Pregnant women should ensure that their diet contains enough nutrients and energy for the proper development and growth of the fetus.
For a healthy pregnancy, the mother's diet must be balanced and nutritious, this includes the right balance of proteins, carbohydrates and fats, and consumption of a wide range of vegetables and fruits.
Some women's diets may be influenced by ethical beliefs, religious requirements, or health conditions, so visiting an OB/GYN is an important part of pregnancy nutrition planning.
Food facts for pregnant women
- A woman's caloric intake increases during pregnancy. Typical weight gain in a singleton pregnancy varies greatly depending on pre-pregnancy weight and other factors.
- Underweight pregnant women are advised to eat the most calories, while overweight women eat lower-calorie foods.
- During pregnancy, a woman's body absorbs iron more efficiently and blood volume increases, so it is necessary to consume more iron to ensure an adequate supply of oxygen to herself and the fetus.
Consequences of poor nutrition during pregnancy
Poor nutrition is potentially dangerous for every person, regardless of gender, age or physiological characteristics. In the case of pregnant women, both the expectant mother and the unborn baby are at risk. In addition, if you don’t monitor your diet during pregnancy, it will be more difficult to improve it later. This will provoke unhealthy eating behavior, which will cause excess weight and associated complexes. With uncontrolled consumption of junk food, a pregnant woman may face obesity and diseases such as diabetes. Poor nutrition, at a minimum, threatens the loss of your previous shape, and at maximum, problems with the stomach and digestion.
Product groups
A pregnant woman should follow a balanced diet that includes:
- Fruits and vegetables. They can be in the form of juice, dried fruits. Canned, frozen or fresh foods usually contain more vitamins and other nutrients. Experts emphasize that it is better to consume fresh fruits than just drink juice, as the natural sugar level in juice is very high.
- Starchy foods rich in carbohydrates. These are potatoes, rice, pasta and bread. They contain carbohydrates and are an important component of proper nutrition during pregnancy.
- Protein. Healthy animal proteins come from fish, lean meat, chicken and eggs. All pregnant women, especially vegetarians, should consider the following foods as good sources of protein: quinoa grain, known as a complete protein (includes all essential amino acids), tofu and soy products, beans, lentils, legumes, nuts, seeds and nut butters.
- Fats. They should not make up more than 30% of a pregnant woman's diet. Scientists report that a high-fat diet may genetically program a child to have diabetes in the future. There are other risks to pregnancy with an excessively high fat diet, so a balance is needed, and Omega-3s or "healthy fats" rather than monounsaturated fats should be the main fat options. Examples of foods high in monounsaturated fats: olive oil, peanut oil, sunflower oil, sesame oil, avocado oil, nuts.
- Cellulose. Whole grains such as wholemeal bread, wild rice, whole grain pasta, legumes and lentils, fruits and vegetables are rich in fibre. Women have a higher risk of developing constipation during pregnancy. Eating plenty of fiber will effectively minimize this problem. Research has shown that eating plenty of fiber during pregnancy reduces the risk or severity of hemorrhoids, which progress as the fetus grows.
- Calcium . It is important to get your daily required amount of calcium. Dairy products such as cheese, milk and yogurt are rich in calcium. If the mother is a vegetarian, she should consume the following calcium-rich foods: calcium-fortified soy milk, tofu with calcium complex, soybeans, broccoli, collards, Chinese cabbage, beans and soy nuts.
- Zinc . This is a vital microelement. It promotes normal cell growth and development, regulates nucleic acid metabolism and protein synthesis. Important for fetal development. The best sources of zinc are chicken, turkey, ham, shrimp, crab, oysters, meat, fish, dairy products, beans, peanut butter, nuts, sunflower seeds, ginger, onions, bran, wheat germ, rice, pasta, cereals, eggs , lentils and tofu.
Healthy lifestyle
Category: Healthy eating.
Happiness, anxious waiting, anticipation and even fear - all these feelings inevitably accompany pregnant women. And it is very important during this period not to give in to emotions, but to remember the responsibility that is an integral part of this time. It is during this period that it is important to follow the basics of a healthy lifestyle, taking into account the requirements of pregnancy. Proper nutrition during pregnancy is the most important, since what a woman eats largely determines how her child will develop. For example, whether a pregnant woman gets enough protein determines whether the child will have enough building material.
