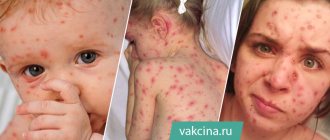
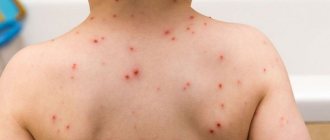
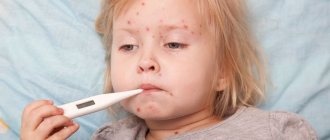
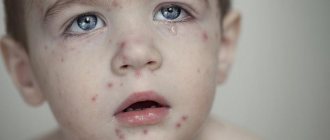
How chickenpox begins in children - the first signs and symptoms in the initial stage (photo)
Chickenpox or varicella is an acute infectious disease caused by viruses of the herpes family. A distinctive feature of chickenpox is a rash on the skin in the form of small blisters. Almost all children aged 2 to 7 years old suffer from chickenpox, especially if they attend kindergarten, since the pathogenic virus is very volatile and can penetrate not only into adjacent rooms, but also into apartments.
In addition, a large percentage of the incidence of chickenpox in children is due to the fact that the latent period of the disease is 14-21 days, due to which the virus has time to spread and cover all children in the group or kindergarten. The chickenpox virus ceases to act until the last rash ends, that is, the virus stops being transmitted when the last blisters begin to heal.
How can you get infected?
The virus is transmitted from person to person by airborne droplets. Chickenpox penetrates through the mucous membranes of the mouth, respiratory tract, and eyes deep into the body.
The chickenpox virus is very persistent and spreads quickly. He has the ability to penetrate even into other rooms and neighboring apartments. This is why children in groups become infected with chickenpox so easily. Just one child in a group who becomes infected with chickenpox immediately becomes dangerous for the children of the entire institution.
Description
Chickenpox, or chickenpox, is an acute anthroponotic (only in humans) infectious disease with an airborne (aerosol) mechanism of virus transmission, characterized by the appearance of a vesicular rash, the presence of fever and general intoxication syndrome.
Cause of chickenpox (chickenpox)
The causative agent (“carrier”) of chickenpox (chickenpox virus) is the human herpes virus type 3 – “Varicella Zoster”. In the environment, the virus is absolutely unstable, highly sensitive to disinfectants and ultraviolet radiation; dies when exposed to high temperatures. It multiplies in the nuclei of affected cells and has a pronounced cytopathic (damages the cell) effect.
The source is patients with all forms of chickenpox, as well as patients with herpes zoster (herpes zoster). The route of transmission of the virus is airborne droplets (aerosol), that is, the virus is released as a result of sneezing, kissing, coughing and, banally, during a conversation, released along with microscopic drops of saliva. The virus has a very high volatility, which makes it very contagious even when located at a distance of 15-20 meters from a sick person. As a result of infection of a pregnant woman, the virus, entering the blood and causing viremia, can penetrate the placenta and enter the fetus with further consequences (described below). The contagiousness of chickenpox is quite high - patients are contagious 24 hours before the first elements of the rash appear and up to 5-6 days from the moment the last rash appears. Sensitivity to chickenpox is quite high, but newborn children have innate immunity, which is passed on from their mother, so chickenpox in children under 6 months of age, as a rule, does not occur.
The largest number of cases occurs under the age of 7 years, and mortality occurs when the disease occurs in old and senile age. The peak incidence of chickenpox occurs in two periods: the autumn period and the transition from autumn to winter (October - December). After suffering from chickenpox, a person develops non-sterile immunity to chickenpox, which remains for life, so repeated cases and relapses of chickenpox are extremely rare.
The incubation period is long and ranges from 9 to 22 days. Chickenpox in adults often occurs with a prodromal period (without clinical manifestations). In children, the disease most often begins with the appearance of elements of a vesicular rash, and only after a few days do general manifestations appear.
Types of chickenpox (classification of chickenpox).
Chicken pox occurs in typical and atypical forms and in terms of severity is mild, moderate and severe. Chickenpox is also classified according to ICD-10 (with meningitis, encephalitis, pneumonia).
Atypical forms of chickenpox are divided into:
- Hemorrhagic form - a common consequence of this form is bleeding, and this form occurs in people with thrombocytopenia.
- Pustular form - develops when a bacterial agent is attached.
- Gangrenous form - can lead to the development of sepsis and occurs most often in patients with weakened immunity.
- The generalized (visceral) form of chickenpox is characterized by development in patients with immunodeficiency. It is very difficult, the symptoms are more pronounced and often ends in death for the sick person.
- The rudimentary form is found in children who received immunoglobulin during the incubation period. It flows quite easily.
The severity of chickenpox is directly determined by the degree of intoxication syndrome and its criteria, as well as the presence of specific vesicular rashes on the skin and mucous membranes. It should be noted that there are also so-called abortive (very mild) cases of the disease, which occur without the appearance of fever and are characterized by the appearance of single rashes on the skin of the abdomen and back. Such chickenpox is detected in kindergarten during examinations during outbreaks.
To the question “how long does chickenpox last?” It is difficult to answer unequivocally, since the duration of the disease directly depends on the form and course of chickenpox. On average, in the classical (typical) course, the duration of the disease is from 12 to 16 days.
Chickenpox (varicella) of newborns
The manifestation and clinical picture of chickenpox directly depends on the time when the pregnant woman was infected with the virus. Fetal syndrome (usually manifested by underdevelopment of the upper and lower extremities, the appearance of scar changes on the skin, atrophy of the cortical structures of the brain, microcephaly - a decrease in the size of the brain and the volume of the skull) occurs very rarely, especially if the pregnant woman was infected in the first trimester of pregnancy . Chickenpox during pregnancy can have consequences for the fetus according to two other criteria:
- In the case when a pregnant woman is infected with the virus 4 days or less before giving birth or within 2-3 days after birth, the newborn may develop a generalized (so-called visceral) form of chickenpox.
