Quick transition Treatment of acute external otitis
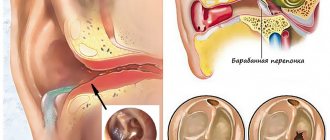
Acute otitis externa is an inflammatory disease of the external auditory canal.
Acute external otitis can be caused by infectious, allergic and dermatological diseases, but its most common cause is an acute bacterial infection.
Acute external otitis can occur at any age, but the peak of the disease occurs in childhood and adolescence (5-14 years).
The incidence is more common in the summer and is apparently associated with increased environmental humidity, heat and swimming.
Sulfur is one of the main protective mechanisms that prevent the development of acute external otitis (AEO)
When it decreases, the environment in the external auditory canal (EA) becomes alkaline instead of acidic, moisture accumulates in the ear and, as a result, the ear canal becomes an ideal breeding ground for microorganisms, which leads to an inflammatory process.
How to treat otitis in adults and children.
July 2, 2021
4134
5
2
Content
- Why does ear pain occur?
- Causes of otitis media
- How can you get infected with otitis media?
- Symptoms of otitis media
- What types of otitis are there?
- How to treat otitis
- The most popular ear drops for adults
- Sofradex
- Otinum
- Normax
- Otirelax
- Tsipromed
- The most popular ear drops for children
- Otipax
- Polydexa
- Garazon
- Otofa
- Anauran
As soon as our ear starts to hurt, we think about ear drops. And it’s good if they are in your home medicine cabinet. But you need to understand that all ear drops have different therapeutic properties. Some help cope with ear congestion, others relieve severe pain. Therefore, it is very important not to self-medicate, but to immediately visit an ENT doctor if discomfort occurs to determine the cause of ear pain.
Why does ear pain occur?
There are different types of ear pain, so you need to learn to determine which conditions require urgent help and which ones you can handle on your own. You can treat your ear yourself, for example, if you have slight discomfort after a long walk or you took a swim in a pond (perhaps water got into your ear). If the symptoms do not go away or even worsen, do not delay visiting a doctor. The ear can also hurt when a lot of wax is released (or, conversely, not enough). But most often the ear hurts due to otitis, sinusitis, caries, sore throat or eczema. Ear pain can also be caused by injury.
Otitis
is a serious inflammation of the ear tissues, which causes acute pain and decreased hearing. Otitis often affects children under three years of age due to the anatomical features of the ear structure.
Indications for use
- Inflammation of the middle and inner ear in children is treated with antibiotics in extreme cases, namely:
- Otitis media develops in a child under two years of age.
- The temperature remains stable above 38°C.
- Acute pain in the ear.
- Constant headache.
If the general condition is normal, then otolaryngologists are in no hurry to prescribe antibiotics to young patients.
Treatment of adults with antibiotics is carried out in the presence of fluid in the ear cavity, prolonged course of otitis and the risk of complications.
Symptoms of otitis media
The very first symptom of otitis media is tinnitus. The following symptoms then appear:
- pain of varying intensity;
- temperature increase;
- general weakness;
- hearing impairment;
- discharge from the ears.
IMPORTANT!
If you or your child have noise and congestion in the ears, urgently go to an otolaryngologist - he will determine the cause and prescribe adequate treatment.
Read also: Top 7 effective remedies for a runny nose The best nasal drops and sprays that quickly and effectively help cure a runny nose.
Complications of IT
- Periauricular cellulitis is manifested by hyperemia, edema, and local hyperthermia of the skin around the auricle. Pain is usually mild and systemic symptoms are usually absent, which helps distinguish cellulitis from malignant otitis externa.
- Malignant otitis externa (necrotizing) is a severe, potentially fatal complication of bacterial Otitis. It is most common in older patients with diabetes or people with weakened immune systems. In this case, the infection spreads to the base of the skull and surrounding soft tissue. There is severe otalgia and discharge from the ear. In the NSP - granulation, edema, erythema, necrosis (death) of the NSP.
What types of otitis are there?
There are several types of otitis:
- Eustachite.
Air exchange in the ear cavity is disrupted, and fluid accumulates there. Which becomes a breeding ground for pathogenic microbes. - Otitis media of exudative type.
Fluid accumulates in the ear cavity, which causes unpleasant symptoms in the patient. Typically, such otitis develops against the background of ARVI, which weakens the immune system. - Acute purulent otitis media.
