What is ascariasis?
The human roundworm is a large dioecious parasite. The male is noticeably smaller than the female, its length is 15-25 cm, the female can reach 26-40 cm, an adult female can lay up to 240 thousand eggs per day. This type of helminth can parasitize the intestines for a year. Ascariasis is common in all climatic zones of the globe, with the exception of permafrost areas, highlands and deserts. According to the WHO Expert Committee, more than 1 billion people in the world suffer from ascariasis every year, most of them are children of preschool and school age. The highest incidence rate is observed in regions with a hot climate: Asia, the North Caucasus, Transcaucasia, Sakhalin and Tomsk regions, Primorsky Krai.
Medicines
Photo: gripptips.ru
Infection with worms is dangerous, especially for children, so every family’s medicine cabinet should contain anti-worm medications and pharmaceutical preparations that have the most effective effect. To combat parasites, you can also use folk remedies, such as garlic, pumpkin seeds, fern extract, but only in addition to ready-made medical forms.
Doctors advise that if a parasite infection is detected, not to prescribe treatment on your own, but to consult a doctor for advice. Children are usually prescribed Nemozol.
Medicines for roundworms
Roundworms are the type of worms that are most often found in children. The use of drugs against ascariasis must be treated very carefully, especially if the drugs are prescribed to preschool children.
Drugs against ascariasis:
- Nemozol;
- Vermox;
- Pyrantel;
- McMiror;
- Piperazine.
Treatment of ascariasis with Nemazol
Pharmacological action of Nemozol for ascariasis.
The active component of the drug, albendazole, has an anthelmintic effect. Nemozol is effective against severe helminthic infestations and leads to the death of roundworms in intestinal cells. The drug Nemozol is eliminated from the body within twelve hours. In patients with diseases of the bile ducts, the period for complete withdrawal of Nemozol may increase. The drug Nemozol is effective against adults, larvae and eggs. Almost all nematodes and tissue parasites are sensitive to the action of the main component of the drug Nemozol.
There are contraindications to treatment with drugs for ascariasis, such as Nemozol:
- infectious intestinal diseases;
- viral diseases;
- pregnancy;
- breastfeeding children;
- days of menstruation.
It is recommended to take the drug Nemozol for ascariasis with fatty foods, which promote its good absorption. For children over two years of age and adults, Nemozol is prescribed in a dosage of one tablet (400 mg) or in a suspension of 20 ml. For children under two years of age, the recommended dose of Nemozol is 200 mg or a suspension of 10 ml. If necessary, Nemazol for ascariasis is taken again after three weeks.
Adults and children over 2 years of age should take 1 tablet of Nemozol with a dosage of 400 mg or 20 ml of suspension. Children under 2 years of age should be given 1 tablet with a dosage of 200 mg or 10 ml of suspension. If necessary, after 3 weeks, Nemozol can be repeated at the original dose.
Nemozol for ascariasis is not prescribed to pregnant women, as well as women who are breastfeeding. Treatment with Nemozol is contraindicated for children under one year of age.
Nemozol is also contraindicated for ascariasis in people with retinal damage, cirrhosis and liver failure.
Nemozol should not be prescribed for ascariasis in patients with depressed bone marrow hematopoiesis.
Side effects of Nemozol for ascariasis.
Exceeding the dosage of Nemozol leads to the following problems:
- nausea;
- dizziness;
- vomit;
- headache;
- gastrointestinal disorder.
In some cases, exceeding the dose of Nemozol for ascariasis leads to an increase in temperature, pressure, allergies and itching. Including the wrong dosage of Nemozol for ascariasis can lead to kidney problems and impaired hematopoiesis. There is no antitote for Nemozol poisoning; overdose is treated by gastric lavage and removal of intoxication.
While taking Nemozol for ascariasis, it is not recommended to drive a car, as it is dangerous.
Treatment with Nemozol for ascariasis is carried out only after consultation with a doctor.