- If a pregnant woman is infected with the virus more than 4 days before giving birth (5 days, a week, a month), she develops antibodies to chickenpox, which, penetrating into the child’s body, can prevent the development of a generalized form.
The consequences of chickenpox (chickenpox)
Both secondary associated infections and chickenpox itself can lead to similar consequences. Complications after chickenpox (typical form) occur quite rarely.
- Bullous impetigo. As a result of the addition of a secondary (bacterial) infection (in particular, Staphylococcus aureus), a disease such as bullous impetigo, characterized by massive lesions of the skin, can develop.
- Skin gangrene. It develops when staphylococcus penetrates the subcutaneous fat and multiplies in the deep layers. Very often this leads to the development of a septic process.
- Wound scarlet fever. The development of such a complication is possible when streptococcus (hemolytic) penetrates into one of the elements of the chicken rash, which leads to the appearance of a small rash throughout the body, characteristic of scarlet fever.
- Pneumonia. Pneumonia is a fairly serious complication of chickenpox, and in the first few days, pneumonia (chickenpox) can lead to respiratory failure and death, especially in people with immunodeficiency and pregnant women. In the future, abscesses and their breakthroughs can form with the formation of fistulas.
Other complications may be phlegmon, lymphadenitis, erysipelas, myocarditis may occur, but the most severe complication is post-varicella encephalitis, the mortality rate of which is 10-15%.
Swimming with chicken pox
There is an opinion that you should not wet the rash of chickenpox at all, because this can lead to generalization of the process. This question can be considered from two sides: when to wet and how to wet. The state of the current plumbing system and the quality of the water indicate that it is undesirable to wet the elements of the rash and bathe with chicken pox, especially before the crust appears. This is due not only to the addition of bacterial flora, but also to the fact that the appearance of a virus in water can lead to the contamination of unaffected areas of the skin, which can subsequently lead to severe intoxication. At the same time, some foreign sources, on the contrary, recommend bathing with chickenpox with the addition of a small amount of potassium permanganate to the water, which will promote better healing and eliminate itching. Based on this, it is possible to unequivocally answer the question “is it possible to wash with chickenpox?” it is forbidden. You just have to remember that even if you decide to wash yourself during the period of illness, you should not rub the elements of the rash with a washcloth. It is advisable to take a shower without steaming your skin.
First signs
How does chickenpox start in children? First of all, the child develops:
- high temperature (up to 39.5°C),
- feverish reaction;
- moderate intensity headache;
- pain in the abdominal area (not always);
- general malaise;
- signs of intoxication (possible nausea and vomiting);
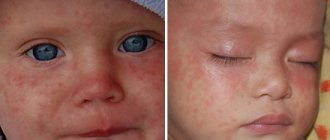
The first signs of chickenpox in children, as a rule, are indistinguishable from “normal” ARVI. The main symptom of chickenpox is a characteristic rash (first small pink spots, and then blisters with clear liquid).
Forms and stages of the disease
The disease occurs with or without obvious symptoms. Dermatologists identify several characteristic forms of chickenpox:
| Light | the rash is not abundant, the condition is satisfactory, there are no secondary rashes, there are no enanthems. |
| Medium-heavy | Intoxication, weakness, and headaches were noted. Repeated rashes are observed, the period is up to five days. A specific rash is noticeable, enanthems are detected. The temperature reaches 39 degrees. |
| Heavy | pronounced intoxication, high temperature (up to 40 degrees). Numerous blisters cover the entire body, including the scalp and genitals. There is a high risk of damage to internal organs. Often the picture is complicated by a pyogenic infection. |
The hidden or atypical form has several varieties. All of them are dangerous with serious complications:
| Generalized | noted in patients receiving chemotherapy and people with reduced immunity. Internal organs, the nervous system, are affected, the brain is affected, and chickenpox pneumonia develops; |
| Hemorrhagic | difficult to treat, the prognosis for a weakened immune system is extremely unfavorable; |
| Gangrenous | the variety is characterized by the addition of pathogenic microflora, severe poisoning of the body, necrosis of certain areas of the skin, and poor health. |
Symptoms and signs of chickenpox in children
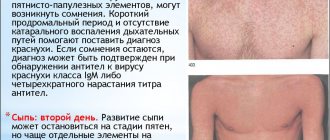
Basically, chickenpox is characterized by a typical, uniform course in all children, with rare exceptions, so the following main symptoms of this disease in the initial stage can be identified (see photo):
- Sudden onset of the disease with the development of intoxication and a sharp increase in temperature.
- Almost simultaneous appearance on the skin, sometimes on the mucous membranes, of typical vesicular elements.
- An undulating course of the disease process with periodic additions of papulovesicles.
- Increase in body temperature with each new wave of rash.
- The formation of crusts on the surface of the bubbles, which subsequently do not leave any scars after recovery.
All stages of chickenpox in children follow each other sequentially and are characterized by certain typical symptoms.
- The initial stage of chickenpox and the child is the incubation period, which covers the time from the penetration of varicella-zoster into the baby’s body until the immediate manifestation of the first clinical symptoms. Its duration is considered to be from a minimum of 5 to a maximum of 21 days, however, on average it can last about 2 weeks. At this time, varicella-zoster actively multiplies and also accumulates in the mucous membranes of the oropharynx and nasal cavity, and is then able to overcome all protective barriers and penetrate the blood. At this moment, the very first sign of chickenpox in children develops: the appearance of a rash on the body, accompanied by a high temperature.
