Syphilitic chancre is an ulcerative or erosive formation that appears in the primary stage of syphilis infection and is its main symptom. There are 13 types of chancre due to syphilis: ordinary and atypical. Syphilis is treated with medications and a special regimen.
Types of chancre
Chancre is an ulceration that occurs 3-90 (on average 21) days from the moment of infection with syphilis, more often in the area of penetration of the pathogen into the patient’s body.
First, a pink spot (inflammation) forms on the skin, then a dense nodule appears in this place, after 7-10 days it becomes necrotic and turns into an ulcer or erosion. If the resulting chancre is not accompanied by itching or pain, then it is called syphiloma. Syphiloma has a regular round or oval shape and clear boundaries that protrude above the skin. The edges are dense, roll-shaped. The bottom of the syphiloma is red, less often – meat-colored, maybe red-brown, and the chancre itself looks varnished, due to the characteristics of the wound.
The size of syphiloma varies from 5 to 30 mm, but there are ulcers of larger or smaller diameter. The main symptom of chancre is a cartilaginous compaction at the base of the ulcer, which can be felt upon palpation. When pressed, the chancre is painless. The skin around the ulcer is clean, without signs of inflammation.
Chancre is formed due to the penetration of Treponema pallidum (spirochete) into the body. For reproduction, the temperature of the human body is suitable for it and after entering the body it actively forms syphilomas. The chancre themselves can be of different types, shapes and sizes.
Classification
By quantity
Single - chancre in the form of a separate neoplasm, or multiple, which looks like several ulcerations.
By origin
Twin chancres occur during simultaneous infection - when the pathogen enters the patient’s body not in one, but in several “places”. That is, instead of one chancre, two or more can be found.
Chancres formed as a result of infection at different times. They appear one after another, in approximately the same place.
The so-called “kissing” chancre, which occurs on contacting surfaces.
Concomitant diseases can contribute to the formation of multiple syphilomas:
- scabies
- acne
- skin injuries
By depth of penetration into tissue
Syphilomas have different depths of tissue damage.
Ulcerative lesions affect the deep layers of the skin. They can pass through the dermis - right down to the subcutaneous tissue. I have a rough bottom covered with purulent plaque. Erosion is located closer to the surface. The bottom is smooth, shiny, and shaped like a saucer.
To size
In addition to standard sizes from 5 to 10 mm, there are giant and dwarf chancres.
Giant chancres are extremely rare and can reach up to 20 cm in diameter. They are localized mainly in areas of accumulation of fatty tissue: on the abdomen, thighs, and pubis. Syphilomas are called dwarf and are the size of a poppy seed - 1-2 mm; they can only be seen through a magnifying glass. They are rare.
By location
Chancre can be located on different parts of the body:
- genital syphilomas are located on the genitals
- extragenital - on any other parts of the body outside the genitals (Fig. 1)
- bipolar syphilomas occur simultaneously both on the genitals and outside the perineum.
Figure 1. Chancre on the index finger of the left hand and in the area of the inner corner of the left eye. Source: CC0 Public Domain
By shape
In addition to the classic round shape, chancre can have a different appearance.
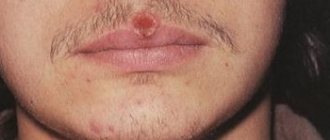
Slit-shaped syphilomas look like cracks. They can form in the corners of the mouth, on the tongue, near the anus. They are rare. Located in the corners of the mouth, they can be perceived by the owner as non-dangerous “jams”.
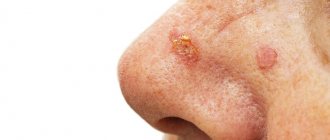
Cortical chancre is not like ordinary syphilomas; it is not concave in shape and is covered with a crust. It usually forms on ulcers that are located in places where their contents dry out easily: the surface of the nose, face, corners of the mouth.
Diphtheritic chancre is covered with an ash-gray film, similar to diphtheria. Happens quite often. It can be localized in any area.
The burn chancre quickly increases in diameter, while its borders lose their regular shape and clear outline, and the bottom changes from smooth to red-grained (Fig. 2). Typically, primary syphilomas do not tend to grow. This is an exception.
Figure 2. Burn syphiloma. Source: CC0 Public DomainCaption
Erosive chancre includes many erosions; ulcers can merge. Formed exclusively on the mucous membranes of the genitals.
