Basalioma: what is it?
Basal cell carcinoma is called basal cell carcinoma of the skin. Despite ongoing research, it is still unknown from which cells the tumor is formed.
It rarely metastasizes and grows slowly. If treatment for basal cell skin cancer is started promptly, complications can be avoided. This type of skin cancer mainly occurs in people over 50 years of age, regardless of gender.
Basalioma can manifest itself in different ways.
There are the following types of tumor:
- Superficial. Occurs more often than others. It looks like a small red spot on the skin, which then begins to itch and peel.
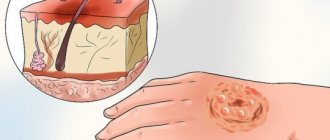
- Nodular. In the initial stages it resembles a dense pimple. Over time, it grows, the skin in the area of the nodule becomes thinner, and blood vessels become visible through it.
- Ulcerative. It usually starts as a nodule, but then an ulcer appears in the center of the formation, which can fester.
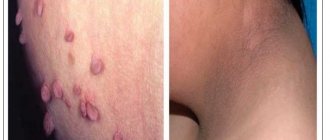
- "Turban" The tumor affects the scalp. Several pink nodules form.
- Nodal. It usually affects the face and neck. It first appears in the form of small dense nodules, which eventually merge into one tumor.
- Warty. Consists of several uneven compactions, looks like a head of cauliflower.
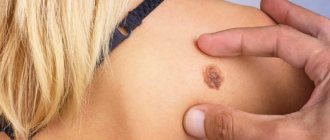
- Pigmented. Basalioma resembles a dark mole, but its surface is uneven and consists of tiny nodules, on the surface of which ulcers can form over time.
- Scar-atrophic. The neoplasm is an ulcer. A scar forms in its center, but along the edges the ulcer continues to grow.
These forms of tumor differ not only in appearance, they can occur in different ways. Treatment of facial basal cell carcinoma in Moscow is carried out in various ways. But it is important to start it as early as possible. Basalioma can spread deeper, destroying healthy tissue.
Why is basal cell carcinoma dangerous?
Basalioma is often characterized by a benign course. There are very few cases of metastases in medical practice.
However, this disease is a type of skin cancer, so it cannot be ignored.
Treatment of basal cell carcinoma of the face with ointments rarely gives a positive result. To avoid further spread of cancer cells, the tumor must be removed, which, unfortunately, is not always possible. Basalioma can be located in dangerous places, for example, close to the eye.
The danger of basal cell carcinoma is that it grows into the deep layers of the skin, especially some of its forms.
The tumor affects other tissues and eats them away. If it is located close to the eye, cancer cells affect the organ of vision, which leads to blindness. Facial muscles, nerves, cartilage and even bones can suffer from the growth of tumor tissue.
If the disease is aggressive and quickly penetrates deep into the tissue, more serious consequences are possible, including damage to brain tissue. “Turban” basal cell carcinomas are especially dangerous in this regard.
For safety and to prevent serious consequences, it is better to remove any manifestation of basal cell carcinoma.
If the tumor is located on the body, it is less dangerous, but still requires surgery. However, basaliomas on the body are not so common; they usually affect open areas of the body.
Causes of basal cell carcinoma
Since basal cell carcinoma is a skin cancer, it is difficult to determine the causes of its appearance. It is believed that this disease can be inherited. The likelihood of encountering basal cell carcinoma if your close relatives have it increases several times.
Experts have also identified provoking factors:
- Exposure to ultraviolet radiation;
- Ingestion of carcinogens into the body;
- Genetic predisposition;
- Injury to moles;
- Bad habits;
- Congenital skin pathologies;
- Skin diseases and viral infections.
photos on the Internet after treatment for basal cell skin cancer. With timely detection and removal, unpleasant consequences and cosmetic defects can be avoided. But prevention is no less important. It is advisable to avoid provoking factors.
Particular attention is paid to sun exposure and solarium abuse.
Such an aggressive effect on the skin provokes a genetic change in the structure of the cell, which can trigger the development of the disease.
It is believed that people with thin and fair skin and freckles are more susceptible to negative factors and are more prone to skin cancer.
This skin reacts more strongly to the sun's rays.
One of the causes of basal cell carcinoma may be decreased immunity. Various infections are more difficult to tolerate. The herpes virus can also lead to skin cancer.
