Otitis is one of the most common diagnoses in the daily practice of an otolaryngologist. In acute otitis media, we observe an inflammatory process affecting one of the parts of the human hearing organ. The appearance of acute pain in the ear is the main symptom signaling the onset of inflammation.
The disease is common among both children and adults. Although children are at increased risk of developing acute inflammation. This is due to the structural features of the child’s ear and weak, fragile immunity.
Diseases of the hearing organ, like any other disease concentrated in the head area, must be treated carefully and responsibly, since an infection through the bloodstream can easily reach the brain and cause irreversible consequences. Therefore, it is necessary to treat an acute inflammatory process as soon as the first prerequisites for the disease appear. Treatment of the disease should be carried out in a hospital, under the supervision of a competent doctor.
In this article we will look at how the disease develops, what treatment methods are available today, how complications of otitis manifest themselves and how to avoid them.
Types of disease
Inflammation that occurs in the organ of hearing can be chronic or acute. In acute cases of otitis, the disease lasts for up to three weeks, in chronic cases - more than three months. The chronic process starts when treatment of the acute form of otitis was not carried out or was not carried out at the proper level. There is also an intermediate form - subacute, when the duration of the disease ranges from three weeks to three months.
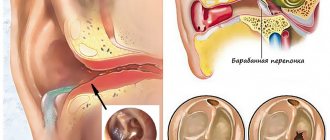
The human hearing organ is divided into three parts: the outer, middle and inner ear. Otitis may appear in each of these areas. Based on the location of the inflammation, acute otitis media is distinguished, and inflammation of the inner ear, otherwise known as labyrinthitis.
External manifestations of inflammation, in turn, are divided into limited, manifesting mainly in the form of a boil of the auricle, and diffuse otitis media. With diffuse otitis, a significant area of the outer ear is affected.
Acute inflammation of the middle ear involves the tympanic cavity of the ear, the auditory (Eustachian) tube and the mastoid process. This type of hearing disease is the most common.
Make an appointment right now!
Call us by phone or use the feedback form
Sign up
The disease of the internal part is called labyrinthitis (this part of the ear is called the labyrinth because of the similarity of its shape to the cochlea). As a rule, inflammation covers the internal part if the treatment of inflammatory disease of the middle ear was carried out late or the treatment for otitis media was chosen incorrectly.
Based on the causes of occurrence, infectious otitis media is distinguished, caused by various pathogens, and non-infectious (for example, arising due to exposure to allergens or ear injuries).
Otitis in acute form can occur in catarrhal (without the formation of secretion in the ear cavity), exudative (with the formation of fluid in the tympanic cavity) and purulent (with the presence of purulent masses) forms.
Hearing organ: structure.
To understand how the disease manifests itself in humans and to understand what processes occur, let’s turn to the structure of our hearing organ. The ear, in our usual understanding, is only the visible part of the hearing organ, so to speak, the tip of the iceberg. This visible part is called the outer ear. It includes the auricle and external auditory canal. Its main function is to catch sounds from the outside and direct them further.
Then comes the middle section, represented by the eardrum, the tympanic cavity with three auditory ossicles and the auditory (Eustachian) tube. Here the incoming sound signal is amplified many times. It is in this department that most inflammation originates.
Next, the sound enters the internal section, which is called the “cochlea”. Here it is converted into microelectric impulses and sent to the brain.
The organ of hearing is a very complex system with well-established operation. Exposure to unfavorable factors can easily disrupt the activity of this well-coordinated mechanism, so taking care of ear health is our direct responsibility.
Acute otitis media of the middle ear: what causes inflammation?
The inflammatory process is always caused by pathogenic microorganisms, which means that the prerequisites for their activation must be present in the body. The causes of otitis media are:
- hypothermia;
- diseases caused by infection (flu, ARVI, measles);
- inflammatory processes of the ENT organs (the tympanic cavity is connected to the nasopharynx via the Eustachian tube, it is not surprising that the infection from the nasopharynx easily penetrates into the middle ear);
- improper nose blowing;
- hypertrophy of adenoid vegetations;
- rhinitis, sinusitis;
- allergic reactions;
- deviated nasal septum;
- foreign object in the ear;
- damage to the hearing organ.
Risk factors
- Age. Children ages 6 months to 2 years are more susceptible to ear infections because of the size and shape of their eustachian tubes and because their immune systems are underdeveloped.
- Children's group. Children in group settings are more likely to get colds and ear infections than children who stay at home because they are exposed to more infections, such as colds.
- Baby food. Babies who drink from a bottle, especially while lying down, are more likely to develop ear infections than babies who are breastfed.
- Seasonal factors. Ear infections are most common during the fall and winter, when colds and flu are common. People with seasonal allergies are at greater risk of ear infections during seasonal allergies.
- Contaminated air. Exposure to tobacco smoke or high levels of air pollution can increase the risk of ear infection.