It makes sense to take into account one important feature: proper nutrition in the early stages of pregnancy will be somewhat different from the diet of a pregnant woman in the last weeks.
Not everyone understands where such differences come from, but understanding the topic will be quite simple. Judge for yourself: in the early stages, important body systems are formed, but the size of the fetus increases slightly. Therefore, in the early stages, healthy nutrition for pregnant women is based on sufficient intake of minerals, vitamins, and the like.
In the second trimester of pregnancy, nutrition should focus on increased protein consumption, since this is when the active growth of the child and its internal organs begins. For all this, building material is needed, that is, protein.
Nutrition in the third trimester of pregnancy is, first of all, vitamins and minerals that are necessary for the development of the internal systems of the child’s body, especially calcium for bone growth and development of the nervous system.
When planning a pregnancy, proper nutrition is also very important. The healthier, more resilient, and stronger a woman’s body is at the time of conception, the greater the chance of successful implantation of the fertilized egg in the uterus. And a certain set of vitamins in the body contributes to the proper development of the embryo.
As you can see, the difference in recommendations for proper nutrition for pregnant women by month, and sometimes even by week, is quite justified. However, there are, of course, general rules for proper nutrition during pregnancy, and these will be discussed further.
General principles of proper nutrition during pregnancy
First of all, it’s worth remembering one simple thing: it’s better to get up from the table slightly hungry than with a heaviness in your stomach from overeating. In this regard, it is better to adhere to the principles of fractional nutrition: eat less, but more often. The ideal option would be to eat 5-6 times a day. The last meal should be 3 hours before bedtime. If the feeling of hunger is unbearable, you can drink a glass of milk or kefir, or eat an apple or pear. This is the most optimal diet for pregnant women.
Proper nutrition during pregnancy, like, in fact, any proper nutrition, involves the exclusion or maximum limitation of fried foods, pickled foods and smoked foods. Food that is steamed, boiled, stewed or baked will be much healthier. Food products for pregnant women should be as fresh and natural as possible, and should not contain preservatives, excess salt, etc.
It is obvious that canned foods, various sausages and other shelf-stable products, if not prohibited, then require strict control over their consumption.
Of course, it is recommended to give up fast food. However, it is worth noting that if you have a choice between staying hungry or eating something that is not very healthy, it is better to choose the latter. A pregnant woman should not starve. Another thing is that if you are faced with such a choice suspiciously often, then you should think about carrying fruit or sandwiches with you.
The balance between such essential nutritional components as proteins, fats, carbohydrates, as well as vitamins and minerals is of great importance. Of course, a balanced diet for pregnant women at different stages requires a different balance of these components; the fact itself remains unchanged.
Meals by week
1–3 weeks of pregnancy
Gynecologists count pregnancy not from the day of conception, since it is almost impossible to calculate, but from the first day of the last menstruation. Consequently, the first 2 weeks of obstetric pregnancy occur before conception.
Planning a pregnancy is an extremely important period on which, whatever one may say, the health of the unborn child and the absence of any complications during pregnancy depend. So it turns out that proper nutrition before pregnancy is of paramount importance. At this stage it is very important to increase the amount of folic acid. Doctors often recommend drinking it in capsule form, but it is much better to get all the vitamins from normal food. Folic acid is found in green leafy vegetables (spinach, lettuce, cabbage, etc.), asparagus, beans and legumes, seeds and nuts, and citrus fruits.
Equally beneficial is eating yellow fruits and vegetables. But it’s better to avoid fatty and sweet foods. This will avoid problems with obesity, as well as reduce the risk of early toxicosis.
Around day 10–14 of the cycle, fertilization occurs and the fertilized egg begins to move towards the uterus. From this time on, we can talk about pregnancy.
3 week
Nutrition at the beginning of pregnancy is a very complex topic, since literally every week the fetus develops new organs and systems, which means the need for vitamins and nutrients is constantly changing.
During the third week of pregnancy, the egg implants and the placenta and membranes begin to develop. For their full development, calcium is needed, which is found in dairy products, nuts, fish, legumes, fruit juices and cereals; and manganese, it can be obtained from nuts, spinach, beets, mushrooms, and animal liver.