Treatment of ascariasis with Vermox
Vermox is one of the most effective drugs for ascariasis, containing the active ingredient Mebendazole. The drug is available in tablet form in a dosage of 100 mg. The drug for ascariasis Vermox should be taken only after consulting a doctor, in a strictly prescribed dosage. Vermox is prescribed for some forms of helminthiasis, including ascariasis.
How to take Vermox correctly
Vermox for ascariasis is taken with water before meals, in the morning and evening, two tablets per day at a dosage of 100 mg, for three days.
Treatment with Vermox is incompatible with alcohol, fatty foods and medications for constipation.
At the end of treatment with Vermox, it is necessary to undergo a control examination for the presence of helminths.
Treatment of children from ascariasis with Vermox
Vermox is intended for children who become infected through contact with animals, in sandboxes, or through contact with other children. Tablets for ascariasis are prescribed by the doctor after testing for worms.
After taking Vermox, the helminths die on the third day and are excreted in the feces.
Before starting treatment, parents should carefully read the instructions for Vermox and act in accordance with them; the exact dose of the drug for ascariasis is prescribed by the doctor, in accordance with the age and weight of the child.
In some cases, treatment of ascariasis is carried out in combination with Vermox and Decaris. These drugs for ascariasis have different components and mechanisms of action on helminths; their overall effect helps to get rid of worms more effectively. Decaris destroys those types of helminths that Vermox cannot cope with.
How often and in what dosage should I give medications for ascariasis so as not to cause side effects? For the first three days of combined treatment with Vermox and Dekaris, it is necessary to monitor the child, see how he sleeps, whether there are any complaints of nausea, dizziness, or convulsions. If symptoms of an overdose of combination treatment appear, you should consult a doctor for advice.
Treatment with Decaris and Vermox for children of preschool and younger age can be carried out every six months. If such a need arises, Vermox plus Dekaris is given four courses per year, but always under the supervision of a pediatrician.
Treatment with Vermox is usually planned; tablets are given in the fall and spring, when the immune system is weakened. For adolescents, treatment is carried out once, with a Vermox tablet in a dosage of 100 mg, after meals. Drink plenty of water.
Treatment of ascariasis with Pyrantel
Treatment of ascariasis with Pyrantel is recommended by doctors all over the world, as this medicine helps to gently get rid of adult worms, their larvae and eggs. Pyrantel for the treatment of ascariasis can be given to children starting from six months of age, after consultation with a pediatrician.
The drug Pirantel has only one contraindication; treatment of ascariasis is contraindicated for people with liver disease.
The course of treatment for ascariasis with Pyrantel can be repeated after three weeks; this scheme is used for simultaneous infection with pinworms and roundworms. In case of weak effectiveness of the drug, the doctor may additionally prescribe treatment for ascariasis with Nemozol.
Use of Macmiror for ascariasis and lamblia
Macmiror is not used for ascariasis, but it is prescribed in combination with other drugs for the treatment of giardiasis and candidiasis.
Advantages of Macmiror:
- does not give side effects;
- easily excreted by the kidneys;
Macmiror acts against ascariasis, salmonellosis and various bacterial infections.
Not recommended for pregnant women and nursing mothers.
Treatment of ascariasis with Vormil and Piperazine
The drug Vormil is used to treat ascariasis, the active substance of the dosage form is albendazole, which destroys helminths at any stage of development. Consumed with fatty foods, in the dosage prescribed by your doctor.
Piperazine, the most commonly prescribed drug for ascariasis, affects the neuromuscular system of parasites, promoting their destruction.
Piperazine for ascariasis is such a mild remedy that it is prescribed even to pregnant women. The drug is contraindicated in diseases of the central nervous system.
Clinical manifestations
The source of infection is a person whose intestines are parasitized by females and males of roundworms. It occurs through alimentary (food), household contact and water routes, when mature roundworm eggs enter the body with vegetables and berries, water, and also through dirty hands. Currently, garden plots where human feces are used to fertilize the soil pose a great danger to the spread of ascariasis. In soil, roundworm eggs can remain viable for up to 10 years. In temperate climates, the infection season lasts from April to October, in warm, humid climates - all year round. This is especially true for those traveling on vacation to southern countries, where it is necessary to use only filtered water for cooking and drinking.
