The onset of pregnancy is an important and joyful period in the life of every woman.
The first trimester is the most crucial time for the entire pregnancy, as the woman’s body is actively restructuring and experiencing stress. It is important to remember and be aware of the key points to ensure that the pregnancy proceeds well and without complications. The first trimester of pregnancy lasts from the first day of the last menstruation until the 13th week (according to the obstetric period).
What happens to the expectant mother
The first sign of pregnancy is the absence of menstruation. Some women notice the appearance of slight spotting and sometimes mistake it for menstruation, so they can find out about their situation by the middle of the first trimester. If the discharge is not abundant, this is normal. One possible reason is the attachment of the embryo to the wall of the uterus.
Another striking symptom of pregnancy is toxicosis. It manifests itself in the form of nausea and vomiting, increased salivation, changes in taste preferences and special sensitivity to odors. It is believed that toxicosis is the body’s reaction to embryonic cells that are “alien” to it. The immune system adapts towards the end of the first trimester. In the meantime, you should be patient, follow a daily routine, eat portions, in small portions, and look for your own way to combat nausea. Some people benefit from crunchy snacks, while others benefit from ginger tea. It is believed that taking folic acid also reduces the symptoms of toxicosis.
Other changes in the body of a pregnant woman
- Frequent urination is associated with the pressure that the growing uterus puts on the bladder.
- Constipation and flatulence - occurs under the influence of progesterone, which reduces smooth muscle tone and slows down intestinal motility.
- Breast pain - the condition is caused by the preparation of the mammary gland for lactation.
- Fatigue and drowsiness, which can only be overcome by getting enough sleep at night and taking extra rest during the day.
- Dizziness and loss of consciousness occur against the background of a decrease in blood pressure due to the active blood supply to the uterus.
Please note that these symptoms do not occur all at once and not necessarily in everyone. Some women do not notice any special changes in the 1st trimester of pregnancy.
The first weeks of pregnancy - symptoms
You can determine whether you are pregnant or not yourself at home. However, these diagnostic methods do not give a 100% result. The final conclusion is issued only by the doctor after examination and appropriate examination. This includes a blood test for hCG, the so-called pregnancy hormone. It is recommended to do it 3-5 days after a missed period. Before that, you can use simple diagnostic methods - take into account the signals of your body, which reacts to the changes taking place.
The first sign of pregnancy for many women is the absence of menstruation . At this moment it’s worth thinking: “Maybe I’m pregnant?” Of course, there may be other reasons for the delay: stress, inflammation of the reproductive system, change in climatic conditions, hormonal imbalances, exacerbation of chronic diseases. In any case, the absence of menstruation should prompt you to undergo a medical examination.
Some women feel that they are pregnant in the first days after conception. This feeling comes on a subconscious level . And as everyone knows, women's intuition is a great thing!
One of the most noticeable symptoms is toxicosis (nausea). The time of its manifestation is different: in the first weeks of pregnancy or in the seventh to tenth week - individually for each woman.
Another symptom is increased basal temperature . For pregnant women, it is 37.2 – 37.3 degrees. The maximum is 38 degrees. After the first trimester, the temperature drops and ceases to be an informative symptom. You need to measure this indicator in the morning, without getting out of bed (even to go to the toilet!), using a rectal thermometer.
In the fifth or sixth week, the breasts enlarge and become more sensitive . Subsequently, it continues to swell, the nipples darken, and the veins on the chest become a little more pronounced.
Appetite increases noticeably , which can cause you to gain weight. Disgust or love for certain foods appears. And this despite the fact that the sense of smell is heightened ! It’s impossible to say what exactly you will devour in unlimited quantities and what you will turn your nose up at. Taste preferences are individual for everyone! Your uterus gradually increases in size and, as a result, puts pressure on your bladder. This makes you go to the toilet more often, regardless of the time of day.
At the eleventh to thirteenth week of pregnancy, mild dizziness and headaches . The reason for this is the increase in blood volume in your body.