The ear cavity fills with pus. The inner ear is affected, so serious consequences are possible.
Sofradex
These ear drops have a combined effect - they can be used for both ear and eye diseases. Sofradex drops contain two active substances: gramicidin and framycetin. These ear drops are a powerful drug; it specifically targets pathogenic bacteria that cause the disease. "Sofradex" is suitable for the treatment of otitis and ear diseases of an allergic nature. Drops for the ears and eyes reduce pain, swelling and inflammation. Thanks to Sofradex treatment, it is possible to restore the natural microflora of the ear. Contraindications include pregnancy, breastfeeding and childhood.
Sofradex
Chinoin (Sanofi-Sintelabo), Hungary
Bacterial diseases of the anterior segment of the eye.
- blepharitis; - conjunctivitis; — keratitis (without damage to the epithelium); - iridocyclitis; - sclerites, episclerites; - infected eczema of the eyelid skin; - otitis externa. from 208
5.0 1 review
719
- Like
- Write a review
Otinum
These ear drops are relatively inexpensive and have good anti-inflammatory effects. The active ingredient of Otinuma is choline salicylate. Doctors prescribe Otinum for otitis of the external and middle ear, including fungal infections. Ear drops perfectly relieve pain literally a few minutes after use. Contraindications include damage to the eardrum and childhood. And so the drug is well tolerated, extremely rarely causing allergic reactions. For otitis media, after about seven days of using Otinum ear drops, complete recovery occurs.
Otinum
Polfa, Poland
Acute otitis media, myringitis, otitis externa;
before washing the external auditory canal to soften hardened earwax before the procedure for its removal. from 177
5.0 1 review
538
- Like
- Write a review
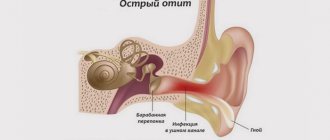
Acute otitis media
According to statistics, acute forms of otitis media account for 30% of the total number of ENT diseases. Most often it occurs in preschool children.
Symptoms of acute otitis media
The disease is characterized by an acute onset with the appearance of the following symptoms:
- earache;
- ear congestion or hearing loss;
- increased body temperature;
- anxiety;
- disturbance of appetite, sleep;
- headache and toothache.
Causes of development of acute otitis media
In most cases, the disease can be caused by various pathogenic microorganisms - viruses, microbes, fungi, etc. In exudate obtained from the middle ear, respiratory viruses are found in 30-50% of cases. The most common causes of otitis are parainfluenza viruses , influenza viruses, rhinoviruses, adenoviruses, enteroviruses, respiratory syncytial viruses, etc.
In 50-70% of patients with acute otitis media, bacteria are detected in the exudate from the middle ear (most often Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae, Moraxella catarrhalis).
Often the cause of otitis is a mixed (viral-bacterial) infection.
When making a diagnosis, a differential diagnosis is made with myringitis (inflammation of the eardrum) and exudative otitis media.
The occurrence of otitis media is directly related to the condition of the nose and nasopharynx: rhinitis and tonsillitis often provoke inflammation of the middle ear.
Otitis often occurs against the background of decreased immunity and immunodeficiency states.
1 Diagnosis of otitis in MedicCity
2 Diagnosis of otitis in MedicCity
3 Diagnosis of otitis in MedicCity
Routes of infection
The most common route of infection into the middle ear is through the auditory tube during rhinitis and sinusitis.
It is possible that infection can penetrate through the blood during influenza, scarlet fever and other infectious diseases.
In rare cases, the infection enters the middle ear through the ear canal due to injury (rupture) of the eardrum.
Stages of acute otitis
There are 5 stages of the disease:
- stage of acute eustachitis: feeling of congestion, noise in the ear, normal body temperature (if there is an infection, it may increase);
- stage of acute catarrhal inflammation in the middle ear: sharp pain in the ear, low-grade fever, inflammation of the mucous membrane of the middle ear, increasing noise and congestion in the ear;
- pre-perforative stage of acute purulent inflammation in the middle ear: sharp unbearable pain in the ear, which radiates to the eye, teeth, neck, pharynx, increased noise in the ear and decreased hearing, increased body temperature to 38-39 degrees, the blood picture becomes inflammatory in nature;
- post-perforation stage of acute purulent inflammation in the middle ear: pain in the ear becomes weaker, suppuration appears from the ear, noise in the ear and hearing loss do not go away, body temperature becomes normal;
- reparative stage : inflammation is stopped, perforation is closed with a scar.
