What position of the baby in the stomach is considered normal?
The doctor may say that the baby is “poorly positioned” or “malpresented.” What is the difference? “Position” is the placement of the fetus relative to the long axis of the uterus: along, across, obliquely. “Previa” indicates that part of the baby’s body that is closest to the “exit”.
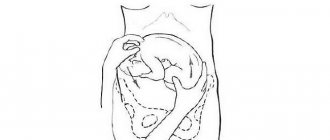
The ideal position of the baby in the uterus is longitudinal with an occipital presentation, that is, head down, with the chin pressed tightly to the chest. This is a physiological position, thought out by nature, when the risk of injury to the baby and mother during childbirth is minimal. And it occurs most often.
Incorrect position or presentation of the fetus is observed in approximately 3.5–6% of cases. The most common of the “non-standard” options is pelvic presentation, leg or breech. There is a facial presentation: the baby's head is thrown back, and it is not the back of the head that appears first, but the face. The most difficult case from the point of view of obstetricians is the transverse or oblique position of the fetus in the uterus.
Some women, whose baby “sat on its butt” or “lay across” during their first pregnancy, are afraid: what if the same thing happens next time? But it is important to understand that the incorrect positioning of the child is a feature of the course of a particular pregnancy and has nothing to do with subsequent ones.
How does childbirth occur with a facial presentation of the fetus?
Diagnosis of this position of the fetus during childbirth is an indication for a cesarean section, so the consequences for mother and baby will be minimal. In some cases, this location is diagnosed late or the woman is already admitted to the maternity hospital at a stage of labor when it is technically impossible to perform the operation.
There are 2 possible placement options for facial presentation:
- Front view: the back is in the front, and the baby's chin is on the right.
- Posterior: the fetal back is located posteriorly, and the chin is palpated on the left.
Spontaneous posterior delivery is possible with a healthy fetus and minimal trauma to the woman, although it will be protracted in time. Placing the child in an anterior view and with a wire point on the face is fraught with serious complications, including the death of the baby, since it is wedged into the pelvic cavity and cannot move further.
If this situation is neglected, a craniotomy (dissection of the head, as a result of which it becomes significantly smaller in volume) is performed on an already dead fetus in order to save the woman’s life.
The onset of labor with facial presentation is often complicated by premature rupture of water and prolapse of umbilical cord loops. This happens due to the fact that there is no tight adhesion between the bones of the woman’s pelvis and the baby’s head.
The biomechanism of childbirth consists of the following points:
- The maximum extension of the child's head, at which it is set to approximately 9.5 cm in size.
Head diameters for different types of fetal presentation: A) occipital; B) head; C) frontal; D) facial
- Then an internal rotation of the head occurs, with the baby resting its hyoid bone on the mother’s symphysis. The front view of the facial presentation stops at this moment, since the child’s forehead rests against the woman’s pubis from the inside, and the chin rests against the sacral cavity. Wedging occurs, which is almost always fatal for the baby.
- With the posterior view, labor proceeds further: the head flexes, the baby’s chin is born, and then the rest of the parts.
- After the head comes out, parts of the body appear, for which the shoulders make an internal turn.
Biomechanism of labor during facial presentation of the fetus
Why me? Possible causes of presentation
This question worries every mother whose baby is settled in her stomach “not as it should be.” There are several possible reasons.
- Pathological hypertonicity of the lower segment of the uterus and decreased tone of its upper sections. The fetal head is pushed away from the entrance to the pelvis and takes a position in the upper part of the uterus. This happens after inflammatory processes, repeated curettage, multiple pregnancies, complicated childbirth, and a scar on the uterus after a cesarean section.
- Features of fetal behavior and development, for example, increased mobility due to polyhydramnios, small head size, prematurity.
- Structural features and anomalies of the uterus and pelvis: bicornuate, saddle-shaped uterus, the presence of septa or fibroids in the uterus, anatomical narrowing or abnormal shape of the pelvis.
- Limitation of fetal mobility: entanglement in the umbilical cord, oligohydramnios, etc.
Usually the position of the baby in the uterus is fixed by the 32nd–34th week of pregnancy. All these reasons only increase the risk that by this time the child will remain in the wrong position, but they cannot be considered a “final verdict.”
Consequences for the child and mother
For a woman, childbirth in a facial presentation can be complicated by the following points:
- weakness of contractions;
- premature rupture of membranes and leakage of amniotic fluid;
- serious ruptures of the perineum, vaginal mucosa and cervix;
- postpartum inflammatory complications due to prolonged labor.
For a child, such births are more dangerous, since we are talking about the life of the fetus. The following complications are possible:
- The formation of facial edema and hematomas in this area almost always occur, and the changes are significant: the face increases in size, its shape is distorted, and the skin color is purplish-bluish. However, by the end of the 2nd week they disappear without a trace and without further impact on the baby’s health. The swelling is explained by the fact that tissue compression leads to prolonged accumulation of blood in the facial area (its outflow is disrupted).