- The stage accompanied by the symptoms described above is called the initial stage, but sometimes it is preceded by a so-called prodromal period, during which a rise in temperature, headaches, weakness, and lethargy are recorded. The temperature with chickenpox in children sometimes reaches 40°C and above.
- As a result of the penetration of the chickenpox virus into the skin, local swelling is formed and a period of rash occurs, which can last from just 2 days to 7 days or even more. It is characterized by the initial formation of a red spot, which quickly takes the form of a papule, then transforms into a vesicle, which subsequently becomes covered with a crust. Most often, the patient’s torso is first affected by the elements of the rash, then the arms, legs, and only after that they can be detected on the face and scalp. This process is also characterized by very disturbing itching, which causes serious discomfort. Along with the formation of a rash, an increase in lymph nodes is observed, as well as the manifestation of symptoms of intoxication of the body.
- The last stage of chickenpox in children is characterized by normalization of body temperature, falling off of crusts, and improvement of the patient’s well-being. At the site of the former pathological element, covered with a crust, brownish pigmentation remains at first, however, over time it disappears. The skin after chickenpox in children, in the absence of constant scratching of itchy elements, with careful treatment and prevention of infection, remains healthy and clean. The average duration from the moment the first signs appear until the skin is completely cleared of crusts is about 3 weeks.
Chickenpox occurs extremely rarely in infants under 6 months of age, since the child is protected by antibodies received from the mother. If the disease is registered in a child under one year old, it proceeds quite easily. The temperature with chickenpox in children of this age is usually low, the period of rash is short, and the intoxication syndrome is practically not expressed. However, this applies to children born to mothers who had chickenpox as children. Otherwise, chickenpox in children under one year of age lasts quite a long time and is severe.
Incubation period and infectiousness in adults
During the incubation period, the chickenpox virus remains in the body from 10 to 21 days. At the same time, in adults, symptoms are absent for a longer period of time, and in children they appear faster.
On average, the incubation period for adults is 16-17 days and is divided into:
- Onset - time from infection to complete adaptation of the virus);
- Development - the virus multiplies, its pathogen accumulates in the body, which leads to the formation of a primary focus of infection;
- Completion - the virus spreads throughout the body, the production of antibodies begins to counteract it, and signs of illness appear.
The incubation period is quite long, making it almost impossible to determine the source of infection. The threat of infecting other people persists for 11-13 days, until the last trace of the rash disappears from the skin.
Severity
Depending on the characteristics of its course in children, chickenpox is divided into three forms:
| Mild degree | characterized by isolated rashes, absence of fever and poor health. Herpetic pimples appear in only 2–3 days. |
| Moderate | all the symptoms that traditionally occur with chickenpox in children are present. These include poor sleep, itchy skin, headaches, and a rise in temperature to high levels. Blisters form within 5–7 days. |
| Severe form | Due to high temperature (up to 40°C), the child experiences nausea and vomiting, headache, delirium, and fever. Papules appear on the body from 7 to 10 days. Multiple rashes cover different areas of the body. It can be found in the mouth and on the genitals. |
Recommendations for treatment
For a speedy recovery you need:
- Maintain bed rest for at least the first 5-6 days after the disease is detected (preferably for the entire 2 weeks while the disease lasts);
- Do not overheat, sweat will only increase the itching and increase the risk of pustules forming;
- Change underwear and bedding every day;
- Drink more water up to 2.5 liters per day;
- Wash your hands with soap;
- Cut your nails short to avoid the risk of scratching a pimple while you sleep;
- Apply a cold compress of baking soda and water to the affected areas, 1 tsp. per glass;
- Add soda to bathing water;
- Observe the temperature of the water;
- After each meal, rinse your mouth with soda, furatsilin solution or decoctions of chamomile, calendula and sage.
If the rash appears in the genital area, then you need to wash yourself daily with a weak solution of potassium permanganate. This will help dry out the pimples and provide the necessary disinfection.
It is not recommended to treat pimples on the mucous membranes, since the skin in these places is very delicate, it can be easily damaged and thereby aggravate the situation.
Chickenpox in infants
It must be remembered that any child over the age of six months can get chickenpox. In most cases, the course of the disease in infants is quite complex: such young children do not tolerate symptoms well, cannot complain and cannot take advice. As a result, they need more careful care and constant attention from the mother.
Chickenpox in newborns is characterized by the same symptoms, but in young children, chickenpox, which occurs in a particularly complex form, can cause serious harm to the body, affecting the development of internal organs. Treatment of chickenpox in infants should be carried out under the strict supervision of a qualified pediatrician.
You should try to ensure that the child does not tear off the scabs from drying out rashes, because This will only make it more itchy and increase the risk of re-infection. The child's hands need to be washed more often, since the causative virus may be present on the skin and under the nails. Nails should be cut short. It is recommended that your baby wear cotton gloves at night.
Chickenpox during pregnancy
If a woman does not have immunity to the chickenpox pathogen at the time of conscious planning of pregnancy, she will be recommended to undergo appropriate vaccination. Infection during pregnancy is dangerous for the fetus until about 20 weeks. At this stage, the virus causes intrauterine death of the fetus, which ends in miscarriage or stillbirth. It is also possible to develop severe defects that lead to disability of the born child.
At later stages, the effect of the virus on the body of both mother and fetus weakens, reaching a second peak immediately before childbirth. Infection with chickenpox in the later stages is fraught with the development of pneumonia, which can also lead to the death of the child. In such cases, special therapy with immunoglobulins and specific antibodies is carried out.