4 week
For 4 weeks, the diet remains the same as for 3, but at this time it is especially important to give up coffee. However, drinking this undoubtedly tasty, but not very healthy drink during pregnancy should be done with extreme caution. Coffee is especially contraindicated in the evening. As you can see, proper nutrition in the first month of pregnancy is not too difficult. Further it will be a little more difficult.
5 week
As a rule, toxicosis of pregnant women begins around this period. To alleviate this condition, you can slightly change your daily menu. Thus, meat and eggs, as well as other animal proteins, can be replaced with nuts, soy and other legumes. Instead of milk, you can eat yogurt and cheese. It wouldn’t hurt to include carrots, mangoes, and apricots in your diet.
week 6
Toxicosis is in full swing, so the morning should start with crackers or unsweetened crackers. It is better to eat them immediately after waking up, without getting out of bed. At this stage, it is better to drink more liquid, at least 8 glasses a day (for example: water with lemon juice or tea with lemon). At night you can eat a handful of raisins.
week 7
At this time, problems with the intestines may arise. Therefore, you should avoid foods that cause gas, including cabbage. It would not be a bad idea to give up those products that strengthen. It is better to introduce prunes, fresh kefir and the like into your diet.
8 week
Ginger tea will help cope with toxicosis, and don't forget about nuts.
9–10 weeks
Give preference to whole grain cereals and wholemeal bread. Brown rice is better than white rice. In general, a pregnant woman’s body requires quite a lot of fiber at this stage.
11–12 weeks
The first trimester of pregnancy is ending, and nutrition at this time should be special. This is the most difficult time, and it is very important to listen to yourself, to your body. If you want to eat a specific dish, it means that it is precisely the substances contained in it that your baby lacks. Of course, you shouldn’t go to extremes.
13–16 weeks
Nutrition in the 2nd trimester during pregnancy is characterized, as already mentioned, by abundant protein consumption. In addition, it is necessary to increase the total daily caloric intake of food. If in the first trimester it is enough to eat 2400–2700 kcal, then from now on you need to eat 2700–2900 kcal.
16–24 weeks
Nutrition during the 6th month of pregnancy should contribute to the development of the baby’s vision and hearing. That is, you need vitamin A and beta-carotene. It is better to eat cabbage, yellow peppers, and carrots at this time. Keep in mind that vitamin A is absorbed only with fats.
24–28 weeks
It is at this time that fractional meals become especially relevant. The uterus is actively growing, takes up more and more space in the abdominal cavity, and begins to put pressure on the stomach. Accordingly, the stomach becomes smaller and it is difficult for it to accommodate large amounts of food. Even when eating small portions, a pregnant woman may experience heartburn. It is better to avoid carbonated drinks and coffee, they also cause heartburn. In general, a pregnant woman’s diet in the third trimester should be as varied as possible, as the baby’s needs grow.
29–34 weeks
During the 8th month, bones are actively growing and teeth are being formed, therefore, it is very important to eat as many foods containing calcium as possible. Fatty acids are simply necessary for brain development, and they contribute to the absorption of calcium. Lack of iron at this stage can lead to the development of anemia in both mother and child. Fatty fish, nuts, red meat, dark green vegetables and seeds are the foods you should eat during this period of pregnancy.
35–40 weeks
Nutrition in the 9th, last month of pregnancy should contribute to the overall strengthening of the mother’s body. After all, she has a very difficult and time-consuming job ahead of her - childbirth. The main source of energy in the body is carbohydrates, and it is their consumption that should become the basis of a pregnant woman’s nutrition before childbirth. Porridge and vegetables are the foods you should eat during this period.
That's all that can be said about nutrition by trimester. An example of a menu for pregnant women by trimester may also be useful. Based on these menus and their explanations, you can create a menu for yourself.
Sample menu for pregnant women for the 1st trimester
1. Breakfast: muesli with yogurt and freshly squeezed pear juice.
2. First snack: salmon sandwich.
3. Lunch: mushroom soup, cabbage salad, herbal tea.
4. Second snack: whole grain bread with cheese.
5. Dinner: carrot salad and vegetable risotto. You can wash everything down with kefir.
In the first trimester, it is very important that a woman receives a large amount of folate and vitamin B6 from food.
