ cells merge and two blastocysts are formed, which are implanted and two fertilized eggs with two embryos are formed. In this case, fraternal twins are formed - bichorionic or dichorionic. Such children are not twins in the strict sense of the word, because they have different sets of chromosomes, they may be of different sexes and not at all similar to each other. 70% of twins born are fraternal. But, in addition to twins, there are also triplets, and in general multiple pregnancies. Various combinations of amniotic membranes and chorions are possible: for example, triplets can consist of two twins and one fraternal child. Ultrasound of LRS easily identifies the type of twins or triplets, but in later stages it is more difficult to do this, because the embryonic chambers will fill the entire uterine cavity. But besides twins and triplets of this type (each embryo is in a separate embryonic chamber), there is a pathological variant of multiple pregnancy (monamniotic monochorionic pregnancy), when the embryos are not separated by an interamniotic septum. In this case, the possibility of conjoined (Siamese) twins and the development of a genetically inferior fetus is possible. Such a pregnancy must be terminated at the earliest possible stage and the development of such a catastrophe must be prevented. It is the ultrasound of the LRS that makes it possible to predict and prevent the tragic development of pregnancy. Since the development of bi-twins occurs due to the ovulation of two follicles, there are two corpora lutea (CL) in the ovaries.
What is the corpus luteum?
VT occurs in the ovary at the site of an ovulated follicle: VT is a temporary hormonal organ. VT is responsible for the production of progesterone, the main hormone of pregnancy; on ultrasound, VT looks like a round formation of heterogeneous soft tissue. It is impossible to determine progesterone deficiency from the image obtained by ultrasound, however, clinical and laboratory studies make it possible to diagnose this deficiency.
As pregnancy progresses, cysts can sometimes form in the VT. The reason cysts form is that the corpus luteum produces small amounts of fluid. Some of this fluid is resorbed by the blood vessels of the ovary, and some remains inside the ovary, forming vesicles, which form cysts (from the Greek root “cyst” - “bubble”). By 10-15 weeks of pregnancy, the VT cyst completely resolves, as the VT itself decreases. VT cysts do not pose a threat to pregnancy, but sometimes a woman may feel pain in the lower abdomen, mistaking it for a symptom of an impending miscarriage.
Can an ultrasound detect signs of an impending miscarriage?
During a miscarriage, the fertilized egg separates from the inner wall of the uterus and, as a result of contraction of the myometrium, it is expelled from the uterine cavity. This process is divided into phases: a threatened miscarriage, one that has begun, one that is “in progress,” and one that has occurred. Excessive tension (hypertonicity) of the uterine muscles is determined by ultrasound.
ONLINE CONSULTATIONS More details
What are the ultrasound signs of an incipient miscarriage?
- An ultrasound sign showing thickening of one of the walls of the uterus can be deceptive, since there is a physiological asymmetry of the walls of the uterus, which is detected even with ultrasound of the LRS. Short-term contractions of the uterus may occur due to the pressure of the vaginal sensor on the area of the isthmus of the uterus. Such a short-term contraction can be taken as a sign of an impending miscarriage. Long-term hypertonicity is distinguished from short-term hypertonicity using a transabdominal sensor with an empty bladder. Congestive hypertonicity, indicating a threat of miscarriage, exists for a long time, and short-term hypertension soon disappears.
- A change in the configuration of the fetal egg, turning its shape into a scaphoid or drop-shaped, a change in the outer contour of the uterus (a tubercle is raised above the even contour of the uterus above the contracted area of the myometrium).
- The most ominous sign of a threatening and incipient miscarriage is bloody discharge formed due to the fact that a certain amount of blood is poured into the uterine cavity next to the fertilized egg - subchorionic hematoma (gravid hematometra). When the fertilized egg invades the uterine wall, it destroys small vessels, while the increasing hematoma puts pressure on the fertilized egg, as a result of which the connection between it and the uterine wall is lost. Ultrasound determines the volume and localization of gravid hematometra, the time of its formation and the tendency to progression. Thus, the cause of pain and bleeding during a threatened miscarriage can be determined by ultrasound, which will help plan a treatment strategy (for hypertonicity of the uterus with and without a hematoma, it will be different and even mutually exclusive). But in the absence of pain in the lower abdomen, bleeding and other signs of a threatening miscarriage, ultrasound data indicating a threat must be interpreted as a purely hardware phenomenon. An analogue of the expression “threat according to ultrasound” can be the expression “headache according to urine analysis”.