Lack of immunity to chickenpox in general is not an indication for termination of pregnancy.
How to treat chickenpox in a child?
Since chickenpox is caused by a virus, it is useless to treat the disease with antibiotics. The doctor may prescribe antibacterial drugs in cases where the course of chickenpox is complicated by the addition of a secondary bacterial infection.
There is no specific treatment against this infection, but necessary measures aimed at alleviating the patient’s condition must be taken. If a child gets chickenpox, the parents' task will be to minimize unpleasant symptoms and alleviate the baby's condition. To do this, at home, you must fulfill the basic conditions necessary for a speedy recovery:
- Observance of strict bed rest;
- Frequent change of underwear and bed linen;
- Increased drinking regimen to reduce intoxication;
- Light dairy-vegetable diet.
At the first unfavorable symptoms, you should call a doctor at home, who will give the necessary advice on care and prescribe medications to alleviate the child’s condition. The most important point of treatment during the active phase is the elimination of severe itching. When a rash appears, the skin itches and itches, and parents need to ensure that the baby does not scratch the itchy areas. This will help avoid the addition of a secondary bacterial infection.
- Blisters on the body should be treated several times a day with antiseptic solutions (green or colorless Castellani liquid). This will help prevent the infection from spreading further throughout the body and reduce the number of rashes. This treatment helps dry out the blisters and form a crust, speeding up recovery.
- To eliminate itching, the doctor may prescribe antihistamines (Suprastin, Diazolin, Diphenhydramine). These drugs effectively eliminate itching and have a mild calming and sedative effect, which will help cope with sleep disorders. The attending physician will select the required dose and dosage regimen.
- If a child has a high temperature, the doctor will prescribe antipyretics (Paracetamol, Nurofen, Efferalgan). It is not advisable to give aspirin to children under 10 years of age.
Drinking plenty of fluids (lemon tea, compotes, juices, green and herbal tea) will help you recover quickly; the liquid will remove toxins from the body. During illness, the child loses his appetite, but it is necessary to maintain his strength. A dairy-vegetable diet will help with this, providing the body with the necessary vitamins and nutrients.
Severe forms of chickenpox affecting internal organs are treated in a hospital. Complex therapy necessarily includes antiherpetic drugs (Zovirx, Acyclovir); immunoglobulin and interferon are used to treat the condition.
What to do if scars appear after chickenpox?
There are various options to solve this problem:
- Ointments and gels for the treatment of scars. A small amount of gel is rubbed into the scar 2-3 times a day. For old scars, apply the gel under the bandage at night. The course of treatment can take from 1 month to a year. For treatment the following are used: Contractubex; Aldara; Dermatix; Kelofibrase; Skarguard.
- Chemical peeling using phenol. Under the influence of aggressive chemicals, the keratinized layer of the epidermis and dermis is removed. After the epidermis is restored (takes up to 2 weeks), the skin becomes smooth.
- Injection of collagen under the skin. The substance fills the skin defect and stimulates the formation of connective fibers.
- Microdermabrasion is the mechanical polishing of the skin with particles of a solid substance (diamond). As a result of microtraumas, collagen production is activated. The procedure allows you to even out the skin texture and make scars less noticeable.
- Laser skin resurfacing. A focused laser beam penetrates the superficial layers of the dermis and heats them, evaporating the water. After the regeneration of skin cells, its surface is leveled. Caution: Carbon dioxide laser treatment may cause the appearance of a hypertrophic keloid scar that rises above the skin. Therefore, an erbium or carbon dioxide laser is used.
Before use, you should consult a specialist.
Folk remedies
There are various ways to get rid of itching due to chickenpox and in traditional medicine:
- At high temperatures, it is advisable to drink cranberry juice, viburnum drink, rosehip infusion, and sea buckthorn tea. Strawberry juice saturates the body well with nutrients and has a pronounced antimicrobial effect.
- Bath with chamomile. 5 tbsp. Pour a tablespoon of inflorescences (dry or fresh) into a liter of hot water, bring to a boil and simmer over low heat for a quarter of an hour, strain. Add the decoction to the filled bath. The procedure takes 10 minutes, perform twice a day.
- Tea tree oil. The only essential oil allowed for direct application to the skin, without conductive oil. If you treat all elements of the rash with tea tree oil using a cotton swab, this will significantly relieve itching and scabies. This procedure promotes disinfection and speedy healing of wounds.
- Mix equally chamomile flowers, coltsfoot grass, chicory grass, calendula flowers, burdock root and immortelle flowers. Brew the prepared mixture with a dose of 40 g with half a liter of boiling water. Let it brew in a thermos for 8 hours. Take 4 times a day, a third of a glass.
- Grind the calendula herb. Heat 60 g of calendula, previously brewed in a liter of water. Pour the strained broth into the bath and bathe the patient for a quarter of an hour in the morning and evening. Do not rub the skin.
Features of treatment and indications for hospitalization
Chickenpox is treated on an outpatient basis, in other words, at home. In this case, the doctor is obliged to carry out explanatory work with the patient about how to behave during illness.
For example, if a patient does not comply with bed rest and personal hygiene, he can aggravate his situation and provoke the development of complications.
Hospitalization for chickenpox is carried out if the following indications are present:
- The appearance of complications;
- The disease is severe;
- The patient does not have the opportunity to isolate himself from healthy people.
In the latter case, the treatment methods used in the hospital are no different from those that the doctor recommends to use at home.
In most cases, a disease such as chicken pox is treated with minimal use of medications, but sometimes synthetic drugs cannot be avoided.