Smoking also has harmful effects on the skin, which absorbs carcinogens, mutagens and other substances from cigarette smoke. All this reduces the protective functions of the skin and contributes to the thinning of the walls of blood vessels.
It is important to promptly treat various skin diseases, eczema, dermatitis, and follow the rules of scar care to avoid their suppuration.
All this significantly increases the risk of encountering basal cell carcinoma. For this reason, prevention plays an important role. Doctors recommend protecting your skin from sun exposure, using sunscreen, avoiding skin injury, protecting it if you have to work with harmful substances, and promptly treating skin diseases.
At the moment, there are two most common forms: superficial and nodular
Superficial (newly identified) BCC:
- most often develops on the skin of the trunk and limbs;
- less common: head and neck;
- in younger patients, with a predominance of women.
Important!
The main development factor is genetic - this is a hereditary mutation that is transmitted to descendants or arises in connection with environmental or other adverse effects of the external environment. Nodular form (first identified) of BCC:
- most often develops on the scalp
- in elderly and senile patients
Causes
As in many other cases associated with cancer, clear and unambiguous reasons for the development of the disease have not yet been identified. But there are a number of factors that, according to doctors, contribute to this disease.
So, the probable causes of basal cell carcinoma include the following:
- prolonged exposure of the skin to sunlight, abuse of solarium;
- regular interaction with substances containing arsenic;
- consumption of liquids that contain a high content of arsenic and heavy metals;
- xeroderma pigmentosum virus;
- skin damage associated with burns, scar development, etc.;
- precancerous diseases that are not treated in time and are left to chance;
- predisposition to the disease due to light skin and hair color, mature age, etc.;
- serious immune disorders.
Obviously, none of these reasons is decisive, but each of them individually or several in combination can contribute to the development of basal cell carcinoma.
Are you experiencing symptoms of basal cell carcinoma?
Only a doctor can accurately diagnose the disease. Don't delay your consultation - call
How common is this skin growth?
- Skin tumors occupy the second place in the cancer incidence of the world's population. And BCC is the most common malignancy among them.
- BCC accounts for almost 80% of all newly diagnosed malignant skin tumors.
However, in reality, a significant number of basal cell carcinomas are not diagnosed in the early stages due to the duration of the development of the process, the latent course of the disease in elderly and senile patients who do not want to consult a specialist, as well as due to the lack of metastasis and severe complications.
Unfortunately, the incidence of BCC increases annually by 4-8%. According to the National Medical Research Center of Oncology named after. N.N. Petrova, in 2021, in the structure of all identified malignant neoplasms, skin cancer was 9.93% in women and 7.05% in men, while in 1995 these figures were 5.5% and 3.9%, respectively.
You will be curious that according to WHO (2017), in Australia, the country with the highest incidence of skin malignancies, two thirds of the population will develop BCC during their lifetime. And in the USA, 1/3 of all cancers are skin cancer, of which 80% are BCC.
It is also necessary to note significant fluctuations in skin cancer incidence rates in the structure of malignant neoplasms in different regions of the world and Russia in particular, depending on national, climatic characteristics and urbanization in general.
Most often, BCC is found in the southern regions, although high population mobility has recently led to the fact that the incidence rates of northern peoples are also steadily increasing, and in women they are consistently higher than in men. The incidence of BCC reaches its maximum in people over 60 years of age. However, in recent decades, the number of young patients has increased significantly. Their share will continue to grow, due to an increase in life expectancy, migration of people across regions of the planet, an increase in the intensity of natural UV radiation due to environmental factors and the more frequent use of artificial ultraviolet radiation.
However, despite the high incidence, age-adjusted metastasis and mortality rates are estimated to be only 0.0028% to 0.5% and 0.12% per 100,000 population, respectively.
Complications and prognosis of basal cell carcinoma
We have already said that basal cell carcinoma is a semi-malignant tumor. It grows slowly and rarely metastasizes. With timely treatment, the prognosis is favorable. Relapses develop in less than 10% of patients. The situation is worse in patients with large basal cell carcinomas or with an infiltrative form of the disease. They have a high risk of relapse and distant metastases. Moreover, such forms of basal cell carcinoma can destroy the underlying tissues, leading to disfigurement of appearance, the development of bleeding, chronic inflammation and dysfunction of the affected segment.
