Osteoarthritis is a joint disease that is most common in older people. As a rule, the disease affects the joints of the hands, hip and knee joints, as well as the lumbar and cervical spine.
Often pathology is recorded in people of a certain profession. So, football players and hockey players are characterized by osteoarthritis of the knee joint, journalists and secretaries - osteoarthritis of the fingers, ballerinas - inflammation of the feet, plasterers, masons and painters - damage to the shoulder joints.
1
X-ray of the cervical spine
2 X-ray of hip joints
3 X-ray stop
Types of osteoarthritis
Depending on the cause of primary and secondary osteoarthritis are distinguished
Primary osteoarthritis appears for an unknown reason, and secondary joint pathology can occur after injuries, inflammatory processes (rheumatoid osteoarthritis, purulent inflammation of the joint, arthritis with systemic lupus erythematosus, etc.), endocrine diseases and metabolic disorders.
Classification by location:
- generalized osteoarthritis - inflammation of all joints of the body;
- Osteoarthritis of the spine can also affect the cervical and lumbar regions. With this pathology, a person feels pain both when moving and during prolonged standing and sitting;
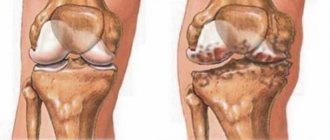
- Osteoarthritis of the hip joint is characterized by pain in the thigh, buttocks and groin. The patient is limping and has difficulty moving. In advanced cases, the thigh muscles atrophy and bone tissue begins to deteriorate;
- Knee osteoarthritis occurs when the knee is injured. When moving, a person feels pain, restriction in movement, which subsequently leads to joint deformation;
- osteoarthritis of the elbow joint - a problem with bending the arm, a tingling sensation is felt in the affected joint;
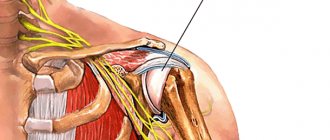
- osteoarthritis of the shoulder joint is characterized by the inability to raise the arm upward, subsequently the shoulder becomes completely immobile;
- Osteoarthritis of the hands appears in women during menopause; the symptoms of the disease are swollen joints and stiffness of movement in the morning.
Don't underestimate osteoarthritis! Advanced disease can lead to impaired mobility and joint deformation. and also to complete loss of ability to work!
Only timely, qualified treatment will help your joints!
Orthopedics and traumatology services at CELT
The administration of CELT JSC regularly updates the price list posted on the clinic’s website. However, in order to avoid possible misunderstandings, we ask you to clarify the cost of services by phone: +7
| Service name | Price in rubles |
| Appointment with a surgical doctor (primary, for complex programs) | 3 000 |
| X-ray of bones and joints of the limbs | 2 200 |
| MSCT of the knee joint | 7 500 |
| MRI of the elbow joint (1 joint) | 7 000 |
All services
Make an appointment through the application or by calling +7 +7 We work every day:
- Monday—Friday: 8.00—20.00
- Saturday: 8.00–18.00
- Sunday is a day off
The nearest metro and MCC stations to the clinic:
- Highway of Enthusiasts or Perovo
- Partisan
- Enthusiast Highway
Driving directions
Symptoms of osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis can develop over a long period of time, sometimes unnoticed. Pay attention to the following signs of joint pathology:
- localized periodic pain in the joint, which appears during exercise and subsides again at rest;
- morning stiffness in the joints;
- the appearance of inflammation in joint tissues;
- swelling in the joint, cracking noise when moving;
- decreased range of motion in the joint;
- loss of mobility and joint deformation.
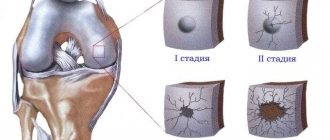
Degrees of osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis stage 1 . Pain during exercise and at rest, joint mobility is slightly limited.