Normax
"Normax" for otitis - drops of complex action against many microbes. The drug is intended exclusively for adults. "Normax" is indicated for infections not only of the ears, but also of the eyes. Thanks to the antibiotic in the composition, it effectively treats diseases such as conjunctivitis, blepharitis, otitis media, eustachitis, and keratitis. Patients note that Normax ear drops are affordable, well tolerated, and quickly relieve the problem. But many people talk about allergic reactions to this drug (then it is better to choose a weaker remedy for otitis media). Normax relieves pain well and is popular among patients.
Normax
Ipca Laboratories, India
Treatment of acute and chronic infectious and inflammatory diseases caused by microorganisms sensitive to the drug: - conjunctivitis (including gonococcal);
- keratitis; - keratoconjunctivitis; - corneal ulcer; - blepharitis; - blepharoconjunctivitis; - trachoma; - otitis externa; - acute and chronic otitis media; - internal otitis media; - infectious eustachitis. Prevention of eye infections after removal of a foreign body from the cornea or conjunctiva, after damage by chemical or physical means, before and after surgery. Prevention of infectious otitis before and after surgery, with ear injuries, removal of a foreign body from the external auditory canal, accompanied by damage to ear tissue from 125
385
- Like
- Write a review
Treatment of otitis media
Otitis is an inflammation of the ear, a general term for any infectious processes in the organ of hearing. Depending on the affected part of the ear, there are
- outer,
- average
- internal otitis (labyrinthitis).
Otitis is common. Ten percent of the world's population will suffer from otitis externa during their lifetime. Every year, 709 million new cases of acute otitis media are registered worldwide. More than half of these episodes occur in children under 5 years of age, but adults also suffer from otitis media. Labyrinthitis, as a rule, is a complication of otitis media and occurs relatively rarely.
Otitis externa is an inflammation of the ear canal. It can be diffuse, or it can occur in the form of a boil. With diffuse external otitis, the skin of the entire ear canal is affected. A boil is a localized inflammation of the skin of the outer ear.
Otitis media
With otitis media, the inflammatory process occurs in the tympanic cavity. There are many forms and variants of the course of this disease. It can be catarrhal and purulent, perforated and non-perforated, acute and chronic.
With otitis media, complications can develop. The most common complications of otitis media include mastoiditis (inflammation of the behind-the-ear part of the temporal bone), meningitis (inflammation of the membranes of the brain), brain abscess (abscess), labyrinthitis.
Labyrinthitis
Internal otitis is almost never an independent disease. It is almost always a complication of inflammation of the middle ear. Unlike other types of otitis, its main symptom is not pain, but hearing loss and dizziness.
Causes of otitis media
- After contact with contaminated water - most often, otitis externa occurs after water containing the causative agent gets into the ear. That is why the second name of this disease is “swimmer’s ear.” Trauma to the skin of the external auditory canal - in addition to the presence of infection in the water, there must also be local conditions that predispose to the development of inflammation: microcracks in the skin, etc. Otherwise, our every contact with unboiled water would end in the development of inflammation in the ear.
- A complication of ARVI, sinusitis - in this case, the causative agent of otitis media penetrates into the tympanic cavity from a completely different direction, the so-called rhinotubal route, that is, through the auditory tube. Usually the infection enters the ear from the nose when a person is sick with ARVI, runny nose or sinusitis. With severe inflammation of the middle ear, the infection can spread to the inner ear.
- In case of infectious diseases, kidney diseases, diabetes mellitus, hypothermia against the background of reduced immunity, the risk of developing inflammation in the middle ear increases. Blowing the nose through 2 nostrils (incorrectly), coughing and sneezing increase the pressure in the nasopharynx, which leads to infected mucus entering the middle ear cavity.
- Mechanical removal of earwax - it is a protective barrier against infections.
- High air temperature and high humidity.
- Foreign objects entering the ear.
- Use of hearing aids.
- Diseases such as seborrheic dermatitis on the face, eczema, psoriasis.