However, spontaneous miscarriage occurs without pain and hypertension. This case is called a failed miscarriage (“anembryony”, “non-developing” or “frozen pregnancy”). During a frozen pregnancy, the vital activity of the embryo stops, and the contractile activity of the uterus, aimed at expelling the non-viable fertilized egg from its cavity, is absent.
The embryo and all elements of the embryonic complex are not visualized by ultrasound at the 5th week of pregnancy in the case of anembryony. This indicates that the development of the embryo stopped before the embryo reached a size of 1-2 mm. Repeated examination at weekly intervals if anembryonia is suspected will help clarify the diagnosis. When the embryo is clearly visible (for example, with a short amniotic leg and a parietal position of the embryo), it becomes possible to exclude aneibryony, in which the fertilized egg grows due to the fluid accumulating in it, but images of the embryo still cannot be obtained.
In the case of anembryony of one of the fertilized eggs during twins, the so-called biamniotic monoembryonic pregnancy, one of the embryos does not develop (failed twins). An “empty” amniotic cavity is found next to the normal one, then, as the fetal egg grows, it crescent-shapedly bends around the image of the normal amniotic cavity and then merges with it completely. An ultrasound phenomenon described as a “double contour of the ovum” or “amniotic thread in the uterine cavity” is a sign of failed twins. This sign does not disrupt the course of a singleton pregnancy.
A miscarriage that occurs after 5 weeks or more is called a frozen pregnancy. In a frozen pregnancy, the embryonic complex is visible (unlike anembryony). However, the embryonic complex consists of poorly differentiated linear objects, in which there are no signs of vital activity - heartbeat and motor activity, characteristic of a normal embryo during a progressive pregnancy.
Normally, with a 5-week pregnancy, the embryo reaches a size of 7-8 mm, with a 6-week pregnancy - 12-13 mm and 18-19 mm - with a 7-week pregnancy. The “growth” of the embryo is called the coccygeal-parietal size (CTD). The “waist circumference” of the embryo also increases - from 2-3 mm to 6-8 in two weeks. “Embryonic pulsation” - heartbeats are detected starting from the 5th week, but the heart on the screen cannot yet be distinguished. At 5-6 weeks of pregnancy, the frequency of contractions is 120-130 beats/min, by 7-8 weeks it reaches up to 200 beats/min. At this time, ultrasound examination already shows the extension movements of the embryo.
The head end can be distinguished from the pelvic end by the 5th week after conception, and by the 6th week tubercles appear in the place of the future limbs. After the 8th week of pregnancy, the internal organs of the fetus are visible, the spine and skull bones are visible by the end of the 7th week. A living, healthy and mobile embryo will meet with the expectant mother and doctor in the ultrasound diagnostic room at 10-14 obstetric weeks (that is, 8-12 weeks from conception). The story about this meeting is yet to come. During pregnancy, the embryo faces many events and dangers, which it can successfully avoid with the help of the mother, the doctor and, of course, medical ultrasound. Soon he will become not an embryo, but a fetus, and a little later - a newborn!
Download our mobile application
More details
Diagnostics
Anembryonia can be suspected if the size of the uterus does not correspond to the gestational age and if there is no fetal heartbeat. If a dynamic determination of the hCG level is carried out, then its insufficient growth is observed. Diagnosis of anembryonia using ultrasound is the main informative method. It is usually detected during a routine examination (week 5-7). An ultrasound detects a fertilized sac in which there is no embryo. If the pregnancy is short, the doctor may prescribe a repeat ultrasound in a week to make sure the embryo has died.
Our equipment
In our work we use the latest achievements of world practice. Our doctors conduct ultrasound examinations using expert-level devices, such as GE LOGIQ E9, GE VIVID 9, GE VOLUSON E8, GE VOLUSON E10.
The VOLUSON E10 ultrasound machine is equipped with a special electronic sensor that allows doctors to diagnose fetal malformations, assess the risk of hereditary pathology, and pregnancy complications with maximum accuracy. From the earliest stages, using the unique Radience Flow modes, it is possible to assess the structures of the fetal heart with maximum accuracy and exclude developmental defects, and the widest range of 3D and 4D capabilities, including the HD life visualization mode, makes it possible not only to evaluate in detail the anatomy of the internal organs of the fetus, but also to see your baby with maximum realism from the very beginning of pregnancy.