Antiviral drugs
Antiviral agents have a negative effect on the DNA of the virus and slow down the spread of the disease. Prescribed individually, the chosen dose of the drug depends on the form of the disease and the ability of the immune system to protect.
The most effective are:
- Acyclovir - taken orally four times a day in an amount of 800 mg for a week or intravenously at 10 mg per kg of body weight for every 8 hours. The course of treatment is up to 10 days. The cost ranges from 130 to 160 rubles ;
- Famciclovir - take 500 mg three times a day for 7-10 days. The cost of the drug is from 1100 rubles ;
- Valaciclovir - taken 1 mg three times a day for 10 days, average cost 380 rubles .
Acyclovir
Famciclovir
Valaciclovir
Antihistamines
Aimed at reducing allergic rashes and vascular permeability. After taking them, the nervous system calms down, sleep improves, and itching practically disappears.
The following drugs affect the body in the manner described above:
- Tavegil - tablets are taken twice a day for normal itching and four times for severe itching. Average price 190 rubles ;
- Suprastin - take up to 4 tablets per day, and treatment continues until crusts appear. Average price 130 rubles ;
- Cetrin - you should take one 10 mg tablet per day, either at one time or dividing the dose into two doses, with a glass of clean water. Average price 180 rubles .
Tavegil
Suprastin
Tsetrin
Medications to reduce high fever
Use only when the temperature rises to 38.5 degrees or higher. Aimed at normalizing temperature and slowing down inflammation.
Most often, patients are prescribed:
- Panadol - to reduce the temperature, it is enough to take 1 tablet three times a day, preferably after eating. Average price 60 rubles ;
- Ibuprofen - to achieve a therapeutic effect, take 2 tablets 3-4 times a day. Average price 50 rubles .
Panadol
Ibuprofen
Antibiotics
They are used in exceptional cases, mainly when the patient has purulent formations and pustules. Antibiotics can stop the development of infection and acne.
The greatest effect is achieved by:
- Oxacillin - administered intravenously, 1 g four times a day for 7 days. The average price for one bottle is 10 rubles ;
- Cefazolin is an antibiotic intended for intramuscular administration, used three times a day for a week. The average price for one bottle is 25 rubles ;
- Augmentin - taken orally in the amount of 2 tablets per day, with a course of treatment of up to 5 days. Average price 340 rubles ;
- Amoxiclav - taken orally before or after meals; to increase the effectiveness of treatment, you must take 2 tablets per day for 1 week. Average price 210 rubles .
Oxacillin
Cefazolin
Augmentin
Amoxiclav
Drugs to remove harmful toxins from the body
Most often these are solutions intended for intravenous administration into the body. They are able to reduce the amount of harmful toxins, speed up their elimination, and have a beneficial effect on blood circulation. Prescribed to patients with severe forms of chickenpox.
A quick therapeutic effect can be achieved with the help of:
- Glucose 5% - the solution is administered by drip into a vein in the amount of 1000-1500 ml per day. The average price per bottle is 30 rubles ;
- Reopolyglucin - 1000 ml of the substance is injected into a vein every day until the end of treatment. The average price is from 60 rubles per bottle.
Glucose 5%
Reopoliglyukin
Specific immunoglobulin
Designed to fight the virus in question.
It is isolated from blood with antibodies already present in it.
When it enters the blood of a sick person, immunoglobulin binds the pathogen, which promotes a speedy recovery.
Zostevir enjoys the greatest confidence among specialists.
It is administered intramuscularly once a day in an amount of 1.5-3 ml, depending on the severity of the disease.
Average cost from 500 rubles .
Products for treating rashes
Pimples that appear on the body begin to itch. Under no circumstances should you scratch them; scars may remain.
To get rid of itching, you can use one of the following medications:
- Calamine - contains zinc oxide. Sold in lotion form, it is used to relieve itching, protect the body from bacteria and relieve swelling. Average price 680 rubles ;
- Acyclovir ointment is used to treat all types of herpes. Prescribed in the presence of complications, the treatment of which requires the use of antiviral drugs, topical application. Average price 25 rubles ;
- Rivanol, Fukortsin are analogues of brilliant green and have an antimicrobial effect. The preparations do not dry out the skin, do not stain clothes, and are washed off with water. Applying them to pimples avoids the risk of developing purulent inflammation. The average price of Rivanol solution is 140 rubles , Fukortsin - 60 rubles ;
- Solcoseryl - protects tissue damaged around pimples from pathogenic microbes entering them. The average cost is 310 rubles .
Calamine
Acyclovir ointment
Rivanol
Fukortsin
Solcoseryl
It is not recommended to treat pimples with brilliant green; the solution dries the skin and causes scars to form at the site of the rash, which is not very pleasant, especially when it comes to visible areas of the skin.
In most cases, drug treatment comes down to taking antipyretics and broad-spectrum antibiotics.
The use of antibiotics and antibacterial drugs can have unpleasant consequences for the body. To avoid them, you should follow all the doctor’s recommendations without trying to treat the disease yourself.
How many days does quarantine last for chickenpox?
Doctors have given an opinion on the contagiousness of the disease: from 4 to 13 days. Therefore, epidemiologists, if it is necessary to announce quarantine measures, close educational institutions for 14 days. During this period, the child cannot be allowed into kindergarten or school.
The first 5-10 days are dangerous for others during this period. You can focus on the appearance of the rash - while it is present on the body, the virus is in active form. During this period, it is very important to limit the patient’s contact with healthy people.
Is it possible to swim if you have chickenpox?