- Wedging of the child when exiting. It is detected more often in the anterior view, so it is extremely important during natural childbirth to promptly identify the location of the child. Any further actions in such a situation do not lead to the birth of a healthy baby; destructive operations have to be performed to save the woman’s life.
- Acute hypoxia, inflammatory complications, shoulder dystocia and other complications that are typical for normal natural childbirth can also occur with facial presentation.
Waiting for hour "X"
During a routine examination, the doctor, even without the use of technology, is able to approximately determine the position of the baby in the tummy: head down or butt.
The diagnosis is clarified using ultrasound, simple and three-dimensional echography. Early diagnosis of the type of malpresentation will allow you to develop a corrective program or prepare for natural childbirth with an incorrect position or cesarean section according to indications, which will protect you from many injuries and complications. Until the 32nd-34th week, the baby can be in any position. He has plenty of room for a life-changing acrobatic flip and preparation for birth. Sometimes, causing mommy and doctors to worry, the baby turns over just before the contractions begin, and sometimes even with their onset.
Possible complications
Head presentation of the fetus at week 20 is not dangerous, but complications can arise if the fetus suddenly begins to change position. If the expectant mother is not diagnosed at a later stage of pregnancy, then it is very difficult to predict the outcome of the birth.
If a woman receives serious injuries during childbirth, she may suffer from severe bleeding and the appearance of fistulas. This negatively affects her health. You may develop fibroids or you may not be able to conceive again.
If a child suffers from hypoxia during a natural birth, this can lead to irreversible developmental changes and even a detailed outcome. When diagnosing an extensor cephalic presentation, birth at home or in water should be excluded.
This will further aggravate the situation and there will be less chance of a favorable outcome. But even if the child is positioned optimally comfortably, delivery should take place under the supervision of a doctor who can quickly respond to any unforeseen situation.
As a rule, at the 36th week, doctors recommend deciding on a maternity hospital. Today, women can choose any establishment, not necessarily in their region of residence or according to their registration.
If labor begins earlier than expected, and the patient is taken to another perinatal center by ambulance, then you must inform the doctor what presentation the fetus is in. This will save time during the examination. It is advisable to have the results of your latest ultrasound with you.
Thus, the cephalic presentation of the fetus can change both at the 20th week and later. It is the type of position of the child in the womb that is important. But even in the most difficult situations, if the doctor makes a timely decision to perform a caesarean section, the risk to the life of the woman and her child is much less.
https://youtu.be/JlqSAd3CSYY
"Coup" plan
If your due date is approaching and your baby is still in the wrong position, don't panic. You should never panic at all, especially if you are pregnant. There is an action plan!
Step 1. Corrective gymnastics...
... will help “persuade” the baby to take the correct position before childbirth. It is carried out after 24 weeks or at certain times in the third trimester. General contraindications to any set of exercises: threat of miscarriage, placenta previa. But there are other features of pregnancy in which doing gymnastics can be dangerous. Before performing any (!) exercises, be sure to consult your doctor!
With breech presentation
- Lie on your side, but not on a soft surface. Lie on one side for 10 minutes, turn to the other, lie down for another 10 minutes. Turn from side to side 3-4 times. Such simple exercises should be performed 2-3 times during the day.
- Lie on your back with your pelvis raised. To do this, place pillows under your legs and lower back. The legs should be 20–30 cm higher than the head. You can spend 10–15 minutes in this position 2–3 times a day.
- Take a knee-elbow position. Stay like this for 15–20 minutes. Repeat 2-3 times a day.
What happens: When performing such exercises, the motor activity of the fetus is stimulated, and it gets more opportunity to turn.
In transverse (oblique) position
- Lie on your side in accordance with the position of the fetus: the head on the left - on the right side, on the right - on the left. The legs are bent at the knee and hip joints. Lie down for 5 minutes.
- Take a deep breath, turn to the opposite side. Lie down for 5 minutes.
- Straighten the leg (in the 1st position - the right one, in the 2nd position - the left one), the other leg remains bent.
- Grab your knee with your hands and move it to the side opposite to the position of the fetus. Bend your torso forward. With your bent leg, describe a semicircle, touching the anterior abdominal wall, take a deep, extended exhalation and, relaxing, straighten and lower your leg.
What happens: A slight mechanical “pushing” of the baby by the muscles into the correct position.
Step 2: Additional steps
- In the transverse position, it is recommended to sleep on the side where the fetal head is located.
- With a breech presentation, turning the baby head down stimulates swimming (after consulting a doctor!).
Step 3. Visit to an osteopath
After the 35th week, a doctor in a hospital setting can rotate the fetus (in transverse and oblique cases, less often in breech presentation). During the entire “operation,” the condition of the mother and child is monitored. The procedure has contraindications and a high risk of complications and injuries, so it is performed in extreme cases.