Outer and inner ear: causes of inflammation
Otitis externa can develop due to improper ear hygiene. If you don't take care of your ears, dirt will accumulate in them, and this is a favorable environment for the growth of bacteria. Excessive hygiene is also harmful: earwax is a natural barrier against the penetration of bacteria into the ear. If you diligently clean the ear canals every day, a person loses this barrier and opens the way for pathogens. Another mistake that leads to acute ear inflammation is cleaning the ears with sharp objects that are not intended for this (toothpicks, matches, hairpins). Such actions can lead to damage to the auricle, which in turn leads to infection entering the wounds. Another factor is dirty water that gets into the ear, which contains pathogens. “Swimmer’s ear” is another name for this type of disease.
As we have already said, inflammation of the internal region occurs due to undertreated otitis media, if due attention has not been paid to the treatment of otitis media. Bacteria can also get here from the meninges, for example, with meningitis. This type of inflammation can be caused by injuries and fractures of the skull or temporal bone.
In order to recognize the disease in time and choose the right treatment, you need to be able to identify its signs.
Polydexa
These ear drops contain an antibiotic and the hormone dexamethasone, so Polidexa effectively removes inflammation and reduces swelling. In addition to antimicrobial, these ear drops also have an antifungal effect, although weakly expressed. "Polydex" is often prescribed in pediatrics (can be used from 2.5 years). Children's drops for otitis media perfectly relieve inflammation and eliminate its symptoms. "Polydex" is considered one of the best remedies for ear diseases and has virtually no age restrictions.
Polydexa
Laboratories Bouchard-Recordati, France
Polydexa is a drug with antibacterial, anti-inflammatory and vasoconstrictor effects for topical use in ENT practice.
When combining these antibiotics, the spectrum of antibacterial action expands on most gram-positive and gram-negative microorganisms that cause infectious and inflammatory diseases of the nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses. from 188
959
- Like
- Write a review
Symptoms
The acute course of the disease is characterized by a rapid onset and pronounced symptoms.
With a disease of the outer ear, a person experiences pain inside, which intensifies when pressing on it from the outside. Acute pain occurs when swallowing and chewing food. The ear itself swells and turns red. The skin of the auricle is itchy, the patient's complaints are reduced to a state of stuffiness and ringing in the ear.
In acute otitis media, the main sign of inflammation is the sudden appearance of sharp shooting pains, which become stronger by night. The pain can radiate to the temples, left or right frontal parts, to the jaw - it is very difficult to endure even for an adult, not to mention children. The following symptoms are also characteristic of acute otitis media:
Friends! Timely and correct treatment will ensure you a speedy recovery!
- fever (up to 39°C);
- tinnitus;
- hearing loss;
- lethargy, malaise, loss of appetite;
- in the exudative form, discharge comes from the ear (usually this discharge is transparent or white);
- Acute purulent otitis media is characterized by suppuration from the ear.
The main symptom of labyrinthitis is dizziness. They can last a few seconds, or they can last for several days.
If you notice one or more of the symptoms described above, you should immediately consult a doctor for treatment.
Prevention
The following tips may reduce your risk of developing otitis media:
- Prevent colds and other illnesses. Teach your children to wash their hands frequently and thoroughly, and not to share food or drinks. Teach your children to cough or sneeze into their hand. If possible, limit the time your child spends in a group setting. Try to keep your child at home when he is sick.
- Avoid secondhand smoke. Try to stay in non-smoking areas.
- Breastfeeding your baby. If possible, breastfeed your baby for at least six months. Breast milk contains antibodies that may provide protection against ear infections.
- If you bottle feed, keep your baby upright. Avoid propping bottles in your baby's mouth while he is lying down. Do not put the bottle in the crib with your baby.
- Talk to your doctor about getting vaccinated. Ask your doctor about which vaccines are appropriate for your child. Seasonal flu shots, pneumococcal and other bacterial vaccines can help prevent ear infections.
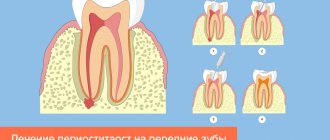
Stages of disease development
Treatment of acute otitis lasts from one to three weeks. There are several stages in the development of the disease. But it is not at all necessary that the patient will go through all of them. If treatment for infectious otitis is started on time and the acute disease is treated by a competent ENT doctor, recovery will not take long.
So, the course of the disease is conventionally divided into several stages:
- Catarrhal. Pathogenic microorganisms begin to actively multiply, triggering an inflammatory process in the ear. At this time, catarrhal edema and inflammation are observed.
- Exudative. Inflammation leads to active formation of fluid (secret). It accumulates and pathogenic microorganisms continue to multiply here. Timely treatment at this stage will allow you to cure otitis media, avoiding complications.
- Purulent. Acute purulent inflammation is characterized by increased formation of purulent masses in the middle ear cavity. They accumulate, the patient experiences pressure from the inside. The state of congestion does not go away. This phase usually lasts from several days to several hours.