- The causes of the development of acute otitis media are also genetic disposition, immunodeficiency states, and HIV infection.
Symptoms of otitis media.
Pain is the main symptom of otitis media. The intensity of the pain can vary: from barely perceptible to unbearable - pulsating, shooting. It is very difficult, and most often impossible, to independently distinguish the pain caused by otitis externa from the pain caused by inflammation of the middle ear. The only clue may be the fact that with otitis externa, pain should be felt when touching the skin at the entrance to the ear canal. Hearing loss is a variable symptom. It may be present in both otitis externa and otitis media, and may be absent in both of these forms of ear inflammation.
Increased temperature - most often there is an increase in body temperature, however, this is also an optional sign.
Discharge from the ear with external otitis almost always occurs. After all, nothing prevents the inflammatory fluid from being released. With otitis media, if there is no perforation (hole) in the eardrum, there is no discharge from the ear. Suppuration from the ear canal begins after a communication appears between the middle ear and the ear canal. I would like to emphasize that perforation may not form even with purulent otitis media. Patients suffering from otitis media often ask, where will the pus go if it does not break out? It's very simple - it will come out through the auditory tube.
Ear noise and ear congestion are possible with any form of the disease. As inflammation of the inner ear develops, dizziness may occur.
Acute otitis media occurs in 3 stages:
- Acute catarrhal otitis - the patient experiences severe pain, intensifying at night, when coughing, sneezing, it can radiate to the temple, teeth, be stabbing, pulsating, boring, hearing and appetite decrease, weakness and high temperature up to 39C appear.
- Acute purulent otitis - there is an accumulation of pus in the middle ear cavity, followed by perforation and suppuration, which can occur on the 2-3rd day of illness. During this period, the temperature drops, the pain decreases, the doctor can perform a small puncture (paracentesis) if the eardrum has not ruptured on its own.
- Recovery stage - suppuration stops, the defect of the eardrum closes (fusion of the edges), hearing is restored within 2-3 weeks Treatment of external otitis
The main treatment for otitis externa in adults is ear drops.
If a person does not have an immunodeficiency (HIV infection, diabetes), antibiotic tablets are usually not needed. Ear drops can contain only an antibacterial drug or be combined - contain an antibiotic and an anti-inflammatory substance. The course of treatment takes 5-7 days. In addition to ear drops, for the treatment of external otitis, the doctor may recommend an ointment with the active ingredient Mupirocin (Bactroban). It is important that the drug does not have a negative effect on the normal microflora of the skin, and there is evidence of the activity of mupirocin against fungi.
Treatment of otitis media and labyrinthitis in adults
Antibacterial therapy
The main treatment for otitis media is an antibiotic. However, treatment of otitis media with antibiotics in adults is another controversial issue in modern medicine. The fact is that with this disease the percentage of spontaneous recovery is very high - more than 90%. There was a period of time at the end of the 20th century when, in a wave of enthusiasm, antibiotics were prescribed to almost all patients with otitis media. However, it is now considered acceptable to do without antibiotics for the first two days after the onset of pain. If after two days there is no tendency to improve, then an antibacterial drug is prescribed. All types of otitis media may require oral pain medications. In this case, of course, the patient must be under medical supervision. The decision about the need for antibiotics is a very important one and should only be made by a doctor. On the one hand, the scales weigh the possible side effects of antibiotic therapy, on the other, the fact that every year 28 thousand people die from complications of otitis media in the world.
The main antibiotics that are used in the treatment of otitis media in adults: Amoxicillin - Ospamox, Flemoxin, Amosin, Ecobol, Flemoxin solutab Aamoxicillin with clavulanic acid - Augmentin, Flemoklav, Ecoclave Cefuroxime - Zinnat, Aksetin, Zinacef, Cefurus and other drugs. The course of antibiotic therapy should be 7-10 days.
Ear drops
Ear drops are also widely prescribed for inflammation of the middle ear. It is important to remember that there is a fundamental difference between drops that are prescribed before perforation of the eardrum and after it appears. Let me remind you that a sign of perforation is the appearance of suppuration. Before perforation occurs, drops with an analgesic effect are prescribed. After the perforation appears, the pain goes away and you can no longer drip pain-relieving drops, as they can harm the sensitive cells of the cochlea. If perforation occurs, there is access for drops inside the middle ear, so drops containing an antibiotic can be instilled. However, ototoxic antibiotics (gentamicin, framycetin, neomycin, polymyxin B), drugs containing phenazone, alcohols or choline salicylate should not be used. Antibiotic drops, the use of which is acceptable in the treatment of otitis in adults: “Tsipropharm”, “Normax”, “Otofa”, “Miramistin” and others.