Book a consultation 24 hours a day
+7+7+78
Clinical signs of basal cell skin cancer
Surface form
- the least aggressive of all “carcinoma” forces the patient to consult a doctor when the tumor is already a fairly significant cosmetic defect or begins to cause inconvenience due to the addition of ulceration. The superficial form of BCC is also called basal cell carcinoma of the trunk and extremities. On the body, most often, it has a multiple character. Radial, extremely slow tumor growth predominates, occupying an area of several centimeters before the onset of invasion and confirmation of the diagnosis. This form is often considered by a specialist as a superficial keratoma and is ignored in senile and elderly people. Visually, it is defined as a flat, pinkish-brownish, slightly scaly formation, with a barely detectable ridge-like edge on palpation, thread-like nodules like a “pearl necklace” along the perimeter of the tumor, pearlescent color and, sometimes, visualized telangiectasia.
With nodular form
basal cell skin cancer, the patient consults a specialist if the tumor size is quite small, since the exophytic component is often subject to constant trauma and, as a consequence, contact bleeding. The process begins with a pearly-light or pink papule, on a wide base, a glossy surface with the absence of a skin pattern and the presence of telangiectasia.
The center of the node often ulcerates, followed by the formation of an eschar and hyperkeratosis. The perimeter roller is also often defined by the classic “pearl necklace”.
Scleroderma-like/sclerosing form of BCC
. The least common but most aggressive form. The skin formation resembles a scar, pale yellow in color, waxy to palpation, glossy. At the same time, the “string of pearls” characteristic of basaliomas in general and telangiectasia are most often absent. It recurs extremely often, due to the spread of the tumor both in area and in depth (the “iceberg” phenomenon). Very often the disease is not diagnosed for a long time due to its atypical picture.
For ulcerated basal cell carcinoma
patients complain of weeping and bleeding in the earliest stages of the tumor, lack of pain, which increases in proportion to the enlargement of the lesion. Subsequently, a secondary infection occurs, which can visually increase the area of the lesion. When this form of tumor occurs on the extremities, it is most often considered by primary care physicians for a long time as trophic ulcers in elderly people, even in the absence of other clinical signs of chronic venous insufficiency.
Complaints of pain appear with locally widespread tumors and are associated with involvement of nerve trunks or bones in the process. Arrosive bleeding is also characteristic of advanced forms of basal cell carcinoma.
Forms of basal cell carcinoma
- Nodular-ulcerative form of basalioma. The disease begins with the formation of dense, clearly defined areas that rise above the surface of the skin - nodules. They may be grey, pink or yellowish. Gradually they increase in size, the skin above them becomes thinner and becomes, as it were, pearlescent. Then they merge with each other and form a plaque with raised edges and a depression inside. Gradually, this depression transforms into an ulcer, which becomes covered with a crust. It, in turn, also grows, infiltrating and destroying the underlying tissue, as a result of which the plaque begins to resemble a crater with very dense edges that resemble cartilage tissue. As the tumor grows, destruction of the underlying tissue occurs.
- Large nodular basalioma. This species develops from a single nodule, which, increasing in size, takes the form of a hemisphere with a diameter of up to 3 cm or more. Its surface may be smooth, but the presence of scales is possible. As the basal cell carcinoma grows, destruction begins on its surface - an ulcer appears, from which bloody discharge oozes.
- Infiltrative form. It is characterized by the most malignant course, since it initially grows “inside” the tissue, destroying it. It is very difficult to determine the clear boundaries of this form of basal cell carcinoma.
- The papillomatous or warty form of basalioma is characterized by neoplasms that resemble papillomas in appearance.
- Superficial basalioma. At the initial stage, it looks like a pink spot. Gradually it grows, thickens and transforms into a plaque. Nodules form along its edges, which also increase in size and, when fused, form a roller. The center of the tumor “sags” and changes color to a darker one. The tumor is not prone to infiltrative growth, but if it is large, infiltration into the underlying tissue is still possible.
- Scleroderma-like basalioma. This type of tumor manifests itself with the formation of a yellowish or whitish plaque. As it grows, its edges become eroded and covered with crusts. When they are separated, an inflammatory reaction occurs. Also, cysts filled with calcifications can develop in the thickness of the tumor.
- Fibrous basal cell carcinoma. This tumor begins with the formation of a nodule, which, as it grows in size, transforms into a plaque. Its surface layer becomes thinner and blood vessels can be seen through it.
- Turban basal cell carcinoma. This type of tumor is most often located on the head. It looks like a bluish hemisphere. In size they can reach 10 cm in diameter. There are several such formations.
