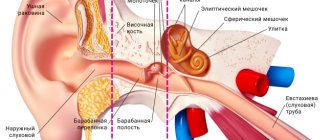
The human ear can detect sounds whose frequency varies from 16 to 20,000 vibrations per second.
Infrasound is a low-frequency sound wave (that is, with a frequency below 16 vibrations), ultrasound is a high-frequency sound wave with a frequency of over 20 thousand vibrations. They are not perceived by the human hearing aid and require the use of special instruments to detect them.
It was the huge number of studies that analyzed the signs of a sound wave and the effects of ultrasound that contributed to the emergence of prerequisites that made it possible to use ultrasound on a large scale in various industrial sectors, in the production of certain medicines, in medicine, physics, modern military technology, biology, the national economy and everyday life. life. Let's take a closer look at the effect of ultrasound on the human body.
What is ultrasound?
The influence of ultrasound and infrasound on the human body is unique. Ultrasound is a high-frequency sound wave that can propagate in solid materials, liquids and gases due to the influence of elastic forces. The origin of ultrasound can be either natural or artificial. Thus, in nature there are sensory organs that make it possible to reproduce and receive vibrations generated by an ultrasonic wave, for example, in dolphins, bats, butterflies, whales, locusts, grasshoppers, crickets, certain species of fish and birds.
Thanks to this, they are able to perfectly navigate in space, including at night, and also communicate with their relatives. Dolphins and whales can send the necessary signals over tens of thousands of kilometers. In addition, dogs and cats can detect ultrasound. The intensity and speed of propagation of ultrasound are directly affected by the characteristics of the substance in which it is transmitted: if it moves away from the source in the air, the sound weakens quite quickly. In liquids, as well as when passing through a solid, the strength of ultrasound decreases slowly. What is the effect of ultrasound on the human body?
Devices for repelling animals and insects
The areas of ultrasound treatment and its application in industrial processes are studied by specialists with specialized education. In everyday life, such information is usually uninteresting. The average person is closer to the opportunity to get rid of pests without chemicals, using a means that is safe for loved ones. This is what ultrasound equipment is. It works silently, with low power consumption and at the same time is highly effective in the fight against various scourges.
Features of devices for repelling cats, rats, dogs and insects with ultrasound:
- mainly require a permanent connection to the power supply network;
- For each type of living creature that you want to get rid of, you need a separate solution;
- Sometimes people do hear a continuous squeaking sound coming from the equipment.
In any case, it is not without its drawbacks. Pets (dogs, cats, guinea pigs, etc.) react negatively to the use of ultrasonic repellers at home. Sometimes people feel the same signs. These are headaches, insomnia at night, drowsiness during the day, irritability or general depression of the nervous system. You can get rid of such consequences only after turning off the device.
Difference from normal sound
It differs from ordinary sound in that it travels in all directions from the source. Ultrasound is essentially a wave in the form of a narrow beam. Such features make it possible to use it for exploring the sea and ocean floor, detecting sunken ships and submarines, as well as various obstacles under water, and accurate distance.
But when propagating in water, ultrasonic waves can cause harm to the organisms that live in it. Under the influence of ultrasound, the fish's sense of balance is disturbed; they float to the surface of the water with their bellies up, and therefore cannot assume their normal position. If exposure to ultrasound is intense and prolonged, exceeding acceptable limits, it will ultimately cause very serious damage and even death to fish. If its influence is temporary and the intensity is not too high, after its cessation the lifestyle and behavior of the fish return to their usual framework.
Ultrasound concept
The possibilities of using ultrasound were studied back in the 19th century. Then two groups of scientists - from England and France - were studying the propagation of various waves in water. In 1883, the first device that operated in the ultrasonic range (whistle) appeared. Around this time, the Curie brothers developed compact piezoelectric resonators. This marked the beginning of the creation of small-sized equipment.