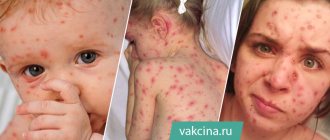
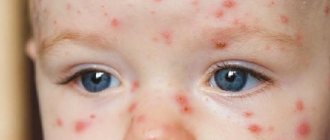
You should also not consume ice made from water of unknown origin. In the small intestine, larvae emerge from the eggs, penetrate into the intestinal wall and penetrate the blood vessels, and then migrate through the bloodstream to the liver and lungs - this is the first stage of parasitism, lasting about 2 weeks. It is then that the first signs of the disease appear: malaise, weakness, possibly an increase in temperature to 38 C - 39 C, chills, a rash in the form of blisters, abdominal pain, nausea and upset stool. A cough appears dry or with a small amount of mucous sputum, and dry and moist rales are heard in the lungs.
At the second stage of parasitism, larvae from the alveoli and bronchioles actively move with the help of the ciliated epithelium along the small and large bronchi and reach the oral cavity, are swallowed again and again enter the intestine, where they reach sexual maturity in 70–75 days. At this stage, the symptoms of invasion can be different and not always clearly expressed: usually these are loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting, cramping pain in the abdomen (around the navel). Some children have diarrhea alternating with constipation. Possible headache, dizziness, increased fatigue; children become capricious, absent-minded, their sleep becomes restless, and night terrors appear.
With massive infestation, young children experience pallor of the skin, mucous membranes, deficiency anemia, and delayed physical development as a result of impaired absorption of vitamins and microelements.
The most likely routes of infection
Ascariasis is not transmitted from person to person by airborne droplets or other contagious means (through a kiss, sneezing, coughing, shaking hands). A prerequisite for infection is the presence of parasite eggs in the soil. Therefore, parasitologists point to the most likely transmission options for ascariasis:
- possible when eating agricultural products (vegetables, fruits, berries, herbs) contaminated with soil particles with remains of human feces;
- neglect of the rules of personal hygiene after working with the soil, on personal plots, during construction, gardening and vegetable gardening;
- swimming in reservoirs, using drinking water from wells and boreholes located near public restrooms, sewer systems and street toilets;
- consumption of any food products of dubious origin - by eating undercooked meat, raw river fish, contaminated with helminth eggs, you can become infected with ascariasis.
How dangerous is ascariasis?
Once in the body, helminths not only feed on it, but also suppress the immune system. The state of immunodeficiency makes the child’s body susceptible to bacterial, viral and other infections, contributes to their protracted course and the formation of carrier status, and reduces the effectiveness of preventive vaccinations. Ascariasis when parasitized by a large number of helminths can be complicated by intestinal obstruction, jaundice, pancreatitis (inflammatory process in the pancreas). In some cases, roundworms, ascending the digestive tract, reach the pharynx and penetrate the respiratory tract, which causes asphyxia (severe breathing difficulties due to lack of oxygen). Sometimes roundworms affect the genitourinary system, causing cystitis and vulvitis.
Factors contributing to helminth infection
It is very easy to become infected with worms; then it is difficult to get rid of such a neighborhood. Worm eggs are introduced into the body by the future carrier of helminthiasis with the help of dirty hands, unwashed fruits, insufficiently cooked meat dishes, eating raw fish and failure to comply with basic hygiene standards.
Pets – cute cats and dogs – can also share worms with their owner. And also people suffering from helminthiasis, but sometimes not even suspecting it. Flies also participate in the spread of worm eggs, transferring them with their paws and proboscis to openly lying food and dishes.
Worm eggs can be found anywhere: on surrounding objects, door handles, on clothes, in dust, in the ground.
You can swallow contaminated water while swimming in any body of water, or become infected while working with soil.
Depending on the method of infection, there are contact helminthiasis (transmitted from person to person), geohelminthiasis (transmitted through the soil) and biohelminthiasis (when infected meat is eaten).