Skin tumor biopsy
A mandatory diagnostic step for skin tumors is morphological verification of the process, for this a biopsy
. The oncologist takes cells or tissues from the site of the tumor and submits them for examination to pathologists, who form their conclusion.
The morphological report contains information about the tumor:
- localization of the process (where the tumor is located);
- diameter (what size is the tumor);
- growth type;
- characteristics of the resection margin (the tumor was completely removed or not).
The oncologist makes a final diagnosis and forms a treatment plan only after receiving the results of the biopsy.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of basal cell carcinoma on a leg, arm, face or other place involves a number of diagnostic measures. This:
- detailed examination by a doctor and medical history;
- dermatoscopy. It is usually not enough for an accurate diagnosis;
- blood and urine tests;
- histology of the diseased area;
- cytology;
- CT, ultrasound, radiography. These studies are carried out if the tumor has already grown into cartilage or bone tissue.
Be careful! Since there are many forms of this disease, and some of its manifestations are similar to wounds, ordinary moles and nevi, only a doctor can make a diagnosis after a thorough examination! If you notice something suspicious and unusual on your skin, be sure to consult a specialist.
Treatment
It is advisable to determine treatment tactics according to the prevalence of the tumor process, its localization, risk factors, and the general somatic condition of the patient. Due to the high incidence of the disease in elderly patients, functional reserves and the presence of concomitant pathology are often of significant importance in determining treatment algorithms for skin tumors.
Surgery
The main treatment method for localized forms of skin tumors is surgical excision.
Radiation therapy
If there are contraindications to surgical treatment (or the patient refuses surgical treatment), radiation therapy is recommended. The choice of the type of radiation therapy (close-focus X-ray therapy, gamma and electron therapy) depends on the capabilities of the medical institution and the patient’s condition. It should be remembered that radiation therapy should not be given to patients with genetically determined skin cancer (for example, Gorlin-Goltz syndrome), xeroderma pigmentosum or scleroderma, since radiation therapy can worsen the course of the disease.
Laser destruction. Photodynamic therapy for basal cell carcinoma
In addition to two fairly well-studied and widely used in clinical practice areas of laser application - low-intensity stimulating laser radiation and high-energy damaging radiation, a third area is rapidly developing - photodynamic therapy of tumors (PDT). Interest in it is due to the fact that tumor destruction is achieved by irradiating it with low-intensity laser radiation, eliminating the risk of uncontrolled thermal damage to the organ wall.
Photodynamic therapy (PDT)
- part of photochemotherapy, in which, in addition to light and drug, oxygen is needed.
Cryogenic therapy
Cryodestruction
- the process of destruction of biological tissues under the influence of extremely low temperatures.
Locally acting therapy
If there are contraindications for surgical or radiation treatment for adults without immunodeficiency (HIV, hepatitis B and C, organ transplantation), it is advisable to use locally acting drugs (ointments). having antitumor activity. Use ointment as recommended by an oncologist.
Indications for use:
- presence of a primary focus of BCC (not relapse);
- size no more than 2 cm;
- superficial spreading form;
- localization on the trunk, neck or limbs (except hands and feet).
Treatment of patients with metastatic and unresectable skin cancer (stage IV)
It is recommended to make a decision on the management tactics of patients with metastatic and unresectable skin cancer within the framework of a multidisciplinary consultation with the participation of a surgeon, chemotherapist and radiation oncologist. Currently, systemic treatment regimens have been developed and are being used in patients with unresectable skin cancer.
The most effective drugs for the treatment of locally advanced basal skin cancer are targeted drugs (target literally translated from English is translated as a target or goal) - that is, this is a treatment when the drug acts specifically on a mutation in the tumor tissue, like a shot at a target. In 2021, one of these drugs was included in the list of vital and essential drugs (VED).
Chemotherapy is selected individually in each specific case.
Folk remedies
At home, the following folk methods are most effective in treating basal cell carcinoma:
- Fresh celandine juice. To obtain it, just break a branch of the plant. After a few seconds, juice will appear on the break, which can be used to lubricate the basal cell carcinoma 3–4 times a day.
- Ointment with burdock and celandine. To prepare the ointment, take 1/2 cup of chopped burdock and celandine herbs and pour in melted lard. Then put the mixture in the oven at 150o for 2 hours. The finished ointment is transferred to a convenient container and left for 2 days at room temperature, after which it is applied to the tumor in a thick layer 3 times a day.
