Causes of heartburn in the throat
Burning and discomfort in the throat can occur in completely healthy people. The most common cause of such symptoms is errors in diet: abuse of spicy or salty foods, caffeine-containing drinks, which cause an increase in the production of hydrochloric acid, causing it to be thrown into the throat. Heartburn can also be caused by smoking and frequent alcohol consumption. A burning sensation is often observed in pregnant women, especially in the second and third trimesters, which is associated with an increase in intra-abdominal pressure and a reflex opening of the cardiac sphincter.
Laryngopharyngeal reflux (LPR)
The backflow of aggressive stomach contents into the cavity of the pharynx and larynx is the main cause of heartburn in the throat. The mechanism of the disease is associated with uncoordinated work of the upper and lower sphincters of the esophagus with constant relaxation of the sphincters of the hypopharynx. As a result of regurgitation (backflow) of liquid contents with a pH below 4, the mucous membrane of the throat is irritated. An important role in the progression of laryngopharyngeal reflux is played by disruption of the reflex reactions of the larynx to an irritant.
The clinical picture of LPR is characterized by a combination of heartburn and nonspecific respiratory complaints: episodic dry cough, mucous discharge from the oropharynx, increased production of saliva. Sometimes the sensation is described by patients as a squeezing “lump in the throat.” An important sign of the disorder is the aggravation of unpleasant symptoms in a horizontal position, due to the entry of more gastric juice into the upper respiratory tract.
Disorders of the acid-producing function of the stomach
The appearance of heartburn can be caused by increased production of hydrochloric acid by the lining cells of the body of the stomach, which provokes the opening of the cardiac sphincter and the reflux of chyme (liquid, partially digested food) into the pharynx. Often the symptom is combined with burning and soreness behind the sternum. A discomfort in the throat also develops due to decreased acid production and stagnation of chyme. In this case, the unpleasant sensations are potentiated by organic acids, which are produced in large quantities during the decomposition of food in the stomach. Typically a burning sensation in the throat is caused by:
- Gastritis
. At the initial stages of mucosal inflammation caused by exposure to bacterial flora, the production of hydrochloric acid increases significantly. A decrease in the pH of gastric juice in combination with uncoordinated contractions of the sphincters leads to the reflux of contents into the overlying sections of the gastrointestinal tract with a feeling of heartburn in the throat. The disease is also manifested by sour belching, constipation and epigastric pain. - Peptic ulcer disease
. The formation of an ulcerative defect in the mucosa, caused by an increase in aggressive factors and a decrease in protective factors, always occurs with pronounced dyspeptic disorders. With a gastric ulcer, heartburn is caused by impaired motility and gaping of the cardiac sphincter. With duodenal ulcers, duodenal-gastric reflux is observed, against the background of which the mucous membrane of the throat is irritated by duodenal contents. - Gastrinoma
. A gastrin-producing tumor located in the pancreas or antrum of the stomach provokes an uncontrolled increase in the secretion of hydrochloric acid, which does not depend on food intake. In this case, sour belching, heartburn in the throat and burning behind the sternum, severe pain in the epigastric region are determined. The condition is aggravated by the addition of steatorrhea, which develops when food is malabsorbed. - Pyloric stenosis
. The transition between the stomach and duodenum is often narrowed due to cicatricial processes in the pylorus, which is accompanied by inhibition of hydrochloric acid production and causes prolonged stagnation of partially digested food masses. As a result, macromolecules decompose with the formation of organic acids. Stretching the gastric wall triggers reverse peristalsis and promotes acid reflux into the pharynx. - Atrophic gastritis
. The disease is of an autoimmune nature or occurs in the late stages of bacterial gastritis, when the lining cells of the mucous membrane are completely destroyed. Heartburn is associated with increased formation of lactic and pyruvic acids due to decomposition and putrefaction of undigested food. The burning sensation is combined with rotten belching, vomiting of eaten food, alternating constipation and diarrhea.