Historical milestones in work on ultrasound devices:
- 1916 - release of the first echo sounder based on quartz elements;
- 1928 - beginning of use in flaw detection to identify cracks and cavities;
- 1936 - first experiments in ultrasonic welding of materials;
- 1937 - attempts to use it to detect brain tumors.
Since the 50-60s of the 20th century, the properties of this type of sound waves have been studied so much that they began to be used literally “everywhere”. For example, they created ultrasonic cleaning devices to remove dirt and old paint. The surface after such treatment retains its original appearance, and no abrasive substances are required for operation. The situation is similar with the inclusion of ultrasound from rats - the rodents leave the room without the use of poisonous agents.
Effect of ultrasound on the human body
Ultrasound affects the human body in a similar way. During the experiment, water was poured into a cupped palm, after which the subject immersed it in the ultrasonic space. At the same time, he experienced painful and unpleasant sensations. Not everyone knows what effect ultrasound has on the human body.
It is worth noting that the essence of the biological influence of ultrasound is still not fully understood. But more likely it is based on local pressures arising in the tissues, as well as a local thermal effect, which is directly related to the energy absorption that occurs when vibrations are suppressed. Since gaseous and liquid media are capable of excellent absorption of ultrasound, while solid substances conduct it, the skeletal system of the human body is also a good conductor. Ultrasound exposure in the human body primarily provokes the appearance of a thermal effect, which is a consequence of the energetic transformation of the ultrasound wave into heat. What else do you need to know about ultrasound and its effect on the human body?
Ultrasound is the name given to mechanical vibrations propagating in elastic media (liquids, gases) and solids. It is perceived with an upper threshold of audibility above 20 kHz, and higher frequencies can also cause a sound sensation, but at very high intensities (120-145 dB).
The maximum permissible level (MAL) of ultrasound is a level that, during daily (except weekends) work, but not more than 40 hours a week, throughout the entire work experience, should not cause diseases or health abnormalities detected by modern research methods in the process work or in the long term of the life of the present and subsequent generations. Compliance with ultrasound guidelines does not exclude health problems in hypersensitive people.
The acceptable level of ultrasound in residential and public buildings is a factor level that does not cause significant concern in humans and does not cause significant changes in the indicators of the functional state of systems and analyzers sensitive to ultrasonic influence.
Ultrasound sources are all types of ultrasonic technological equipment, ultrasonic devices and equipment for industrial, medical, and household purposes, generating ultrasonic vibrations in the frequency range from 18 kHz to 100 MHz and higher. Ultrasound sources also include equipment during the operation of which ultrasonic vibrations arise as a concomitant factor.
Contact medium is a medium (solid, liquid, gaseous) in which ultrasonic vibrations propagate using the contact transmission method.
Sources of ultrasound in production are equipment in which ultrasonic vibrations are generated to perform technological processes, technical control and measurement, as well as installations during the operation of which ultrasound appears as a related factor.
Ultrasound has a mainly local effect on the body, since it is transmitted through direct contact with an ultrasonic instrument, workpieces or environments where ultrasonic vibrations are excited. Ultrasonic vibrations generated by low-frequency industrial equipment have an adverse effect on the human body. Long-term systematic exposure to airborne ultrasound causes changes in the nervous, cardiovascular and endocrine systems, auditory and vestibular analyzers. The most characteristic is the presence of vegetative-vascular dystonia and asthenic syndrome.
The degree of severity of the changes depends on the intensity and duration of exposure to ultrasound and increases in the presence of high-frequency noise in the spectrum, while a pronounced hearing loss is added. If contact with ultrasound continues, these disorders become more persistent.
Requirements to limit the adverse effects of ultrasound on workers and the public
Direct contact of a person with the working surface of the ultrasound source and with the contact medium during the excitation of ultrasonic vibrations in it is prohibited.
In order to avoid contact with ultrasound sources, it is necessary to use:
• remote control of ultrasound sources;
• automatic blocking, i.e. automatic shutdown of ultrasound sources when performing auxiliary operations (loading and unloading products, linen, medical instruments, etc., applying contact lubricants, etc.);
• devices for holding an ultrasound source or objects that can serve as a solid contact medium.