Prevention and treatment
If a child is diagnosed with roundworms, do not panic. It is necessary to treat simultaneously everyone who was in contact with him (as a rule, these are family members). Treatment prescribed by a pediatrician is carried out at home and only in case of massive infestations - in a hospital. Treatment should be comprehensive, taking into account the presence of concomitant diseases and the condition of the body as a whole. A complete protein diet, enzyme preparations (Creon, Mezim, etc.) are recommended; sometimes sorbents and multivitamins are needed.
Considering that helminthic infestations, as well as anthelmintic drugs, contribute to the development of intestinal dysbiosis, it is necessary to restore the intestinal flora with the help of fermented milk products and probiotics. Previously, products of plant origin were mainly used as anthelmintic agents: male fern extract, tansy and wormwood flowers, pumpkin seeds. But at present these drugs are not prescribed, because They are ineffective, have a lot of side effects, are toxic to the child’s body and require long-term use, sometimes up to 2 weeks.
Recently, new drugs have been created that have high anthelmintic activity, safety, and ease of use (once), which is very important for children. Some drugs are effective against different helminths at the same time: mebendazole (Vermox) or nemozol, pyrantel (Helmintox), decaris. You should not be afraid of the toxic effects of drugs. Since modern medicines are almost not absorbed from the intestines into the blood and have few side effects.
After a course of treatment, the signs of chronic intoxication disappear in the little patient, the condition of the skin improves, and the child becomes calmer. This indicates that the presence of chronic intoxication caused by helminthiasis is much more dangerous to health than a course of anthelmintic therapy.
Diagnostics
Photo: v.img.com.ua
In order to identify ascariasis and the presence of roundworms in the human body, it is necessary to undergo a full clinical examination. Most often, you just need to take a stool or blood test. After passing such tests, it will be clear whether infection has occurred. Of course, there are cases when tests may not show the presence of roundworms, but this happens in very rare cases. Therefore, after the first signs of the disease, you must immediately consult a doctor and get tested.
How to diagnose ascariasis in the human body?
In the early stages of infection, it is often very difficult to make an accurate diagnosis, because the signs of ascariasis are quite weak. Therefore, you should not act independently and make such a diagnosis without visiting a doctor and conducting laboratory tests. After all, it may be wrong, but the real disease will develop and bring complications. Diagnosis of ascariasis is carried out taking into account clinical and laboratory data, and epidemiological studies are also taken into account. To make a correct diagnosis, the specialist collects data:
- Source of infection and its possible manifestations;
- The duration of the period following the appearance of the first symptoms;
- Who did the patient contact with before seeing a doctor?
In children, the presence of ascariasis can be determined only three months after infection. Since in the early stages the helminths are not yet sufficiently developed, and the signs are not at all expressed, therefore it is very difficult to make an accurate diagnosis. But do not forget that it is necessary to consult a doctor after the first symptoms, because the impact of these parasites on a child’s body can be very harmful. Children are often scraped for worms, in which their presence is clearly visible.
Laboratory and clinical tests for ascariasis
Diagnosis of roundworms can be carried out in various ways, depending on the stage of the disease. There are several types of laboratory tests that can determine the presence of roundworms in the body at any stage:
- Parasitological method - helps to identify worms at an early stage of development;
- Serological and hematological methods help to detect specific bodies in human blood. A blood test for ascariasis can determine the stage of immunological reactions and show the level of leukocytes, because during infection it can increase (but not always);
Also, such methods determine the titers of ascariasis in the blood; this is a very important factor by which their level in the body can be determined.
At later stages, scatological examinations of feces are carried out, which make it possible to verify the presence of roundworms in the human body. But there are cases when, after examining stool, the diagnosis is not confirmed, although the disease does occur. Ascaris larvae may be absent from human feces if there is only one female (or male) in the body, which does not have the ability to reproduce. It is possible that during this period a person is treating another disease with special drugs that also prevent the proliferation of roundworms. Therefore, in some cases, a stool test may show a negative result. That is why doctors resort to biochemical tests that show the presence of roundworms and volatile fatty acids.