Lack of embryos in the IVF protocol – who is to blame and what to do?
On June 4-6, 2021, the next conference “Cornerstone Aspects of Reproductive Medicine” (CARM) was held in Moscow. As always, our doctors took part in it. At the embryology section, Yulia Alekseevna Koloda, a reproductive doctor, candidate of medical sciences, medical director of our reproduction center, spoke to her colleagues.
The topic of Yulia Alekseevna’s report is “Adverse embryological outcomes: Who is to blame and what to do?” These questions, of course, concern not only specialists. Therefore, we will briefly and, as simply as possible, retell the doctor’s report to future parents.
What are adverse embryological outcomes?
This is about the sad situation when the ART program does not reach the point of transfer, because there is nothing to transfer. The reasons may be different:
- poor response to stimulation – few mature, high-quality oocytes were obtained;
- few eggs were fertilized;
- blastocysts have not formed from fertilized eggs (blastocyst is the stage of embryo development that is considered optimal for transfer into the body of the expectant mother);
- blastocysts were formed, but of poor quality.
What is the reason?
The older the woman, the more difficult it is to obtain a sufficient number of high-quality eggs as a result of stimulation. Age is an obvious culprit in adverse embryological outcomes. But not the only one.
There is evidence of the negative effects of oxidative stress (the process of cell damage as a result of oxidation), obesity, and psychological stress[1]. Of course, this list also includes alcohol and smoking. The issue may be a genetic disorder in one of the partners or problems with sperm.
A separate story is the retrieval of immature oocytes and empty follicle syndrome. This happens if follicles that have not reached 14 mm are punctured, if LH and hCG do not work as expected. Empty follicle syndrome (EFS) can be associated both with disorders of folliculogenesis and with other reasons: errors during puncture, use of low-quality drugs, incorrect introduction of a trigger (at the wrong time, not completely), etc. EFF is more common with low ovarian reserve, in late reproductive age, with obesity, PCOS.
What can you do before your next attempt?
In preparation for the next ART program, both partners need to give up alcohol and smoking and normalize body weight. The expectant mother should take folic acid supplements in dosages recommended by the attending physician. Normalizing sleep and rest patterns can play a positive role (according to a recent systematic review[2], lack of sleep negatively affects ART outcomes, but more research is required).
Research is actively underway in the direction of adjuvant (additional) therapy. A recently published review[3] showed that adjuvant therapy with DHEA, testosterone, coenzyme Q10 and growth hormone is effective in patients with poor response: with a lower dose of stimulation drugs, the number of embryos and clinical pregnancy rates increased. But large studies are needed to confirm the findings.
In addition, after an unsuccessful program, patients are advised to:
- genetics,
- andrologist,
- psychologist.
What can you do during your next stimulation?
How to stimulate the ovaries in the new protocol to increase the chances of success? There are different approaches. The fertility specialist may use a different stimulation protocol, change the type of ovarian stimulation drugs or their dosage. Another trigger for the final maturation of eggs or the use of a double trigger may be effective when a combination of drugs is used [4] (ovulation triggers are drugs that ensure the final maturation of eggs), increasing the time between the introduction of the trigger and puncture of the follicles. It all depends on the specific situation.
IVF or ICSI?
A solution to the problem may be to use another method of fertilization - for example, ICSI or PIXI instead of IVF. However, in the absence of male factor infertility or low fertilization rates, routine use of ICSI or PICSI for all oocytes is not recommended[5]. The role of PIXI and other sperm selection methods continues to be studied and requires large studies on this issue.
If again there are no quality blastocysts
What if patients have had multiple ART programs in the past resulting in poor quality embryos? Maybe in this case we can simply transfer those embryos that we are able to obtain? Several studies have been conducted to answer this question. Thus, in 2020, the results of a retrospective study of 2585 cryotransfers of category BB blastocysts (good quality embryos) and 102 cryotransfers of category CC blastocysts (usually such embryos are not transferred or cryopreserved) were published [6]. It showed that transfer of CC blastocysts leads to pregnancies and the birth of healthy children. Although clinical pregnancy and live birth rates were lower in the CC blastocyst group compared with BB blastocysts (21.6% vs. 51.3% and 16.7% vs. 41.4%, respectively), assessment of neonatal outcomes did not demonstrate significant differences in body weight of newborns, the frequency of low birth weight children, early neonatal mortality and congenital malformations.