Contrary to popular misconceptions, you can and should swim when you have chicken rash. The main thing is to take a warm bath; the water should not be hot or cold. The baby should also walk in the fresh air, but avoid contact with other children. In such conditions, treatment will be more effective, and the patient will be able to avoid complications and other severe consequences of chickenpox.
How many days does a child have fever with chickenpox?
Very often, the temperature for this disease rises during the prodromal period - when preliminary symptoms appear. The increase in temperature may not be very critical - up to about 38 degrees, sometimes with a feeling of nausea and even vomiting.
The temperature may rise and fall slightly throughout the course of the disease - with each new rash on the baby's skin. During such periods, it is necessary for the baby to drink enough fluids, rest and get a good night's sleep. It is not recommended to reduce the temperature with antipyretic drugs if it has not reached high values.
It is strictly forbidden to give aspirin to your child. However, timely prevention will help avoid complications, and even infection with chickenpox itself. The main thing is to do everything in a timely manner and completely isolate the baby from contact with patients.
How to prevent chickenpox?
Chickenpox can be prevented through vaccination. Specific prevention is carried out with live vaccines from a weakened varicella zoster virus (for example, the Belgian vaccine Varilrix). Vaccination is especially recommended for young children, and in the United States for the elderly, to prevent herpes zoster and postherpetic neuralgia.
In clinical trials, it was found that individuals who were vaccinated were either not susceptible to chickenpox or experienced it in a very mild form.
Chickenpox vaccines
Vaccination is necessary for those categories of people who have reduced immunity and, as a result, a high risk of severe and complicated course of the disease. These include the following categories:
- persons with malignant diseases,
- HIV-infected,
- those groups of people who have severe chronic pathology,
- patients taking glucocorticosteroids.
Vaccination indicated:
- for preventive purposes, especially recommended for high-risk categories: - routine vaccination at the age of 12-15 months, - routine second dose at the age of 4-6 years.
- for emergency prevention of those who have not had chickenpox and have not been vaccinated, but are in contact with patients.
The minimum interval between doses of varicella vaccine is 3 months for children under 13 years of age.
Although single-dose programs are effective in preventing severe varicella disease, as demonstrated by a study in Australia (one of the few countries to include varicella vaccination as part of its national immunization program), evidence suggests that it is not necessary to interrupt transmission of the virus. two doses are required. Emerging school outbreaks and high rates of chickenpox, although usually not severe, have prompted some countries to implement a two-dose vaccination schedule.
Vaccination is the most effective medical intervention ever invented by man.
Used materials
- https://www.cdc.gov/vaccines/pubs/pinkbook/varicella.html - etiology, pathogenesis, clinical features, prevention of chickenpox
- https://www.who.int/immunization/sage/meetings/2014/april/5_The_potential_impact_Varicella_vaccination_Low_Middle_Income_Countries_feasibility_modeling.pdf?ua=1&ua=1 – vaccination for chickenpox
- https://www.who.int/immunization/diseases/varicella/en/ - about the epidemiology of chickenpox and herpes zoster
- https://www.who.int/bulletin/volumes/92/8/13-132142/en/ - research on the effectiveness of vaccination against chickenpox and herpes zoster in Australia.
- https://www.who.int/immunization/position_papers/varicella_grad_effectiveness_2_doses.pdf?ua=1 - about the effectiveness of vaccination against chickenpox.
- https://www.who.int/wer/2014/wer8925.pdf?ua=1&ua=1 – epidemiology, diagnosis, treatment, some positions on vaccination for chickenpox and herpes zoster.
- Vozianova Zh. I. Infectious and parasitic diseases: In 3 volumes - K.: Health, 2000. - T. 1. - 904 p.
- Golubovskaya O. A. Infectious diseases. - M.: VSV "Medicine", 2012. - 728 p. + 12 s. color. on
Author: Anastasia Lishnevskaya, infectious disease doctor Source: MMK Formed
Advice from Doctor Komarovsky
The most common question that concerned parents ask their favorite doctor concerns the effects of brilliant green in children with chickenpox. Evgeniy Komarovsky’s answer is unequivocal - there is no therapeutic effect from such an action, brilliant green serves only as an indicator of the period of contagiousness. Lubricating the blisters with a colored solution every day, one day mommy notices that there are no new rashes. From this moment the countdown begins for the last five days, when the baby can pose a danger to others.
The doctor draws the attention of parents to the fact that the viral infection, which is chickenpox in children, is not susceptible to antibiotics and does not require special medications during the normal course of the disease. Only in adolescence, when the disease is too severe, do doctors prescribe antiherpetic drugs.
The main advice that Dr. Komarovsky gives for mothers of sick children:
- avoid overheating, which increases itching;
- cut your nails short, wear gloves if necessary, and do your best to distract the baby from combing the bubbles;
- do not give aspirin so as not to cause liver complications;
- scratching the blisters leads to bacterial infection and the likelihood of marks for life;
- chickenpox quite strongly suppresses the immune system, so after suffering from the disease you should refrain from visiting kindergarten and devote more time to walks.
Regarding vaccinations, Komarovsky believes, sensible parents should not have any discussions. However, he reminds that vaccination against chickenpox is voluntary, so mothers and fathers will have to take responsibility for its implementation.
Consequences
The most dangerous consequences of chickenpox include:
- Weakening of the immune system and, as a consequence, loss of its ability to resist more serious viruses;
- Loss of ability to work due to problems with internal organs;
- Lethal outcome is possible if the patient develops chickenpox pneumonia, encephalitis, high fever and hepatitis.
The described consequences can be avoided if you consult a doctor in a timely manner and follow all his recommendations.