Osteoarthritis grade 2 . The pain intensifies, and a crunching sound is heard when moving the joints. Limitation of mobility in the joints, the appearance of restrictions in the range of motion. Treatment is conservative, without surgery.
Osteoarthritis grade 3 . Constant pain in the joints, which intensifies with movement, persistent contractures. Significant limitation of joint mobility. If the legs are affected, a person can move only with the help of a cane, crutches, or walker.
1 General blood test
2 Diagnosis of osteoarthritis
3 Consultation with a rheumatologist
Degrees
- First degree - a moderate pain syndrome appears, which is difficult to differentiate from other types of pathologies. The only diagnostic method is to check the composition of the synovial fluid.
- Second degree - a person notices a decrease in mobility and crunching in the joints. Complex diagnostics and conservative treatment are required.
- Third degree – accompanied by complete stiffness of the joints. A person not only cannot bend his arms and legs, but also notices a curvature, which is noticeable upon visual inspection. At the severe stage, cartilage tissue is completely destroyed.
Causes of the disease
A number of reasons can contribute to the appearance of the disease:
- injury or overstrain of joints due to increased physical activity;
- decrease in the amount of estrogen in women during menopause;
- elderly age;
- joint surgery;
- excess body weight;
- hereditary predisposition;
- disruption of the activity of endocrine organs;
- osteoporosis, etc.
Diagnosis of osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis of the joints is detected using the following studies:
- X-ray diagnostics;
- Ultrasound of joints;
- MRI of joints;
- blood tests: general and biochemical;
- diagnosis of synovial fluid.
1 MRI of joints
2 Diagnosis of osteoarthritis
3 Consultation with a rheumatologist
Treatment of osteoarthritis
Treatment of osteoarthritis is a long-term process, during which it is necessary to follow all the recommendations of an orthopedic doctor and rheumatologist.
When treating deforming osteoarthritis, analgesics and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are used to relieve pain and improve the functioning of the diseased joint.
To reduce inflammation of the synovium of the joint and relieve acute pain, the doctor may prescribe injections of corticosteroid hormonal drugs that are given inside the joint.
To prevent the destruction of joint tissue, chondoprotectors are prescribed.
If necessary, surgical procedures can be used, which include removal of the affected parts of the joint and endoprosthetics. One of the optimal treatment methods is arthroscopy.
Why is arthroscopy needed?
Arthroscopy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure used to diagnose and treat the affected part of the joint.
Today, arthroscopic surgery is considered one of the best types of surgical treatment, with which you can not only replace and remove damaged tissue, but also restore the joint itself. And also analyze the condition of various bones.
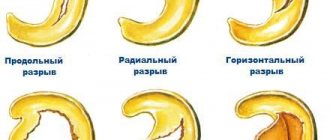
Main types of atroscopy:
- Arthroscopy of the knee joint (or meniscus). In case of rupture of the meniscus, posterior and anterior cruciate ligaments, artificial grafts or those taken from the patient’s own ligaments can be used.
- Arthroscopy of the shoulder joint . Indispensable for the prevention and treatment of lesions of the shoulder joint. Athletes often experience a rotator cuff tear, while other patients often experience joint instability and shoulder dislocation.
- Arthroscopy of the hip joint . Used to assess the condition of the femur and other articular elements and provide appropriate treatment. This manipulation is carried out much less frequently and only by specialists with extensive experience.
- Arthroscopy of the elbow joint is prescribed as a diagnosis for pain in the arm and any problems with flexion-extension of the limbs. For arthritis, a surgical form of this technique is possible.
- Arthroscopy of the ankle joint . Pathology of the ankle joint is characterized by a fairly large number of indications for surgery. A month after arthroscopy, the patient can move comfortably, leaning on a stick.
Indications for arthroscopy
The arthroscopic technique is universal and is used for both diagnosis and surgical treatment.
