There are two menisci in the knee joint - the outer (lateral) and the inner (medial). They are located between the thigh and lower leg and act as shock absorbers. Cartilaginous layers in the knee reduce friction of joint surfaces and the load on the joint when walking, running and jumping. The inner meniscus of the knee joint is less mobile than the outer one; it is injured 4-7 times more often.
Meniscus injuries rank first among knee injuries and often occur as a result of sports injuries.
Why is a meniscus needed?
The meniscus plays a vital role in the functioning of the musculoskeletal system. It is a kind of connecting link between the bones of the femur and the shin, while it separates them so that when moving they do not touch, which means they are not injured or destroyed. On the other hand, the meniscus limits bone movement, which prevents dislocation and reduces the rate of wear and tear on the joint.
First of all, the meniscus performs a stabilizing function. It promotes displacement of all components of the joint only in a certain direction. In addition, the meniscus protects the cartilage and bone at the junction from destruction. Thanks to him, the entire knee mechanism slides against each other without being subject to friction. At the same time, the meniscus provides a shock-absorbing function. Its fibrous structure can both stretch and compress, relieving stress on tendons and ligaments.
Kinds
Kinds
- Partial rupture, in which there is a focal violation of integrity while maintaining the general anatomical structure and shape of the meniscus.
- Complete rupture - a violation of integrity affects the entire thickness of the cartilage, resulting in a fragment that can be displaced relative to other structures of the knee.
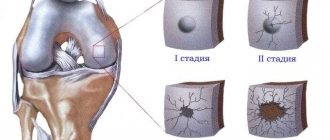
To more accurately determine the severity of damage, there is a classification according to Stoller, which distinguishes 4 degrees:
- Grade 0 – no changes.
- Grade 1 – there are small focal changes.
- 2nd degree - more pronounced changes that have a linear shape and do not extend beyond the surface of the cartilage.
- Grade 3 – changes affect the entire thickness of the cartilage, with a complete rupture of the meniscus.
Classification of a tear of the medial meniscus of the knee is possible based on the results of a thorough clinical examination, as well as objective diagnostic data, in particular using MRI (magnetic resonance imaging is necessary for Stoller classification).
Types of Meniscus Damage
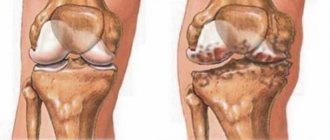
Although the meniscus can stretch, this does not mean that it is elastic like a ligament. When subjected to extreme tension, the tissue tears. Tears can be complete, incomplete, longitudinal, patch-like, transverse and fragmented. During an injury, rupture can occur with complications. This happens when torn fragments dislodge and damage nearby soft tissue.
There are several types of damage:
- Complete rupture, when the posterior or anterior horn completely detaches along with the body near the joint capsule.
- Rupture of only the internal fragment located away from the joint capsule.
- Damage to both the internal zone and the area located next to the joint capsule.
Cartilage tissue can be damaged both due to the constant negative impact of traumatic factors, and as a result of a progressive destructive process inside the joint.
Development mechanism
Development mechanism
Stability, strength, shock absorption of the knee, as well as a fairly high range of motion in it, are provided by cartilages located in the gap between the femoral condyles and the recesses of the tibia. They are paired. There are two menisci – the outer (lateral) and the inner (medial). These cartilages are characterized by a crescent-shaped shape. The wide part is called the body. Narrow areas face anteriorly and posteriorly. These are called the anterior and posterior horns.
The internal cartilage has a more rigid fixation by ligaments, so it is more likely to undergo changes. Violation of integrity is realized due to several basic mechanisms, which include a pronounced bruise, a fall on a bent limb (the cartilage is especially often injured when falling on a hard surface with a sharp edge - a step, a curb), as well as tucking (rotation of the lower leg with a fixed thigh or vice versa) . The damage is primarily localized in the area of the posterior horn, since it has the least strength.
Severity of meniscus injury
Before prescribing a course of treatment, the doctor must determine the severity of the injury. This is due to the fact that minor injuries do not require hospitalization or surgery. There are three degrees of severity of rupture:
- The pain is moderate, swelling is not obvious.
- The pain is severe, but its severity dulls over time, swelling is pronounced, and a hematoma is present.
- Acute pain, extensive swelling, hematoma, impossible to step on the affected leg.
Regardless of the extent of the rupture, the affected joint must be shown to a doctor. This is because improper healing of cartilage tissue can reduce the functionality of the knee joint and lead to lameness.