A psychological feature of a pregnant woman is great variability in mood . Uncontrolled changes at this level are associated with a large number of hormones. These physical changes also explain fatigue . After a short period of housework or other stress, a pregnant woman needs rest.
Here are some of the main symptoms that accompany women during pregnancy. However, it is worth noting that each organism is individual. Some people have all of the above symptoms, while others only have some of them.
How does the baby develop in the 1st trimester?
On average, 6 days after fertilization, the embryo will reach the uterus and attach to its wall. Then the amnion is formed, from which the amniotic sac will later develop, and the placenta, through which the unborn child will receive all the nutrients and oxygen.
At 5-6 weeks, the cardiovascular system, liver and spleen, respiratory tract, and neural tube begin to develop, which subsequently transforms into the nervous system. The embryo develops the rudiments of legs and arms. In the middle of the 1st trimester of pregnancy, during an ultrasound, you can already hear his heart beating - at a frequency of 120-140 beats per minute. The brain is actively forming: it is divided into 2 hemispheres, primary neural connections are formed.
From 8-9 weeks of pregnancy, the baby turns from an embryo into a fetus, since by this moment all organs and systems have already been formed. The reproductive system is developing, eyelids, jaw contours, and nose are already visible on the face. Fingers appeared on the hands and feet.
By the end of the first trimester, the fetus already weighs 15-20 grams. He moves actively, knows how to frown, yawn, and sucks his thumb. Distinguishes the taste of mother's dinner and hears everything that happens outside the womb.
Condition of the fetus in the first month of pregnancy
The embryo attaches to the uterine mucosa, which becomes looser. Neither the placenta nor the umbilical cord have yet formed; The fetus receives the substances necessary for development through the villi of the outer shell of the embryo - the chorion. Due to the absence of a placenta, which performs a barrier function, at this stage the fetus is especially vulnerable to unfavorable substances in the mother’s blood: viruses, active ingredients of drugs, nicotine, ethanol, etc. To partially protect the fetus from infection, the passage of the cervix is closed with a mucus plug .
The size of the embryo at the end of the first month is only about 1 mm. Internal organs, skin, and the central nervous system begin to form.
Tests and ultrasound of the first trimester
You can register for pregnancy at the antenatal clinic from 8-9 weeks. You will have to undergo an extensive list of tests:
- general and biochemical blood test;
- general urine analysis;
- tests for HIV, AIDS, hepatitis, TORCH infections and STDs;
- coagulogram;
- smear on vaginal microflora.
It is also important to determine your blood type and Rh factor; an ECG is performed to diagnose possible heart pathologies.
The gynecologist will give you a referral to other specialists: a therapist, an ENT specialist, a dentist, an ophthalmologist. If you have chronic diseases, you should consult with specialized doctors.
First pregnancy screening
Consists of an ultrasound and a blood test for the hCG hormone and PAPP-A protein. Performed from 10 to 13 weeks of pregnancy. Allows you to identify complex fetal malformations, including those incompatible with life. The results are not final; sometimes invasive diagnostic methods are required - chorionic villus biopsy or amniocentesis.
The first days of delay: who is at risk?
Expectant mothers who are likely to have health problems during pregnancy and while carrying a healthy baby:
* There is any chronic disease - for example, diabetes, high blood pressure, chronic pyelonephritis and others. * Previous pregnancies ended in miscarriages, frozen pregnancies, and the birth of a premature baby. * Previously had infertility. * Pregnancy test is positive or doubtful, but there is bloody discharge from the vagina. Possible ectopic pregnancy. * Presence of gynecological diseases: inflammatory (uterus, fallopian tubes, ovaries) and benign neoplasms (endometriosis, fibroids, fibroids).
If you are at risk, visit an obstetrician-gynecologist from the first days of a missed period.
Possible problems in the first trimester
Of particular danger in the first trimester of pregnancy are complications such as ectopic and frozen pregnancies, increased uterine tone and the threat of miscarriage. Alarming symptoms for which you should immediately seek medical help are:
- bloody vaginal discharge, especially abundant and scarlet in color;
- severe weakness and fever;
- a woman has a tightening in her lower abdomen, the pain can be sharp and sudden;
- Symptoms of pregnancy suddenly disappear - nausea, engorgement of the mammary glands.
