ATTENTION! From December 2021, a new medical center will open for you at the address: Dmitrovskoye Shosse, 81 (5 min. walk from Selegerskaya metro station), where you can receive a wide range of medical services, including CT (computer tomography).
- home
- Urology Clinic
- Treatment of orchiepididymitis
Orchiepididymitis is an inflammation of the testicle and its epididymis. The disease can develop with inflammatory diseases of the genitourinary system - urethritis, prostatitis, vesiculitis, epididymitis, or after testicular trauma. The disease is an infectious disease of the male genital area and poses a serious danger to a man’s intimate health. The inflammatory process that occurs in the testicle, in an advanced state, passes to its appendage. This condition causes discomfort, pain, and also causes complications. Medical urologists treat orchiepididymitis.
Treatment: how it goes
Treatment of orchiepididymitis must begin at the first symptoms, so the prognosis for a quick and complete cure is most favorable. Treatment takes place in a hospital setting and the doctor monitors the healing process on a daily basis. The man is prescribed bed rest and wearing special underwear that will pull the affected testicle up.
Conservative method
After testing and identifying the pathogen, the doctor will prescribe an antibiotic that will eliminate the infection. At the same time, cold compresses should be applied to the sore testicle, which will eliminate discomfort and help relieve swelling. When treatment for acute epididymitis orchioepididymitis is completed, the patient will begin to attend physical procedures (magnet, ultrasound, electro and laser therapy) to restore the ability of the testicle to function normally.
Surgical method
Particularly complex conditions require surgical treatment of orchiepididymitis. It is necessary to act radically in cases where complications have developed - blockage of the vas deferens, abscess in the scrotum, fistulas, testicular infarction, infertility, oncological process.
Urologists
Erkov Igor Viktorovich Urologist andrologist
Cost of admission 2500
₽
Make an appointment
Fomenko Alexander Pavlovich Urologist andrologist
Cost of admission 2500
₽
Make an appointment
Symptoms
There are three forms of the disease:
- Spicy.
- Chronic.
- Abscessive type of flow.
Acute orchiepididymitis on both the left and right appears immediately after the onset of the disease: severe pain appears even in places where it should not be. Swelling and increase in size of the scrotum are accompanied by pain, which can be felt even in the lower back. Acute orchiepididymitis on the right is diagnosed less often than on the left, this is due to the anatomy of the male external genitalia.
The acute form of epididymitis orchiepididymitis is distinguished by specific symptoms:
- Severe pain in the groin that is impossible to cope with on your own.
Pain in the scrotum when touched, which radiates to the perineum or groin area, swelling, redness, shine of the skin. The doctor diagnoses hardening of testicular tissue. The patient's body temperature rises to 39 degrees.
Chronic form:
- Periodic appearance of symptoms. It is this form of orchiepididymitis that causes the development of oncology and infertility, since treatment begins at the wrong time and time is lost.
Symptoms of chronic orchiepididymitis: constant or recurrent pain in the testicle, which may worsen during sports. Body temperature can rise to 40 degrees.
The tuberculosis bacillus, which also provokes the development of the disease, can cause fistulas. This condition, if left untreated, quickly turns into an abscessive form, when pus and an unpleasant odor appear. This form is extremely dangerous for a man’s health; it can cause infertility, testicular infarction, and a tumor process. Already on the second day of this course of the disease, complications begin to develop.
Treatment of inflammation of the testicle and its epididymis (orchitis and epididymitis) in Voronezh
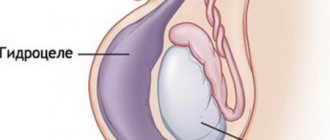
The testicles are a paired organ located in the scrotum. Its main functions: the production of testosterone (through which a man’s sexual and social ambitions are realized) and sperm (through which the transfer of male genetic material is realized). Therefore, often complications or consequences of orchitis (inflammation of the testicle) are impotence and infertility. The appendage is an organ in the form of a dense cord adjacent to the side of the testicle. Sperm maturation occurs in this organ. Therefore, complications or consequences of epididymitis (inflammation of the appendage) are often infertility. As a rule, orchitis and epididymitis occur and develop together (inflammation easily spreads from the testicle to the epididymis and vice versa). Therefore, the diagnosis and treatment of these diseases are no different from each other, and will be discussed further in the article in one block.
Causes of orchitis and epididymitis:
1. Infection . The testicle is an organ isolated from the environment. Therefore, when inflammation appears in it (and the cause of inflammation is usually an infection), the question naturally arises: where did it come from? The prostate is often the source of infection. When there is inflammation in it (prostatitis), the infection travels down the vas deferens into the testicle. However, the immunity in the testicle destroys the normal microflora without problems. There are microorganisms - chlamydia, ureaplasma, trichomonas and gonorrhea, which “break through” the immune system and cause inflammation. Diagnosis of prostatitis and STDs is a key point in identifying the causes of inflammation of the testicle and its epididymis.