To protect hands from the adverse effects of contact ultrasound in solid, liquid, gaseous media, as well as from contact lubricants, it is necessary to use oversleeves, mittens or gloves (outer rubber and inner cotton).
Hand-held ultrasonic sources must have a shape that provides minimal tension to the muscles of the hand and upper shoulder girdle of the operator and meet the requirements of technical aesthetics.
The surface of hand-held ultrasound sources in places of contact with hands should have a thermal conductivity coefficient of no more than 0.5 W/m deg., which eliminates the possibility of cooling the hands of workers.
To reduce the adverse effects of ultrasound during contact transmission in the cold and transitional periods of the year, workers must be provided with warm overalls in accordance with the standards established in the given climatic zone or production.
Stationary ultrasonic sources that generate sound pressure levels exceeding standard values must be equipped with sound-absorbing casings and screens and located in separate rooms or soundproof booths.
To protect operators servicing low-frequency stationary ultrasonic sources from electromagnetic fields, it is necessary to shield feeder lines.
When systematically working with sources of contact ultrasound for more than 50% of the working time, it is necessary to take two regulated breaks - a ten-minute break 1 - 1.5 hours before and a fifteen-minute break 1.5 - 2 hours after the lunch break to carry out physioprophylactic procedures (thermal hydro procedures , massage, ultraviolet irradiation), as well as therapeutic exercises, vitaminization, etc.
General strengthening procedures (vitaminization, ultraviolet irradiation, sets of gymnastic exercises, etc.) must also be carried out by those working under conditions of exposure to low-frequency air ultrasound.
To protect workers from the adverse effects of airborne ultrasound, noise suppressors should be used.
Persons at least 18 years of age who have completed the appropriate training course and safety instructions are allowed to work with ultrasonic sources.
Persons exposed to contact ultrasound during work are subject to preliminary, upon hiring, and periodic medical examinations in accordance with Order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of the Russian Federation No. 302n dated April 12, 2011.
Stimulates blood circulation
In addition, it causes microscopic stretching and contraction of the tissue (this is called micromassage), and also stimulates blood circulation. In this regard, there is an improvement in the functioning of various tissues of the human body and blood flow. In addition, ultrasound can have a stimulating effect on the course of metabolic processes and reflex nervous action. It promotes changes not only in the organs it affects, but also in other organs and tissues.
Harm of intense influence
In this case, intense and prolonged influence destroys cells and leads to their death. This is due to the fact that cavities are formed in body fluids under the influence of ultrasound (this phenomenon is called cavitation), which causes tissue death. An ultrasound wave can also destroy many microorganisms, and this helps inactivate viruses such as encephalitis or polio. The effect of ultrasound on protein causes a disruption in the structure of its constituent particles and their further disintegration. In addition, it destroys red and white blood cells in the blood, its coagulability and viscosity increase significantly, and ROE also accelerates. The ultrasound wave has a depressing effect on cellular respiration, reduces the amount of oxygen consumed by it, and causes the inactivation of a number of hormones and enzymes.
So the effect of ultrasound on the human body is still not very good.
Consequences for the human body
High-intensity ultrasound can cause the following effects in humans:
- the appearance of increased pain syndrome;
- baldness;
- hemolysis;
- clouding of the lens and cornea of the eye;
- increase in the content of lactic and uric acid, cholesterol in the blood;
- small hemorrhages in a number of organs and tissues of the body;
- significant hearing defects;
— pathological formation and destruction of bone tissue;
- destruction of nerve cells and cells of the organ of Corti. These are the main diseases caused by exposure to ultrasound.
As a result of prolonged exposure to ultrasound, excessive drowsiness, dizziness, high fatigue, symptoms of vegetative-vascular dystonia (sleep disorders, memory defects, apathy, indecision, decreased appetite, fearfulness, tendency to depression, etc.) appear.
Where is the effect of ultrasound on the body most often used?