Also, in some cases, diagnosis of worms can be carried out using x-ray examination. After all, after roundworms pass through the pulmonary system, small focal inflammations appear, which are clearly visible on photographs for a long time.
Diagnosis of ascariasis in children
Laboratory diagnosis of ascariasis in children at an early stage is carried out based on clinical and epidemiological data that appears in the child’s blood, with a microscopic sputum smear and chest x-ray. Serological laboratory testing methods have not been recognized as effective and therefore are not widely used. In a child, an accurate diagnosis of roundworms can be made only after three months after infection, when the chronic intestinal stage begins and they become sexually mature. This is why stool examination is carried out, after which their presence is visible.
Also, in some cases, worms can be detected during X-rays of the intestines and chest. You should not delay getting examined and seeing a doctor, because children can develop serious complications and developmental disorders. Treatment must begin immediately after examination and detection of harmful parasites in the body.
Diagnosis in the early stages will help to start treatment in a timely manner and get rid of worms faster.
Classification
For the most curious readers, we have compiled a detailed clinical classification of ascariasis. It is based on several criteria:
1. By type:
- typical (manifest);
- atypical (asymptomatic).
2. By stages:
- early (migration);
- late (intestinal).
3. According to the severity of clinical manifestations:
- light;
- moderate severity;
- heavy.
4. For complications:
- uncomplicated;
- with intestinal complications;
- with extraintestinal complications.
In ICD-10 (International Classification of Diseases, 10th revision), the disease is coded B77.
Special studies
Among the special studies that are effective in diagnosing the disease are serotological methods. They are based on the detection of antibodies to helminths that appear after invasion. The body's natural resistance to parasites changes the composition of the blood serum, but reactions are recorded only at the beginning of the migration phase, and they do not appear in the intestinal phase. Serotological tests include:
- immunofluorescence study;
- rapid erythrocyte sedimentation test;
- various reactions - ring-pretation, indirect hemagglutination, precipitation, complement fixation, and so on.
X-ray equipment is also used during examinations - if it is necessary to exclude/confirm ascariasis signs and damage to the intestines and lungs. The images can reveal intestinal obstruction and the presence of the volatile Leffler infiltrate in the lung tissue, but the helminths themselves, like their larvae, are not detected. The difference can only be revealed by comparing several images, but for this you need to take an x-ray again, which is undesirable.
Ultrasound does not detect the localization of roundworms; it can be used to diagnose organ damage and symptoms of damage to the digestive tract - pancreatitis, colitis, Crohn's disease, ulcers. The causes are not determined with precision, so ultrasound examinations are needed mainly to differentiate diseases. A clear picture of toxic damage to the body and the lack of useful substances due to their absorption by parasites is given by irido-scanning on IridoScreen devices, which shows deviations in the balance of microelements in different organs.
intestinal ascariasis
Symptoms during the migration phase
At an early stage, the disease often does not cause symptoms, especially in children. However, with the accumulation of parasites and the amount of dangerous waste products they secrete, an allergic syndrome develops, a blistering rash appears, and swelling occurs due to the molting of larvae. With massive invasion, the time for manifestation of manifestations decreases, and they themselves become pronounced - cough, pain, allergic anaphylactic shock. In the acute course, patients have a low-grade fever, sometimes up to +40°C, and last for a week or more; due to infection and intoxication, the person begins to quickly get tired, weaken, and have decreased performance.
Liver syndrome in the migration phase is characterized by discomfort in the abdomen, changes in blood composition - bilirubin, the level of ALT and other enzymes increase. When coughing, chest pain is felt, and blood “streaks” appear in the sputum. If you conduct a medical examination at this moment, you will hear large-bubble rales and a shortened pulmonary percussion sound. At the migration stage, the signs of roundworms are similar to the symptoms of tuberculosis, even oncology. This:
- sudden change in blood pressure;
- suffocation;
- enlarged lymph nodes and so on.
rash due to ascariasis