Step 4. Consolidate the result
As soon as the efforts have been crowned with success and the little “striker” has decided to take the correct position, it is important to help him “get a foothold.” To do this, purchase a prenatal bandage, wear it throughout the day and do a special exercise (consult a doctor!).
Sit on the floor, spread your knees to the sides and press them as close to the floor as possible. Press your feet together. Stay in this position for 10–15 minutes. You can do this several times a day.
What happens: stretching of the ligaments and muscles of the pelvis, which promotes the insertion of the head into the pelvis.
How to turn your baby over before delivery
It is impossible to turn the fetus into the occipital position either before or during labor. If the baby is established this way, then there are reasons, often unknown at the time of delivery. There are no gymnastic exercises or special techniques. Often, facial presentation is formed from frontal (when the wire point is the child’s forehead) already with the onset of contractions.
We recommend reading about the features of difficult childbirth. From the article you will learn about which births are considered difficult, how to manage a difficult birth, and possible complications for mother and baby.
And here is more information about how fetal rotation is performed.
The frequency of facial presentation is small, no more than 0.2% of all births. However, doctors should always be wary of this condition, as it can threaten the life of the mother and child. Modern obstetricians, when detecting such an arrangement of the baby, are inclined to perform a caesarean section, this way they can avoid unpleasant consequences and get a living mother and baby.
Malposition of the fetus: truth and myths
...improper position of the fetus is a 100% indication for delivery through cesarean section
No! A caesarean section is recommended in 60–70% of cases of abnormal position of the fetus in the uterus. But most often, the indication for it is not only a non-standard location, but also a number of related reasons. Natural childbirth with breech presentation is classified as pathological: its course and outcome are significantly complicated, which forces the issue to be decided in favor of a cesarean section. And in case of transverse or oblique position, facial presentation, surgical intervention is absolutely necessary.
... natural birth with breech presentation is most dangerous for boys.
Yes! When a boy is born from this position, there is a risk of injury to the scrotum, especially if the buttocks and legs are raised high. This can lead to infertility and other problems in the future. Another danger is direct thermal and painful irritation of the baby’s scrotum during a vaginal examination of the mother, moving through the birth canal, which provokes premature breathing of the baby. Therefore, a caesarean section is indicated.
...if you put headphones “with music” on your stomach, the baby will become interested and roll over.
No! In most cases, if the baby turns over, it means that he has matured enough to prepare for childbirth and was able to physically perform this “trick”. And the music has nothing to do with it. If the baby is “unwilling” or unable to roll over, these methods will especially not work.
...breech presentation negatively affects the joints.
Yes! Possible underdevelopment of joints and congenital dislocation.
...pregnancy with breech presentation is more often accompanied by complications than with cephalic presentation.
Yes! About 3 times. Complications are often accompanied by hypoxia and delayed fetal development, an abnormal amount of amniotic fluid, and entanglement of the umbilical cord.
Diagnostics
Head presentation of the fetus at the 20th or later week of pregnancy is determined during ultrasound. But at such an early stage, the location of the fetus does not have any serious significance.
The ultrasound report should indicate the presentation of the fetus, but this is just a description of the position in which the child was at the moment when the ultrasound examination was performed. In general terms, you can determine the type of presentation starting from the 28th week. In this case, an obstetrician-gynecologist talks with the pregnant woman.
A specialist can use external research methods. First of all, the height of the uterine fundus is measured. Also, an obstetrician-gynecologist can palpate the presenting part through the woman’s abdominal cavity.
If a breech presentation is diagnosed, then in this case the fetal buttocks will be clearly palpable in the lower part of the patient’s abdomen. The doctor cannot confuse them with the head, since they are less mobile and more soft.
If the location is transverse, then the child’s head will be located on the right or left side. Also, with this diagnosis, deviations from the norm in the height of the uterine fundus are often recorded.
The doctor can determine what position the baby is in by listening to the lower abdomen in the area below the belly button. If the heartbeat is observed exactly there, then the presentation is cephalic. With a pelvic or transverse position, the heartbeat will be strongest in the navel area or, conversely, above it.
To do this, at each examination, starting from the 28th week, the obstetrician-gynecologist must not only measure the diameter of the abdomen using a centimeter tape, but also palpate it to determine what position the fetus is currently in.
However, this diagnosis allows only to determine the general features of the situation. Even the best gynecologist cannot test the degree of extension of the head. That is why additional ultrasound is performed. It allows you to clarify the type of cephalic presentation, as well as approximately determine the weight of the unborn child and the structural features of his body.
Only an ultrasound can immediately reveal that the umbilical cord has become entangled or diagnose placenta previa. Therefore, ultrasound examinations are mandatory in later stages of pregnancy. Thanks to ultrasound, it is possible to determine whether a natural birth can be carried out.