Arthroscopic technique
Arthroscopic technique
Thanks to the introduction of arthroscopic surgery into clinical practice, it was possible to achieve a significant reduction in the morbidity of surgical treatment and reduce the length of time required for:
- tissue regeneration and restoration of mobility;
- the entire course of treatment and a person’s stay in a medical institution.
Postoperative recovery
After surgical procedures, regardless of the method of their implementation, the patient remains in the hospital of a medical institution for a certain period of time. A set of measures is prescribed aimed at speedy tissue regeneration of the postoperative wound area and prevention of complications:
- Limitation of leg mobility.
- Periodic treatment of surgical suture materials with special antiseptics, which are usually used in the form of a solution.
- Prescribing antibacterial agents to prevent infection.
- The use of hemostatic medications to prevent bleeding, especially after open surgery.
The average postoperative period is determined by the method of performing the operation. It varies from 3-5 to 10 days.
Causes of meniscus injury
First of all, chronic diseases affect the destruction of the meniscus. They make its tissues fragile, thin and inelastic. It is enough to slip and make an awkward sudden movement, and a rupture will occur. This can happen even without the fact of a fall. Diseases that reduce the quality of meniscus tissue:
- rheumatoid arthritis;
- gout;
- gonarthrosis;
- chronic intoxication.
The most traumatic movement for the meniscus is rotation of the leg with the knee joint bent. This is why meniscal tears are common in hockey players and skiers - both sports involve a characteristic movement of the leg in a bent position.
Etiology
Damage to cartilage in the form of a rupture of varying severity occurs due to the influence of various etiological (causal) factors, the most common of which are:
- Previous or acute knee injury that results from excessive flexion of the joint, a blow or fall on the joint, or twisting of the leg (rotation of the hip while the shin is locked). Traumatic changes predominantly occur in young people who lead an active lifestyle or engage in outdoor sports.
- Degenerative-dystrophic changes in cartilage tissue, developing against the background of age-related changes, nutritional disorders (trophism) and leading to a decrease in its strength. This reason often occurs in older people, which is associated with general age-related changes (involution processes).
- Congenital weakening of cartilage structures, caused by changes at the genetic level (the functional activity of genes responsible for the synthesis of the intercellular substance of cartilage tissue changes). Damage to the meniscus in this case develops against the background of normal stress in children or young people.
- Long-term inflammation of the structures of large joints, leading to disruption of their functional state. This etiological factor occurs during the development of an autoimmune pathological process (rheumatoid arthritis, rheumatism), characterized by the formation of autoantibodies by immunocompetent cells that affect their own tissues, mainly the structures of the musculoskeletal system.
Knowledge of the factors that became the main cause of meniscus damage allows a medical specialist to select the optimal rehabilitation, as well as make recommendations regarding the prevention of its development.
Symptoms indicating a meniscus injury
The difficulty in independently recognizing a meniscal injury is that when it ruptures, the pain spreads throughout the entire leg. A person is not able to understand that the source is localized in the knee. Only after a long time the pain will subside and remain only in the joint area.
Symptoms differ for two types of tears: medial and lateral meniscus.
If the medial meniscus is damaged:
- there is severe pain inside the knee joint;
- when you try to strain the sore leg, a painful shooting occurs along the entire leg;
- it is impossible to bend the knee joint;
- inflammation of the synovium.
If the lateral meniscus is damaged:
- pain stretches along the lateral ligament when trying to stand on the leg;
- inflammation of the synovial membrane;
- blockade of the knee joint - forced immobilization.
When cartilage tissue ruptures, the following symptoms are typical:
- a loud click and an incessant crunch at the moment of bending;
- the presence of edema, which clearly distinguishes the diseased knee joint from the healthy one;
- local redness, accompanied by an increase in body temperature at the site of injury.
- pain when going up or down stairs.
Any tear of the meniscus can be accompanied by bleeding inside the joint. When fragments of the rupture are mixed, a complete or partial block of the knee may be observed - they will no longer be able to move.
Conservative therapy
Conservative therapy
Once a medial meniscus tear has been diagnosed, treatment without surgery is prescribed only on the basis of certain criteria, which include the location, characteristics and severity of the damage. The medical specialist must take into account the cause of the pathological condition.