Chancroid herpetiformis is named for its resemblance to genital herpes. This is an erosive formation, in the field of which there are many small ulcers with clearly defined edges. Similar to Folman's balanitis, but in this case the ulcers do not merge.
How chancroid develops
Primary syphiloma forms after the incubation period has passed: 3-4 weeks after contracting the infection. It occurs in places with skin lesions in which natural body fluid contaminated with bacteria has entered: sperm, secretion of the uterine cervix.
An ulcer does not appear immediately. Initially, a red spot appears on the infected area, which, under the influence of treponemas and cells of the immune system, thickens and turns into a nodule. The compaction is not accompanied by pain or discomfort, and therefore often goes unnoticed by the patient.
Over the next 7-10 days, the nodule develops: it increases in size, thickens and then ulcerates. Ulceration can be of two types: superficial, in the form of erosion, or deep, in the form of an ulcer. The ulcer or erosion takes on its final form: it acquires clear, pronounced boundaries, an even oval or round shape.
At the bottom of the manifested syphiloma, a liquid is released containing a large number of pale treponema and cells of the immune system. The bottom itself acquires a pronounced red tint with bluish notes.
This type of chancre persists for 1-2 months, after which the process of healing and tightening begins. This signals the transition of the disease to a secondary, more dangerous and severe stage.
3-4 days before the chancre disappears, multiple rashes appear on the patient’s body, often accompanied by burning and itching.
Localization
Since syphilis is transmitted primarily through sexual contact, chancroid is most often localized on the genitals. However, clinical practice shows that syphilomas are almost as often found in the mouth and anus.
This means that chancre can appear anywhere, the place of its localization can be:
- penis and scrotum
- labia and clitoris
- posterior commissure and anal area
- pubis
- oral cavity: lips, gums, tongue and throat
- inner thighs
- chest and stomach
- face
- rarely - eyelids, conjunctiva of the eyes
Chancre can be located inside the genital organs, for example, on the walls of the vagina or cervix, then syphiloma is difficult to detect.
Atypical forms of syphilitic chancre
{banner_banstat5}
Atypical chancres are types of syphilomas that differ from the usual types in one or more characteristics.
These include:
- Chancroid felon:
an ulcer with jagged edges that appears on the fingers. Most often it occurs on the index finger and thumb, accompanied by shooting pain, swelling, blue discoloration and suppuration. This is an “occupational disease” of surgeons and gynecologists who violate safety regulations. - Indurative edema:
chancre in the genital area, causing severe swelling, bluish skin and swelling of the genitals. Occurs on the labia and foreskin. Not accompanied by pain or inflammation. - Amygdalitis:
unilateral, less often bilateral chancre, located on the tonsils. Enlarges and deforms the tonsil on which it is located, which can cause pain. The color of the tonsil tissue does not change, so the disease can be confused with a sore throat.
With the exception of these features, atypical forms of chancroid do not differ in any way from the usual varieties. The development of atypical syphilomas, the time of their appearance and disappearance are similar to the classical forms.
Stages of development
Incubation period
The incubation period - from the moment of infection to the appearance of symptoms of the disease - lasts on average from 2 weeks to 2 months, although observations of longer duration are known. It all depends on the state of immunity at the time of infection. Long asymptomatic periods usually occur in people who were taking antibacterial drugs to treat other diseases at the time of infection.
During the incubation period, Treponema pallidum multiplies in the lymphatic system until it reaches a maximum concentration. They then enter the bloodstream and spread throughout the body. At this time, the disease does not manifest itself in any way and is not detected in blood tests, but the person is already infected. Without realizing it, he or she is putting the sexual partner at risk if they have unprotected sex.
Important! Treponema pallidum can reproduce in a small temperature range, around 37 °C. Therefore, to treat syphilis, the method of pyrotherapy is practiced - increasing body temperature. The patient is given drugs that increase body temperature, as a result of which treponema is deprived of the opportunity to reproduce. This method is considered the most effective for nonspecific treatment of syphilis.
Chancre formation
Figure 3. Development of syphiloma.
Source: CC0 Public Domain Once in soft tissue, treponema begins to actively multiply. During this period, a slight increase in temperature and an increase in nearby lymph nodes, which can be palpated, are possible. Inflammation develops at the site of infection - this is how immune cells try to destroy the enemy.
