In the human oral cavity, on the surface of the mucous membrane there are three pairs of large salivary glands. One pair of them - the parotid - are located in front and under the auricle. These are the largest salivary glands. The second pair - the submandibular pair - is located under the lower jaw, slightly below the back teeth. The third pair - the sublingual salivary glands - are located under the mucous membrane of the floor of the oral cavity on the left and right sides of the tongue.
All three pairs of salivary glands produce a specific secretion - saliva. Saliva is produced in the body through special ducts located inside the oral cavity.
The main function of saliva in the body is to ensure normal and healthy digestion. Saliva softens hard pieces of food, preparing them to enter the stomach. It also helps a person swallow these softened food pieces.
If a person begins to experience inflammation of the salivary glands, saliva ceases to perform its main function. The process of saliva production malfunctions, and it becomes more and more difficult to swallow food.
If you experience pain, inflammation, or bleeding gums, do not wait for the symptom to go away on its own. You can muffle it with painkillers, but it is impossible to stop the inflammatory process without the intervention of a specialist! Consult your dentist. Dentistry on Shchelkovskaya Diamed is located near the Shchelkovskaya metro station. We work for you seven days a week. You can make an appointment with a dentist by calling 8 (495) 221-21-18 or filling out the online appointment form.
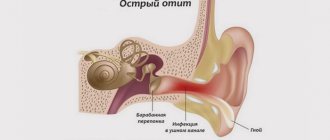
Why does inflammation of the salivary glands begin?
Inflammation of the salivary glands occurs in two types.
Epidemic sialadenitis
The causes of epidemic sialadenitis are viral diseases and infections. A common cause of inflammation of the salivary glands is mumps. The virus in this disease passes from one person to another through airborne droplets. The inflammatory process in the salivary glands occurs with a strong increase in their size.
Non-epidemic sialadenitis
Another cause of inflammation of the salivary glands is the formation of a blockage of the salivary duct. Disturbances in the functioning of the duct can occur due to severe mechanical injuries, the entry of foreign bodies into them, or the development of salivary stone disease in a person - sialolithiasis.
A very common reason for the development of inflammation of the salivary glands is irregular adherence to oral hygiene rules. Non-epidemic parotitis - this is the medical name for inflammation of the parotid salivary glands - can occur as a result of an infectious disease (pneumonia, influenza, typhus, encephalitis are at risk) or as a consequence of surgical intervention.
Symptoms of chronic sialadenitis
At the initial stage of parenchymal sialadenitis , symptoms are usually absent. The main complaints are related to a feeling of dry mouth. In the future, there may be a painful swelling in the neck, an unpleasant taste in the mouth, and nagging pain. Without treatment, the surface of the salivary gland becomes lumpy, and saliva separation is difficult.
With interstitial sialadenitis, a separate area of the inflamed gland may bother you. Complaints of hearing loss are rarely observed. With increasing inflammation, the salivary gland increases in size; upon palpation, the unevenness of its surface is felt, and the secretion of saliva is impaired.
Ductal sialadenitis affects people of advanced age or with weakened immune systems. Inflammation is accompanied by an obsessive salty taste in the mouth. When pressing on the mouth of the duct, cloudy saliva is released. The mouth of the excretory duct itself is noticeably thickened.
How sialadenitis manifests itself
The most common symptoms of inflammation of the salivary glands include:
- pain during eating, swallowing food;
- redness or swelling of the face or neck;
- disturbance of taste sensations;
- the presence of an unpleasant taste in the mouth;
- dry mouth;
- difficulty opening the mouth;
- the appearance of shortness of breath;
- general increase in body temperature.
It is worth considering that in acute sialadenitis, the symptoms subside as quickly and sharply as they appeared. But this is not a reason to forget about the problems that only recently tormented you. The fact is that the disease does not go away, but only goes into a quiet stage, which can subsequently lead to the development of chronic sialadenitis.
Sialadenitis can be accompanied by complications if treatment is not started on time or all the instructions of the attending physician are not followed. The most common complications include:
- formation of ulcers at the bottom of the oral cavity;
- abscess (purulent inflammation) of the salivary glands;
- re-infection.