It is usually possible to prescribe conservative measures if small changes have been identified that do not extend beyond the surface of the cartilage. An incomplete meniscal tear can be treated without surgery using medications, physical therapy, and rehabilitation measures. During treatment, the knee is provided with functional rest, which is achieved by immobilization (immobilization) using tight bandages or a plaster splint.
Which specialist treats a meniscus injury?
A traumatologist treats problems of the musculoskeletal system. But due to the fact that unpleasant symptoms can develop several days after the fall that led to the rupture, not everyone thinks to visit the emergency room. As a last resort, it would not be a mistake to contact a therapist - after an examination, he will determine the problem and give the necessary direction. If there is no clinic with specialized specialists in the city, you will need to visit a surgeon. He will conduct an examination and, if necessary, provide treatment.
Physiotherapeutic procedures
Physiotherapy involves the use of various physical factors that reduce the severity of inflammatory, degenerative-dystrophic processes, and also promote faster tissue restoration. For this, depending on the severity of the pathological process and the technical capabilities of the medical institution, the following can be used:
- ozokerite;
- mud baths;
- electrophoresis with various anti-inflammatory drugs.
The duration of use of physiotherapeutic procedures is determined individually by a medical specialist. They are usually combined with drug treatment.
Diagnosis of knee injury
Acute pain and the serious condition of the patient do not allow one to determine by eye at the time of injury exactly which of the components of the knee joint was damaged. This could be a meniscus, a ligament or a tendon rupture. Symptoms become typical only after 14 days. Until this moment, modern research methods will come to the aid of specialists:
- ultrasound;
- MRI;
- CT.
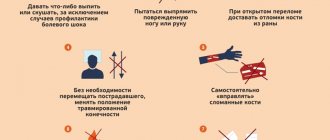
As first aid, before the ambulance arrives or until the patient is taken to the emergency room, it is necessary to apply ice to the knee and ensure that the limb is immobile.
What treatment methods are used at the Quality of Life clinic?
A properly designed rehabilitation treatment program will shorten the recovery period, reduce the risks of serious complications (including post-operative ones), and allow professional athletes to return to their normal rhythm of life and return to training. We have established methods and experience in treating representatives of all sports after injuries: skiers, basketball players, athletes, gymnasts.
The key to effective recovery after injuries to the knee joint is an integrated approach. If a meniscus injury occurs, the patient is treated by a well-coordinated team of specialists - an osteopath, a psychologist, a neurologist, and a rehabilitation specialist. We have the necessary experience and equipment to deliver treatment safely and effectively. Gradually, step by step, we will help restore motor activity after damage to the meniscus of the knee joint and restore lost joint functions.
Osteopathic correction
Osteopathic treatment methods allow in some cases to avoid surgery on the menisci and restore their function naturally. In addition, osteopathic correction allows you to reduce the dosage of potentially unsafe medications, and sometimes completely stop taking them.
Soft manual techniques: • reduce pain in the menisci; • increase mobility in the joint; • eliminate swelling and inflammation.
If permanent injury to the menisci of the knee joint is associated with scoliosis, pelvic or sacral misalignment, planovalgus foot deformity and other skeletal deformities, osteopathic correction eliminates these causes.
In addition, osteopathic treatment methods remove obstacles - congestion in blood vessels, ligaments of the knee joint, muscles surrounding the meniscus, as well as in nervous tissue that is not present in the meniscus.
Possibilities of physical therapy exercises
Osteopathic correction at the Quality of Life Clinic is complemented by physical therapy. Performing general developmental exercises can improve blood circulation in the injured leg and strengthen muscles and ligaments. In the first days after removing the splint, exercises are performed in a gentle manner.
For the rehabilitation of patients, exercises are also prescribed in the Neurac kinesiotherapy unit. Gravity loads in a rehabilitation simulator train stabilizer muscles, improve coordination and restore anatomically correct biomechanics of movements.
physical therapy complex
complex of physical therapy
After the basic therapeutic course, restorative procedures and measures are prescribed. They involve special physical training in a physical therapy complex (PT). In this case, the load on the knee increases in stages, and this allows the cartilage structures to adapt to it in order to avoid repeated damage.
Due to the fact that the joint is in a state of functional rest for quite a long time, there is a risk of developing contractures (connective tissue adhesions), so rehabilitation with exercises is necessary to prevent the development of this complication. The duration of the course of such measures depends on the type of treatment performed, as well as on the severity of the damage. Typically it varies over a period of time from several months to six months.