01.12.2020
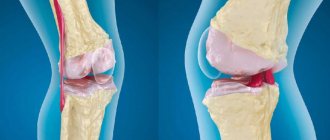
A Baker's cyst is a ball-shaped lump on the back of the knee joint. At its core, a cyst is a popliteal capsule filled with fluid. When the knee joint is bent, the ball is practically invisible. But when it is extended, the seal comes out and it becomes possible to palpate it.
The size of a popliteal hernia can reach 10 cm. Despite the fact that this disease is a benign tumor, at the same time this pathology can be classified as dangerous due to possible complications. The disease occurs in both adults and children. In its advanced state, Baker's cyst negatively affects a person's musculoskeletal system and can lead to the need for surgical intervention.
Reasons for the development of the disease
Factors that contribute to the formation of Baker's cyst have been studied for many years. Modern traumatologists and orthopedists identify a number of reasons that entail the development of a neoplasm:
- Hard physical labor.
- Intense sports activities with stress on the knee joints.
- Inflammatory processes in the joint. The motor activity of the knee joint depends on the synovial fluid, which acts as a shock absorber. It washes all the structural elements of the joint and, as it were, lubricates them. During inflammation, synovial fluid leaks from the joint into the tendon bursa. She cannot return back, since the valve prevents this. This is how a cyst is formed. Moreover, the longer the inflammation lasts, the more fluid is produced in the knee joint and removed from it, the larger the size of the Baker cyst becomes.
- Dystrophic changes caused by osteoarthritis, osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis.
- Injuries - rupture of knee ligaments, damage to cartilage, meniscus.
- Excess weight, which puts excessive stress on the knee joints.
Diagnostics
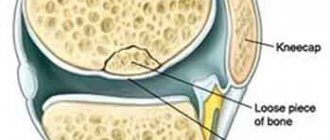
Evaluation of knees suspected of having popliteal cysts may include standard radiographs, arthrography, ultrasound, and MRI. Early in the diagnosis, it may be helpful to obtain plain radiographs to identify other conditions associated with popliteal cysts, such as osteoarthritis, inflammatory arthritis, and articular bodies (arthremphys). Additionally, loose articular bodies may be visible in a Baker's cyst on plain radiographs.
You can read about pain in the anterior knee joint here.
Direct arthrography was initially used to identify popliteal cysts. Direct arthrography involved intra-articular injection of gas or iodinated contrast medium followed by mobilization of the joint to enhance contrast in the cyst. Spot radiographs or fluoroscopy were then used to determine the presence of contrast in the cysts. Disadvantages of this method include the use of ionizing radiation and the use of invasive methods to administer contrast.
The advantages of ultrasound are its low cost, non-invasive use and absence of radiation. The main disadvantage is that it depends on the user (training of the researcher). Ultrasound is able to detect Baker's cysts in almost 100% of cases, but does not differentiate them from other pathological conditions such as meniscal cysts or myxoid tumors; it also does not detect other knee pathologies that are often associated with these cysts.
Magnetic resonance imaging remains the gold standard for diagnosing Baker's cysts and differentiating them from other conditions. It evaluates soft tissue abnormalities and has the added benefit of being accurate in diagnosing associated joint disorders, allowing the full spectrum of associated disorders to be assessed.
By
Baker's cyst symptoms
The initial stage of the formation of a Baker's cyst does not bring any unpleasant sensations to a person. Symptoms increase as the tumor grows larger. Pain occurs when nearby nerve fibers are compressed. Involvement of nerve endings and surrounding soft tissues in the process entails a number of unpleasant symptoms:
- tingling feeling in the lower part of the leg;
- numbness of the sole;
- restriction in movement;
- feeling of fullness under the knee;
- edema;
- pain that intensifies with physical activity, walking;
- a change in skin pigmentation, first over the area of the cyst, and then throughout the entire limb.
The insidiousness of Baker's cyst is that a long asymptomatic course is followed by rapid growth and the development of complications.
Lack of medical treatment causes:
- Atrophy of the lower leg muscles due to compression of blood vessels and nerves. The patient experiences constant pain, so he spares the leg and limits physical activity. The imaginary calmness of the limb gives less pronounced unpleasant sensations.
- Disorder of local sensitivity, the appearance of trophic ulcers. Impact on the surrounding feeding vessels and disruption of innervation invariably provokes the development of thrombophlebitis, and in severe cases, gangrene, which is difficult to treat conservatively.
- Compression of the knee vein leads to stagnation of venous blood, subsequently phlebitis, thrombosis and varicose veins.
- Rupture of the cyst membrane. A serious condition, which is accompanied by severe swelling of the lower leg, intense pain, and increased body temperature.
- Thromboembolism and ischemia are the most severe complications that can lead to death.