From the outside, the inflammation site looks like a bright pink patch of skin. Then a characteristic dense nodule forms on the skin - the rudiment of the future chancre (Fig. 3). It enlarges, thickens and after a week and a half ulcerates.
If the ulcer is covered with a crust, then the chancre is also called cortical. If you press on it, a yellowish liquid will come out, in which there is a high concentration of treponemes. This type of syphiloma is called “crying chancroid.”
Discharge from chancre is contagious, and contact with it can transmit infection. This danger is especially high when chancre is located in the mouth - there is a high risk of infecting a partner with syphilis even through a kiss.
The formation of chancre indicates the end of the incubation period and the onset of the primary stage of syphilis. Chancre does not bother the wearer with either itching or pain, which is bad - a person may simply not pay attention to it and waste time.
The primary stage is the most favorable for the destruction of the pathogen. During this period, a complete and rapid recovery is possible with timely administration of antibacterial therapy. In the future, coping with the disease will become more and more difficult.
Healing chancre
An ulcerated chancre lasts 6-7 weeks, then healing begins. Erosion can pass without a trace, but sometimes it leaves a dark pigment spot. When the ulcer heals, a scar remains. A few days before the chancre disappears, profuse itchy rashes may appear on the body.
At this stage, syphilis enters the secondary stage.
Important! Healing of chancre is often mistaken for recovery. This is wrong. In fact, the disease continues to develop, spreading throughout the body.
What is the difference between soft chancre and hard chancre?
There is a chancroid similar to hard - soft chancre (chancroid). It, like syphilis, is sexually transmitted, but occurs due to infection not by Treponema pallidum, but by bacteria of the genus Haemophilus influenzae.
Chancroid differs from hard chancroid in the following ways:
- there is no hard cartilaginous base (that’s why chancroid is called “soft”)
- the edges of the ulcer are not hard, but soft, spreading
- characterized by copious discharge of pus
- painful
- color hot pink, red
Lymphogranuloma venereum - complications
Late complications can occur several years after the initial lesion:
- Elephantiasis is a syndrome characterized by elastic, hard swelling of the legs (ivory) or external genitalia. This occurs with chronic stagnation of lymph due to inflammatory (filariasis, lymphogranuloma venereum) or non-inflammatory factors. It is important to treat the underlying disease; conservative (compression bandages, massage) and surgical (lymphatic drainage) treatment is also used.
- Genital strictures are cicatricial narrowings that occur as a result of injury or inflammation.
- “Identification reaction” on the skin is an allergic reaction to an inflammatory focus.
- Erythema multiforme is an increased change in the skin, usually the size of a smaller or larger coin. Color varies from light red to brownish red. The central part quickly recedes and becomes pale in color, while the edges of the change persist, retaining a reddish hue.
- Erythema nodosum - manifests itself as painful nodules on the legs. It is more common in young people, especially women. This is an allergic reaction to various microorganisms and medications. During treatment, it is important to eliminate the predisposing factor. The prognosis is very good.
Diagnostics
Several basic methods are used to detect syphilis:
- Detection of treponema pallidum using a microscope in a scraping taken from a chancre.
- The serological method (Wassermann reaction) - when specific proteins that are produced by the immune system in response to the appearance of treponemes in the body are determined, is not effective for primary syphilis.
- The microprecipitation reaction is a rapid diagnosis, also based on the body’s production of antibodies.
- Specific tests RIF, RIT, RPGA, etc. – difficult to set up, time-consuming and expensive. Used to identify latent syphilis, in complex atypical cases, in differential diagnosis and for the diagnosis of late syphilis.
If treponema is detected immediately using microscopy, additional studies are not required to prove infection. Upon detection of treponema, treatment is prescribed immediately.
Sometimes it is necessary to carry out a whole range of diagnostic measures to establish an accurate diagnosis, so it is impossible to diagnose the disease yourself; you need to consult a doctor.
Prices for services
Initial appointment with a urologist FOR MEN + ultrasound of the prostate gland (assessment of complaints, medical history, if necessary, rectal digital examination, ultrasound of the prostate gland in men)
Primary appointment – visiting a doctor of a specific specialty for the first time. Includes a conversation with the patient, an initial examination, anamnesis, if necessary, a digital rectal examination, and an ultrasound of the prostate gland. The price is valid from 02/01/2021 The price is not valid for appointments at the branches of Bolshevikov Ave. and Prosveshcheniya Ave. Make an appointment
550 ₽
Repeated appointment with the urologist
Make an appointment
700 ₽
Treatment
It should be noted: in advanced cases, when it is not possible to get rid of chancre, as well as with extensive tissue necrosis, they resort to surgical removal of syphiloma.