Paracentesis or tympanotomy
In some situations, inflammation of the middle ear may require minor surgical intervention - paracentesis (or tympanotomy) of the eardrum. It is believed that the need for paracentesis arises if, despite antibiotic therapy for three days, the pain still continues to bother the person.
Paracentesis is performed under local anesthesia: a small incision is made in the eardrum with a special needle, through which pus begins to emerge. This incision heals well after the suppuration stops.
Treatment of labyrinthitis is a complex medical problem and is carried out in a hospital under the supervision of an ENT doctor and a neurologist. In addition to antibacterial therapy, agents are needed that improve microcirculation inside the cochlea and neuroprotective drugs (protecting nervous tissue from damage).
Prevention of otitis
Preventive measures for otitis externa include thoroughly drying the ear canal after bathing. You should also avoid traumatizing the ear canal - do not use keys and pins as ear instruments. For people who often suffer from inflammation of the outer ear, there are drops based on olive oil that provide skin protection when swimming in a pond, for example, Vaxol.
Prevention of otitis media consists of general strengthening measures - hardening, vitamin therapy, taking immunomodulators (drugs that improve immunity). It is also important to promptly treat nasal diseases, which are the main causative factor of middle ear inflammation.
Otirelax
The active ingredients of these combined action ear drops are phenazone and lidocaine. Otirelax relieves inflammation and relieves pain. ENT doctors prescribe these ear drops for bacterial and viral infections. The drug is easy to use thanks to a bottle with a dropper. "Otirelax" is prescribed for otitis media externa, as well as inflammation after ear injuries. As for pregnancy and breastfeeding, the decision to prescribe Otirelax is made by the attending physician.
Otirelax
Rompharm, Romania
For local symptomatic treatment and pain relief in adults and children (including newborns) for: otitis externa;
in complex therapy of otitis media with an intact eardrum; barotraumatic otitis. from 174
373
- Like
- Write a review
Tsipromed
"Tsipromed" is considered the best inexpensive antibiotic drops for otitis media. These are strong ear drops that destroy not only active bacteria, but also “dormant” ones. Tsipromed is prescribed exclusively to adults. These ear drops very rarely cause allergic reactions, so they are often prescribed for many ear and eye diseases. Many patients respond well to Tsipromed drops, because the product treats otitis media well and saves if water gets into the ear.
Tsipromed
Promed Exports, India
A synthetic broad-spectrum antibacterial drug from the group of second-generation fluoroquinolones for the treatment of acute external otitis, otitis media caused by sensitive strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa or Staphylococcus aureus.
from 91
344
- Like
- Write a review
Treatment of acute external otitis
To reduce pain, including before being examined by a doctor, it is recommended to use systemic painkillers, such as ibuprofen or paracetamol.
If the eardrum is intact, drops containing painkillers (for example, lidocaine) can be used. However, the advantage still remains with systemic anesthesia, and the issue of using drops with anesthetics is still controversial.
- For mild cases of ON, local agents containing acetic acid and/or glucocorticoid are indicated. Treatment is aimed at changing the environment in the NSP to a more acidic one, as well as reducing inflammation.
- For moderate cases, local agents are prescribed that contain an antibiotic or an antibiotic in combination with a glucocorticoid. The antibiotic must have activity against the most common pathogens of ONO - the drugs of choice are ciprofloxacin, neomycin, polymyxin B. If perforation of the eardrum is suspected, the use of drops containing aminoglycosides should be avoided.
- In severe cases, in addition to local therapy, the option of additional systemic antibacterial therapy is considered - most often oral forms of quinolones (ciprofloxacin or ofloxacin).
Drugs for local use remain the treatment of choice for ANO, as they allow creating a high concentration of the drug at the site of inflammation.
There are no randomized studies comparing topical and oral antibiotic therapy. But according to available data, the addition of an oral antibiotic to local antibacterial therapy for uncomplicated ANO does not have a significant effect on the course of the disease and recovery time.