Sample menu for pregnant women for the 2nd trimester
In the second trimester, it is important for pregnant women to have omega-3 acid, calcium, vitamin D and iron in their diet.
1. Breakfast: oatmeal with milk, apple and cinnamon, chamomile tea.
2. First snack: almonds with prunes.
3. Lunch: lentil soup, seaweed salad, cranberry juice.
4. Second snack: sandwich with herring.
5. Dinner: omelet with mushrooms and yogurt.
Sample menu for pregnant women for the 3rd trimester
Carbohydrates and vitamin K play a special role here.
1. Breakfast: pancakes with cream cheese and sour milk.
2. First snack: a cheese sandwich made from whole grain bread.
3. Lunch: fish soup, tuna and herb salad, rosehip broth.
4. Second snack: cheesecake.
5. Dinner: fish with rice and fermented baked milk.
Special nutrition for pregnant women
But this is not all the nutritional features of pregnant women. In some cases, women develop pathologies during pregnancy that require special nutrition. So, with anemia in pregnant women, special nutrition is simply necessary. A woman experiencing pregnancy anemia should consult a doctor not only about drug treatment, but also about an appropriate diet. With this disease, it is very important to increase the consumption of foods containing iron. Iron can be obtained from animal products (lean red meat, fish, poultry) and vegetable (nuts, dried porcini mushrooms, spinach, buckwheat, legumes, etc.) origin. In addition, it is important not only to know what foods to consume, but also in what combinations, as this affects the absorption of iron in the human body. Vitamin C increases the absorption of iron in the body, that is, the combination of foods containing iron and vitamin C is beneficial. Products containing calcium (dairy products) and tannin (tea, coffee) prevent the absorption of iron in the intestines. Therefore, their use should be separated.
If obesity develops during pregnancy, there may be a need for dietary nutrition for pregnant women. It is important to remember that a pregnant woman should not choose a diet for weight loss without consulting a doctor. The risk of developing pathologies and abnormalities is too great, both in the mother’s body and in the child’s body.
Mono-diets and diets that require prolonged fasting are especially harmful. Both contribute to exhaustion and vitamin deficiency. It will take a very long time to restore the condition of the body, the supply of nutrients and vitamins, and it is completely impossible to compensate for the harm that such diets cause to the child.
Iron and pregnancy
Iron makes up the bulk of hemoglobin, the oxygen-carrying pigment and major protein in red blood cells. During pregnancy, the amount of blood in the mother's body increases by almost 50%. More iron is needed to produce more hemoglobin.
If iron stores are insufficient, the mother may develop anemia. Iron deficiency can lead to premature birth, low birth weight, stillbirth, neonatal death, as well as fatigue, irritability, depression (in the mother) during pregnancy.
Anemia in late pregnancy increases the risk of losing large amounts of blood during childbirth.
Foods that are rich sources of iron:
- dried fruits;
- egg yolk;
- whole grain cereals, if fortified with iron;
- liver, but doctors and most nutritionists advise pregnant women to avoid excessive consumption of this product because it contains a lot of vitamin A, which can harm the fetus;
- lean meat;
- oysters that have undergone heat treatment;
- poultry meat (chicken, turkey);
- moose, tuna;
- lean lamb, pork and shellfish also contain iron, but less than other foods;
- legumes (soybeans, beans, dried beans and peas);
- nuts and almonds;
- vegetables, especially dark greens: broccoli, spinach, dandelion leaves, asparagus, kale;
- grains: brown rice, oats, millet and wheat.
Consequences of inadequate nutrition
The issue of nutrition during pregnancy is vitally important, has been thoroughly studied, and at the same time remains for most doctors and especially expectant mothers beyond the scope of problems that should be seriously worried about. In fact, the first time most pregnant women hear anything about nutrition from their doctor is when they gain excess weight or when their blood glucose level is high. By interviewing your friends, you can easily make sure that even very conscientious and attentive doctors do not worry if a woman weighs little or does not gain enough. Meanwhile, with improper and inadequate nutrition, the following serious complications can arise.