In all other cases, the chancre itself is not treated and specific treatment for uncomplicated chancre is not carried out. For secondary and combined infections, topical antibacterial drugs may be prescribed: baths with benzylpenicillin and dimexide, applications with mercury or mercury-bismuth ointment. If the chancre is located in the oral cavity, rinsing is recommended: a solution of furatsilin, boric acid (2%), or gramicidin (2%).
The main task is to get rid of syphilis as quickly as possible and with minimal losses. Therefore, to treat syphilis, penicillin antibiotics are used - short and long-acting (durant) penicillins: Bicillin-1, Bicillin-5, Oxacillin, Ampicillin (semi-synthetic penicillin). The drug of choice for the treatment of syphilis is benzylpenicillin.
Reserve drugs for penicillin intolerance: tetracyclines (doxycycline), macrolides (azithromycin, erythromycin), cephalosporins (ceftriaxone).
Administration of drugs is by injection - intravenous or intramuscular.
Source: CC0 Public Domain
The treatment regimen depends on the stage of the disease, location, degree of damage, etc. In any case, the dose of the drug and the number of courses of treatment are calculated by the doctor individually.
During treatment, control tests are carried out to confirm the effectiveness of the drugs.
Treatment of syphilis at an early stage is the most effective and creates all the prerequisites for a complete cure without consequences and complications.
Recommendations for the treatment period
During the treatment period, it is necessary to stop sexual intercourse. When chancre is localized on the fingers, it is recommended to wear protective gloves. If syphiloma is found in the mouth, it is necessary to separate personal items from common ones - dishes, toothbrushes, etc.
If there are chancres on the body, the use of bed linen, towels, and washcloths should be individual. Syphilis is not transmitted through public places (toilet, etc.).
Sexual partners of sick people receive preventive treatment without fail, including pregnant and lactating women.
Important! You should definitely complete the full course of treatment! Under no circumstances will syphilis go away spontaneously. Untreated syphilis will move to the next stage, increasing the risk of complications and persistent deterioration of the patient’s condition.
Clinical serological control (CSC)
All family members of the sick person, both adults and children, need to receive preventive treatment after sexual or close household contact with patients with early forms of syphilis. 3 months after the end of preventive treatment, a single clinical and serological examination is carried out.
Clinical serological control (CSC) after the end of specific treatment of the patient is carried out once every 3 months during the first year of observation. Then once every 6 months in subsequent years with non-treponemal (simple serological) tests, once a year with the corresponding treponemal test (a complex test to identify possible latent forms of syphilis), which was used in diagnosing the disease. The duration of CSC is determined individually depending on the results of treatment.
Children born to seropositive mothers who did not have congenital syphilis, regardless of whether they received preventive treatment or not, are subject to observation for 1 year. Children receiving specific treatment are on CSC for 3 years.
Prevention
Since the mode of transmission of the disease is mainly sexual, preventive measures consist of maintaining fidelity to sexual partners - this is the most effective prevention of sexually transmitted diseases. When having sexual contact with an unverified person, you should always use a condom.
Barrier contraception (condom) provides almost 100% protection against syphilis infection.
In any case, after accidental contact, it is necessary to independently treat the genital area with antiseptic agents: miramistine or chlorhexidine.
If an unplanned contact occurs without protective equipment, or the integrity of the condom is damaged in the process, doctors recommend visiting a prenatal clinic as soon as possible and receiving a preventive injection, which will almost 100% prevent the development of syphilis.
Ulcus molle (chancroid, soft chancroid)
Ulcus molle is a classic sexually transmitted disease caused by the bacterium Haemophilus ducreyi. Usually found in the tropics - Africa, Asia, Central and South America. The disease occurs 20 times more often in men than in women. Chancroid is particularly important in the context of HIV (AIDS), given the high incidence of both diseases in Africa.
Haemophilus ducreyi is a rod-shaped gram-negative bacterium. In cell culture it takes the form of multirow chains.