Which doctor should I contact for help?
Sometimes a dentist can diagnose sialadenitis, which occurs without pronounced symptoms, when examining the oral cavity. But, in the case of a pronounced tumor, which is accompanied by pain and fever, it is worth contacting a therapist as soon as possible, who will perform an examination, prescribe the necessary diagnostics and recommend which doctor to make an appointment with. For uncomplicated inflammation, conservative treatment will be effective, including:
- taking medications (antipyretic, painkillers, and, if necessary, antibacterial or antiviral);
- compresses;
- physiotherapeutic procedures.
In some cases, consultation with a surgeon, endocrinologist or gastroenterologist may be required, depending on the complications that arise.
Consultations with a doctor online Taking care of your health is a life priority for everyone. Communicate with doctors online and receive qualified assistance without leaving your home. Try it
Note! The information on this page is provided for informational purposes only. To prescribe treatment, you must consult a doctor.
Diagnosis and treatment of inflammation of the salivary glands
How is sialadenitis diagnosed?
Sialadenitis is diagnosed by a dentist during an examination of the oral cavity or by a therapist if you go to a multidisciplinary clinic with the disease. During the examination, a significant increase in the salivary glands is usually detected, and sometimes the discharge of purulent fluid. In the case of a bacterial infection, the salivary glands become painful.
If the attending physician suspects an abscess, the patient is usually prescribed an ultrasound examination. Our Dentistry is located in the same building as the multidisciplinary clinic “Diamed” on Shchelkovskaya. You will be able to quickly receive treatment and undergo the necessary diagnostic and treatment procedures.
Tumors of the salivary glands
About 60% of all diagnosed neoplasms of the salivary glands are benign in nature. These are adenomas, adenolymphomas, papillary cystadenolymphomas and polymorphic tumors. The remaining 40% are intermediate stages (mucoepidermoid neoplasms and carcinomas), as well as sarcomas and cancers, accounting for 10-25% of cases.
To make a correct diagnosis, a complete examination is necessary, which includes, in addition to the standard set of laboratory tests, diagnostic methods such as:
- Ultrasound;
- X-ray examination;
- MRI;
- biopsy;
- histological examination.
In most cases, surgical treatment is indicated, which consists of removing the tumor node.
Disease prevention
To prevent inflammation of the salivary glands you need:
- brush your teeth regularly;
- strengthen the immune system;
- promptly treat chronic infectious diseases in the mouth (pharyngitis, stomatitis).
It is easier to treat inflammation of the salivary gland in acute form. Sialosis or chronic form of sialadenitis requires surgical intervention. In such a situation, it is important to prevent new exacerbations of the disease and its transition to severe stages.
Treatment and symptoms of sialadenitis depend on the form of the disease and the causes of its occurrence. A seemingly frivolous disease can lead to blood poisoning and death.
Location and functions of the salivary gland
In total, humans have 3 glands:
- submandibular;
- glands under the tongue;
- parotid
Every day the glands produce about 2 liters of saliva. It is necessary to prevent pathogenic microorganisms from multiplying in the oral cavity. The liquid is also involved in the process of digesting food and breaks down complex carbohydrates.
The glands located near the ears are responsible for internal secretion. The released liquid performs several important functions:
- increases the resistance of mucous membranes to infections and viruses;
- enhances the perception of taste;
- accelerates the digestion process and facilitates the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract;
- promotes normal articulation.
Saliva contains about 60 types of enzymes, proteins, mucin, and amylase. Another important component in the liquid is phosphatase. It is involved in the mineralization of teeth and bone structures
To maintain the microflora of the oral cavity, not only the qualitative, but also the quantitative factor of saliva is important. With insufficient fluid production in the mucous membranes, an inflammatory process develops and dental diseases occur (caries, periodontitis, etc.). An equally serious consequence of sialadenitis is demineralization of the enamel. Too active fluid production is also dangerous for the body, as it provokes dehydration.
There are small glands in the oral cavity. They are localized in the cheeks, hard and soft palate, tongue and lips.