- Golden mustache juice. To obtain juice, the whole golden mustache plant is washed and passed through a meat grinder. The crushed plant is collected in gauze and the juice is squeezed into a convenient container. Then a cotton swab is moistened in this juice and applied to the basal cell carcinoma for a day.
These traditional methods can be used until it is possible to remove the basal cell carcinoma in order to slow down the growth of the tumor as much as possible and prevent it from growing into deep-lying tissues.
What is the essence of the technique
Photodynamic removal of skin basalioma begins with a dropper - a photosensitizer drug is injected into the patient’s blood, which increases the photosensitivity of tissues. The photosensitizer has the special property of being retained only in old, atypical, damaged and cancer cells. 2-3 hours after injection, the tissues are irradiated with a laser according to a special scheme. The photosensitizer is activated by light and enters into a complex photochemical reaction, which results in the release of toxic compounds and reactive oxygen species that destroy cancer cells. The duration of the procedure depends on the size and number of tumors and takes from 20 minutes to 2.5 hours.
I would like to especially emphasize once again that each changed cell accumulates a photosensitizer. Therefore, after correctly performed photodynamic therapy, we can say that there are no cancer cells left in the treatment area . This means that there is simply nowhere for relapse to occur.
It is this targeted effect on cancer cells that ensures complete tumor removal and an excellent aesthetic result after the procedure.
2.What does basal cell carcinoma look like?
Basal cell carcinoma usually begins as a small, dome-shaped lump, often with small superficial blood vessels. The skin in this area may look shiny and translucent, as if pearlescent. Some basal carcinomas contain the pigment melanin, and because of this they appear dark rather than shiny. Because of these variations, it can be difficult to distinguish basal cell carcinoma from benign skin lesions without a biopsy.
Basal cell skin cancer grows slowly. It may take months or even years before it reaches a serious stage. Although basal cell carcinoma metastasizes to other organs and tissues very rarely, skin changes can damage or disfigure the eye, ear, or nose if the tumor grows nearby.
Visit our Oncology page
Why is the PDT method poorly represented in Europe and the USA?
Many patients ask me a reasonable question: why, if the PDT method is so effective, is it little known in the USA and Europe? The main reason for this state of affairs is the inflated cost of the photosensitizer in these countries - the cost of the drug there is about 3,000 US dollars. This is a high price; therefore, PDT of basal cell carcinoma is not covered by insurance companies. And if the method is not used, then it does not develop or develops very weakly. I have been practicing photodynamic therapy for more than 10 years, and the accumulated experience allows me to achieve complete cure of the most complex tumors.
To get advice on whether photodynamic therapy for basal cell carcinoma is indicated for you, and to calculate the cost of the procedure, send your medical history and tests by e-mail or call + 8 (800) 555-77-26 in Moscow. The reception is conducted by Afanasyev Maxim Stanislavovich, oncologist, doctor of medical sciences, professor and member of the academic council of the First Moscow State Medical University named after. THEM. Sechenov Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation, surgeon, expert in the treatment of basal cell carcinoma. Reception is carried out in 5 clinics in Moscow, as well as in centers in Makhachkala, Kursk, Stavropol, Barnaul, Samara and other regions of Russia. You can check the date, location of the appointment in your city and sign up for a consultation with the administrator by phone. For assistance in preparing the material, I thank Tatyana Georgievna Grishacheva, research fellow at the Center for Laser Medicine of PSPbSMU named after Acad. I.P. Pavlova.
Prevention
Older people should definitely know that basal cell carcinoma is a disease whose risk increases with the number of years lived. To prevent the disease, you need to follow a few simple tips.
- Monitor your diet and limit your intake of animal proteins. It is worth paying attention to nuts, seeds and vegetables.
- In the summer, try not to go outside during hours of maximum solar activity (from 11 a.m. to 4 p.m.). When visiting the beach, apply a special cream with a protection factor of at least 20 units to unprotected skin. Attention should be paid to the skin of the face and neck, since this is the favorite place for localization of basal cell carcinoma.
- It is important not to traumatize old scars.
- It is necessary to carefully treat wounds that do not heal well. They can provoke the appearance of pathology.
- Maintain personal hygiene when working with carcinogenic substances and lubricants.
- Use cosmetic creams to prevent dry skin.
This article is posted for educational purposes only and does not constitute scientific material or professional medical advice.