Indications for arthroscopic diagnosis:
- joint instability;
- various dislocations and subluxations;
- the appearance of chronic inflammation in bone tissue;
- meniscal cyst,
- injury to the meniscus and cartilage in the knee joint;
- ligament ruptures in the knee;
- removal of foreign bodies, as well as growths and adhesions from the articular cavity;
- washing joints and removing excess fluid;
- arthrosis and arthritis.
How is arthroscopy performed?
Arthroscopy can be performed under either general or local anesthesia. Local anesthesia is usually sufficient. The duration of the manipulation is from half an hour to an hour (depending on the type of problem and the required surgical intervention).
Knee arthroscopy is performed through small incisions in the knee area. The knee cavity is washed with a special solution; this is done to improve the visibility of the articular surfaces and remove pathological fluid from the joint.
During diagnostic arthroscopy, an arthroscope is inserted into the cavity of the knee joint, which transmits an accurate picture of the condition of the joint to the monitor.
If surgical treatment , the doctor inserts the necessary surgical instruments through other incisions in the joint. After the manipulation, sutures and sterile patches are applied, then the joint is bandaged. If all the doctor’s instructions are followed, after 1.5-2 months the patient can return to normal life.
1 Consultation with a rheumatologist
2 Consultation with a rheumatologist
3 Consultation with an orthopedist
Pathogenesis
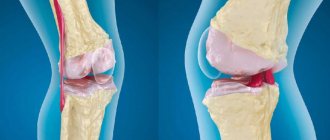
The pathology is based on the destruction of hyaline cartilage. Several processes occur within a given tissue, including matrix catabolism, anabolism, or remodeling. The main element of tissue is the matrix, which should contain the optimal amount of chondrocytes, collagen, water, glycoproteins, and proteglicans. Chondrocytes are cartilage cells that are responsible for cushioning the joint during movement. They respond to the volume of nutrients in the matrix, which leads to anabolism or catabolism. Therefore, the condition of cartilage tissue depends 100% on them.
At the initial stage of osteoarthritis, proteoglycagens change structure. They shrink and absorb liquid, but cannot retain it in the required amount. The absorption of fluid by collagen leads to a decrease in protective capacity, which in the future leads to dehydration and destructive processes due to a decrease in the strength of collagen fibers. Because of this, the cartilage softens and cracks reach the bone tissue. Destructive processes lead to redistribution of mechanical load. This provokes the appearance of osteophytes and changes in the shape of the articular surfaces.
In the development of pathology, inflammation of the synovial membrane plays a special role, which leads to the accumulation of exudate. The inflammatory process develops intensively at the site of attachment to the cartilage. Additionally, the synthesis of anti-inflammatory cytokines is impaired, which leads to a decrease in the volume of collagen and proteoglycans. This provokes increased sensitivity of the nerve endings in the affected area and acute pain. Further maintenance of the inflammatory process leads to the destruction of the synovial membrane, which enhances the production of anti-inflammatory cytokines.
At the next stage, lipomatosis and sclerosis appear, which provokes the appearance of microfractures primarily in the subchondral bone. Next, intraosseous hypertension forms due to the destruction of blood vessels, and the growth of neoplasms and thickening of bone trabeculae begins. Due to the proliferation of osteophytes, the contact area of the joints decreases, and the pressure on soft tissue increases. The joint becomes deformed and pain appears. Further, irreversible changes may occur due to tissue hypoxia.
Prevention of osteoarthritis
To prevent osteoarthritis, you need to lead a healthy lifestyle. Compliance with an orthopedic regimen, physical therapy, proper nutrition, rest and sleep patterns - all this will help keep your joints healthy for many years.
The MedicCity clinic pays special attention to the diagnosis and treatment of osteoarthritis, gout, osteoporosis, lupus erythematosus and other rheumatoid diseases.
We take a comprehensive approach to maintaining the health of patients: after treating the underlying disease, you can take courses in massage, manual therapy, physical therapy, etc.
Easy movement for you and your joints!