2. Hypothermia . With prolonged low temperatures or sudden changes in temperature, immunity in the testicles decreases to a critical level. An infection that gets into the testicle (even a normally non-pathogenic microflora), due to the same prostatitis, receives excellent conditions for reproduction and causes inflammation. Identifying hypothermia in the patient's history is extremely important for correct diagnosis.
3. Trauma . Athletes, participants in road accidents and simply people who have received a domestic injury to the testicles are at risk of developing orchitis and epididymitis. During injury, the so-called blood-testis barrier (the barrier between blood plasma and testicular tissue) is destroyed. As a result, the body begins to produce antibodies (killer cells) to the testicular tissue - a severe, autoimmune form of orchitis develops, often leading to infertility.
There are acute (disease duration no more than 2 months) and chronic (disease duration more than 2 months) orchitis and epididymitis.
Symptoms (signs) of acute orchitis and epididymitis
1. Severe pain in the testicle or scrotum, preventing even walking 2. Increased (over 37°) temperature 3. General intoxication: weakness, malaise, loss of appetite, sweating, chills 4. On examination - the testicle is sharply enlarged in size, purple-cyanotic colors, painful to the touch
Symptoms (signs) of chronic orchitis and epididymitis
1. Periodic, dull aching pain in the testicle or scrotum, intensifying after sex or physical activity. 2. Upon examination, the testicle and epididymis are compacted, lumpy, the epididymis is fused to the testicle
Possible complications (consequences) of orchitis and epididymitis
1. Transition of inflammation to the purulent stage with the development of a testicular abscess . The time factor plays a key role here. If acute orchitis lasts more than 3 days, the likelihood of developing purulent melting of the testicle increases sharply. There is only one treatment at this stage - surgery (decompression of the testicle or its resection, up to complete amputation in severe cases).
2. Chronic inflammation . As a rule, this is facilitated by patient self-medication. Taking the wrong antibiotics, in the wrong doses and for the wrong duration, leads to the elimination of the symptoms of the disease and creates a false sense of complete recovery in the patient. However, orchitis remains and turns into a chronic, relapsing form, in which periods of exacerbation (obvious symptoms) are followed by periods of remission (calm).
3. Impotence . Often a consequence of chronic orchitis. Decreased testosterone production caused by chronic inflammation of the testicle underlies severe, endocrine, form of impotence. This form of erectile dysfunction is quite difficult to treat.
4. Infertility . Occurs in 30-40% of patients who have suffered acute orchitis and epididymitis and in 50-70% of those with chronic epididymitis. The reason is both a decrease in the production of sperm that is normal in quantity and quality, and a disruption in the transportation of sperm along the vas deferens to the urethra, due to the formation of adhesions. Treatment is lengthy and extremely costly, both in time and finances.
Treatment of orchitis and epididymitis with folk remedies and at home
It is absolutely ineffective and extremely dangerous due to the high probability of developing a purulent stage of orchitis or its chronicity (loss of time and development of resistance to antibiotics in microorganisms). The testicles are a vital organ for a man, and experiments with self-medication can have very detrimental consequences, both for potency and his reproductive function.
How do I treat orchitis and epididymitis?
1. Treatment of acute orchitis and epididymitis.
If the first symptoms are detected, an urgent consultation with a urologist is necessary!
A big role here is played by the timeliness of the diagnosis and differentiation of the situation when the process has already entered the purulent stage and surgery is required. Narrow-spectrum antibiotics with tropism (directionality) to testicular tissue are prescribed. This gives a quick and pronounced effect. As a rule, a clinical response (a sharp improvement in the patient’s well-being) occurs on the 3rd day. Subsequently, medications are prescribed to help completely relieve inflammation and restore testicular function.
2. Treatment of chronic orchitis and epididymitis
After establishing a diagnosis and identifying the causes supporting the chronic inflammatory process (STDs, adhesions, etc.), a course of treatment is prescribed. Several courses lasting 2-3 weeks are conducted at intervals of 3 months. This scheme allows the testicular tissue to regenerate as much as possible and restore lost function. The course includes drugs that improve microcirculation, testoprotectors (drugs that improve testicular regeneration) and absorbable medications. In addition, to enhance the effect, physiotherapy is prescribed: laser, magnet, ultrasound. In most cases, depending on the stage of the disease, within 6-12 months. there is a pronounced clinical improvement.