The basis of treatment for otomycosis is NSP toilet and local antifungal therapy - the drugs of choice are clotrimazole and miconazole. Systemic antifungals are indicated for patients with suspected invasive fungal disease.
General recommendations
- During treatment, the ear should be protected from water - while bathing, a cotton swab soaked in petroleum jelly or glycerin should be placed in the ear.
- It is necessary to refrain from water sports for 7-10 days.
- You should limit the wearing of hearing aids and headphones as much as possible until the pain completely subsides and there is no discharge from the ear.
How is acute external otitis treated at the Rassvet Clinic?
For ONO, we give preference to local empirical therapy. An important stage of treatment is the toilet of the NSP, performed by an otorhinolaryngologist. In the clinic, we perform it under a microscope, which makes the procedure less traumatic and more effective. During the procedure, pathological discharge and granulations are removed from the ear canal, which in turn increases the effectiveness of local treatment.
Our otorhinolaryngologists select medications for local treatment based on otoscopy and medical history. Not only the effectiveness of the antibiotic against the most common pathogens is taken into account, but also their side effects and possible drug resistance.
We prescribe systemic antibiotics only when indicated. First, compared with local therapy, systemic antibiotics may increase the likelihood of drug resistance. Secondly, the use of only oral agents without local antibacterial therapy may lead to relapse of the disease, which is likely due to lower concentrations of antimicrobial drugs at the site of inflammation.
Acute external otitis media resolves within 7-14 days. With a longer course or repeated changes of tactics during the treatment period, frequent relapses, we always exclude other diseases, including immunodeficiency states and oncology.
Otipax
These ear drops are one of the best that pediatricians and family doctors recommend for otitis media. The main active ingredients of Otipax are phenazone and lidocaine: they “work” well in tandem, relieving inflammation and pain relief. Otipax, due to its safety, can be prescribed to pregnant and lactating women, as well as to children from birth. Otipax perfectly treats all forms of otitis media and any viral ear infections. Noticeable relief occurs within 2 minutes after using these ear drops, which, by the way, are suitable not only for children, but also for adults.
Otipax
Biocode, France
Combined preparation for topical use in the form of ear drops.
It has an antiseptic (disinfecting), local anesthetic (local anesthetic) and anti-inflammatory effect. from 172
5.0 1 review
865
- Like
- Write a review
Basic drugs of antibacterial therapy
Treatment of otitis media is complex and an antibiotic is prescribed as the main medication. Depending on the severity of the disease, local and general remedies are used:
- Drops in the ears. The doctor prescribes drops with antibacterial and anti-inflammatory effects, as well as combination medications. Corticosteroid ear products are not prescribed to children under five years of age. The course of treatment lasts from 5 to 7 days, but relief occurs within 2-3 days.
- Antibacterial ointments. Therapy is prescribed for otitis of the external ear and lasts 10-14 days. For convenience, a cotton swab is made, moistened with medicine and placed in the ear canal.
- Injections. Intramuscular or intravenous injections are used less frequently and only if serious complications are likely.
- Pills. The ENT doctor prescribes penicillin antibiotics, fluoroquinolones, cephalosporins or macrolides. Adults take the tablets, and children are given medications in the form of a suspension. It is worth noting that first-generation fluoroquinolones are prescribed only to persons over 18 years of age.
Penicillins
Penicillins are considered first-line antibiotics and are most often used in treatment. They kill most pathogenic bacteria, but you need to know that contraindications include pregnancy, breastfeeding, and liver disease. The penicillin series of drugs is non-toxic and is available in many forms.
Maximum effectiveness is achieved in the treatment of uncomplicated otitis media. Unfortunately, penicillins quickly become addictive. If the drugs do not improve your well-being after a couple of days, then the ENT doctor chooses a drug from the cephalosporin series.
Cephalosporins
The mechanism of action is similar to penicillins, but the effectiveness of eliminating pathogens is higher and the risk of side effects is lower. Antibiotics of this group are prescribed for the treatment of otitis in children, and also as a basis for the treatment of purulent otitis.