Non-thermal effects
The non-thermal effects of ultrasound have been studied in vitro (“in vitro”). These include:
- Increasing the rate of reverse development of inflammation;
- Acceleration of fibrinolysis (that is, the destruction of a blood clot);
- Stimulation of the activity of fibroblasts (connective tissue cells), activation of protein biosynthesis, tissue regeneration, healing of bone fractures, activation of angiogenesis (growth of new vessels);
- Increasing the density of collagen fibrils (a component of connective tissue);
- Increased tendon extensibility.
Use of Ultrasound in Medicine
The therapeutic effect of ultrasound is due to its ability to penetrate tissue, warm it up and provide micromassage. It should be noted that ultrasound probably has a number of specific effects, since deep heating of tissues is achieved through other methods, but a positive effect in some cases occurs only after using ultrasound.
Taking into account the reflex mechanism, ultrasound can be used not only to directly influence the epicenter of pain, but also to influence it indirectly.
Thanks to the properties mentioned above, ultrasound, under a number of conditions, can have a bactericidal, antispasmodic, anti-inflammatory and analgesic effect. The use of ultrasound can be combined with other therapeutic techniques. Due to increased biological activity, care must be taken when treating with ultrasound. Positive results from its therapeutic use have been obtained in a number of diseases. It is very effective in the treatment of neuralgia, myalgia, neuritis of amputated limbs, periarthritis, arthritis and arthrosis. Many people are interested in whether ultrasound is harmful to humans.
Thermal effects
The thermal bioeffects of ultrasound are associated with its ability, at a certain frequency, to individually increase the temperature of the area to which its influence is directed. The degree of temperature increase depends on the ultrasound parameters, tissue characteristics and the degree of blood supply to this tissue.
Thus, the positive effects of therapeutic ultrasound are as follows:
- It is possible to heat structures at a depth of 8 cm if deep exposure is necessary;
- The procedure of ultrasound exposure of scar tissue increases their ability to heal;
- A local increase in temperature of 1 degree Celsius has been proven to reduce muscle spasm, pain, chronic inflammation and increase blood flow in that specific area of the body. Modern therapeutic applications of ultrasound:
- Lithotripsy (destruction of kidney and gallstones);
- For tumors of various origins (the mechanism of destruction by ultrasound of the vessels that supply blood to this tumor is used);
- Restoration of nerves when they are damaged (shown using the example of traumatic damage to the facial nerve);
- Destruction of blood clots in blood vessels;
- Acceleration of healing of bone fractures;
- Acceleration of wound healing;
- Phonophoresis (use of ultrasound to deliver drugs to the source of damage);
Thus, ultrasound is used in modern medicine not only for diagnosis, but also for the treatment of various pathologies. Unfortunately, the therapeutic effects of ultrasound on the pelvic organs have been little studied and this method of influence in gynecology is now not widely used, however, all the data obtained in world science lead scientists to the need to search for indications for the use of the biological effects of ultrasound in gynecology.
Overall Impact
The general effect of ultrasound on the human body is confirmed, in particular, by the fact that when a number of joints are affected, it is often enough to limit the therapy to one of them, since there is a parallel improvement in the remaining joints. Positive results were obtained in the treatment of spondylitis, ankylosing spondylitis, varicose, flaccid granulating and trophic ulcers, and obliterating endarteritis using ultrasound.
There are separate indications of the positive use of ultrasound in bronchial asthma, duodenal and gastric ulcers, bronchiectasis, pulmonary emphysema, Meniere's disease and otosclerosis. There are also observations that indicate that preliminary skin scoring enhances the effectiveness of X-ray irradiation.
Is ultrasound dangerous for humans?
The question of the dangers of ultrasound irradiation is often raised. An example is the usual reaction of babies to ultrasound examinations - many begin to toss and turn and try to shield themselves from the radiation with their hands. It is not recommended to avoid the event, because due to the constant speed of ultrasound, the location of the fetus and the absence (presence) of congenital diseases are determined. The same conversations arise when seeking services like ultrasound removal of acne. Or treatment of joints, stomatitis, stomach ulcers.