Cost of treatment
Examination and treatment are carried out according to medical standards
1. Acute orchiepididymitis
• Initial appointment (gathering complaints, medical history, clinical examination, making a preliminary diagnosis, prescribing an examination program) - 1000 rubles. • Basic examination (UAC, OAM, ultrasound of the scrotum, examination for STDs) - 3,500 rubles. • Repeated appointment (analysis of examination results, making a final diagnosis, prescribing a treatment regimen) – 600 rubles. • Treatment: Medicines - antibiotics (injectable forms) and anti-inflammatory drugs - on average 3,000 rubles per course. After eliminating the main inflammation for 3 months. restorative therapy - 1500-2000 rubles/month. (drugs that stimulate regeneration). If necessary, a course of physiotherapy is carried out. • Cont. tests (OAC, OAM, ultrasound of the scrotum) after 3 months. – 1000 rub.
2. Chronic orchiepididymitis
• Initial appointment (gathering complaints, medical history, clinical examination, making a preliminary diagnosis, prescribing an examination program) - 1000 rubles. • Basic examination (CBC, OAM, ultrasound of the scrotum, TRUS, total testosterone, spermogram, PCR for STDs) - 5,000 rubles. • Repeated appointment (analysis of examination results, making a final diagnosis, prescribing a treatment regimen) – 600 rubles. • Treatment: For 1 course (2-3 weeks) - medications (very average) - 2000 rubles. + physiotherapy – 1000 rub.\ session 10 sessions. From 1 to 3 courses are carried out depending on the speed of regeneration and the degree of functional restoration in a particular patient. • Cont. tests (OAC, OAM, ultrasound of the scrotum) at the end of each course - 1000 rubles.
When to see a doctor
A 19-year-old man complained of acute severe pain in the right testicle, weakness, malaise and fever up to 38°. Sick for 7 days after swimming in the ice hole for baptism. On examination, the right testicle is sharply painful to the touch, the skin of the scrotum is bluish-purple in color. Ultrasound of the scrotum shows diffuse inflammation of the right testicle with transition to the right appendage and the formation of a focus of purulent melting (abscess). Due to the fact that time was lost, the patient was urgently hospitalized in the on-duty urology department, where he underwent surgery (testicular decompression). Thanks to the professionalism of my colleagues, the testicle was saved. After discharge from the hospital, the condition lasted for 6 months. course of rehabilitation treatment with a diagnosis of chronic orchiepididymitis. After 6 months The examination results were for the most part normal. PS after recovery, the patient promised not to swim in bodies of water for baptism anymore
Recommendations of urologists and prevention
Experts urge men not to ignore the symptoms of acute orchiepididymitis, not to treat themselves, and not to endure pain and discharge from the genitourinary canal. You should immediately consult a doctor for medical help, because the sooner treatment for epididymitis orchioepididymitis is started, the greater the chances of a successful recovery. If treatment is started on time, the recovery period will take several days.
Prevention measures
You can prevent the development of the disease by following your doctor's recommendations. Sexually transmitted infections are the cause of the development of epididymitis orchioepididymitis in men. Using a condom during sexual intercourse will reduce the risk of infection. And injuries to the external genitalia can provoke the development of infection, in which case you should definitely visit a doctor for diagnostics. Also, the testicles need to avoid hypothermia, wear underwear made of natural fabrics, and treat genitourinary diseases in a timely manner so that there are no complications in the future.
Causes of development of orchiepididymitis
The cause of orchiepididymitis, like any other inflammatory process, is infection by microbes. Usually these are Trichomonas, causative agents of chlamydia and other STIs. They enter the testicle from the urethra or prostate through the bloodstream or through the vas deferens.
In other cases, the source of microbes is inflammation of the urethra, injury to the testicles.
The development of this pathology is promoted by blood stagnation in the pelvis, hypovitaminosis, perineal trauma, and prostate surgery (occasionally).
Contraindications
You cannot have sex during the course of the disease, as well as during its treatment. This can cause infection of the partner and also lead to complications.
Also, you should not visit the sauna, go to the pool, avoid physical activity and swim in a pond in order to prevent the disease from getting worse and to prevent excessive infection activity.
Only after comprehensive and complete treatment of orchiepididymitis can you return to your normal lifestyle.
Diagnosis of orchiepididymitis
The presence of pronounced and characteristic symptoms allows you to confidently make a diagnosis directly during a medical examination. It is extremely easy to distinguish inflammation of the testicle and its epididymis from any other pathology - by typical and clear signs.
But additional research is still needed. They help to clarify the type of microorganism that caused the inflammation, correctly stage the process (determine the stage), and choose the appropriate treatment. An ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs and kidneys located in the retroperitoneal space is prescribed. For laboratory tests, patients donate blood and urine - they perform general clinical blood and urine tests, a blood test for the immunodeficiency virus, for antibodies to parenteral hepatitis, and a blood test for syphilis.
Urethroscopy and microscopic analysis of prostate discharge, as well as analysis of a smear of the contents of the urethra, help to establish the exact cause of the pathology. They also do bacterial culture: they isolate opportunistic microflora, determine its sensitivity to antibiotics, perform a PSA (prostate-specific antigen) test, and carry out PCR diagnostics.