However, there are also studies that have demonstrated an increased risk of chromosomal abnormalities and malformations when poor quality embryos are transferred.
Transfer of low-quality blastocysts or embryos that have not reached the blastocyst stage (days 5-6 of development) can be used in patients with a history of receiving multiple poor-quality embryos after being informed of the possible risks.
In situations where no additional approaches allow achieving the desired goal - the birth of a healthy baby, donor biomaterial is used: donor oocytes or donor sperm, or both (so-called “cross-fertilization”).
Conclusion
Canceling a transfer in an IVF program, even in several programs in a row, is not a reason to give up. Specialists may use different approaches depending on the specific case:
- Change preparation for stimulation.
- Change the type of protocol, dosage, type of drugs for stimulation.
- Apply another trigger.
- Schedule an additional examination with your partner and prepare for the next ART program.
- Use another fertilization method.
- Change your migration strategy.
- Use donor biomaterial.
Continue to move towards success by trusting your doctor and strictly following his instructions. In this case, the experience of a reproductive specialist and his professionalism when performing stimulation and puncture of follicles are very important.
Make an appointment with a “Life Line” fertility specialist by phone or send a request using the form below. You and I will succeed! [1] Meldrum DR, Casper RF, Diez-Juan A, Simon C, Domar AD, Frydman R Aging and the environment affect gamete and embryo potential: can we intervene? Fertil Steril. 2021 Mar;105(3):548-59. doi: 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2016.01.013. Epub 2021 Jan 23. [2] Gabriela Caetano, Ines Bozinovic, Charlotte Dupont, Damien Leger, Rachel Levy, Nathalie Sermondade. Impact of sleep on female and male reproductive functions: a systematic review Fertil Steril. volume 115, issue 3, P715-731, March 01, 2021. [3] Yu Zhang, Chao Zhang, Jing Shu, Jing Guo, Hsun-Ming Chang, Peter C. K. Leung, Jian-Zhong Sheng, Hefeng Huang. Adjuvant treatment strategies in ovarian stimulation for poor responders undergoing IVF: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. Hum Reprod Update. 2020 Feb 28;26(2):247-263. [4] Chi-Huang Chen, Chii-Ruey Tzeng, Peng-Hui Wang, Wei-Min Liu, Heng-Yu Chang, Huang-Hui Chen & Ching-Hui Chen. Dual triggering with GnRH agonist plus hCG versus triggering with hCG alone for IVF/ICSI outcome in GnRH antagonist cycles: a systematic review and meta-analysis Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2018 Jul;298(1):17-26. [5] Intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) for non-male factor indications: a committee opinion. Practice Committees of the American Society for Reproductive Medicine and the Society for Assisted Reproductive Technology. Fertil Steril. 2020 Aug;114(2):239-245. doi: 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2020.05.032. Epub 2021 Jul 9. [6] Li, M., Yin, M., Wu, L. et al. Pregnancy and neonatal outcomes of morphologically grade CC blastocysts: are they of clinical value?. Arch Gynecol Obstet 302, 1511–1521 (2020).
Pregnancy management
When a long-awaited pregnancy occurs, you really need to find your doctor. This should be a person you can trust, with whom you can easily find mutual understanding, who respects privacy and confidentiality. These are the kind of obstetricians and gynecologists who work in Scandinavia to make pregnancy as easy as possible, and the birth of a baby remains a joyful memory.
You can find our pregnancy management programs here.
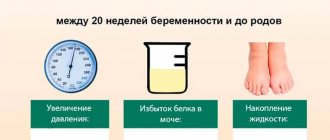
Department of Pregnancy Pathology
Despite the naturalness of the process, not every pregnancy goes smoothly, and you need to be prepared for this. Therefore, in Scandinavia, the pregnancy pathology department operates around the clock: you can come here if you have any symptoms or complications and count on timely and high-quality help.
Causes
The causes of anembryonia are still being studied. It is believed that the embryo dies due to its inferiority. This occurs with genetic pathologies that are incompatible with life. Gene defects can be inherited or caused by damaging factors.
In addition to a genetic abnormality, the cause of embryo death can be:
- exposure and radiation;
- exposure to harmful chemicals;
- acute infections in the short term;
- bad habits (smoking, alcoholism and drug addiction);
- inflammatory processes of the genital organs;
- stress;
- taking certain medications;
- a sharp change in hormonal levels.
Therefore, to avoid such a situation, pregnancy should be planned.