For the expectant mother:
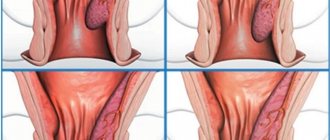
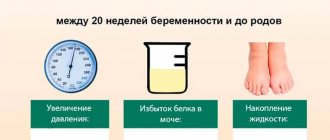
- Late toxicosis of pregnancy (preeclampsia) is a painful condition in which fluid retention in the body (hydropsis of pregnant women), loss of protein in the urine, and increased blood pressure develop successively. Ultimately, if left untreated, severe brain complications develop, including seizures and coma, hemorrhages in vital organs, and the mother and child may die. Modern official medicine states that the cause of this condition is unknown. It is not true! It will be shown below that it is known and easily preventable.
- Miscarriage (premature birth and miscarriages) - because Due to improper nutrition, the placenta cannot develop normally.
- Premature placental abruption - close to childbirth, the placenta begins to separate from the wall of the uterus, the baby may die (50% chance), and the mother experiences bleeding. This occurs, among other things, due to the tendency to thicken the blood and form blood clots in the vessels of the uterus and placenta.
- Anemia (anemia) - due to insufficient intake or absorption of proteins, iron, and vitamins.
- Infectious complications, including those of the lungs, liver and kidneys.
- Weak labor, prolonged labor, exhaustion of the expectant mother during childbirth.
- Postpartum hemorrhage and decreased blood clotting.
- Slow healing of perineal wounds, the uterus contracts slowly after childbirth.
The child has:
- Intrauterine growth retardation, and intrauterine death is also possible.
- Low birth weight, as well as prematurity, low viability.
- Encephalopathy, decreased mental abilities.
- Hyperexcitability and hyperactivity.
- Reduced resistance to infections in utero, during and after childbirth, susceptibility to various diseases.
- Convincing yourself to take care of proper nutrition is not easy, but the results are worth it.
Foods to Avoid
During pregnancy the following are contraindicated:
- Shark meat, swordfish and marlin, or eat them in minimal quantities due to possible mercury content.
- Raw or partially cooked meat.
- Raw shellfish (there is a risk of bacterial or viral contamination that can cause food poisoning; some bacteria and viruses can also cross the placenta and cause harm to the fetus).
- Raw eggs, including any foods with raw or partially cooked eggs in them. Eggs must be well cooked to avoid salmonella contamination.
- Pate (vegetable or meat).
- A soft, ripened cheese such as blue-veined, brie or camembert.
- High-calorie foods (cakes, cookies, chips and candies) should be kept to a minimum. Many of these options are high in sugar and fat, have low nutritional content and can contribute to excess weight gain.
All foods must be cooked or else there is a risk of contamination with listeria (bacteria that can cause potentially fatal infections in pregnant women and their children).
Attention: squirrels!
We will start with proteins, because, as we will see later, it is with disorders of protein metabolism, with protein deficiency that the majority of the complications that were mentioned at the beginning are associated. Below you will see why.
Here's what proteins provide during pregnancy:
- growth and development of the baby, placenta, uterus and mammary glands of the mother (constructive role), as well as reserves that will be used during breastfeeding
- transport of nutrients, vitamins, microelements (including iron), calcium (transport role)
- immune protection, since antibodies against bacteria and viruses are proteins (protective role)
- optimal functioning of the coagulation and anticoagulation systems (no bleeding or blood clots occur) (from 4-5 months of pregnancy the content of fibrinogen, prothrombin, blood coagulation factors V, VII, VIII, X increases - all these are proteins)
- maintaining plasma osmotic pressure; this is a property that does not allow the liquid part of the blood to leave the vascular bed, thereby preventing the occurrence of edema and blood thickening; at normal osmotic pressure of plasma, the blood volume is sufficient to provide nutrition and respiration for both mother and child, and the fluidity of the blood ensures the best blood supply; Proteins albumin and sodium chloride, that is, table salt, are responsible for this most important quality.
It is easy to understand what protein metabolism in the body depends on:
- from protein intake from food
- from digestion and absorption in the gastrointestinal tract (mainly in the stomach and small intestine)
- on the function of the liver (it is it that produces the main necessary proteins - construction, protective, necessary for coagulation)
- on the intensity of breakdown and loss of proteins (this applies to increased physical activity and some kidney diseases).