To confirm the diagnosis, a blood test for hCG and ultrasound diagnostics are required. Treatment is most often carried out in a hospital setting. It will not be possible to save an ectopic or frozen pregnancy; in these cases, it is more about the life and health of the woman. In case of increased tone or threat of miscarriage, help can be obtained in most cases; it is only important to contact specialists in time.
The best prevention of complications
- Pregnancy planning, which includes a preliminary consultation with a gynecologist, a series of tests and treatment of sexually transmitted diseases - common causes of infertility and miscarriages.
- Proper nutrition, adequate sleep and a healthy lifestyle. Such seemingly simple rules help to successfully conceive and bear a child.
- Regular visits to the gynecologist. Don't miss scheduled visits to your doctor to ensure timely diagnosis of problems during pregnancy.
Complications during pregnancy
The most common ailments.
- Lack of sexual desire.
- Heartburn.
- Nausea.
- Constipation.
- Increased appetite.
- Frequent changes in mood.
- Weakness and drowsiness.
- Increased pigmentation.
- Pain in the mammary glands.
- Dizziness.
In what cases should you immediately consult a doctor?
- Severe pain in the lower abdomen.
- Bloody issues.
- Fainting.
- Pain when going to the toilet.
- Frequent vomiting.
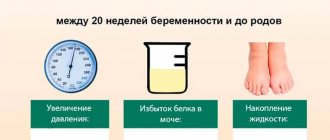
- Increased blood pressure.
- Increased swelling.
- Leakage of amniotic fluid.
- Discharge with a pungent odor.
- Spotting.
What medications should you not take?
Is it possible to take medications during the first trimester of pregnancy? Any medications can be taken only after consulting a doctor, but there are medications that should absolutely not be taken.
These include:
- antibiotics from the group of tetracyclines, fluoroquinolones;
- antifungal drugs;
- antihistamines;
- drugs that increase blood pressure;
- analgesics;
- antidepressants.
Do's and don'ts
Fortunately, it is quite difficult to harm a healthy pregnancy, and most common prohibitions are simply myths and prejudices, such as the belief that a pregnant woman should not cut her hair or knit.
Among the unconditional prohibitions of the first trimester of pregnancy are lifting weights, smoking and alcohol, heat stress, and hazardous sports.
Is it possible to have sex?
If there are no contraindications, then intimate intimacy at any stage of pregnancy will not harm the fetus. It is reliably protected by amniotic fluid and the walls of the uterus. Therefore, decide this issue based on your own desires, and if you have any disorders, for example, vaginal bleeding, be sure to consult a gynecologist.
Can I take medications?
The effect of many drugs, especially in the first trimester, has been poorly studied in pregnant women. Therefore, it is better to consult a specialist. Sometimes you simply cannot do without medication, as, for example, with a high temperature. Prolonged fever is dangerous for the fetus, so it must be stopped. If you have a chronic disease that will lead to serious deterioration without treatment, you should choose the safe ones together with your doctor.
What to expect during pregnancy: a list of the most common problems
- Uncomfortable walking and sleeping position.
Walking will be difficult due to the significant load on the pelvis. The gait will look strange, but this is quite normal for pregnant women. You can alleviate the situation by doing gymnastics. In the later stages of pregnancy, you will also find it more difficult to get into bed. But you will have to come to terms with this condition. - Edema
. Edema appears due to the fact that the fluid content in the body increases. The legs and face swell especially at the end of pregnancy. You can cope with swelling with proper nutrition, exercise and some medications - these will be prescribed by a gynecologist. - Haemorrhoids.