It is not recommended to treat chickenpox on your own, as has already been mentioned several times above. Under unfavorable circumstances, chickenpox may become only the first milestone in a series of health problems.
Possible complications
Fortunately, most children recover well from chickenpox. However, in some categories of patients the disease may have unfavorable outcomes, such as:
- Hepatitis;
- Pathology of the structures of the eyeball (keratitis);
- Encephalitis. This pathology is manifested by severe damage to the central nervous system, manifested by seizures. This is due to the high tropism of the virus to nervous tissue. In most cases, this complication is detected in patients on days 7-12 of the disease. A persistent disorder of higher nervous activity in the form of idiocy occurs relatively rarely;
- Pustular skin lesions: phlegmon, abscesses or boils. They are the result of penetration of pathological microorganisms into the liquid inside the vesicle, which, upon contact with neutrophils, can form pus;
- Pneumonia. Most often diagnosed in adults. A feature of chickenpox pneumonia is the extreme paucity of clinical symptoms. The diagnosis can only be made by x-ray, and the image reveals small inflammatory foci throughout almost the entire length of the lung tissue;
- Myocarditis is inflammation of the heart muscle. It is manifested by dullness of heart sounds, pain in the heart area, as well as changes in the cardiogram;
- Nephritis is an inflammatory kidney disease that most often occurs on the 10th-12th day of illness. In most cases, this pathology goes away on its own and does not require any specific therapy.
However, chickenpox can still serve as a reason for the appearance of another disease, not as a complication. As you already know, chickenpox is a type of herpes virus, therefore the virus remaining in the body is inactive and occurs in a latent state. However, as a result of repeated exposure to the chickenpox virus and a number of associated factors, it can lead to the occurrence of a disease such as herpes zoster.
When did chickenpox start?
Chickenpox has been known since ancient times. For some time it was considered a mild form of smallpox, and only in 1772 was it identified as a separate disease. And in 1909, it was found that chickenpox and shingles have the same pathogen, which was later confirmed by laboratory tests. Subsequent study of the virus led to the development of a live attenuated varicella vaccine in Japan in the 1970s. The vaccine was licensed for use in the United States in March 1995.
Is it worth getting vaccinated?
Doctors began vaccinating children against chickenpox relatively recently. The composition of the vaccine is represented by live but weakened pathogens. The first vaccination is usually given at 12–14 months. The chickenpox vaccine is re-administered after 3 to 5 years. Adolescents and adults who do not have natural immunity are vaccinated twice, with an interval of 1 month or more between injections.
Young children tolerate chickenpox vaccinations well, and pediatricians do not record any adverse reactions. However, if the child is part of a group of frequently ill children, it is necessary to consult with the local pediatrician about the advisability of vaccination. A weakened body may react to vaccination with unpredictable phenomena.
Chickenpox vaccine for adults
The chickenpox vaccine is not included in the mandatory vaccination schedule and is used only at the request of the person. Vaccination against chickenpox among adults can be used at any time, especially if the person has not previously suffered from this pathology in an active clinical form. In most situations, persons whose work involves daily contact with children are interested in vaccination against chickenpox, since chickenpox is a fairly common infectious pathology among organized children's groups.
Currently, vaccines such as Okavax and Varilrix, which exhibit identical effectiveness, are used to vaccinate against chickenpox in adults.
- Vaccination using the Varilrix vaccine is used in most situations as an emergency preventive measure, and its effectiveness directly depends on the time of use. Thus, in a situation where more than 72 hours have passed since a healthy person came into contact with a chickenpox-infected patient, vaccination is considered irrational. Vaccination against chickenpox using the Varilrix vaccine should be carried out twice at intervals of three months. Among the contraindications to the use of the Varilrix vaccine, it should be noted that the patient has signs of immunodeficiency or any acute infectious pathology.
- The Okavax vaccine is a live chickenpox vaccine and is approved for use in both children and adults. Vaccination using Okavax is a subcutaneous injection of one dose of the drug in the projection of the outer surface of the shoulder. In most situations, vaccination against chickenpox in adults proceeds without complications, however, in some situations, the patient may experience a short-term local reaction in the form of slight swelling, thickening or hyperemia in the projection of the direct injection. An absolute contraindication for vaccination against chickenpox using a live vaccine is any trimester of pregnancy and severe somatic pathology accompanied by immunodeficiency.
In a situation where vaccination against is carried out routinely in relation to a woman of reproductive age, it should be carried out no later than three months before the expected pregnancy. Active synthesis of specific antibodies against the chickenpox virus in adults, which is observed after vaccination with a live vaccine, may be accompanied by the appearance of a low-intensity rash on the skin, the pathomorphological elements of which are similar to those of chickenpox. This condition is considered by infectious disease specialists as reactive and does not require drug correction. The effectiveness of chickenpox vaccination has a limited duration of thirty years.
Medicines
Photo: pumpen.de
Medicines against chickenpox are used for the following purposes:
- the virus is destroyed using antiviral drugs;
- Elimination of itching is carried out using antipruritic agents;
- signs of general intoxication (fever, headache) are eliminated with the help of NSAIDs;
- Prevention of bacterial complications is carried out with drugs with a bactericidal effect.
Local drugs play a leading role in the treatment of chickenpox. Antiseptic solutions are necessary at the stage of vesicle formation. The blisters on the skin are lubricated with solutions of brilliant green and potassium permanganate. The mucous membranes are treated with hydrogen peroxide. To relieve itching, apply glycerin to the area of the rash and wipe the skin with diluted alcohol or vinegar.