Upon examination and palpation of the cyst, a somewhat painful oblong neoplasm under the knee is determined, which has an elastic, dense structure. The size of the tumor can vary from small to large. In the early stages of a cyst, the skin over it does not change color.
Consequences and complications
With the development of a popliteal cyst and its untimely treatment, the following complications may develop:
- Infectious processes.
- Neurovascular compression - this condition can lead to the development of thrombophlebitis, impaired blood flow, compression neuropathies , varicose veins , deep vein thrombosis . Therefore, in case of vascular compression, surgical intervention is urgently necessary.
- Rupture of Baker's cyst - with this development, internal bleeding may occur, swelling, fever and pain are noted. It is rupture that is the most common complication of this pathology.
How to treat Baker's cyst of the knee
Therapeutic tactics for Baker's cyst depend on the duration of development of the pathology, the size of the formation, and the clinical picture. Treatment can be either conservative or surgical. Conservative methods include physiotherapeutic procedures, the prescription of symptomatic medications, and puncture of the cyst.
The puncture consists of evacuating the liquid contents of the cyst with a syringe and further administering one of the glucocorticoid drugs (diprospan, flosterone). All manipulations are performed under general or local anesthesia and with mandatory ultrasound control.
The following medications are prescribed:
- steroid hormones in the form of injections;
- hydrocortisone;
- painkillers;
- anti-inflammatory;
- muscle relaxants.
The drugs are prescribed only by a doctor, all injections are performed in a medical facility.
Conservative therapy
An orthopedist is involved in eliminating the type of pathology in question; if the need arises, surgeons are involved in the implementation of the therapeutic process.
Conservative treatment of Becker cyst under the knee involves the following approaches:
- unloading the joint;
- physiotherapeutic treatment;
- puncture of the tumor, followed by evacuation of the contents and administration of medications.
For therapeutic purposes, sclerosing agents are administered, in particular, a 5% alcohol solution of iodine, hormonal, and cytostatic drugs are used.
- Physiotherapeutic treatment . Electrophoresis and UHF are recognized as the most effective methods. It is permissible to implement these treatment options only after excluding an oncological process.
- Puncture . Performed to evacuate the contents of the hernia. When the tumor reaches stage 2-3, the contents of its capsule have a jelly-like consistency. The compacted neoplasm is difficult to puncture and subsequent evacuation of the internal part. Also in this case there is no point in administering corticosteroids.
- A positive result is provided by hormonal treatment . Cortisone therapy is effective in 50% of all clinical cases. The scientific idea of using hormonal drugs was first developed and applied by rheumatologists. Patients with a hernia that occurred against the background of rheumatoid arthritis were subject to observation. Therapeutic tactics made it possible to evaluate that after intra-articular administration of glucocorticosteroids, the size of the tumor decreased.
Pumping out liquid.
Since then, hormones have been injected directly into the popliteal swelling. Hydrocortisone emulsion was actively used, combining it with antibiotics.
Important! If the patient has hormonal diseases - problems with the thyroid gland, diabetes mellitus, a disorder of the adrenal cortex - it is necessary to inform the doctor about the existing disorders.
of Becker cyst is not always possible
leads to complete elimination of the tumor. Statistics show that in 6 out of 10 cases, the atheroma has to be excised surgically. Such results serve as the basis for the search for new therapeutic approaches and the development of more effective conservative methods of therapy.
Physical therapy complex
Physical therapy is prescribed to patients who have undergone surgery to remove a Baker's cyst, or as an additional method for conservative treatment.
Exercise therapy classes have several goals:
- strengthen the ligaments of the knee joint;
- stretch the gluteal, thigh, calf and quadriceps muscles;
- stretch your hamstrings.
Specially designed exercises help eliminate fatigue, reduce the tone of tense muscles, and restore blood supply to the limb.
The exercise therapy complex includes the following exercises:
- alternately bending and straightening the legs at the knees while sitting on a chair;
- a similar exercise, but with weights on the ankles;
- chair squats and stand-ups;
- pulling your legs to your chest while sitting on the floor.
For maximum therapeutic effect, it is necessary to perform exercises under the supervision of a specialist – a rehabilitation specialist.
The patient must follow certain rules:
- Warm up your muscles before starting exercise.
- Do not engage in sports training that places intense stress on your knees.
- Do not overwork your leg muscles, perform all exercises measuredly. If muscles become tired, stop training.
- All exercises are performed on a special surface.
All patients with a Baker's cyst in the popliteal fossa are recommended to take long walks (up to 20 km per day), swimming in the pool, and exercise on an exercise bike. You can learn about the exercise therapy complex by following the link.