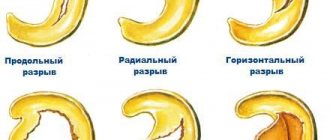
- Perforated. At this stage, accumulated pus causes a rupture of the eardrum, and purulent masses emerge from the tympanic cavity to the outside. At this moment, the patient begins to feel noticeable relief, the high temperature decreases, and the pain gradually disappears. It happens that the eardrum is unable to rupture, then the doctor manually punctures the eardrum (paracentesis) and thereby releases purulent masses out into the ear canal.
- Reparative phase - the release of pus is completed. The hole in the eardrum closes. As a rule, after proper symptomatic treatment, the patient quickly recovers.
Complications and preventive measures
As a rule, if you start treating the disease on time, treatment of acute purulent otitis, exudative or inflammation of any other kind, you can avoid any complications.
However, if treatment is not carried out and the disease progresses, the diagnosis can become chronic. The most serious consequences are: meningitis, encephalitis, brain abscess, facial neuritis, hearing loss. But these dangerous conditions can only appear when patients persistently neglect treatment for otitis media.
Preventive measures include the fight against existing foci of inflammation in the body, competent and timely treatment of ENT diseases, proper ear hygiene and, of course, strengthening the immune system.
Sofradex
These ear drops have a combined effect - they can be used for both ear and eye diseases. Sofradex drops contain two active substances: gramicidin and framycetin. These ear drops are a powerful drug; it specifically targets pathogenic bacteria that cause the disease. "Sofradex" is suitable for the treatment of otitis and ear diseases of an allergic nature. Drops for the ears and eyes reduce pain, swelling and inflammation. Thanks to Sofradex treatment, it is possible to restore the natural microflora of the ear. Contraindications include pregnancy, breastfeeding and childhood.
Sofradex
Chinoin (Sanofi-Sintelabo), Hungary
Bacterial diseases of the anterior segment of the eye.
- blepharitis; - conjunctivitis; — keratitis (without damage to the epithelium); - iridocyclitis; - sclerites, episclerites; - infected eczema of the eyelid skin; - otitis externa. from 208
5.0 1 review
719
- Like
- Write a review
Carrying out treatment
It is much easier to cure acute otitis media if treatment for the disease begins as early as possible. Treatment should be carried out under the supervision of an otolaryngologist. Complex treatment includes the following activities:
- for acute pain, taking analgesics is indicated to relieve pain;
- to bring down the temperature you need to take antipyretic drugs;
- in difficult cases, antibiotic treatment is carried out;
- local treatment consists of using special ear drops, which are prescribed individually in each case. Self-selection of drops, as well as antibacterial drugs, is fraught with dangerous consequences for health.
- Antihistamines help relieve swelling;
- a good effect is achieved during physiotherapeutic procedures;
- surgical intervention: opening of the eardrum (paracentesis) is carried out if spontaneous rupture has not occurred.
All ENT doctor’s prescriptions must be followed in full: after all, following treatment recommendations is the key to a quick recovery.
Garazon
The active ingredients of these ear drops for children are gentamicin and betamethasone. “Garazon” for otitis media acts locally and specifically “hits” the source of infection. These ear drops relieve swelling, improve capillary permeability, and are prescribed for seasonal allergies. "Garazon" for otitis media can be used in children from 8 years of age. By the way, the drug is also suitable for the treatment of eye diseases (even with the presence of pus). Relief occurs literally 20 minutes after using the drug. Many patients highly praise these ear drops because they are effective and at the same time quite affordable.
Garazon
Schering-Plough Labo NV, Belgium
Combined drug in the form of drops, used in ophthalmology and otolaryngology. The effect of the drug is due to the components included in its composition. Gentamicin is a broad-spectrum antibiotic from the group of aminoglycosides that has a bactericidal effect. Betamethasone sodium phosphate - GCS, has a local anti-inflammatory effect, suppressing cellular and fibrinous exudation and normalizing increased capillary permeability, which is manifested by a decrease in local hyperemia, edema and effusion.
118
- Like
- Write a review
What not to do during treatment
Some patients are overly self-confident and believe that a disease such as otitis media can be easily cured with the help of folk remedies and “grandmother’s” recipes. A wide variety of methods are used. This is a huge misconception!
The first mistake is that no foreign objects should be placed in the ear canal. Some are trying to use phytocandles, others, for example, geranium leaves. Such measures are fraught with the fact that leftover leaves may get stuck in the ear, which will provoke increased inflammation.
The second mistake is the use of heat and warming compresses for the purulent form of the disease. Some people replace compresses with a heating pad. At this stage of the disease, thermal heating will only increase the proliferation of bacteria.
The third mistake is trying to instill various oils or variations of alcohol into the ears. If during such treatment a perforation of the eardrum occurs, such instillations will not only cause pain, but will also cause scarring in the middle ear and eardrum.
Diagnostics
The success of treatment of labyrinthitis depends on its timely diagnosis. The doctor asks the patient about how long ago the symptoms appeared, their connection with head movements, medications taken, and concomitant diseases. Then a neurological and ENT examination, otoscopy are performed, and hearing acuity is assessed.
If necessary, additional research methods are prescribed - computer or magnetic resonance imaging of the skull.
The main task of diagnosis is to exclude a transient ischemic attack or stroke.