General medications are selected individually if indicated. In case of pustule formation and secondary infection, short courses of antibiotics in an average dose are prescribed. In case of immune deficiency and severe disease, antiviral drugs and immunostimulants are added to the treatment regimen. With pronounced symptoms and during pregnancy, it is possible to use specific anti-chickenpox immunoglobulin.
Fenkarol
Fenkarol is a relatively new anti-allergy drug on the pharmaceutical market, but has already proven its effectiveness and safety. The product is good at relieving itching and inflammation due to chickenpox. Typically, Fenkarol is well tolerated and has no side effects. The only contraindication is pregnancy.
Fenkarol
Olaina Chemical Plant, Latvia
- hay fever;
- acute and chronic urticaria; - angioedema; - allergic rhinitis; — dermatoses (including eczema, psoriasis, atopic dermatitis); — neurodermatitis; - skin itching. from 176
478
- Like
- Write a review
Poksklin
Cooling mousse "Poksklin" for chickenpox has a completely natural base (panthenol, aloe vera, chamomile and lavender). The product cools and reduces scratching, so scars do not form. “Poksklin” relieves inflammation, has an antiseptic effect and accelerates the healing process of wounds.
Poksklin
PharmaVal AS, Netherlands
Poksklin cooling hydrogel was developed to relieve the symptoms of chickenpox over large areas of the body.
While spreading thick creams and ointments over the body can damage the blisters, the cooling hydrogel is very easy to apply and does not cause friction in sensitive areas when applied to the skin. PoxClean provides an immediate cooling effect, which significantly relieves itching. For this purpose, it can be used as many times as necessary. PoxClean contains the ingredient 2QR, a biologically active antibacterial complex. This component helps your child's natural skin immunity to block harmful bacteria. The antibacterial component in PoxClean is a polysaccharide obtained from the plant extract of Aloe Vera. It creates a barrier on the skin, thereby preventing the penetration and spread of bacteria on the surface of the skin. from 272
5.0 1 review
204
- Like
- Write a review
Diagnostics
Photo: frame.org.uk
How can you tell if a person is infected with chickenpox? To determine this, there is laboratory diagnostics, where an analysis for chickenpox is carried out. Laboratory doctors take your blood to test for antibodies to chickenpox (in both children and adults).
This blood test is a comprehensive diagnostic aimed at detecting the Zoster virus in the body. In addition, the current state of immunity is assessed. Depending on the reaction to chickenpox, doctors can conclude whether further vaccination and treatment are needed, or whether the body already has permanent immunity to chickenpox.
In what cases will a blood test be performed for chickenpox?
Such a diagnosis is primarily prescribed when the clinical picture for a given disease is atypical, namely: there is severe intoxication and uncharacteristic rashes on the skin. If doctors cannot accurately diagnose or confirm the disease, and the person does not remember whether he suffered this disease as a child, a blood test for chickenpox is also carried out. Women who are planning a pregnancy must undergo this test.
Blood is drawn in the usual way and looks at two indicators: IgG immunoglobulins, which form in the blood when a person begins to recover, and IgM immunoglobulins, which appear after contracting the disease.
How exactly is the analysis deciphered?
If the concentration of antibodies exceeds the normal value, then the person has chickenpox, but if the concentration is lower, the person is considered healthy. The following indicators are distinguished:
- IgG negative, IgM positive. Primary acute infection.
- IgG positive, IgM negative. The virus has been reactivated.
- IgG negative, IgM negative. The person has never had chickenpox.
- IgG positive, IgM positive. The man had previously had chickenpox.
How to prepare for the analysis?
No special preparation is required. The only thing that is advisable to do is to avoid spicy and fatty foods during the test.
Signs of chickenpox
Everyone knows what chicken pox looks like. The first sign of chickenpox is specific red rashes all over the body. But relying on such signs without the appropriate knowledge and trying to diagnose such a disease yourself is still not worth it. For doctors, such a symptom can indicate many other diseases, including dermatological ones.
In addition to red rashes on the body, it is worth paying attention to the general deterioration of well-being coupled with elevated body temperature. The patient's temperature can reach up to thirty-nine degrees Celsius. The rash is predominantly localized on the surface of the face, scalp, body, arms and legs. It is extremely rare on the palms and soles of the feet. Over time, the rash lesions grow in size, acquiring a clearly round or oval shape. The size of individual vesicles can reach up to five millimeters. The contents of the rash are mostly transparent, sometimes cloudy. After two or three days, the vesicles dry out, leaving behind a hard crust that falls off after two to three weeks. In children, scars do not remain after they fall off. In the case of adults who have been ill at a fairly decent age for such a disease, scars are a fairly common problem. Sometimes the rash can be found on the mucous membrane of the mouth, larynx, and the surface of the genital organs. A characteristic sign of chickenpox is a strong increase in the size of the lymph nodes. After the first week, the temperature returns to normal against the background of parallel drying of the rash, and the patient’s well-being improves. Some people still experience severe itching by this time.
Chickenpox has several degrees of manifestation, and they usually occur in the following three forms:
- Light form. This form is characterized by elevated temperature up to 37 degrees, general weakness and fatigue. The rashes on the body are quite small, and their duration on the body ranges from one to two days.
- Medium shape. The average severity of chickenpox is characterized by an increase in temperature to 39 degrees; patients often complain of migraines, vomiting, poor sleep and complete loss of appetite. The skin rashes are quite large. The rash begins to appear on the mucous membrane, and the duration of the period is about five to six days.
- Severe form. The temperature rises to 40 degrees, and the patient feels significantly worse compared to the two previous stages. A person suffers from a severe headache and dizziness, he vomits, he does not eat anything, and he is delirious. The rash on the body is profuse and very itchy, and lasts from seven to eight days.