Hemorrhoids are a condition that causes the veins in the lower rectum to become enlarged. An unpleasant disease causes pain and itching. You can try to treat hemorrhoids with special ointments and suppositories, but it is better to contact your gynecologist so that he can tell you exactly what you need. Prevention of hemorrhoids: place a pillow under your feet while sleeping, periodically do exercises for the internal muscles. - Kidney problems
. In the first and last months of pregnancy, you want to go to the toilet much more often than before pregnancy. This is quite normal: the uterus grows and in the later stages the baby literally rests against the mother’s bladder. If you feel pain when going to the toilet, be sure to consult a gynecologist. During pregnancy, the genitourinary system is very susceptible to infections. - Constipation
. More than 70% of women suffer from constipation during pregnancy. You can prevent trouble by drinking more water per day (about 10 glasses) and following a diet. You need to eat food containing fiber. Try adding kefir and beets to your diet. - Skin problems
. During pregnancy, the skin becomes oilier. After childbirth, the hormonal levels will be restored, and everything will work out. - Dental problems.
It's no secret that teeth decay during pregnancy. You can prevent the problem by taking calcium.
Nutrition, vitamins and minerals
There is no special diet for pregnant women. There is no need to eat for two either. Your diet should be healthy and balanced, that is, it must include 3-4 servings of vegetables and fruits, 2-3 servings of cereals and cereals, lean meat and fish, and dairy products.
Since nutrition should be healthy, it does not involve eating cakes, sausages, or fast food. But if the pregnancy proceeds without complications, then nothing bad will happen from one cake a week or sausage. The main thing is that it is infrequent.
There is no need to eliminate red fish, peanuts, chocolate, citrus fruits or other common allergens unless you have a reaction to them. It has been proven that such a diet does not prevent the development of allergies in a child.
Alcohol is prohibited in all trimesters of pregnancy because it has a teratogenic effect, that is, it disrupts the development of the fetus by penetrating the placenta.
Do you need multivitamins?
Until recently, all pregnant women were prescribed vitamin complexes. Now experts believe that it is better to “extract” all the necessary microelements and vitamins from ordinary foods. If your diet is varied, this is not difficult to do. But in addition you should still take:
- folic acid, which reduces the risk of neural tube pathologies in the 1st trimester of pregnancy;
- vitamin D, a deficiency of which occurs in our region due to prolonged absence of sun throughout the year;
- iron supplements - if you do not eat meat or are predisposed to anemia (you have an asthenic physique or have previously decreased hemoglobin).
Checklist for the 1st trimester of pregnancy
- Get your first pregnancy screening before the end of the first trimester.
- Visit your gynecologist regularly, and before each visit, do not forget to take a general urine test.
- Don't forget about physical activity: it reduces the risk of pregnancy complications and prepares the body for childbirth.
- Before the cold season, be sure to get a flu shot; it is safe for both you and the fetus.
- Eat a healthy diet, stop smoking, and limit your caffeine intake to 200 mg per day.
- Check out our pregnancy calendar to know what you need to be prepared for at different stages of pregnancy.
Entrust your pregnancy management to the specialists of the Medical Women's Center. All tests, screenings, studies and consultations with specialists at a time convenient for you under one roof. We create individual observation programs and have successful experience in supporting complicated pregnancies.
The importance of the initial period
Despite the fact that the first month of pregnancy is quite difficult to determine, it is the most important for the health of the unborn child. It is in the first month that implantation occurs, the correctness of which determines both the future course of pregnancy and the development of the fetus. Ideally, if pregnancy is planned in advance, then even before its onset the woman adjusts her lifestyle, gives up bad habits and switches to a healthier diet. If pregnancy turns out to be a surprise, then at the first, even indirect, signs, you should switch to a healthy lifestyle as quickly as possible.
Particular attention should be paid to the nutrition of the expectant mother. Here's what the WHO Regional Office for Europe report on Healthy maternal nutrition: a better start in life says: “Inadequate maternal nutrition in the earliest stages of life, in utero and early life can have both short- and long-term consequences. impact; in particular, increase the risk of non-communicable diseases and obesity throughout later life. <…>Poor nutritional conditions before and during pregnancy can cause short-term and long-term changes in weight-height parameters, body composition and metabolic reactions of the offspring.”*