Here's how protein deficiency manifests itself during pregnancy:
- the earliest signs are insufficient weight gain and an increase in hemoglobin (HGB) and hematocrit (Ht); Please note - a high hemoglobin level (above 120 g/l) in the second and third trimester is a reason not to be happy, but to be wary, since it usually indicates blood thickening as a result of a lack of protein and a decrease in circulating blood volume
- delayed intrauterine development of the child (according to measurements of the height of the uterine fundus and abdominal circumference, as well as ultrasound), its malnutrition
- the appearance of edema (due to a drop in plasma osmotic pressure, the liquid part of the blood leaves the vessels into the tissues)
- increased blood pressure (this is a “reaction of despair” - due to a decrease in the volume of circulating blood, the body is forced to reduce the lumen of blood vessels and increase the pressure in them so that the remaining blood circulates more intensely)
- an increase in liver enzymes, indicating liver suffering due to protein starvation
- preeclampsia and eclampsia (expressed in headaches, increased reflexes, blurred vision and, finally, convulsions) are the most dangerous complications of gestosis, requiring urgent hospitalization
(For reference: the normal level of total serum protein is 65-85 g/l, a decrease to 60 g/l already indicates severe gestosis; serum albumin is normally 35-55 g/l, when it decreases to 30 g/l l edema develops; normal hematocrit is 0.36 - 0.42 l/l; weight gain of 2.3 - 4.5 kg over the period from 24 to 28 weeks is normal and indicates an adequate increase in circulating blood volume).
Should pregnant women avoid caffeine?
If a pregnant woman consumes too much caffeine during pregnancy, there is an increased risk of low birth weight for the baby, which can lead to health problems later in life. The risk of miscarriage increases.
Not only does coffee contain caffeine, but so do many foods and drinks. Some carbonated drinks, energy drinks, chocolate and tea include this element. Many cold and flu remedies also contain caffeine.
A pregnant woman should consult a doctor before taking any medicine. It has been established that you can drink no more than 200 ml of coffee per day. A standard mug of instant drink contains 100 ml of caffeine.
Healthy food plate
The main meal should include:
- 1 serving of protein product (meat, fish)
- 1 serving of starchy food (pasta, potatoes)
- 2 servings of vegetables + 1 fruit + 1-2 servings of dairy products
Today it is believed that there should be no special diet to prevent the development of food allergies in a child. On the contrary, it has been proven that artificial avoidance of certain foods can provoke the paradoxical development of an allergy in a baby to this particular product, because he was not introduced to it while in his mother’s tummy. The diet should be as varied and complete as possible.
Weight gain
First, you need to calculate your body mass index (BMI). A woman whose figure is from 18.5 to 24.9 should gain 11.4-15.9 kg within 9 months. An overweight woman at the beginning of pregnancy typically gains between 6.8 and 11.4 kg.
Recommendations for weight gain may also vary depending on the fetus's age, development, and current health status. Excessive or insufficient weight gain can affect the health of both the unborn baby and the mother.
Basic dietary rules during pregnancy
A nutrition plan, dynamic calorie calculation, nutrient balance is the job of the doctor who is seeing the expectant mother. One of the main indicators on which an individual program depends is body mass index. Successful pregnancy and childbirth largely depend on normal weight gain during pregnancy. Therefore, if women are underweight, they are prescribed a high-calorie diet, and if they are overweight, low-calorie diets are recommended even before conception in order to bring the body back to normal.
Body mass index is the ratio of weight in kilograms to the square of dew in meters. Dependence of weight gain on body mass index for:
- too thin (BMI less than 18.5) – 12.5-18 kg;
- normal (18.5-24.9) – 11.5-16 kg;
- full (25-29.9) – 7-11 kg;
- obese (over 30) – 5-9 kg.
Regular meals. The gaps between individual meals should not be too long. With fractional nutrition, the concentration of nutrients in the blood is more stable, which has a beneficial effect on the development of the fetus. If before pregnancy a woman ate 2-3 times a day, then, while pregnant, she should eat 5-6 times. That is, she will have to divide her usual portions of food in half.