Polydexa
These ear drops contain an antibiotic and the hormone dexamethasone, so Polidexa effectively removes inflammation and reduces swelling. In addition to antimicrobial, these ear drops also have an antifungal effect, although weakly expressed. "Polydex" is often prescribed in pediatrics (can be used from 2.5 years). Children's drops for otitis media perfectly relieve inflammation and eliminate its symptoms. "Polydex" is considered one of the best remedies for ear diseases and has virtually no age restrictions.
Polydexa
Laboratories Bouchard-Recordati, France
Polydexa is a drug with antibacterial, anti-inflammatory and vasoconstrictor effects for topical use in ENT practice.
When combining these antibiotics, the spectrum of antibacterial action expands on most gram-positive and gram-negative microorganisms that cause infectious and inflammatory diseases of the nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses. from 188
959
- Like
- Write a review
Garazon
The active ingredients of these ear drops for children are gentamicin and betamethasone. “Garazon” for otitis media acts locally and specifically “hits” the source of infection. These ear drops relieve swelling, improve capillary permeability, and are prescribed for seasonal allergies. "Garazon" for otitis media can be used in children from 8 years of age. By the way, the drug is also suitable for the treatment of eye diseases (even with the presence of pus). Relief occurs literally 20 minutes after using the drug. Many patients highly praise these ear drops because they are effective and at the same time quite affordable.
Garazon
Schering-Plough Labo NV, Belgium
Combined drug in the form of drops, used in ophthalmology and otolaryngology. The effect of the drug is due to the components included in its composition. Gentamicin is a broad-spectrum antibiotic from the group of aminoglycosides that has a bactericidal effect. Betamethasone sodium phosphate - GCS, has a local anti-inflammatory effect, suppressing cellular and fibrinous exudation and normalizing increased capillary permeability, which is manifested by a decrease in local hyperemia, edema and effusion.
118
- Like
- Write a review
Otofa
Otofa ear drops are inexpensive, but they have a strong effect. Doctors prescribe Otofu as an antibiotic for acute and chronic ear diseases. Otofa drops are allowed for children, but are contraindicated for pregnant women. These ear drops are a powerful antibiotic (the active ingredient is rifampicin). The only disadvantage of these drops is that they do not relieve pain. But, despite this, Otofa is considered a very high-quality and noteworthy drug for otitis media.
Otofa
Laboratories Bouchard-Recordati, France
Acute and chronic otitis: external otitis;
acute otitis media (including with perforation of the eardrum); chronic otitis media; conditions after surgical interventions on the middle ear. from 152
5.0 1 review
525
- Like
- Write a review
Diagnostics
Common symptoms of ENO include otalgia (ear pain), which may be triggered or worsened by touching the pinna of the ear; itching; discharge from the ear and hearing loss (including due to swelling of the LES).
There are mild, moderate and severe forms of the disease, with symptoms ranging from mild discomfort and itching in the ear, otalgia, to lymphadenopathy and fever.
During otoscopy (examination of the ear), swelling and hyperemia (redness) of the NSP is noted, discharge in the lumen is yellow, brown, white or gray; the eardrum can be only partially visible, sometimes hyperemic.
With otomycosis, the otoscopic picture may vary depending on the type of fungus - dark, black dotted plaque with aspergillosis (Aspergillus niger); white, curdled with candidiasis (Candida albicans).
The diagnosis of ANO should always be questioned if the patient has a perforated eardrum, in which case inflammation of the outer ear may be secondary.
To make a diagnosis and prescribe treatment, in the vast majority of cases, it is enough to assess symptoms, collect anamnesis and otoscopy results.
Ear culture is performed in cases of severe disease, frequent relapses, and ineffective empirical therapy. Microbiological testing is also indicated for patients with chronic external otitis, after ear surgery, and in immunodeficient conditions (after transplantation, patients with HIV, patients undergoing chemotherapy or radiation therapy).
Differential diagnosis
- Contact dermatitis - can be caused by medications (including ear drops), cosmetics or shampoos. Itching in this case is the dominant symptom.
- Chronic suppurative otitis media—symptoms include ear discharge, possibly otalgia, decreased hearing, ringing in the ears, or dizziness.
- Carcinoma is cancer of the NSP. It is rare, but in the early stages is often indistinguishable from IT. The final diagnosis is made by biopsy of the affected area.
- Psoriasis - there is redness and flaking of the skin of the NSP, the process often extends to the auricle.