Diet
Diet for sore joints
- Efficacy: therapeutic effect after 2-3 months
- Terms: 2-6 months
- Cost of products: 1700-1800 rubles. in Week
Nutrition should be complete and rational, while the menu should include foods that strengthen bones and joints. It is recommended to include the following products in your diet:
- Fatty fish.
- Vegetables, greens.
- Lactic acid products.
- Bran.
- Nuts.
- Jelly, jelly, marmalade.
In general, nutrition should be rational and not lead to excess weight gain, since extra pounds have a bad effect on the joints of the legs.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapeutic procedures are prescribed after relief of an acute inflammatory process or during the rehabilitation period after surgery. A pronounced effect is obtained during a series of sessions:
- mechanical traction - prevents the development of atrophy;
- massage of the knee joint and lower legs - to restore blood supply and nutrition of soft tissues;
- electrophoresis - activates tissue regeneration, normalization of metabolic processes;
- UHF, infrared laser therapy - to relieve pain, eliminate inflammation and swelling;
- magnetic therapy - restores metabolic processes and restores damaged tissue at the cellular level;
- hydrogen sulfide, radon baths - for the prevention of thrombophlebitis, varicose veins, stimulation of local blood circulation.
During physiotherapy, the condition of the damaged knee joint and the degree of its motor activity are constantly assessed. You can learn more about physiotherapy methods here.
Criteria for evaluation
Outcome measures are used to define and evaluate the expected results of a therapy/procedure, which must be compared with the results found in the patient.
- Western Ontario and McCaster University Pain Subscale (WOMAC) : a multidimensional instrument that measures 17 functional activities, 5 pain-related activities, and assesses joint stiffness. It measures pain and dysfunction.
- Visual analog scale (VAS) : measures pain from 0 to 10 (no pain to severe pain). It is easy for the patient to determine what level of pain they have.
- Rauschning and Lindgren classification : used to evaluate outcome and therapeutic effectiveness (0 to 3).
- Newcastle-Ottawa scale : a simple scale for assessing the quality of non-randomized controlled trials.
Surgery
Surgical removal of Baker's cyst of the knee joint is carried out according to certain indications:
- ineffectiveness of drug and physiotherapeutic treatment;
- excessively large size of the tumor;
- presence of signs of rupture of the cyst membrane;
- signs of necrotic changes in the popliteal fossa;
- impairment of motor functions in the knee joint.
Surgical removal of the tumor is performed in one of the following ways: traditionally, using an arthroscope or laser.
Traditional removal is performed under local anesthesia. The doctor makes an incision over the cyst, isolates it and resects it. After removal, the surgical wound is inspected, the blood vessels are coagulated and sutured layer-by-layer.
Arthroscopy involves minimally invasive surgical removal of a Baker's cyst. During the operation, soft tissues are practically not injured and blood vessels are not damaged. The cyst is removed using special instruments. The entire process is displayed on the monitor, as a micro-video camera is inserted into the knee joint.
The laser provides high temperature - up to 800 ° C, with which the cyst is coagulated. The liquid contents are evacuated, and a light guide is inserted into the cyst cavity. Next, it is heated and the walls of the cavity are glued together.
Features of treatment of the disease in children
Baker's cyst is most often found in children under 7 years of age. As a rule, pathology does not appear on its own, but against the background of inflammatory diseases of the joints or after injuries. The symptoms of the disease are practically no different from the clinical picture that develops in adults.
If the Baker's cyst does not cause discomfort in the child and does not grow rapidly, it is monitored for some time. Surgical treatment is prescribed only for severe impairment of the motor function of the knee joint. In children, good therapeutic results can be achieved through systematic physiotherapeutic procedures and exercise therapy.
Prevention
Prevention of Becker cyst comes down to the following:
- Treatment of diseases of the knee joint.
- Be careful when playing sports, protect your knees from injury with protectors.
- Periodic courses of taking chondroprotectors, especially after 40 years, which are aimed at preserving cartilage tissue.
- Eliminate infections present in the body.
If you notice pain and discomfort in the popliteal area, do not hesitate to visit a doctor - this is the key to successful treatment and the absence of dangerous complications.
Treatment of Baker's Cyst in Naberezhnye Chelny
Only an experienced doctor can make the correct diagnosis, identify the root cause of the pathological process and prescribe adequate treatment for Baker’s cyst. At the Center for Restorative Medicine in Naberezhnye Chelny, a specialist in the field of orthopedics and traumatology can easily diagnose and treat any joint pathologies.
The cost of the clinic's services can be found by following the link. If you have any questions regarding the treatment of Baker’s cyst and other pathologies of the musculoskeletal system, you can make an appointment with a doctor by calling +7 (8552) 78-09-35, +7 (953) 482-66-62. It is important to remember that timely contact with a specialist speeds up the healing process, so don’t wait, call right now!