The truth about the dangers of ultrasound radiation:
- real negative consequences occur with prolonged exposure;
- pain effects occur only when the sound pressure level exceeds 90–120 dB;
- Ultrasound examination and treatment are contraindicated for certain diseases.
If you use technology after consultation with your doctor, problems usually do not arise. In everyday life, it is recommended to use factory-made devices, which necessarily take into account the limits on radiation power.
Contraindications to the use of ultrasound
It is forbidden to voice the genitals, growing bones, tumors, heart areas (this can cause angina pectoris). In case of hypertension, pulmonary tuberculosis, pregnancy, hyperthyroidism, changes in parenchymal organs, the use of ultrasound is also contraindicated. If it is used on an ever wider scale, it is necessary to organize careful monitoring of patients who come into contact with ultrasound in order to identify early symptoms of the disease and carry out the required preventive and therapeutic measures in a timely manner. There is also evidence of the positive effect of ultrasound on some forms of neuritis and cancer. But the width of the safe area between the positive and damaging effects has not yet been determined with precision.
We examined the effect of ultrasound on the human body.
Is ultrasound harmful or not?
The American Institute of Ultrasound in Medicine, based on numerous studies and experimental work, made the following conclusion in 1993:
“There have never been any documented biological effects in patients or device operators caused by ultrasound at the intensity typical of modern diagnostic ultrasound units. Although it is possible that such biological effects may be identified in the future, current evidence indicates that the benefit to the patient from the prudent use of diagnostic ultrasound outweighs the potential risk, if any."
More than 16 years have passed with frequent, widespread use of ultrasound, and there are no reports of negative effects of diagnostic ultrasound. It is important to distinguish between ultrasound used in diagnostic devices and other types of ultrasound, which is used in many areas. They differ in their characteristics.
Accessibility, non-invasiveness, high information content, absence of contraindications and speed of implementation are the main advantages of ultrasound diagnostics.
But ultrasound is an integral part of the patient examination. The ultrasound conclusion should not be assessed independently, but only in conjunction with complaints, examination, laboratory data and other studies. Ultrasound doctors write their conclusions not for you, the patients, but for your attending physicians, who will make the final diagnosis and prescribe treatment.
The information content of ultrasound is high, but many factors influence the accuracy of diagnosis: the quality and class of equipment, lighting, preparation and body type of the patient himself, and the “eye of the beholder”.
Preparing for an ultrasound is very important, but many people often neglect it. It is in your power to help the doctor.
Preparation for abdominal ultrasound : 2-3 days before the upcoming examination, a light diet is recommended without consuming foods that increase intestinal motility and gas formation. Flour products, brown bread, raw vegetables and fruits, legumes, milk, juices, carbonated and alcoholic drinks are excluded. It is recommended to take Espumisan for 2 days. The study is carried out strictly on an empty stomach: do not drink, do not eat (except for patients with diabetes). If the study is carried out in the afternoon, a light breakfast is allowed no later than 6 hours before the study.
The same preparation will be required if you have been prescribed an ultrasound of the kidneys, adrenal glands, or pelvic organs , because gases in the intestines and increased peristalsis can interfere with the examination of these organs.
Examination of the bladder and pelvic organs in both women and men through the abdominal wall will require filling the bladder. It is necessary to drink 1 liter of still water an hour before the test and not urinate.
No preparation is required when examining superficial organs (thyroid gland, blood vessels, salivary glands, lymph nodes, mammary glands), heart, soft tissues, joints.
During ultrasound of the mammary glands and pelvic organs in women, the timing of the examination is determined by the attending physician. If the timing is not specified by the doctor, then examination of the mammary glands is recommended to be carried out from the 7th to the 10th day of the menstrual cycle. Ultrasound can be done as often as necessary in each specific situation.
Take care of yourself!
The article was prepared by Natalya Mikhailovna Mekhanoshina.