Small meals, when no more than 4 hours pass between meals, help you avoid overeating. A woman does not experience strong hunger, so satiety comes faster. You should not eat large portions so as not to exceed your daily calorie intake and disrupt your diet. In addition, overeating leads to poor absorption of food and intoxication, which is extremely undesirable for the baby.
Drink at least 2 liters of water per day. Normal water balance is extremely important for pregnant women. Dehydration provokes intoxication and also increases the risk of premature contractions. One of the signs of a lack of water in the body is dark urine. Drinking during and after meals, as well as between meals, will help correct the situation. Moreover, it should be pure water, and not any other drinks. You should also avoid carbonated drinks, both sweet and artificially sweetened. Sudden jumps in glucose can trigger the so-called diabetes of pregnant women, and the gases themselves irritate the stomach and lead to bloating.
Food should not be dry. You can eat everything – soup and crackers. But very dry food should be washed down with water to avoid the bonding effect. In pregnant women, the growing fetus puts pressure on the large intestine and rectum, leading to difficulty defecating and constipation. And dry food further enhances this effect.
There should be breakfasts. If you have no appetite in the morning, then you need to drink a glass of water; after half an hour your stomach will require food. But you should not eat heavy food for breakfast (eggs, meat, cottage cheese). It is better to eat some porridge with fruit, maybe with a little sugar or honey.
Avoidance of spicy foods is mandatory. Moreover, not only hot peppers should be excluded from the diet, but also foods such as garlic, fresh and fried onions, horseradish, and mustard. They increase appetite and irritate the digestive organs, enter the blood and amniotic fluid, causing undesirable reactions in the developing organism.
Vitamin supplements
You should consult your doctor before taking any supplements:
- Iron . A pregnant woman should consume 27 mg of iron per day. A sufficient amount of iron enters the body with a healthy diet. Women may experience heartburn, nausea, or constipation when taking medications with this element. To avoid problems, you need to take the tablets with meals, starting with smaller doses and then gradually increasing the amount of the drug.
- Folic acid . It is recommended that folic acid supplementation before the 12th week of pregnancy be 400 mcg per day.
- Vitamin D . A pregnant woman should take a supplement containing 10 mcg of vitamin D per day. The sun's rays trigger its synthesis in the body.
- Zinc. Zinc deficiency during pregnancy can lead to adverse pregnancy outcomes for the mother and fetus. After evaluating several studies, it was found that pregnant women who took zinc supplements were 14% less likely to have a preterm birth.
Pregnant women should avoid taking too much vitamin A as it may harm the baby. The exception to this rule is when a doctor recommends it for a specific reason. For example, it can be determined that the mother does not have enough vitamin of this element during pregnancy, in which case taking the supplement is justified, but strictly as prescribed.
Alternative to caffeine
At the moment, the effects that caffeine-containing products have on the developing fetus are not fully understood. These products include coffee, Coca-Cola, Pepsi, tea, and chocolate.
There is an assumption that caffeine has a negative effect on the child’s nervous system much more than on a pregnant woman. The reason is that the fetal systems and organs are still immature and can be damaged by consuming caffeine-containing products.
Instead of caffeinated drinks, it is advisable to consume ANY SUBSTITUTES for decaffeinated coffee; fruit teas; freshly squeezed juices or juice drinks based on natural juice; soups, broths; milk; water, mineral water.
The caffeine content in a cup of coffee is 146 mg, in Coca-Cola - 65 mg, in tea - 46 mg.
Second half of pregnancy
Speaking about the first half of pregnancy, we talked in detail about the changes that occur from week to week. This is understandable: the future baby worked a lot on himself, growing literally by leaps and bounds, turning from a tiny grain of rice into a little man. At the same time, the expectant mother was getting used to her new position, learning to do everything for two, eating right and creating all the conditions for her baby to develop and grow.
And now the time has come when the baby focused on growth, and the expectant mother has already learned how to properly prepare for her upcoming motherhood and saw a lot of advantages in her difficult situation. Now the two can even communicate. Mom often talks to her baby, plays music for him, walks a lot, and the baby does his best to make it clear that he hears everything and even seems to understand.