Other diseases of the digestive system
The feeling of heartburn in the throat often indicates diseases of the underlying parts of the digestive system. Burning and pain in the laryngopharynx are sometimes detected with irritation and erosion of the mucous membrane due to the ingress of small intestinal contents with a large amount of bile acids. Secondary disorders of the motor function of the smooth muscles of the gastrointestinal tract and incoordination of the gastric sphincters aggravate the symptoms. The main causes of heartburn are:
- Duodenitis
. Dyspeptic disorders, along with pain, are the main signs of inflammation of the duodenum. A burning sensation in the throat occurs due to the irritating effect of hydrochloric acid and bile acids on the mucous membrane of the pharynx. Unpleasant sensations are combined with nausea and vomiting, a tendency to unstable stools, and bitter belching. The cholecyst-like form of the disorder occurs as biliary colic. - Enzyme deficiency
. Heartburn with a decrease in exocrine pancreatic function is a sign of exacerbation of chronic pancreatitis and gastrointestinal motility disorders caused by duodenogastric reflux. Characteristic signs are steatorrhea and lientorrhea - the discharge of loose, grayish stool with undigested food debris. Malabsorption leads to rapid weight loss. - Perisplenitis
. Heartburn due to inflammation of the spleen capsule usually has a neuro-reflex nature and is caused by impaired gastric motility. The symptom is accompanied by burning pain in the left hypochondrium, which radiates to the scapula, left arm and cardiac region. A typical combination of pain with an increase in body temperature and signs of general intoxication of the body. Unpleasant manifestations intensify with physical activity, coughing, sneezing. - Adductor loop syndrome
. Frequent episodes of stagnation of digested food in the blind part of the intestine in diseases of the operated stomach lead to distension of the intestine and its throwing back into the stomach. The smooth muscles of the gastric wall reflexively contract, then aggressive chyme enters the esophagus and pharynx. In addition to burning sensations in the throat, vomiting after eating, a feeling of heaviness and fullness in the epigastrium, and weight loss are possible.
Neurological diseases
Dyspeptic disorders in pathologies of the central nervous system are often provoked by dysregulation of the autonomic innervation of the abdominal organs. Symptoms such as heartburn, nausea, and abdominal pain are usually signs of visceral paroxysms. Unpleasant sensations from the gastrointestinal tract are often combined with other types of autonomic reactions: pallor, increased sweating, rapid heartbeat. A burning sensation in the throat area is caused by:
- Temporal lobe epilepsy
. Heartburn and other dyspeptic disorders arise due to the involvement in the pathological process of the autonomic centers responsible for the innervation of internal organs. These symptoms manifest themselves both as individual somatosensory paroxysms and as an “aura” before a typical epileptic attack. Over time, epilepsy leads to emotional and intellectual impairment. - Alcoholic encephalopathy
. Burning sensation, discomfort in the throat, nausea and vomiting, and bowel movements are warning signs of the disease. They are associated with the local and general toxic effects of ethanol and its metabolites. The full clinical picture of the disease is characterized by visual and auditory hallucinations, alternating periods of chaotic excitation and depression of the central nervous system. In severe cases, brain dysfunction develops into psychoorganic syndrome and dementia.
Itsenko-Cushing's disease
Heartburn with overproduction of adrenal hormones is formed due to increased production of gastrin and hydrochloric acid in the stomach. A decrease in the acidity of gastric juice and impaired motility of the upper parts of the digestive tract cause the flow of acidic contents into the laryngopharynx. In addition to dyspepsia, in Itsenko-Cushing's disease, pathognomonic signs of the pathology are determined: Cushingoid appearance (significant fat deposits in the torso area, moon-shaped face), purple stretch marks (skin stretch marks) on the thighs and abdomen, cardiovascular pathology.
Viral infections
The combination of dyspeptic disorders with respiratory symptoms is characteristic of measles in young children. Periodic reflux of gastric chyme is associated with functional disorders of gastrointestinal motility due to general intoxication and the specific action of the pathogen. Heartburn in the throat is a secondary nonspecific symptom that occurs against the background of the main manifestations: lacrimation, serous rhinitis, dry cough. The destruction of the epithelial layer under the influence of viral particles aggravates the burning sensation in the laryngopharynx.