Treatment depending on the form of the disease
When drawing up a treatment regimen, the nature of the pathology must be taken into account. Acute sialadenitis is treated on an outpatient basis, following all the doctor’s recommendations. Viral forms of the disease are useless to treat with antibacterial drugs. The acute form of viral sialadenitis is eliminated with the help of immunomodulators and drugs with Interferon. Additionally, medications are used to alleviate the symptoms of the problem: anti-inflammatory, wound-healing, antipyretic. To reduce the concentration of viral pathogens in the body, plenty of warm fluids are required.
Acute bacterial sialadenitis requires adherence to a salivary diet and the use of antibacterial drugs. This type of illness is treated in a hospital. The drugs are administered to the patient into the affected gland 2 times a day. For home treatment, antibiotics are used in capsules or injection solutions. The oral cavity is rinsed with a warm solution of Dioxidin.
Acute forms of sialadenitis in a child are treated with compresses on the affected area. The procedure is performed once a day for 30 minutes
Of the physiotherapy procedures used to treat calculous sialadenitis, UHF is noted. For difficulty eating and severe swelling, blockades with Novocaine and Penicillin are used. To prevent the formation of adhesions during inflammation of the salivary gland, intravenous injections of Contrical or Trasylol are prescribed.
Chronic forms of the disease are treated in almost the same way as acute ones. In this case, it is important to maintain active saliva formation to prevent the occurrence of purulent plugs.
For chronic disease, treatment includes:
- massage the affected area with the introduction of antibacterial agents;
- novocaine blockades;
- electrophoresis with Galantamine;
- galvanization;
- course intake of potassium iodide;
- periodic injection of Iodipol into the gland (once every 3 months).
Iontophoresis is a modern physiotherapeutic procedure to combat inflammation of the salivary glands.
Folk remedies
Drug treatment of sialadenitis is supported by home treatment. To do this, they use natural ingredients, the effectiveness of which has been tested by generations of people. You can make compresses, decoctions, etc. from natural ingredients. The main goal of this method of therapy is to alleviate the symptoms of the disease and increase the body's resistance.
Therapeutic compresses
A compress made from homemade cottage cheese is effective. The milk product is evenly distributed over a gauze bandage and applied to the problem area for 1 hour. The procedure is performed once a day, replacing the old cottage cheese with a new one.
A decoction of celandine works well for signs of inflammation of the parotid salivary gland: 3 tbsp. l. vegetable raw materials are poured with 300 ml of water and simmered for 15 minutes over low heat. A cotton pad is moistened in the decoction and applied to the lesion. Instead of celandine, you can use other plants: hemlock, calendula.
A good addition to therapeutic compresses is daily consumption of carrot juice. The product promotes the healing of affected areas of the submandibular gland. It is recommended to drink at least 200 ml of the product per day
Herbal infusions
Medicines increase the secretion of saliva and contribute to the death of pathogenic microorganisms in the oral cavity. You can treat sialadenitis:
- chamomile – has an anti-inflammatory effect and relieves swelling;
- mint – activates the salivary gland and eliminates bad breath;
- raspberry leaves – have a regenerating effect.
Before using each of the listed remedies, it is recommended to consult a specialist, especially if multicomponent medications are used for therapy. The means that help one person are not always effective for another. In addition, the treatment of sialadenitis in children and adults requires a different approach.
Treatment
Sialadenitis rarely affects the patient's life expectancy, but untimely treatment leads to a decrease in its quality. It is easier to deal with the problem in the acute stage. Treatment of inflammation of the salivary gland includes taking medications: anti-inflammatory, painkillers, enhancing salivary secretion, etc. Drug treatment is supported by physiotherapeutic procedures: UHF radiation, alcohol-camphor compresses. You can learn more about the treatment of each type of disease from this article.
During treatment, the patient must follow certain requirements: stop smoking and drinking alcohol; eat fresh fruits and vegetables; consume foods that increase saliva production (a slice of lemon, sauerkraut).
Only complicated forms of sialadenitis require surgical intervention. After surgery, patients require oral cleansing with antibiotics. This helps prevent secondary infection of the salivary glands.
The patient may be offered another treatment method if physiotherapy and conservative treatment are unsuccessful. Such procedures include galvanization of clogged ducts and removal of the salivary gland.
The photo shows the galvanization procedure