Survey
A gastroenterologist examines patients with discomfort and a burning sensation in the throat. The diagnostic search is primarily aimed at a comprehensive study of the morphological and functional state of the esophagus, stomach, and upper intestines. The diagnostic plan necessarily includes an examination of the respiratory tract to assess the degree of pathological changes. The most valuable for identifying the root causes of heartburn are:
- Endoscopic examination
. Endoscopy allows you to visualize the mucous membrane and detect signs of inflammatory or ulcerative processes in the gastrointestinal tract wall. According to indications, the method is supplemented with a biopsy of suspicious foci of the mucous membrane of the upper digestive tract or manometry of the lower esophageal sphincter. - Study of gastric secretion
. Daily measurement of pH in the stomach is necessary to determine the type of secretory activity of parietal cells. In patients with heartburn, the acidity level in the lower third of the esophagus should also be measured, since a decrease in pH less than 4 indicates the entry of aggressive gastric juice. - X-ray methods
. Taking a series of radiographs at certain intervals after oral contrast helps to detect ulcerative destructive defects in the mucous membrane. Flow of contrast agent into the esophagus indicates insufficiency of the cardiac sphincter of the stomach. - Research of ENT organs
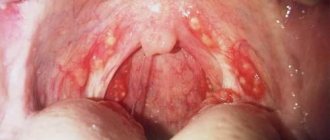
. To confirm the presence of inflammatory or erosive changes in the throat, the upper respiratory tract is examined using special endoscopes or laryngeal mirrors: pharyngoscopy, laryngoscopy. Additionally, a swab is taken from the throat and nose to exclude infectious diseases.
To clarify the diagnosis for complaints of heartburn in the throat, laboratory tests are used: the level of pancreatic amylase and lipase is determined, the concentration of gastrin and pepsinogen in the blood is measured, and specific serological tests are performed. After excluding all organic and functional diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, an examination by a neurologist may be required.
Daily pH-metry of the stomach
Common cold
A cold affects your throat, nose, sinuses, and airways. Although antibiotic treatment may not help in some cases (because the cold is caused by a virus), the common cold usually goes away on its own within 1-2 weeks2.
Common cold symptoms include runny and congested nose, cough, headache, burning sensation and sore throat. Some symptoms can be relieved with over-the-counter pain relievers and lozenges, such as Strepsils® menthol-eucalyptus flavored sore throat and nasal congestion. However, you should contact your doctor immediately if you are unsure about treatment options or if you feel unwell.
Symptomatic therapy
Episodic heartburn in the throat is often associated with dietary errors, so to relieve it, it is important to properly adjust the diet. To reduce discomfort, it is recommended to radically limit the intake of salty and spicy foods, smoked foods, strong tea and coffee. You need to eat 4-5 times a day in small portions, chewing food thoroughly. In many patients, symptoms completely disappear after quitting smoking and reducing the amount of alcohol consumed.
To reduce the frequency and duration of heartburn episodes, it is advisable to avoid wearing tight belts, corsets and fanny packs. Sleeping on a high pillow can help reduce the likelihood of attacks at night. If a burning sensation in the throat is observed constantly and does not disappear after correcting food habits, this indicates a gastrointestinal disease. Before a clinical diagnosis is established, antacids, proton pump inhibitors, and prokinetics can be used to relieve symptoms.
What to do? ↑
If you experience an obsessive burning sensation, you should not self-medicate, but should go to a therapist. After examining you, the doctor will determine which of the highly specialized specialists you need: a gastroenterologist, an otolaryngologist or an endocrinologist. Treatment of diffuse goiter, gastritis or sore throat is fundamentally different, and without determining what exactly caused the symptom, it is absolutely impossible to start therapy.
You can only slightly relieve the symptoms on your own with certain manipulations, which should be performed only against the background of the main treatment, without replacing it. These include:
- moisturizing the laryngeal mucosa, aerosols or inhalation using a nebulizer with alkaline mineral water. Irrigation of the throat relieves dryness, soreness and burning;
- create a diet of warm, liquid or semi-liquid food that will not injure the larynx. Avoid hot, spicy, too salty and hard foods;
- reduce the load on the vocal cords as much as possible, try not to talk at all, especially not to shout or sing.
Note! These recommendations are not able to eliminate the cause of the burning sensation, but act only as symptomatic therapy, alleviating the patient’s condition for a while. Therefore, contacting a specialist for adequate treatment should be mandatory.